内核参数总结
| 内核参数 | 默认值 | 作用 | 参数值 |
|---|---|---|---|
| vm.panic_on_oom | 0 | oom的时候是否强制panic | 0表示遇到OOM的时候,不panic,而是启动OOM Killer; 1表示在有cpuset、memory policy、memcg约束情况下的OOM,不panic,而是启动OOM Killer; 2表示OOM的时候强制系统panic; |
| vm.oom_kill_allocating_task | 0 | 决定触发OOM时优先kill哪种进程 | 0表示OOM的时候kill内存占用最大的那个; 1表示kill当前申请内存时触发OOM的进程 |
| vm.oom_dump_tasks | 1 | 用来记录OOM时记录哪些日志。包括进程使用的虚拟内存总量、物理内存、进程的页表信息等 | 0表示关闭日志打印 非0有三种情况打印进程内存使用情况 1. 由OOM导致的kernel panic 2. 没有找到符合条件的进程kill 3. 找到符合条件的进程并kill |
| /proc/PID/oom_score | 用来控制进程打分,由内核通过内存消耗计算得出,分数越高,越容易被选中kill | ||
| /proc/PID/oom_score_adj | 0 | 用来控制进程打分,由用户自定义,取值范围[-1000,1000],-1000表示禁止OOM Kill杀死该进程。分数越高,越容易被选中kill | [-1000,1000] |
| /proc/PID/oom_adj | 0 | 功能同oom_score_adj。内核中已经废弃该参数。系统中对oom_score_adj或oom_adj中任一个进行设置,内核都会进行两者之间的相互转换。 | [-17,15] |
统计系统内oom_score分数最高的进程
oomscore.sh
#!/bin/bash
for proc in $(find /proc -maxdepth 1 -regex '/proc/[0-9]+'); do
printf "%2d %5d %s\n" \
"$(cat $proc/oom_score)" \
"$(basename $proc)" \
"$(cat $proc/cmdline | tr '\0' ' ')"
done 2>/dev/null | sort -nr | head -n 10
内核源码流程
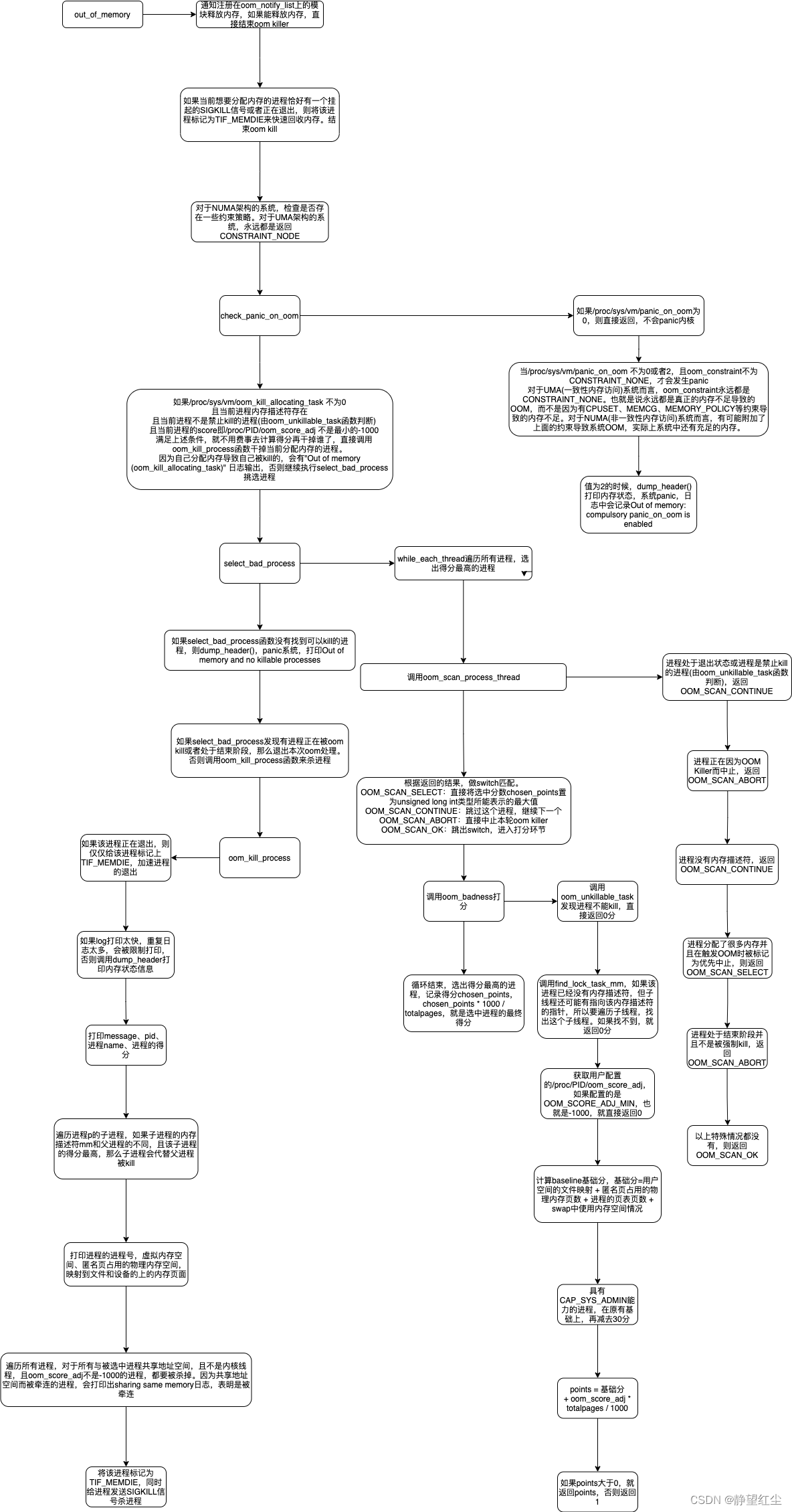
内核源码分析
内核版本:v3.10-rc7
oom的内核源码位于mm/oom_kill.c
主函数:out_of_memory,触发OOM时,就是调用的这个函数
/**
* out_of_memory - kill the "best" process when we run out of memory
* @zonelist: zonelist pointer
* @gfp_mask: memory allocation flags
* @order: amount of memory being requested as a power of 2
