作为一名资深面试官,我见过太多候选人在 Kafka 这个环节"翻车"。本文从实战角度出发,深入剖析 Kafka 的核心原理,帮你在面试中脱颖而出。
一、架构设计:不只是发布订阅那么简单
1.1 整体架构深度解析
大多数人对 Kafka 的理解停留在"消息队列"层面,但资深面试官更关注你对分布式系统设计的理解。

核心面试问题:为什么 Kafka 能支撑如此高的吞吐量?
答案不是简单的"批处理",而是多层次的设计:
// Kafka Producer 核心优化机制
public class KafkaProducerOptimization {
// 1. 批处理机制 - 不是简单的攒批
private void demonstrateBatching() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 批处理大小:达到16KB或等待10ms就发送
props.put("batch.size", 16384);
props.put("linger.ms", 10);
// 内存缓冲区:32MB,满了会阻塞
props.put("buffer.memory", 33554432);
// 压缩算法:网络和存储双重优化
props.put("compression.type", "lz4");
}
// 2. 零拷贝技术 - 这是性能的关键
public void demonstrateZeroCopy() {
// Kafka 使用 sendfile() 系统调用
// 数据直接从页缓存传输到网络缓冲区
// 避免了用户空间和内核空间的数据拷贝
// 传统方式:4次拷贝 + 2次上下文切换
// Kafka方式:2次拷贝 + 2次上下文切换
}
// 3. 顺序写入优化
public void sequentialWriteOptimization() {
// Kafka 将随机写转换为顺序写
// 顺序写磁盘性能 > 随机写内存
// 这就是为什么 Kafka 不需要复杂的索引结构
}
}
1.2 分区机制:不只是负载均衡

深度问题:如何保证相同用户的消息有序?
public class PartitionStrategy {
// 1. 自定义分区器 - 业务层面的有序性
public class UserPartitioner implements Partitioner {
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes,
Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
if (keyBytes == null) {
return ThreadLocalRandom.current().nextInt(
cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic));
}
// 相同用户ID分配到同一分区
String userId = new String(keyBytes);
return Math.abs(userId.hashCode()) %
cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic);
}
}
// 2. 分区数量设计原则
public void partitionDesignPrinciples() {
// 分区数 = max(预期吞吐量/单分区吞吐量, 预期消费者数量)
// 单分区吞吐量通常为 10MB/s (网络限制)
// 分区数量影响:
// - 并行度:消费者数量不能超过分区数
// - 端到端延迟:分区越多,延迟越高
// - 文件句柄:每个分区对应多个文件
}
// 3. 热点分区问题解决
public void hotPartitionSolution() {
// 问题:某些key的数据量远超其他key
// 解决方案1:二级分区
String enhancedKey = originalKey + "_" +
(System.currentTimeMillis() / 1000 % 10);
// 解决方案2:自定义路由算法
// 对热点key进行特殊处理,分散到多个分区
}
}
二、副本机制:CAP理论的工程实践
2.1 ISR机制深度剖析
面试官最爱问的问题:Kafka如何在可用性和一致性之间平衡?

public class ISRMechanism {
// 1. ISR维护机制
public class ISRManager {
private final long replicaLagTimeMaxMs = 10000; // 10秒
private final long replicaLagMaxMessages = 4000; // 4000条消息
public void updateISR(Partition partition) {
Set<Integer> newISR = new HashSet<>();
long leaderLEO = partition.getLeaderLEO();
long currentTime = System.currentTimeMillis();
for (Replica replica : partition.getReplicas()) {
if (replica.isLeader()) {
newISR.add(replica.getBrokerId());
continue;
}
// 检查时间延迟
long timeLag = currentTime - replica.getLastFetchTime();
// 检查消息延迟
long messageLag = leaderLEO - replica.getLEO();
if (timeLag <= replicaLagTimeMaxMs &&
messageLag <= replicaLagMaxMessages) {
newISR.add(replica.getBrokerId());
}
}
partition.updateISR(newISR);
}
}
// 2. 高水位线更新机制
public void updateHighWatermark(Partition partition) {
// HW只能向前移动,不能后退
long newHW = partition.getISRReplicas().stream()
.mapToLong(Replica::getLEO)
.min()
.orElse(0L);
if (newHW > partition.getHighWatermark()) {
partition.setHighWatermark(newHW);
// 通知消费者可以读取更多数据
notifyConsumersNewDataAvailable();
}
}
// 3. 不同acks级别的影响
public void demonstrateAcksLevels() {
// acks = 0: 不等待确认,最高性能,可能丢失数据
// acks = 1: 等待Leader确认,平衡性能和可靠性
// acks = all: 等待ISR所有副本确认,最高可靠性
// 关键点:acks=all + min.insync.replicas=2
// 确保至少有2个副本确认,防止脑裂
}
}
2.2 Leader选举:超越Raft的设计
public class LeaderElection {
// Kafka的Leader选举不是基于Raft,而是基于ISR
public void leaderElectionProcess() {
// 1. Controller选择新Leader
// 从ISR中选择第一个活跃的副本作为新Leader
// 不需要复杂的投票过程
// 2. Unclean Leader Election
// 当ISR为空时的选择:
// unclean.leader.election.enable = true: 从非ISR副本选举
// unclean.leader.election.enable = false: 分区不可用
}
// 3. Controller故障转移
public class ControllerFailover {
public void handleControllerFailover() {
// 所有Broker监听ZK的/controller节点
// 第一个创建临时节点的成为Controller
// 新Controller需要:
// 1. 从ZK读取所有分区状态
// 2. 重新进行Leader选举
// 3. 向所有Broker发送LeaderAndIsr请求
}
}
}
三、存储机制:为什么选择文件系统而不是数据库
3.1 日志存储结构

核心问题:为什么Kafka比传统消息队列快?
