一、为什么要考虑Window UI的线程安全问题?
Access to Windows Forms controls is not inherently thread safe. Ifyou have two or more threads manipulating the state of a control, it ispossible to force the control into an inconsistent state. Other thread-relatedbugs are possible, such as race conditions and deadlocks. It is important tomake sure that access to your controls is performed in a thread-safe way.
1. Windows程序消息机制
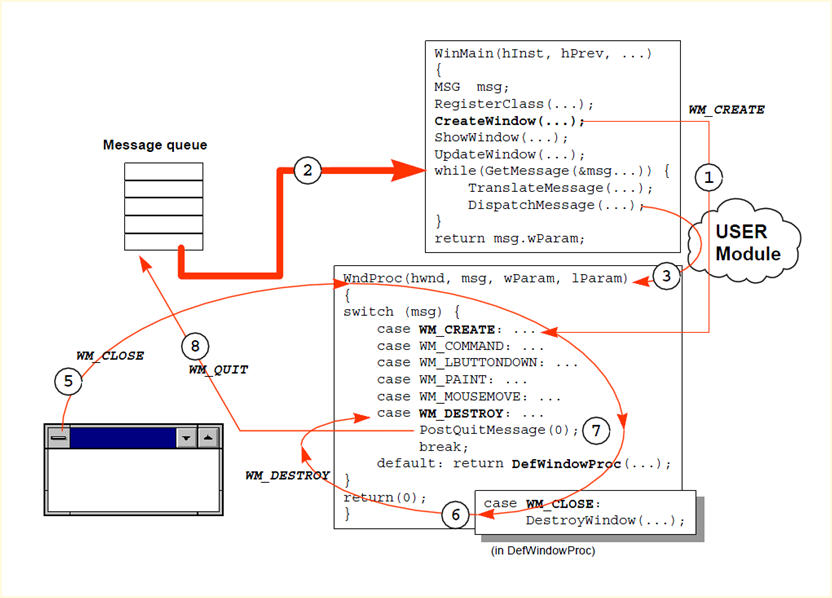
Windows GUI程序是基于消息机制的,有个主线程维护着一个消息泵。这个消息泵让windows程序生生不息。
Windows GUI程序的消息循环
Windows程序有个消息队列,窗体上的所有消息是这个队列里面消息的最主要来源。这里的while循环使用了GetMessage()这个方法,这是个阻塞方法,也就是队列为空时方法就会被阻塞,从而这个while循环停止运动。
这个主线程维护着整个窗体以及上面的子控件。当它得到一个消息,就会调用DispatchMessage方法派遣消息,这会引起对窗体上的窗口过程的调用。窗口过程里面当然是程序员提供的窗体数据更新代码和其它代码。
2. .Net里面的消息循环
public static void Main(string[] args)
{
Form f = new Form();
Application.Run(f);
}
.Net窗体程序封装了上述的while循环,这个循环就是通过Application.Run方法启动的。
3、线程外操作GUI控件的问题
如果从另外一个线程操作Windows窗体上的控件,就会和主线程产生竞争,造成不可预料的结果,甚至死锁。因此Windows GUI编程有一个规则,就是只能通过创建控件的线程来操作控件的数据,否则就可能产生不可预料的结果。
(The .NETFramework helps you detect when you are accessing your controls in a mannerthat is not thread safe. When you are running your application in the debugger,and a thread other than the one which created a control tries to call thatcontrol, the debugger raises an InvalidOperationExceptionwith the message, "Control (control name) accessed from a thread otherthan the thread it was created on.")
二、.Net中Control类的ISynchronizeInvoke接口方法
.Net里面,为了方便地解决线程安全的UI问题,Control类实现了ISynchronizeInvoke接口,提供了Invoke和BeginInvoke方法来提供让其它线程更新GUI界面控件的机制。
public interface ISynchronizeInvoke
{
[HostProtection(SecurityAction.LinkDemand, Synchronization=true, ExternalThreading=true)]
IAsyncResult BeginInvoke(Delegate method, object[] args);
object EndInvoke(IAsyncResult result);
object Invoke(Delegate method, object[] args);
bool InvokeRequired { get; }
}
1、window消息发送--线程间和进程间通信机制
Windows消息机制是windows平台上的线程或者进程间通信机制之一。Windows消息值其实就是定义的一个数据结构,最重要的是消息的类型,它就是一个整数;然后就是消息的参数。消息的参数可以表示很多东西。
Windows提供了一些API用来向一个线程的消息队列发送消息。因此,一个线程可以向另一个线程的消息队列发送消息从而告诉对方做什么,这样就完成了线程间的通信。有些API发送消息需要一个窗口句柄,这种函数可以把消息发送到指定窗口的主线程消息队列;而有些则可以直接通过线程句柄,把消息发送到该线程消息队列中。
用消息机制通信
SendMessage是Windows API,用来把一个消息发送到一个窗口的消息队列。这个方法是个阻塞方法,也就是操作系统会确保消息的确发送到目的消息队列,并且该消息被处理完毕以后,该函数才返回。返回之前,调用者将会被暂时阻塞。
PostMessage也是一个用来发送消息到窗口消息队列的API函数,但这个方法是非阻塞的。也就是它会马上返回,而不管消息是否真的发送到目的地,也就是调用者不会被阻塞。
2、ISynchronizeInvoke接口的Invoke and BeginInvoke
Invoke或者BeginInvoke方法都需要一个委托对象作为参数。委托类似于回调函数的地址,因此调用者通过这两个方法就可以把需要调用的函数地址封送给界面线程。这些方法里面如果包含了更改控件状态的代码,那么由于最终执行这个方法的是界面线程,从而避免了竞争条件,避免了不可预料的问题。如果其它线程直接操作界面线程所属的控件,那么将会产生竞争条件,造成不可预料的结果。
使用Invoke完成一个委托方法的封送,就类似于使用SendMessage方法来给界面线程发送消息,是一个同步方法。也就是说在Invoke封送的方法被执行完毕前,Invoke方法不会返回,从而调用者线程将被阻塞。
使用BeginInvoke方法封送一个委托方法,类似于使用PostMessage进行通信,这是一个异步方法。也就是该方法封送完毕后马上返回,不会等待委托方法的执行结束,调用者线程将不会被阻塞。但是调用者也可以使用EndInvoke方法或者其它类似WaitHandle机制等待异步操作的完成。
(但是在内部实现上,Invoke和BeginInvoke都是用了PostMessage方法,从而避免了SendMessage带来的问题。而Invoke方法的同步阻塞是靠WaitHandle机制来完成的。)
3、使用场合问题
如果你的后台线程在更新一个UI控件的状态后不需要等待,而是要继续往下处理,那么你就应该使用BeginInvoke来进行异步处理。
如果你的后台线程需要操作UI控件,并且需要等到该操作执行完毕才能继续执行,那么你就应该使用Invoke。否则,在后台线程和主截面线程共享某些状态数据的情况下,如果不同步调用,而是各自继续执行的话,可能会造成执行序列上的问题,虽然不发生死锁,但是会出现不可预料的显示结果或者数据处理错误。
可以看到ISynchronizeInvoke有一个属性,InvokeRequired。这个属性就是用来在编程的时候确定,一个对象访问UI控件的时候是否需要使用Invoke或者BeginInvoke来进行封送。如果不需要那么就可以直接更新。在调用者对象和UI对象同属一个线程的时候这个属性返回false。在后面的代码分析中我们可以看到,Control类对这一属性的实现就是在判断调用者和控件是否属于同一个线程的。