* @nodemask: nodemask passed to page allocator
* @force_kill: true if a task must be killed, even if others are exiting
*
* If we run out of memory, we have the choice between either
* killing a random task (bad), letting the system crash (worse)
* OR try to be smart about which process to kill. Note that we
* don't have to be perfect here, we just have to be good.
*/
void out_of_memory(struct zonelist *zonelist, gfp_t gfp_mask,
int order, nodemask_t *nodemask, bool force_kill)
{
const nodemask_t *mpol_mask;
struct task_struct *p;
unsigned long totalpages;
unsigned long freed = 0;
unsigned int uninitialized_var(points);
// 默认初始化constraint为CONSTRAINT_NONE
enum oom_constraint constraint = CONSTRAINT_NONE;
int killed = 0;
// 通知注册在oom_notify_list上的模块,释放一些内存出来,如果能释放一些,freed > 0,那么直接返回
blocking_notifier_call_chain(&oom_notify_list, 0, &freed);
if (freed > 0)
/* Got some memory back in the last second. */
return;
/*
* If current has a pending SIGKILL or is exiting, then automatically
* select it. The goal is to allow it to allocate so that it may
* quickly exit and free its memory.
*
* 如果当前想要分配内存的进程恰好有一个挂起的SIGKILL信号或者正在退出,则自动选中这个进程
* 将该进程标记为TIF_MEMDIE,目的是快速退出释放内存
*/
if (fatal_signal_pending(current) || current->flags & PF_EXITING) {
set_thread_flag(TIF_MEMDIE);
return;
}
/*
* Check if there were limitations on the allocation (only relevant for
* NUMA) that may require different handling.