public class KafkaStorage {
// 1. 消息格式优化
public class MessageFormat {
// Kafka消息不包含消费状态,极大降低存储开销
public void demonstrateMessageStructure() {
// 传统MQ: 每条消息包含多个消费者的状态
// Kafka: 消息 + Offset,状态由Consumer管理
// MessageSet批量写入,减少系统调用
// 压缩算法在批量级别,不是消息级别
}
}
// 2. 稀疏索引设计
public class SparseIndex {
private static final int INDEX_INTERVAL = 4096; // 4KB
public void buildIndex() {
// 不是每条消息都建索引,而是每4KB建一个索引项
// 查找时:二分查找索引 + 顺序扫描
// 空间换时间的经典案例
// 索引文件格式:
// [相对offset(4字节) | 物理位置(4字节)]
}
public MessagePosition findMessage(long targetOffset) {
// 1. 二分查找.index文件
IndexEntry entry = binarySearchIndex(targetOffset);
// 2. 从索引位置开始顺序扫描.log文件
return scanLogFromPosition(entry.position, targetOffset);
}
}
// 3. 日志清理策略
public void logCleanupStrategies() {
// Delete策略:基于时间或大小删除
// 适用场景:临时数据、日志流
// Compact策略:保留每个key的最新值
// 适用场景:状态存储、CDC
// 核心算法:两阶段标记-整理
public void compactProcess() {
// Phase 1: 构建最新offset映射
Map<String, Long> latestOffsets = buildLatestOffsetMap();
// Phase 2: 重写日志文件,只保留最新记录
rewriteLogWithLatestRecords(latestOffsets);
}
}
}
四、消费者机制:比你想象的复杂
4.1 消费者组协调协议
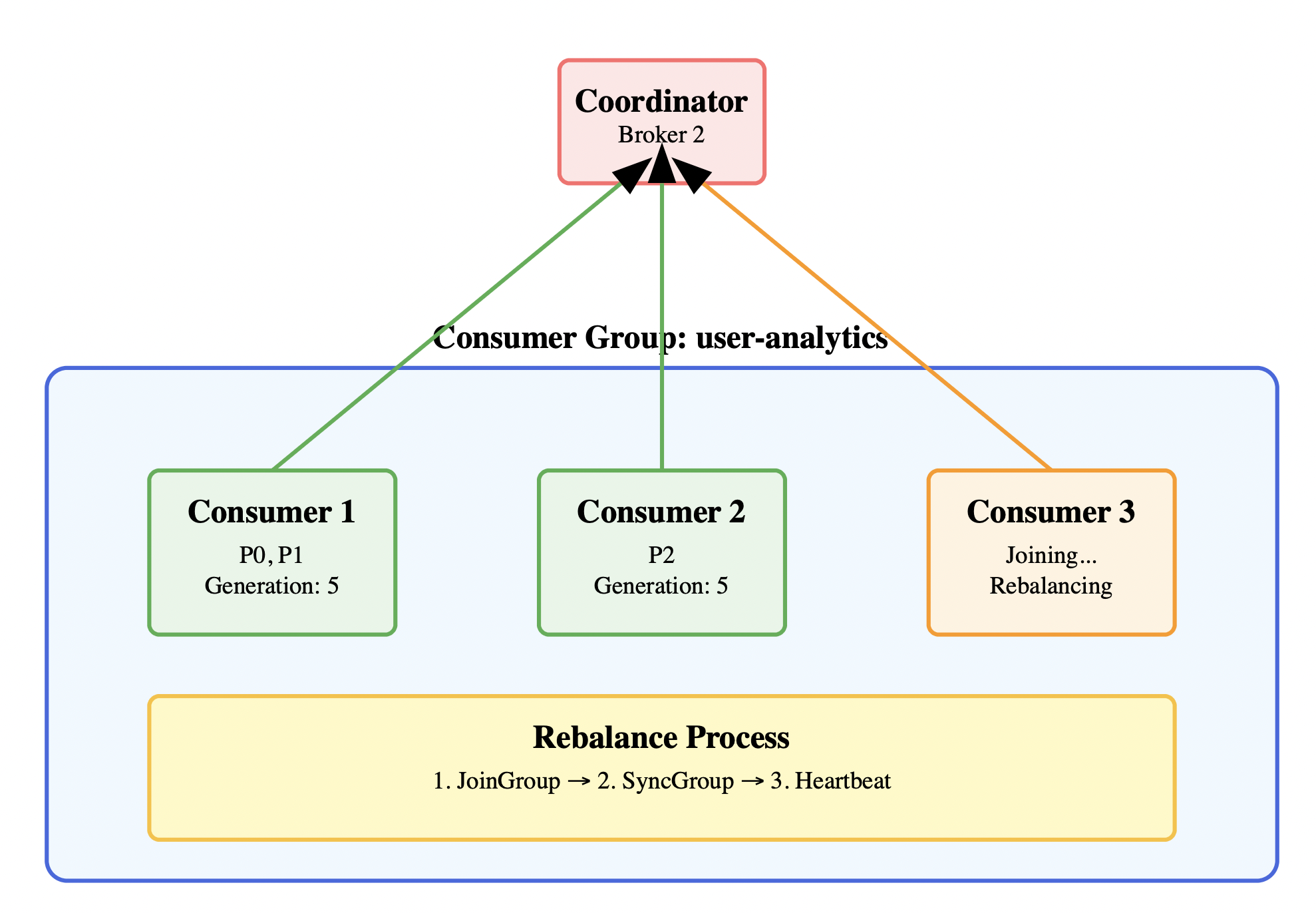
public class ConsumerGroupCoordination {
// 1. 消费者协调协议详解
public class RebalanceProtocol {
public void joinGroupProcess() {
// JoinGroup阶段:所有消费者发送JoinGroup请求
JoinGroupRequest request = new JoinGroupRequest();
request.setGroupId("user-analytics");
request.setMemberId(""); // 首次为空
request.setProtocolType("consumer");
request.setSupportedProtocols(Arrays.asList("range", "roundrobin"));
// Coordinator选择第一个发送请求的为Leader
// Leader负责分区分配计算
}
public void syncGroupProcess() {
// SyncGroup阶段:Leader计算分配方案,所有成员同步
if (isLeader()) {
Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment =
calculateAssignment();
SyncGroupRequest request = new SyncGroupRequest();
request.setGroupAssignment(assignment);
return request;
} else {
// 非Leader成员发送空的SyncGroup请求
return new SyncGroupRequest();
}
}
}
// 2. 分区分配策略
public class AssignmentStrategies {
// Range策略:按Topic分配连续分区
public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> rangeAssignment(
List<String> consumers, List<TopicPartition> partitions) {
Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> assignment = new HashMap<>();
// 按Topic分组
Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> topicToPartitions =
partitions.stream().collect(
Collectors.groupingBy(TopicPartition::topic));
for (Map.Entry<String, List<TopicPartition>> entry :
topicToPartitions.entrySet()) {
List<TopicPartition> topicPartitions = entry.getValue();
int partitionsPerConsumer = topicPartitions.size() / consumers.size();
int consumersWithExtraPartition = topicPartitions.size() % consumers.size();
for (int i = 0; i < consumers.size(); i++) {
String consumer = consumers.get(i);
int start = i * partitionsPerConsumer +
Math.min(i, consumersWithExtraPartition);
int length = partitionsPerConsumer +
(i < consumersWithExtraPartition ? 1 : 0);
assignment.computeIfAbsent(consumer, k -> new ArrayList<>())
.addAll(topicPartitions.subList(start, start + length));
}
}
return assignment;
}
// Sticky策略:最小化重新分配
public Map<String, List<TopicPartition>> stickyAssignment() {
// 复杂算法,尽量保持原有分配
// 只重新分配必要的分区
// 适用于有状态的消费者