thread-safe call to aWindows Forms control
1)Query the control's InvokeRequiredproperty.
2)If InvokeRequired returns true, callInvoke/BeginInvoke with a delegate thatmakes the actual call to the control.
3)If InvokeRequired returns false, call thecontrol directly.
这里需要纠正一个误区,那就是Control类上的异步调用BeginInvoke并没有开辟新的线程完成委托任务,而是让界面控件的所属线程完成委托任务的。
三、利用CLR为Delegate类提供的BeginInvoke方法
通过一个委托来进行同步方法的异步调用,也是.net提供的异步调用机制之一。但是Delegate.BeginInvoke方法是从ThreadPool取出一个线程来执行这个方法,以获得异步执行效果的。也就是说,如果采用这种方式提交多个异步委托,那么这些调用的顺序无法得到保证。而且由于是使用线程池里面的线程来完成任务,使用频繁,会对系统的性能造成影响。
Delegate.BeginInvoke也是将一个委托方法封送到其它线程,从而通过异步机制执行一个方法。调用者线程则可以在完成封送以后去继续它的工作。但是这个方法封送到的最终执行线程是运行库从ThreadPool里面选取的一个线程。
(delegate关键字声明的委托,不但继承了委托的方法,并且CLR还提供了两个特殊的方法BeginInvoke和EndInvoke)
using System;
using System.Threading;
namespace MyNameSpace
{
/// <summary>
/// 声明一个委托 委托的名字是AsyncHandler
/// </summary>
/// <param name="name"></param>
public delegate void AsyncHandler();
static class AsyncTest
{
public static void Method()
{
Console.WriteLine("AsyncTest类中的Method()函数的线程ID是{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);//Environment.CurrentManagedThreadId
if (Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)//判断当前线程是否托管在线程池上
{
Console.WriteLine("AsyncTest类中的Method()函数的线程托管于线程池");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("AsyncTest类中的Method()函数的线程没有托管在线程池上");
}
}
}
class Program
{
static void Main(string[] args)
{
Console.WriteLine("Program类中的Main()函数的线程ID是{0}", Thread.CurrentThread.ManagedThreadId);//Environment.CurrentManagedThreadId
if (Thread.CurrentThread.IsThreadPoolThread)//判断当前线程是否托管在线程池上
{
Console.WriteLine("Program类中的Main()函数的线程托管于线程池");
}
else
{
Console.WriteLine("Program类中的Main()函数的线程没有托管在线程池上");
}
Console.WriteLine();
//把Method 方法分配给委托对象
AsyncHandler async = AsyncTest.Method;
//发起一个异步调用的方法,返回IAsyncResult 对象
IAsyncResult result = async.BeginInvoke(null, null);
//这里会阻碍线程,直到方法执行完毕
async.EndInvoke(result);
Console.Read();
}
}
}
四、makethread-safe calls by usingBackgroundWorker (The preferred way)
To execute a time-consumingoperation in the background, create a BackgroundWorker and listen for eventsthat report the progress of your operation and signal when your operation isfinished. You can create the BackgroundWorker programmatically or you can dragit onto your form from the Components tab of the Toolbox. If you create the BackgroundWorkerin the Windows Forms Designer, it will appear in the Component Tray, and itsproperties will be displayed in the Properties window.
To set up for a backgroundoperation, add an event handler for the DoWork event. Call your time-consuming operationin this event handler. To start the operation, callRunWorkerAsync. To receive notifications ofprogress updates, handle theProgressChanged event. To receive a notificationwhen the operation is completed, handle theRunWorkerCompleted event.
Note
You must be careful not tomanipulate any user-interface objects in your DoWork event handler. Instead, communicate to theuser interface through theProgressChanged andRunWorkerCompleted events.
BackgroundWorker events are not marshaled across AppDomain boundaries. Do not use a BackgroundWorkercomponent to perform multithreaded operations in more than one AppDomain.






















 107
107

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