* 对于NUMA架构的系统,检查是否存在一些约束策略
* 对于UMA架构的系统,永远都是返回CONSTRAINT_NONE
* 设置totalpages
*/
constraint = constrained_alloc(zonelist, gfp_mask, nodemask,
&totalpages);
// 非CONSTRAINT_MEMORY_POLICY约束,nodemask要置为NULL,这个参数就是用来标记MEMORY_POLICY策略的
mpol_mask = (constraint == CONSTRAINT_MEMORY_POLICY) ? nodemask : NULL;
// 检查/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom的设置
// 0表示遇到OOM的时候,不panic,而是启动OOM Killer;
// 非0和2表示在有cpuset、memory policy、memcg约束情况下的OOM,不panic,而是启动OOM Killer;
// 2表示OOM的时候强制系统panic;
check_panic_on_oom(constraint, gfp_mask, order, mpol_mask);
// 如果/proc/sys/vm/oom_kill_allocating_task 不为0
// 且当前进程内存描述符存在
// 且当前进程不是禁止kill的进程
// 且当前进程的score即/proc/PID/oom_score_adj 不是最小的-1000
// 满足上述条件,就不用费事去计算得分再干掉谁了,直接就干掉当前分配内存的进程。
if (sysctl_oom_kill_allocating_task && current->mm &&
!oom_unkillable_task(current, NULL, nodemask) &&
current->signal->oom_score_adj != OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN) {
get_task_struct(current);
// 因为自己分配内存导致自己被kill的,会有"Out of memory (oom_kill_allocating_task)" 日志输出
oom_kill_process(current, gfp_mask, order, 0, totalpages, NULL,
nodemask,
"Out of memory (oom_kill_allocating_task)");
goto out;
}
// 针对oom_kill_allocating_task为0或者当前进程不能kill的时候,挑选进程来kill
p = select_bad_process(&points, totalpages, mpol_mask, force_kill);
/* Found nothing?!?! Either we hang forever, or we panic.
* 找不到进程可以kill,那系统直接panic,dump当前系统所有进程的内存状态等信息。打印no killable processes
*/
if (!p) {
dump_header(NULL, gfp_mask, order, NULL, mpol_mask);
panic("Out of memory and no killable processes...\n");
}
// 判断上一次oom killer选择kill的进程是否还在结束中,或者有一些进程正在结束,如果是,退出本次oom处理
// 否则调用oom_kill_process函数来kill进程
if (PTR_ERR(p) != -1UL) {
oom_kill_process(p, gfp_mask, order, points, totalpages, NULL,
nodemask, "Out of memory");
killed = 1;
}
out:
/*
* Give the killed threads a good chance of exiting before trying to
* allocate memory again.
*/
if (killed)
schedule_timeout_killable(1); // kill完成后,主动让出cpu
}
check_panic_on_oom函数,由/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom内核参数来控制OOM的时候,是否必须panic
/*
* Determines whether the kernel must panic because of the panic_on_oom sysctl.
*/
void check_panic_on_oom(enum oom_constraint constraint, gfp_t gfp_mask,
int order, const nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
// /proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom为0,则直接返回,不会内核panic
if (likely(!sysctl_panic_on_oom))
return;
if (sysctl_panic_on_oom != 2) {
/*
* panic_on_oom == 1 only affects CONSTRAINT_NONE, the kernel
* does not panic for cpuset, mempolicy, or memcg allocation
* failures.
*
* 当/proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom 不为0或者2,且oom_constraint不为CONSTRAINT_NONE,才会发生panic
* 对于UMA(一致性内存访问)系统而言,oom_constraint永远都是CONSTRAINT_NONE。
* 也就是说永远都是真正的内存不足导致的OOM,而不是因为有CPUSET、MEMCG、MEMORY_POLICY等约束导致的内存不足。
* 对于NUMA(非一致性内存访问)系统而言,有可能附加了上面的约束导致系统OOM,实际上系统中还有充足的内存。
*/
if (constraint != CONSTRAINT_NONE)
return;
}
// /proc/sys/vm/panic_on_oom 值为2的时候,直接系统panic,打印相关日志,日志中会记录compulsory字段
dump_header(NULL, gfp_mask, order, NULL, nodemask);
panic("Out of memory: %s panic_on_oom is enabled\n",
sysctl_panic_on_oom == 2 ? "compulsory" : "system-wide");
}
select_bad_process函数,挑选合适的进程kill。
/*
* Simple selection loop. We chose the process with the highest
* number of 'points'.