}
}
// 3. Offset管理
public class OffsetManagement {
public void commitOffset() {
// 自动提交:enable.auto.commit=true
// 问题:可能导致消息丢失或重复消费
// 手动提交:更精确的控制
public void manualCommit() {
try {
// 处理消息
processMessages(records);
// 同步提交:阻塞直到提交成功
consumer.commitSync();
// 异步提交:不阻塞,但需要处理失败
consumer.commitAsync((offsets, exception) -> {
if (exception != null) {
// 记录失败,可能需要重试
log.error("Commit failed", exception);
}
});
} catch (Exception e) {
// 处理异常,可能需要回滚
}
}
}
}
}
4.2 消费性能优化
public class ConsumerOptimization {
// 1. 批量消费优化
public void batchConsumption() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 一次poll获取更多数据
props.put("max.poll.records", 1000);
// 增加fetch大小
props.put("fetch.min.bytes", 50000);
props.put("fetch.max.wait.ms", 500);
// 预取优化
props.put("max.partition.fetch.bytes", 1048576);
}
// 2. 多线程消费模型
public class MultiThreadConsumer {
private final int threadCount = 10;
private final ExecutorService executor =
Executors.newFixedThreadPool(threadCount);
public void consume() {
while (running) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100);
// 按分区分发到不同线程
for (TopicPartition partition : records.partitions()) {
List<ConsumerRecord<String, String>> partitionRecords =
records.records(partition);
// 同一分区的消息保证顺序处理
executor.submit(() -> processPartition(partition, partitionRecords));
}
}
}
private void processPartition(TopicPartition partition,
List<ConsumerRecord<String, String>> records) {
// 处理分区数据
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
processMessage(record);
}
// 处理完成后提交offset
commitPartitionOffset(partition, records.get(records.size() - 1).offset() + 1);
}
}
// 3. 背压处理
public class BackpressureHandling {
private final Semaphore semaphore = new Semaphore(1000);
public void handleBackpressure() {
while (running) {
ConsumerRecords<String, String> records = consumer.poll(100);
for (ConsumerRecord<String, String> record : records) {
try {
// 获取许可,控制处理速度
semaphore.acquire();
// 异步处理
CompletableFuture.runAsync(() -> {
try {
processMessage(record);
} finally {
semaphore.release();
}
});
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
break;
}
}
}
}
}
}
五、性能调优:生产环境的实战经验
5.1 Producer性能调优
public class ProducerTuning {
// 1. 关键参数调优
public Properties getOptimizedProducerConfig() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 批处理优化
props.put("batch.size", 32768); // 32KB,默认16KB
props.put("linger.ms", 20); // 等待20ms,默认0
props.put("buffer.memory", 67108864); // 64MB,默认32MB
// 压缩优化
props.put("compression.type", "lz4"); // lz4 > snappy > gzip
// 网络优化
props.put("send.buffer.bytes", 131072); // 128KB
props.put("receive.buffer.bytes", 65536); // 64KB
// 重试优化
props.put("retries", Integer.MAX_VALUE);
props.put("max.in.flight.requests.per.connection", 5);
props.put("enable.idempotence", true);
return props;
}
// 2. 异步发送优化
public class AsyncSendOptimization {
private final KafkaProducer<String, String> producer;
private final Semaphore inflightSemaphore = new Semaphore(10000);
public void sendAsync(String topic, String key, String value) {
try {
inflightSemaphore.acquire();
ProducerRecord<String, String> record =
new ProducerRecord<>(topic, key, value);
