一:创建线程
使用两种不同的方法创建线程,每个线程打印从0到4的日志信息。为了更好的看到打印信息的顺序,在每个打印里会休眠不同的时间。
1.1 PrintThread 继承于Thread类实现打印线程
public class PrintThread extends Thread{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("PrintThread "+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.2 PrintRunnable重新Runnable实现打印线程
public class PrintRunnable implements Runnable{
@Override
public void run() {
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("PrintRunable "+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
}
}
1.3 运行线程查看结果:
/**
* @function: 普通调用线程,线程会交替执行
*/
public static void printNormal() {
PrintThread printThread = new PrintThread();
printThread.start();
PrintRunnable printRunnable = new PrintRunnable();
new Thread(printRunnable).start();
}
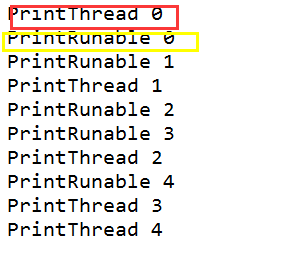
结果如下图:
如果仔细观察上边的打印信息,发现是交错打印的。如果想实现两个不同线程按顺序执行,比如PrintThread执行完在执行PrintRunnable。如果想实现不同线程间有顺序执行,有两种方案,第一种使用join的字段,第二种使用对象锁。
二:通过join()方法实现线程有序执行
2.1 实现代码:
/**
* @function: 有顺序的调用线程,通过join的方法,保证一个个线程按顺序执行
*/
public static void printOrder() {
try {
// 通过join的方法,保证一个个线程按顺序执行
PrintThread printThread = new PrintThread();
printThread.start();
printThread.join();
PrintRunnable printRunnable = new PrintRunnable();
Thread threadRunnable= new Thread(printRunnable);
threadRunnable.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
2.2 执行结果:
2.3 原因分析:
其实Join方法实现是通过wait(oject提供的方法),当main线程调用printThread.join时候,main线程会获得线程对象 printThread的锁(wait 意味着拿到该对象的内置对象锁),调用该对象的wait(等待时间),直到该对象唤醒main线程,比如printThread执行完之后。
这就意味着main 线程调用printThread.join时,必须能够拿到线程printThread对象的锁,如果其他线程获取了printThread对象的锁,它是无法wait的.
3通过外部对象锁Lock实现
3.1代码:不同的线程传入一个外部的对象锁,两个线程使用的是同一把外部锁
public class PrintLockThread extends Thread{
private Lock lock;
public PrintLockThread(Lock lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("PrintLockThread "+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(2);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
lock.unlock();
}
}
public class PrintLockRunnable implements Runnable{
private Lock lock;
public PrintLockRunnable(Lock lock) {
super();
this.lock = lock;
}
@Override
public void run() {
lock.lock();
for (int i = 0; i < 5; i++) {
System.out.println("PrintLockRunnable "+i);
try {
Thread.sleep(1);
} catch (InterruptedException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
lock.unlock();
}
}
//调用代码
public static void printOrderByLock() {
try {
Lock lock = new ReentrantLock();
PrintLockThread printThread = new PrintLockThread(lock);
printThread.start();
PrintLockRunnable printRunnable = new PrintLockRunnable(lock);
Thread threadRunnable= new Thread(printRunnable);
threadRunnable.start();
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
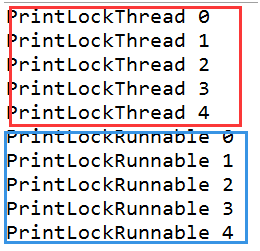
3.3 运行结果及分析
结果分析: 两个线程PrintLockThread和PrintLockRunnable内部都需要传入一个Lock锁对象,在各自允许期间,调用锁锁住代码,执行完,释放锁,让下一个线程接着使用。注意传入的锁必须是同一个锁,才能起到锁住线程的作用。























 489
489

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