*
* (not docbooked, we don't want this one cluttering up the manual)
*/
static struct task_struct *select_bad_process(unsigned int *ppoints,
unsigned long totalpages, const nodemask_t *nodemask,
bool force_kill)
{
struct task_struct *g, *p;
struct task_struct *chosen = NULL;
unsigned long chosen_points = 0;
rcu_read_lock(); // RCU读锁,遍历线程的过程中,禁止抢占
do_each_thread(g, p) {
unsigned int points;
// 根据oom_scan_process_thread函数的返回值,判断究竟是忽略该进程,还是计算对应的得分,还是直接中止本次挑选
switch (oom_scan_process_thread(p, totalpages, nodemask,
force_kill)) {
// 如果该进程被选中,则直接将chosen_points设置为unsigned long int类型的最大值
case OOM_SCAN_SELECT:
chosen = p;
chosen_points = ULONG_MAX;
/* fall through */
case OOM_SCAN_CONTINUE:
continue;
case OOM_SCAN_ABORT: // 进程处于结束阶段或者正在被oom kill
rcu_read_unlock();
return ERR_PTR(-1UL);
case OOM_SCAN_OK:
break;
};
// 给进程打分,如果该进程的分数比上一个选中的进程分数高,则将选中的进程替换为该进程
points = oom_badness(p, NULL, nodemask, totalpages);
if (points > chosen_points) {
chosen = p;
chosen_points = points;
}
} while_each_thread(g, p);
if (chosen)
get_task_struct(chosen);
rcu_read_unlock();
*ppoints = chosen_points * 1000 / totalpages;
return chosen;
}
oom_scan_process_thread函数
enum oom_scan_t oom_scan_process_thread(struct task_struct *task,
unsigned long totalpages, const nodemask_t *nodemask,
bool force_kill)
{
// 进程的状态处于退出状态,则直接返回,不用管,继续下一个进程
if (task->exit_state)
return OOM_SCAN_CONTINUE;
// 当前进程是init进程、内核线程等情况时,直接返回,不用管,继续下一个进程
if (oom_unkillable_task(task, NULL, nodemask))
return OOM_SCAN_CONTINUE;
/*
* This task already has access to memory reserves and is being killed.
* Don't allow any other task to have access to the reserves.
*
* 有进程正在因为OOM Killer而中止,则中止本次OOM Killer
*/
if (test_tsk_thread_flag(task, TIF_MEMDIE)) {
if (unlikely(frozen(task)))
__thaw_task(task);
if (!force_kill)
return OOM_SCAN_ABORT;
}
// 进程的内存为0,直接返回,不用管,继续下一个进程
if (!task->mm)
return OOM_SCAN_CONTINUE;
/*
* If task is allocating a lot of memory and has been marked to be
* killed first if it triggers an oom, then select it.
* 进程分配了很多内存并且在触发OOM时被标记为优先中止,则选中该进程
* !!(p->signal->oom_flags & OOM_FLAG_ORIGIN);
*/
if (oom_task_origin(task))
return OOM_SCAN_SELECT;
// 进程处于结束阶段并且不是被强制kill
if (task->flags & PF_EXITING && !force_kill) {
/*
* If this task is not being ptraced on exit, then wait for it
* to finish before killing some other task unnecessarily.
*/
if (!(task->group_leader->ptrace & PT_TRACE_EXIT))
return OOM_SCAN_ABORT;
}
return OOM_SCAN_OK;
}
oom_badness函数,计算得分
/**
* oom_badness - heuristic function to determine which candidate task to kill
* @p: task struct of which task we should calculate
* @totalpages: total present RAM allowed for page allocation
*
* The heuristic for determining which task to kill is made to be as simple and
* predictable as possible. The goal is to return the highest value for the
* task consuming the most memory to avoid subsequent oom failures.