producer.send(record, (metadata, exception) -> {
try {
if (exception != null) {
handleSendError(record, exception);
} else {
handleSendSuccess(metadata);
}
} finally {
inflightSemaphore.release();
}
});
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
Thread.currentThread().interrupt();
}
}
}
// 3. 事务处理优化
public class TransactionalProducer {
public void optimizedTransaction() {
producer.initTransactions();
try {
producer.beginTransaction();
// 批量发送事务消息
List<ProducerRecord<String, String>> batch = prepareBatch();
for (ProducerRecord<String, String> record : batch) {
producer.send(record);
}
// 发送消费offset(用于exactly-once语义)
Map<TopicPartition, OffsetAndMetadata> offsets = getOffsetsToCommit();
producer.sendOffsetsToTransaction(offsets, "consumer-group-id");
producer.commitTransaction();
} catch (Exception e) {
producer.abortTransaction();
throw e;
}
}
}
}
5.2 Broker性能调优
public class BrokerTuning {
// 1. JVM调优
public void jvmTuning() {
// JVM参数建议:
// -Xms6g -Xmx6g # 堆大小,不要超过32GB
// -XX:+UseG1GC # G1垃圾收集器
// -XX:MaxGCPauseMillis=20 # GC暂停时间目标
// -XX:G1HeapRegionSize=16m # G1区域大小
// -XX:+UnlockExperimentalVMOptions
// -XX:+UseZGC # ZGC用于超大堆
// 页缓存是关键:留足内存给OS
// 如果机器32GB内存,JVM堆6GB,OS页缓存26GB
}
// 2. 磁盘I/O优化
public void diskIOTuning() {
// 关键配置
Map<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
// 日志刷盘策略
configs.put("log.flush.interval.messages", 10000);
configs.put("log.flush.interval.ms", 1000);
// 段文件配置
configs.put("log.segment.bytes", 1073741824); // 1GB
configs.put("log.roll.hours", 168); // 7天
// 压缩配置
configs.put("log.cleaner.threads", 2);
configs.put("log.cleaner.io.max.bytes.per.second", 104857600); // 100MB/s
// 复制配置
configs.put("replica.fetch.max.bytes", 1048576); // 1MB
configs.put("num.replica.fetchers", 4);
}
// 3. 网络调优
public void networkTuning() {
// Socket配置
Map<String, Object> configs = new HashMap<>();
configs.put("socket.send.buffer.bytes", 102400); // 100KB
configs.put("socket.receive.buffer.bytes", 102400); // 100KB
configs.put("socket.request.max.bytes", 104857600); // 100MB
// 网络线程配置
configs.put("num.network.threads", 8);
configs.put("num.io.threads", 16);
// 请求队列配置
configs.put("queued.max.requests", 500);
}
// 4. 监控关键指标
public class MonitoringMetrics {
public void monitorCriticalMetrics() {
// 1. 网络指标
// - RequestsPerSec:请求速率
// - NetworkProcessorAvgIdlePercent:网络线程空闲率
// 2. 磁盘指标
// - LogFlushRateAndTimeMs:刷盘速率和时间
// - LogSize:日志大小增长
// 3. 复制指标
// - ReplicaLag:副本延迟
// - UnderReplicatedPartitions:副本不足的分区
// 4. GC指标
// - GC pause time
// - GC frequency
// 5. 操作系统指标
// - CPU usage
// - Memory usage
// - Disk I/O
// - Network I/O
}
}
}
六、故障排查:生产环境常见问题
6.1 性能问题诊断
public class TroubleshootingGuide {
// 1. 消息堆积问题
public void diagnoseLag() {
// 步骤1:确定堆积位置
// kafka-consumer-groups.sh --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
// --describe --group mygroup
// 步骤2:分析堆积原因
public void analyzeLagCause() {
// Consumer处理慢:
// - 检查消费者处理逻辑耗时
// - 检查下游服务响应时间
// - 检查GC情况
// 分区分配不均:
// - 检查分区分配策略
// - 检查热点分区
// 网络问题:
// - 检查网络延迟
// - 检查带宽利用率
}
}
// 2. 重复消费问题
public class DuplicateConsumption {
public void identifyDuplicateCauses() {
// 原因1:Consumer重启时offset未提交
// 解决:减小auto.commit.interval.ms或使用手动提交
