时间限制:1 秒
内存限制:32 兆
特殊判题:否
提交:929
解决:523
-
题目描述:
-
We are all familiar with pre-order, in-order and post-order traversals of binary trees. A common problem in data structure classes is to find the pre-order traversal of a binary tree when given the in-order and post-order traversals. Alternatively, you can find the post-order traversal when given the in-order and pre-order. However, in general you cannot determine the in-order traversal of a tree when given its pre-order and post-order traversals. Consider the four binary trees below:

All of these trees have the same pre-order and post-order traversals. This phenomenon is not restricted to binary trees, but holds for general m-ary trees as well.
-
输入:
-
Input will consist of multiple problem instances. Each instance will consist of a line of the form
m s1 s2
indicating that the trees are m-ary trees, s1 is the pre-order traversal and s2 is the post-order traversal.All traversal strings will consist of lowercase alphabetic characters. For all input instances, 1 <= m <= 20 and the length of s1 and s2 will be between 1 and 26 inclusive. If the length of s1 is k (which is the same as the length of s2, of course), the first k letters of the alphabet will be used in the strings. An input line of 0 will terminate the input.
-
输出:
-
For each problem instance, you should output one line containing the number of possible trees which would result in the pre-order and post-order traversals for the instance. All output values will be within the range of a 32-bit signed integer. For each problem instance, you are guaranteed that there is at least one tree with the given pre-order and post-order traversals.
-
样例输入:
-
2 abc cba 2 abc bca 10 abc bca 13 abejkcfghid jkebfghicda
-
样例输出:
-
4 1 45 207352860
-
答疑:
解题遇到问题?分享解题心得?讨论本题请访问:http://t.jobdu.com/thread-7768-1-1.html
解题思路:
其实这个题是求解给出n叉树的前序和后序遍历,问该n叉树有多少种。
有人已经做过分析了,而且很详细,贴过来过来。如果一遍没看懂,建议多看几遍。
【分析过程】
例一:已知二叉树的先序遍历为:abc,后序遍历为:cba,求满足条件的二叉树的个数。
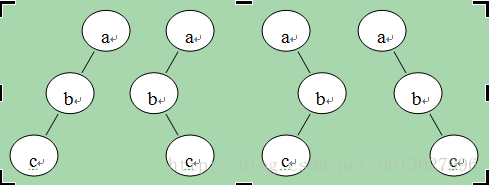
分析:首先容易得出二叉树的根结点一定是a,再由剩下的先序遍历结点序列bc(第一个结点为b)和后序遍历结点序列cb(最后一个结点为b),可知结点bc共同组成根结点a的一个子树,且其中结点b一定是该子树的根结点。这个子树可以是根结点a的左子树,也可以是右子树。如下图所示:

所以,满足条件的二叉树的个数sum至少为2(sum=2)。又因为对于结点bc来说,c不管是其左结点还是右结点,都满足先序和后序遍历的要求。因此满足条件的二叉树的个数sum=sum*2=2*2=4。其形状如下图所示:
例二:已知10叉树的先序遍历为:abc,后序遍历为:bca,求满足条件的10叉树的个数。
分析:首先容易得出二叉树的根结点一定是a,再由剩下的先序遍历结点序列bc和后序遍历结点序列bc完全相同,可知结点bc不能组成根结点a的一个子树,结点b和c只能是根结点a的叶结点,并且结点b一定处于结点c的左边。因为是10叉树,所以根结点a可以有10个子结点,设编号为1~10,则结点b和c的编号可以是:(1,2)、(1,3)、(1,4)、(1,5)、(1,6)、(1,7)、(1,8)、(1,9)、(1,10)、(2,3)、(2,4)、……,由组合数知识可知符合条件的共有
 种。
种。
例三:已知13叉树的先序遍历为:abejkcfghid,后序遍历为:jkebfghicda,求满足条件的13叉树的个数。
分析:首先容易得出二叉树的根结点一定是a,再由剩下的先序遍历结点序列bejkcfghid(第一个结点为b)和后序遍历结点序列jkebfghicd(最后一个结点为d),其首尾结点不一样,可知结点集合{bejkcfghid}不可能构成根结点的一个子树,也就是说,根结点a的子树至少为2个,且第1个子树的根结点必为b(由剩下的先序遍历结点序列bejkcfghid可得),再由剩下的后序遍历结点序列jkebfghicd可知,第一个子树由结点集合{jkeb}组成;而在先序遍历结点序列bejkcfghid中位于第一个子树结点集合{bejk}后的第一个结点是c,因此可推导出第二个子树的根结点必为c,再由后序遍历结点序列jkebfghicd可知其结点集合为{cfghi};同理可得第三个子树的结点集合为{d},因此,根结点a的有3个子树,因为是13叉树,所以这3个子树的形态有
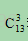 种组合方式。
种组合方式。
第一个子树由先序遍历结点序列bejk和后序遍历结点序列jkeb组成,设符合条件的子树数为m1;
第二个子树由先序遍历结点序列cfghi和后序遍历结点序列fghic组成,设符合条件的子树数为m2;
第三个子树由先序遍历结点序列d和后序遍历结点序列d组成,因此d为叶结点,设符合条件的子树数为1;
M1和m2的值求解同样也是由先序和后序遍历求符合条件的13叉树个数的问题,按照上述思路可递归实现,得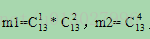
1、设符合条件的n叉树的个数为sum,初值为1;
2、根据n叉树的先序遍历求出根结点,根结点的子树数为k(初值为0),n叉树结点个数为m;
3、找出先序遍历中根结点后一个结点和后序遍历中根结点前一个结点,如果这两个结点相同,则n叉树只有一个子树(k=1),从树的形态上讲,这个子树可以是根结点的第1个子树或第2个子树……或第n个子树,因此共有
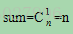 种;
种;
4、如果这两个结点不相同,则说明根结点存在多个子树;从后序遍历的第一个结点开始找与先序遍历中根结点后一个结点相同的结点,并记下位置t1,则后序遍历1~ t1之间的结点和先序遍历2~ t1+1之间的结点构成了根结点的第一个子树(k=1);接着从后序遍历的第t1+1个结点开始找与先序遍历中第t1+2结点相同的结点,并记下位置t2,则后序遍历t1+1~ t2之间的结点和先序遍历t1+2~ t2+1之间的结点构成了根结点的第二个子树(k=2);若t2+1<m,则根结点还有其它子树,按上述方法重复查找,直到t2+1=m。则根结点的k个子树全部确定,其形状排列方式共有
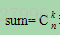 种;
种;
5、若根结点的k个子树只有一个结点,则结束求解,否则对根结点的k个子树按本解题策略分别进行递归求解,求解其符合条件的子树的个数sum1、sum2、sum3……、sumk;则
 。
。
【分析结束】
其实总结起来就是分析每个树有多少个子树,递归思想可以解决。
注意排列方法数求解过程,不要做重复计算,否则肯定会超时。
#include <iostream>
#include <fstream>
#include <string>
using namespace std;
long dfs(string s1, string s2, int n);
long comb(int n, int m);
int main()
{
int n;
string s1, s2;
while (cin >> n >> s1 >> s2) {
cout << dfs(s1, s2, n) << endl;
}
return 0;
}
long dfs(string s1, string s2, int n)
{
if (s1.length() == 1) return 1;
else {
long sum = 1;
int count = 0;
string tmp1, tmp2;
s1 = s1.substr(1);
s2 = s2.substr(0, s2.length() - 1);
while (s1.length() != 0) {
string::size_type p = s2.find(s1[0]);
tmp1 = s1.substr(0, p + 1);
tmp2 = s2.substr(0, p + 1);
s1 = s1.substr(p + 1);
s2 = s2.substr(p + 1);
count++;
sum *= dfs(tmp1, tmp2, n);
}
return comb(n, count) * sum;
}
}
long comb(int n, int m)
{
long a = 1, b = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < m; i++) {
a *= (n - i);
b *= (m - i);
}
return a / b;
} (2)不错的
#include <iostream>
#include <string.h>
#include <string>
#include <stdio.h>
using namespace std;
char str1[30],str2[30];
string pre,post;
int n;
int c[23][23];
//组合数计算
void initc(){
c[1][0] = c[1][1] = 1;
for(int i=2; i<23; i++){
c[i][0] = 1;
for(int j=1; j<=i; j++){
c[i][j] = c[i-1][j] + c[i-1][j-1];
}
}
}
int getCnt(string left,string right){
int cnt=0;
int res = 1;
if(left.size() <= 1) return n; //只有一个元素,可以放置n个位置
for(int i=0; i<left.length();){
int j=i;
while(j<left.length() && right[j] != left[i]) j++ ;
//一层的单个叶子节点不考虑
if(j>i)
res *= getCnt(left.substr(i+1,j-i), right.substr(i,j-i));
cnt++;
i = j+1;
}
res *= c[n][cnt];
return res;
}
int main() {
freopen("in.txt","r",stdin);
initc();
while(cin >> n ){
if(!n) break;
cin >> pre >> post;
int ans = 1;
if(pre.length() > 1)
ans = getCnt(pre.substr(1,pre.length()-1), post.substr(0, pre.length()-1) );
cout << ans << endl;
}
return 0;
}
#include <stdio.h>
#include <string>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int c[21][21];
int n;
long long test(string pre, string post) {
long long sum = 1;
int num = 0;
int k = 0, i;
pre.erase(pre.begin());
post=post.substr(0, post.length()-1);
while (k < pre.length()) {
for (i = 0; i < post.length(); i++)
if (pre[k] == post[i]) {
sum *= test(pre.substr(k, i - k + 1),
post.substr(k, i - k + 1));
num++; //num代表串被分成了几段(例如 (bejkcfghid,jkebfghicd) = (bejk, cfghi, d) )
k = i + 1;
break;
}
}
//cout << pre << " " << post <<" " << t1 << " =" << num << endl << endl;
sum *= c[num][n]; //从n中取num个的取法个数
return sum;
}
void getsc() {
int i, j;
c[0][1] = c[1][1] = 1;
for (i = 2; i < 21; i++) {
c[0][i] = 1;
for (j = 1; j <= i; j++){
if (i == j)
c[j][i] = 1;
else
c[j][i] = c[j - 1][i - 1] + c[j][i - 1];
}
}
}
int main() {
string pre, post;
getsc();
while ((cin >> n >> pre >> post) && n) {
cout << test(pre, post) << endl; //printf("%ld\n",test(pre,post));
}
return 0;
}
/**************************************************************
Problem: 1044
User: coder
Language: C++
Result: Accepted
Time:0 ms
Memory:1520 kb
****************************************************************/







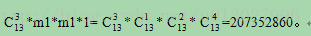














 1465
1465











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