*/
unsigned long oom_badness(struct task_struct *p, struct mem_cgroup *memcg,
const nodemask_t *nodemask, unsigned long totalpages)
{
long points;
long adj;
// 不能杀的进程不杀
if (oom_unkillable_task(p, memcg, nodemask))
return 0;
// 父进程已经detached自己的mm,但是子线程还有指向该mm的指针。
// 遍历进程的子线程,找出这个子线程并返回
// 如果找不到,就返回0
p = find_lock_task_mm(p);
if (!p)
return 0;
// 获取配置的/proc/PID/oom_score_adj
// 如果配置的是OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN,也就是-1000,就直接返回0
adj = (long)p->signal->oom_score_adj;
if (adj == OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN) {
task_unlock(p);
return 0;
}
/*
* The baseline for the badness score is the proportion of RAM that each
* task's rss, pagetable and swap space use.
*
* get_mm_rss(): get_mm_counter(mm, MM_FILEPAGES) + get_mm_counter(mm, MM_ANONPAGES)。用户空间的文件映射和匿名页占用的物理内存页数
* p->mm->nr_ptes: Page table pages: 进程的页表页数
* get_mm_counter: swap中使用内存空间情况
*/
points = get_mm_rss(p->mm) + p->mm->nr_ptes +
get_mm_counter(p->mm, MM_SWAPENTS);
task_unlock(p);
/*
* Root processes get 3% bonus, just like the __vm_enough_memory()
* implementation used by LSMs.
*
* 具有CAP_SYS_ADMIN能力的进程,在原有基础上,再减去30分
*/
if (has_capability_noaudit(p, CAP_SYS_ADMIN))
adj -= 30;
/* Normalize to oom_score_adj units */
adj *= totalpages / 1000;
points += adj;
/*
* Never return 0 for an eligible task regardless of the root bonus and
* oom_score_adj (oom_score_adj can't be OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN here).
*/
return points > 0 ? points : 1;
}
oom_unkillable_task函数,用来判断哪些进程不能轻易被kill
/* return true if the task is not adequate as candidate victim task. */
static bool oom_unkillable_task(struct task_struct *p,
const struct mem_cgroup *memcg, const nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
// 通过gid判断进程是否是init,如果是,直接返回true,因为1号进程不能被kill
if (is_global_init(p))
return true;
// 内核线程不能被kill,直接返回true
if (p->flags & PF_KTHREAD)
return true;
/* When mem_cgroup_out_of_memory() and p is not member of the group */
// 如果开启了CONSTRAINT_MEMCG,但是这个进程不是开启MEMCG策略的这组进程的成员,则返回true,不需要kill
if (memcg && !task_in_mem_cgroup(p, memcg))
return true;
/* p may not have freeable memory in nodemask */
// 在NUMA系统中,如果进程是因为CONSTRAINT_MEMORY_POLICY约束导致的内存不足,返回true,不需要kill
if (!has_intersects_mems_allowed(p, nodemask))
return true;
return false;
}
oom_kill_process函数,真正执行kill的函数
/*
* Must be called while holding a reference to p, which will be released upon
* returning.
*/
void oom_kill_process(struct task_struct *p, gfp_t gfp_mask, int order,
unsigned int points, unsigned long totalpages,
struct mem_cgroup *memcg, nodemask_t *nodemask,
const char *message)
{
struct task_struct *victim = p;
struct task_struct *child;
struct task_struct *t = p;
struct mm_struct *mm;
unsigned int victim_points = 0;
static DEFINE_RATELIMIT_STATE(oom_rs, DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_INTERVAL,
DEFAULT_RATELIMIT_BURST);
/*
* If the task is already exiting, don't alarm the sysadmin or kill
* its children or threads, just set TIF_MEMDIE so it can die quickly
*
* 如果该进程正在退出,仅仅给这个进程标记上TIF_MEMDIE,可以退出的更快
*/
if (p->flags & PF_EXITING) {
set_tsk_thread_flag(p, TIF_MEMDIE);
put_task_struct(p);
return;
}
// 如果log打印太频繁,会禁止打印日志,否则打印该进程的内存状态信息
if (__ratelimit(&oom_rs))
dump_header(p, gfp_mask, order, memcg, nodemask);
task_lock(p);
// 打印message, pid, 进程name, 进程的得分
pr_err("%s: Kill process %d (%s) score %d or sacrifice child\n",
message, task_pid_nr(p), p->comm, points);
task_unlock(p);
/*
* If any of p's children has a different mm and is eligible for kill,
* the one with the highest oom_badness() score is sacrificed for its
* parent. This attempts to lose the minimal amount of work done while
* still freeing memory.