// 原因2:Rebalance过程中的重复处理
// 解决:实现幂等消费逻辑
// 原因3:消息处理超时
// 解决:增大max.poll.interval.ms
}
// 幂等消费实现
public void idempotentConsumption() {
// 使用Redis实现消息去重
public boolean isProcessed(String messageId) {
String key = "processed_message:" + messageId;
return redisTemplate.hasKey(key);
}
public void markAsProcessed(String messageId) {
String key = "processed_message:" + messageId;
// 设置过期时间,避免内存泄漏
redisTemplate.opsForValue().set(key, "1", 24, TimeUnit.HOURS);
}
}
}
// 3. 消息丢失问题
public class MessageLoss {
public void preventMessageLoss() {
// Producer端配置
Properties producerProps = new Properties();
producerProps.put("acks", "all"); // 等待所有ISR确认
producerProps.put("retries", Integer.MAX_VALUE); // 无限重试
producerProps.put("enable.idempotence", true); // 启用幂等性
// Broker端配置
Properties brokerProps = new Properties();
brokerProps.put("min.insync.replicas", 2); // 至少2个副本确认
brokerProps.put("unclean.leader.election.enable", false); // 禁止非ISR选举
// Consumer端配置
Properties consumerProps = new Properties();
consumerProps.put("enable.auto.commit", false); // 手动提交offset
}
}
// 4. 分区倾斜问题
public class PartitionSkew {
public void detectSkew() {
// 检查每个分区的消息量和消费速率
// kafka-run-class.sh kafka.tools.ConsumerOffsetChecker
// 监控每个分区的大小
// du -sh /var/kafka-logs/topic-partition-*
}
public void resolveSkew() {
// 解决方案1:重新设计分区键
// 原来:userId作为key
// 改进:userId + timestamp的哈希作为key
// 解决方案2:增加分区数
// kafka-topics.sh --alter --topic mytopic
// --partitions 20 --bootstrap-server localhost:9092
// 解决方案3:自定义分区器
public class BalancedPartitioner implements Partitioner {
@Override
public int partition(String topic, Object key, byte[] keyBytes,
Object value, byte[] valueBytes, Cluster cluster) {
// 实现更均匀的分区逻辑
return customPartitionLogic(key, cluster.partitionCountForTopic(topic));
}
}
}
}
}
七、高级特性:深入理解Kafka生态
7.1 Kafka Streams深度解析
public class KafkaStreamsAdvanced {
// 1. 状态存储和容错
public class StateStoreAndFaultTolerance {
public void demonstrateStateStore() {
StreamsBuilder builder = new StreamsBuilder();
// 创建状态存储
StoreBuilder<KeyValueStore<String, Long>> storeBuilder =
Stores.keyValueStoreBuilder(
Stores.persistentKeyValueStore("user-clicks"),
Serdes.String(),
Serdes.Long()
);
builder.addStateStore(storeBuilder);
KStream<String, String> clicks = builder.stream("clicks");
// 使用状态存储进行有状态处理
clicks.transform(() -> new Transformer<String, String, KeyValue<String, Long>>() {
private KeyValueStore<String, Long> stateStore;
@Override
public void init(ProcessorContext context) {
stateStore = (KeyValueStore<String, Long>)
context.getStateStore("user-clicks");
}
@Override
public KeyValue<String, Long> transform(String key, String value) {
Long currentCount = stateStore.get(key);
Long newCount = (currentCount == null) ? 1L : currentCount + 1L;
stateStore.put(key, newCount);
return new KeyValue<>(key, newCount);
}
@Override
public void close() {}
}, "user-clicks");
}
// 容错机制:Changelog Topic
public void changelogMechanism() {
// 每个状态存储都有对应的changelog topic
// 状态变更会写入changelog,用于故障恢复
// Recovery过程:重放changelog重建状态
}
}
// 2. 时间语义和窗口操作
public class TimeAndWindowing {
public void windowOperations() {
StreamsBuilder builder = new StreamsBuilder();
KStream<String, String> events = builder.stream("events");
// 滚动窗口:不重叠的固定大小窗口
KTable<Windowed<String>, Long> tumblingCounts = events
.groupByKey()
.windowedBy(TimeWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(5)))
.count();
// 滑动窗口:重叠的固定大小窗口
KTable<Windowed<String>, Long> hoppingCounts = events
.groupByKey()
.windowedBy(TimeWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(5))
.advanceBy(Duration.ofMinutes(1)))
.count();
// 会话窗口:基于活动的动态窗口
KTable<Windowed<String>, Long> sessionCounts = events
.groupByKey()
.windowedBy(SessionWindows.with(Duration.ofMinutes(30)))
.count();
}
// 时间语义配置
public void configureTimeSemantics() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 事件时间 vs 处理时间
props.put(StreamsConfig.DEFAULT_TIMESTAMP_EXTRACTOR_CLASS_CONFIG,
WallclockTimestampExtractor.class);
// 乱序处理:允许的最大延迟
props.put(StreamsConfig.WINDOW_STORE_CHANGE_LOG_ADDITIONAL_RETENTION_MS_CONFIG,
24 * 60 * 60 * 1000L); // 24小时
}
}
// 3. 流表连接
public class StreamTableJoins {
public void demonstrateJoins() {
StreamsBuilder builder = new StreamsBuilder();
KStream<String, String> orders = builder.stream("orders");
KTable<String, String> users = builder.table("users");
// Stream-Table Join:流事件与表状态连接
KStream<String, String> enrichedOrders = orders.join(users,
(orderValue, userValue) -> {
// 将用户信息附加到订单
return enrichOrder(orderValue, userValue);
});
// Stream-Stream Join:需要时间窗口
KStream<String, String> payments = builder.stream("payments");
KStream<String, String> orderPayments = orders.join(payments,
(orderValue, paymentValue) -> combineOrderPayment(orderValue, paymentValue),
JoinWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(10)));
}
}
}
7.2 Kafka Connect深度应用
public class KafkaConnectAdvanced {
// 1. 自定义Connector开发
public class CustomSourceConnector extends SourceConnector {
@Override
public void start(Map<String, String> props) {
// 初始化连接器配置
this.config = new CustomConnectorConfig(props);
// 建立外部系统连接
this.externalClient = createExternalClient(config);
}
@Override
public List<Map<String, String>> taskConfigs(int maxTasks) {
// 根据最大任务数分配工作
List<Map<String, String>> configs = new ArrayList<>();
// 获取需要监控的数据源列表
List<String> dataSources = getDataSources();
// 将数据源分配给不同的任务
int sourcesPerTask = Math.max(1, dataSources.size() / maxTasks);
for (int i = 0; i < maxTasks; i++) {
Map<String, String> taskConfig = new HashMap<>(config.originalsStrings());
int startIndex = i * sourcesPerTask;
int endIndex = Math.min((i + 1) * sourcesPerTask, dataSources.size());
if (startIndex < dataSources.size()) {
taskConfig.put("assigned.sources",
String.join(",", dataSources.subList(startIndex, endIndex)));
configs.add(taskConfig);
}
}
return configs;
}
@Override
public Class<? extends Task> taskClass() {
return CustomSourceTask.class;
}
}
// 2. 错误处理和死信队列
public class ErrorHandlingStrategy {
public void configureErrorHandling() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 错误容忍配置
props.put("errors.tolerance", "all");
props.put("errors.log.enable", true);
props.put("errors.log.include.messages", true);
// 死信队列配置
props.put("errors.deadletterqueue.topic.name", "connect-dlq");