*
* 遍历进程p的子进程,如果子进程的内存描述符mm和父进程的不同,且该子进程的得分最高,那么子进程会代替父进程被kill
*/
read_lock(&tasklist_lock);
do {
list_for_each_entry(child, &t->children, sibling) {
unsigned int child_points;
if (child->mm == p->mm)
continue;
/*
* oom_badness() returns 0 if the thread is unkillable
*/
child_points = oom_badness(child, memcg, nodemask,
totalpages);
if (child_points > victim_points) {
put_task_struct(victim);
victim = child;
victim_points = child_points;
get_task_struct(victim);
}
}
} while_each_thread(p, t);
read_unlock(&tasklist_lock);
rcu_read_lock();
p = find_lock_task_mm(victim);
if (!p) {
rcu_read_unlock();
put_task_struct(victim);
return;
} else if (victim != p) {
get_task_struct(p);
put_task_struct(victim);
victim = p;
}
/* mm cannot safely be dereferenced after task_unlock(victim) */
mm = victim->mm;
pr_err("Killed process %d (%s) total-vm:%lukB, anon-rss:%lukB, file-rss:%lukB\n",
task_pid_nr(victim), victim->comm, K(victim->mm->total_vm),
K(get_mm_counter(victim->mm, MM_ANONPAGES)),
K(get_mm_counter(victim->mm, MM_FILEPAGES)));
task_unlock(victim);
/*
* Kill all user processes sharing victim->mm in other thread groups, if
* any. They don't get access to memory reserves, though, to avoid
* depletion of all memory. This prevents mm->mmap_sem livelock when an
* oom killed thread cannot exit because it requires the semaphore and
* its contended by another thread trying to allocate memory itself.
* That thread will now get access to memory reserves since it has a
* pending fatal signal.
*
* 对于所有与被选中进程共享地址空间,且不是内核线程,且oom_score_adj不是-1000的进程,都要被杀掉
* 因为共享地址空间而被牵连的进程,会打印出sharing same memory日志,表明是被牵连
*/
for_each_process(p)
if (p->mm == mm && !same_thread_group(p, victim) &&
!(p->flags & PF_KTHREAD)) {
if (p->signal->oom_score_adj == OOM_SCORE_ADJ_MIN)
continue;
task_lock(p); /* Protect ->comm from prctl() */
pr_err("Kill process %d (%s) sharing same memory\n",
task_pid_nr(p), p->comm);
task_unlock(p);
do_send_sig_info(SIGKILL, SEND_SIG_FORCED, p, true); // 向进程传递SIGKILL信号
}
rcu_read_unlock();
set_tsk_thread_flag(victim, TIF_MEMDIE); // 标记该进程已经被oom_killer选中,正在被kill
do_send_sig_info(SIGKILL, SEND_SIG_FORCED, victim, true);
put_task_struct(victim);
}
dump_header和dump_tasks函数,打印进程内存状态等日志
static void dump_header(struct task_struct *p, gfp_t gfp_mask, int order,
struct mem_cgroup *memcg, const nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
task_lock(current);
// 打印是哪个进程触发了OOM
pr_warning("%s invoked oom-killer: gfp_mask=0x%x, order=%d, "
"oom_score_adj=%hd\n",
current->comm, gfp_mask, order,
current->signal->oom_score_adj);
// 打印当前进程的cpuset信息。包括cpuset的name和该进程可以访问哪些memory node
cpuset_print_task_mems_allowed(current);
task_unlock(current);
// 打印进程的栈信息
dump_stack();
// 如果是memcg限制的进程,打印跟memcg相关的OOM信息
if (memcg)
mem_cgroup_print_oom_info(memcg, p);
else
// 否则打印整个系统的内存使用情况
show_mem(SHOW_MEM_FILTER_NODES);
// 如果打开了oom_dump_tasks参数,就会调用dump_tasks函数dump用户空间所有进程的内存状态
if (sysctl_oom_dump_tasks)
dump_tasks(memcg, nodemask);
}
static void dump_tasks(const struct mem_cgroup *memcg, const nodemask_t *nodemask)
{
struct task_struct *p;
struct task_struct *task;
pr_info("[ pid ] uid tgid total_vm rss nr_ptes swapents oom_score_adj name\n");
rcu_read_lock();
// 遍历系统中所有进程
for_each_process(p) {
// 如果是不可被Kill的进程,直接下一个
if (oom_unkillable_task(p, memcg, nodemask))
continue;
//从当前进程或者该进程的子线程判断mm锁是否存在,如果存在,则返回包含该锁的当前进程或者该进程的子线程
task = find_lock_task_mm(p);
//如果这是内核线程或者进程p的所有子线程都不存在内存描述符mm,task为NULL,则直接跳过,不kill,同时这些进程的内存状况信息也不打印
if (!task) {
/*
* This is a kthread or all of p's threads have already
* detached their mm's. There's no need to report
* them; they can't be oom killed anyway.