props.put("errors.deadletterqueue.topic.replication.factor", 3);
props.put("errors.deadletterqueue.context.headers.enable", true);
}
// 自定义错误处理器
public class CustomErrorReporter implements ErrorReporter {
@Override
public Future<Void> report(ProcessingContext context, Throwable error) {
// 记录详细错误信息
log.error("Processing error for record: {}", context.record(), error);
// 发送告警
alertingService.sendAlert("Kafka Connect Error",
buildErrorMessage(context, error));
// 写入监控系统
metricsCollector.incrementErrorCount(context.connector(),
error.getClass().getSimpleName());
return CompletableFuture.completedFuture(null);
}
}
}
// 3. 性能优化配置
public class ConnectPerformanceTuning {
public void optimizePerformance() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// 任务配置
props.put("tasks.max", 4);
// 批处理配置
props.put("producer.batch.size", 32768);
props.put("producer.linger.ms", 20);
props.put("consumer.max.poll.records", 1000);
// 内存配置
props.put("producer.buffer.memory", 67108864); // 64MB
props.put("offset.flush.interval.ms", 60000); // 1分钟
// 并发配置
props.put("producer.max.in.flight.requests.per.connection", 5);
props.put("consumer.fetch.min.bytes", 50000);
}
}
}
八、面试真题解析
8.1 架构设计题
题目:设计一个实时用户行为分析系统,日峰值10亿条消息,要求秒级延迟,如何使用Kafka?
public class RealTimeAnalyticsSystem {
// 1. 整体架构设计
public void systemArchitecture() {
/*
* 数据流:
* App/Web -> API Gateway -> Kafka (raw-events)
* -> Kafka Streams (processing) -> Kafka (processed-events)
* -> Consumer -> Redis/HBase -> API -> Dashboard
*/
}
// 2. Kafka集群规划
public void clusterPlanning() {
// 容量规划:
// 10亿条/天 ≈ 11,574条/秒 (峰值可能是平均值的10倍)
// 假设每条消息1KB,峰值吞吐量:100MB/s
// 分区规划:
// 单分区最大吞吐量:10MB/s
// 至少需要:100MB/s ÷ 10MB/s = 10个分区
// 考虑增长和容错:建议20-30个分区
// 集群规模:
// 副本因子:3
// 存储需求:1KB × 10亿 × 7天 × 3副本 = 21TB
// 建议:6个Broker,每个4TB SSD
}
// 3. 关键配置优化
public Properties getOptimizedConfig() {
Properties props = new Properties();
// Producer配置(高吞吐)
props.put("acks", "1"); // 平衡可靠性和性能
props.put("batch.size", 65536); // 64KB批处理
props.put("linger.ms", 10); // 10ms等待
props.put("compression.type", "lz4"); // 快速压缩
props.put("buffer.memory", 134217728); // 128MB缓冲
// Topic配置(高性能存储)
props.put("log.segment.bytes", 1073741824); // 1GB段文件
props.put("log.retention.hours", 168); // 7天保留
props.put("log.cleanup.policy", "delete"); // 删除策略
props.put("min.insync.replicas", 2); // 最少2个同步副本
return props;
}
// 4. 实时处理逻辑
public void realTimeProcessing() {
StreamsBuilder builder = new StreamsBuilder();
// 原始事件流
KStream<String, UserEvent> rawEvents = builder.stream("raw-events");
// 实时聚合:5分钟滚动窗口
KTable<Windowed<String>, Long> userActivityCounts = rawEvents
.filter((key, event) -> event.getEventType().equals("click"))
.groupByKey()
.windowedBy(TimeWindows.of(Duration.ofMinutes(5)))
.count(Named.as("user-activity-counts"));
// 异常检测:基于滑动窗口的阈值检测
KStream<String, Alert> anomalies = userActivityCounts
.toStream()
.filter((windowedKey, count) -> count > ANOMALY_THRESHOLD)
.map((windowedKey, count) -> KeyValue.of(
windowedKey.key(),
new Alert(windowedKey.key(), count, "High activity detected")
));
// 输出到不同的topic
anomalies.to("alerts");
userActivityCounts.toStream().to("user-metrics");
}
}
8.2 性能优化题
题目:Producer发送消息的吞吐量只有预期的50%,如何排查和优化?
public class ThroughputOptimization {
// 1. 问题排查步骤
public void troubleshootingSteps() {
// Step 1: 检查Producer配置
checkProducerConfig();
// Step 2: 检查网络状况
checkNetworkLatency();
// Step 3: 检查Broker性能
checkBrokerPerformance();
// Step 4: 检查分区策略
checkPartitionStrategy();
// Step 5: 检查应用逻辑
checkApplicationLogic();
}
// 2. 逐项检查和优化
public void optimizationChecklist() {
// 配置优化
Properties props = new Properties();
// 问题1:批处理太小
// 原配置:batch.size=16384 (16KB)
// 优化后:batch.size=65536 (64KB)
props.put("batch.size", 65536);
// 问题2:等待时间太短
// 原配置:linger.ms=0
// 优化后:linger.ms=20
props.put("linger.ms", 20);
// 问题3:缓冲区太小
// 原配置:buffer.memory=33554432 (32MB)
// 优化后:buffer.memory=134217728 (128MB)
props.put("buffer.memory", 134217728);
// 问题4:压缩算法选择
// 原配置:compression.type=gzip
// 优化后:compression.type=lz4
props.put("compression.type", "lz4");
// 问题5:并发连接数
// 原配置:max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=1
// 优化后:max.in.flight.requests.per.connection=5
props.put("max.in.flight.requests.per.connection", 5);
}
// 3. 应用层优化
public class ApplicationOptimization {
// 异步发送模式
public void asyncSendPattern() {
CompletableFuture<List<RecordMetadata>> futures = new ArrayList<>();
for (Message message : messages) {
CompletableFuture<RecordMetadata> future = CompletableFuture.supplyAsync(() -> {
try {
return producer.send(createRecord(message)).get();
} catch (Exception e) {
throw new RuntimeException(e);
}
});
futures.add(future);
}
// 等待所有发送完成
CompletableFuture.allOf(futures.toArray(new CompletableFuture[0])).join();
}
// 连接池优化
public class ProducerPool {
private final List<KafkaProducer<String, String>> producers;
private final AtomicInteger currentIndex = new AtomicInteger(0);
public ProducerPool(int poolSize) {
this.producers = IntStream.range(0, poolSize)
.mapToObj(i -> new KafkaProducer<String, String>(getProducerConfig()))
.collect(Collectors.toList());
}
public KafkaProducer<String, String> getProducer() {
int index = currentIndex.getAndIncrement() % producers.size();
return producers.get(index);
}
}
}
// 4. 监控和度量
public void monitoringOptimization() {
// 关键指标监控
// 1. record-send-rate: 发送速率
// 2. batch-size-avg: 平均批处理大小
// 3. compression-rate: 压缩比
// 4. buffer-available-bytes: 可用缓冲区
// 5. record-queue-time-avg: 队列等待时间
// JMX监控示例
public void enableJMXMonitoring() {
Properties props = new Properties();
props.put("metric.reporters", "org.apache.kafka.common.metrics.JmxReporter");
props.put("auto.include.jmx.reporter", true);
}
}
}
九、总结:面试中的加分点
9.1 深度理解展示
- 不要只背概念:理解Kafka为什么这样设计,解决了什么问题
- 结合实际场景:能够根据具体业务需求选择合适的配置
- 性能调优经验:有过生产环境性能问题的排查和解决经验
- 监控和运维:了解如何监控Kafka集群健康状态
9.2 常见误区避免
- 过度设计:不是所有场景都需要exactly-once语义
- 盲目追求高可用:要在性能和可靠性之间找平衡
- 忽略运维复杂性:Kafka不是部署完就不管的系统
- 不考虑数据倾斜:分区策略设计要考虑数据分布
9.3 面试准备建议
- 动手实践:搭建Kafka集群,运行示例代码
- 阅读源码:理解关键流程的实现原理
- 关注社区:了解最新特性和最佳实践
- 总结经验:整理自己在项目中遇到的问题和解决方案
记住,优秀的候选人不仅要懂技术,更要能将技术应用到实际业务中解决问题。面试官更看重的是你的工程思维和解决问题的能力,而不是死记硬背的理论知识。
本文从实战角度深入剖析了Kafka的核心原理和性能优化,希望能帮助你在面试中脱颖而出。记住,技术的价值在于解决实际问题,而不是炫技。

























 1237
1237

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