*/
continue;
}
//经过前面判断,对于有资格的task,开始打印相应的信息(pid, uid, tgid, vm size, rss, pgtables_bytes, swapents, oom_score_adj value, name)
pr_info("[%5d] %5d %5d %8lu %8lu %7lu %8lu %5hd %s\n",
task->pid, from_kuid(&init_user_ns, task_uid(task)),
task->tgid, task->mm->total_vm, get_mm_rss(task->mm),
task->mm->nr_ptes,
get_mm_counter(task->mm, MM_SWAPENTS),
task->signal->oom_score_adj, task->comm);
//释放的这个锁,是在函数find_lock_task_mm里面加的
task_unlock(task);
}
rcu_read_unlock();
}
补充
当前系统是否是NUMA体系结构
lscpu命令查看
# lscpu
Architecture: x86_64
CPU op-mode(s): 32-bit, 64-bit
Byte Order: Little Endian
CPU(s): 8 # 共有8个逻辑CPU
On-line CPU(s) list: 0-7
Thread(s) per core: 2 # 每个core有2个Threads
Core(s) per socket: 4 # 每个socket有4个core
Socket(s): 1 # 共有1个socket
NUMA node(s): 1 # 共有1个NUMA nodes,所以每个socket有1个node
Vendor ID: GenuineIntel
CPU family: 6
Model: 106
Model name: Intel(R) Xeon(R) Platinum 8338C CPU @ 2.60GHz
Stepping: 6
CPU MHz: 2593.906
BogoMIPS: 5187.81
Virtualization: VT-x
Hypervisor vendor: KVM
Virtualization type: full
L1d cache: 32K
L1i cache: 32K
L2 cache: 4096K
L3 cache: 16384K
NUMA node0 CPU(s): 0-7
Flags: fpu vme de pse tsc msr pae mce cx8 apic sep mtrr pge mca cmov pat pse36 clflush mmx fxsr sse sse2 ss ht syscall nx pdpe1gb rdtscp lm constant_tsc arch_perfmon rep_good nopl xtopology cpuid tsc_known_freq pni pclmulqdq vmx ssse3 fma cx16 pcid sse4_1 sse4_2 x2apic movbe popcnt tsc_deadline_timer aes xsave avx f16c rdrand hypervisor lahf_lm abm 3dnowprefetch cpuid_fault invpcid_single ibrs ibpb stibp ibrs_enhanced tpr_shadow vnmi flexpriority ept vpid fsgsbase tsc_adjust bmi1 avx2 smep bmi2 erms invpcid avx512f avx512dq rdseed adx smap avx512ifma clflushopt clwb avx512cd sha_ni avx512bw avx512vl xsaveopt xsavec xgetbv1 xsaves arat avx512vbmi umip pku ospke avx512_vpopcntdq la57 rdpid arch_capabilities
总的Threads = 1(socket) * 4(cores) * 2(Threads) = 8
Linux capabilities相关命令
yum install libcap-ng-utils
# 查看当前有特殊cap的所有进程
pscap -a
# 查看指定进程的cap
getpcaps PID
# 显示文件系统中支持cap的文件
filecap
# 获取可执行文件的cap
getcap xxx






















 6449
6449











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








