摘要: 决策树是对数据进行分类,以此达到预测的目的。该决策树方法先根据训练集数据形成决策树,如果该树不能对所有对象给出正确的分类,那么选择一些例外加入到训练集数据中,重复该过程一直到形成正确的决策集。决策树代表着决策集的树形结构.
决策树是一种依托决策而建立起来的一种树。在机器学习中,决策树是一种预测模型,代表的是一种对象属性与对象值之间的一种映射关系,每一个节点代表某个对象,树中的每一个分叉路径代表某个可能的属性值,而每一个叶子节点则对应从根节点到该叶子节点所经历的路径所表示的对象的值。决策树仅有单一输出,如果有多个输出,可以分别建立独立的决策树以处理不同的输出。
我们统计了14天的气象数据(指标包括outlook,temperature,humidity,windy),并已知这些天气是否打球(play)。如果给出新一天的气象指标数据:sunny,cool,high,TRUE,判断一下会不会去打球。
| outlook | temperature | humidity | windy | play |
| sunny | hot | high | false | no |
| sunny | hot | high | true | no |
| overcast | hot | high | false | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | false | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | false | yes |
| rainy | cool | normal | true | no |
| overcast | cool | normal | true | yes |
| sunny | mild | high | false | no |
| sunny | cool | normal | false | yes |
| rainy | mild | normal | false | yes |
| sunny | mild | normal | true | yes |
| overcast | mild | high | true | yes |
| overcast | hot | normal | false | yes |
| rainy | mild | high | true | no |
这个问题当然可以用朴素贝叶斯法求解,分别计算在给定天气条件下打球和不打球的概率,选概率大者作为推测结果。
现在我们使用ID3归纳决策树的方法来求解该问题。
预备知识:信息熵
熵是无序性(或不确定性)的度量指标。假如事件A的全概率划分是(A1,A2,...,An),每部分发生的概率是(p1,p2,...,pn),那信息熵定义为:

通常以2为底数,所以信息熵的单位是bit。
补充两个对数去处公式:
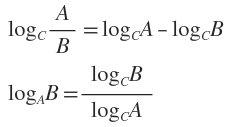
ID3算法
构造树的基本想法是随着树深度的增加,节点的熵迅速地降低。熵降低的速度越快越好,这样我们有望得到一棵高度最矮的决策树。
在没有给定任何天气信息时,根据历史数据,我们只知道新的一天打球的概率是9/14,不打的概率是5/14。此时的熵为:
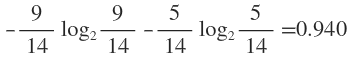
属性有4个:outlook,temperature,humidity,windy。我们首先要决定哪个属性作树的根节点。
对每项指标分别统计:在不同的取值下打球和不打球的次数。
下面我们计算当已知变量outlook的值时,信息熵为多少。
outlook=sunny时,2/5的概率打球,3/5的概率不打球。entropy=0.971
outlook=overcast时,entropy=0
outlook=rainy时,entropy=0.971
而根据历史统计数据,outlook取值为sunny、overcast、rainy的概率分别是5/14、4/14、5/14,所以当已知变量outlook的值时,信息熵为:5/14 × 0.971 + 4/14 × 0 + 5/14 × 0.971 = 0.693
这样的话系统熵就从0.940下降到了0.693,信息增溢gain(outlook)为0.940-0.693=0.247
同样可以计算出gain(temperature)=0.029,gain(humidity)=0.152,gain(windy)=0.048。
gain(outlook)最大(即outlook在第一步使系统的信息熵下降得最快),所以决策树的根节点就取outlook。
接下来要确定N1取temperature、humidity还是windy?在已知outlook=sunny的情况,根据历史数据,我们作出类似table 2的一张表,分别计算gain(temperature)、gain(humidity)和gain(windy),选最大者为N1。
依此类推,构造决策树。当系统的信息熵降为0时,就没有必要再往下构造决策树了,此时叶子节点都是纯的--这是理想情况。最坏的情况下,决策树的高度为属性(决策变量)的个数,叶子节点不纯(这意味着我们要以一定的概率来作出决策)。
Java实现
最终的决策树保存在了XML中,使用了Dom4J,注意如果要让Dom4J支持按XPath选择节点,还得引入包jaxen.jar。程序代码要求输入文件满足ARFF格式,并且属性都是标称变量。
实验用的数据文件:
@relation weather.symbolic
@attribute outlook {sunny, overcast, rainy}
@attribute temperature {hot, mild, cool}
@attribute humidity {high, normal}
@attribute windy {TRUE, FALSE}
@attribute play {yes, no}
@data
sunny,hot,high,FALSE,no
sunny,hot,high,TRUE,no
overcast,hot,high,FALSE,yes
rainy,mild,high,FALSE,yes
rainy,cool,normal,FALSE,yes
rainy,cool,normal,TRUE,no
overcast,cool,normal,TRUE,yes
sunny,mild,high,FALSE,no
sunny,cool,normal,FALSE,yes
rainy,mild,normal,FALSE,yes
sunny,mild,normal,TRUE,yes
overcast,mild,high,TRUE,yes
overcast,hot,normal,FALSE,yes
rainy,mild,high,TRUE,no程序代码:
package com.dfsj;
import java.io.BufferedReader;
import java.io.File;
import java.io.FileReader;
import java.io.FileWriter;
import java.io.IOException;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.Iterator;
import java.util.LinkedList;
import java.util.List;
import java.util.regex.Matcher;
import java.util.regex.Pattern;
import org.dom4j.Document;
import org.dom4j.DocumentHelper;
import org.dom4j.Element;
import org.dom4j.io.OutputFormat;
import org.dom4j.io.XMLWriter;
public class ID3 {
private ArrayList<String> attribute = new ArrayList<String>(); // 存储属性的名称
private ArrayList<ArrayList<String>> attributevalue = new ArrayList<ArrayList<String>>(); // 存储每个属性的取值
private ArrayList<String[]> data = new ArrayList<String[]>();; // 原始数据
int decatt; // 决策变量在属性集中的索引
public static final String patternString = "@attribute(.*)[{](.*?)[}]";
Document xmldoc;
Element root;
public ID3() {
xmldoc = DocumentHelper.createDocument();
root = xmldoc.addElement("root");
root.addElement("DecisionTree").addAttribute("value", "null");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
ID3 inst = new ID3();
inst.readARFF(new File("/home/orisun/test/weather.nominal.arff"));
inst.setDec("play");
LinkedList<Integer> ll=new LinkedList<Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<inst.attribute.size();i++){
if(i!=inst.decatt)
ll.add(i);
}
ArrayList<Integer> al=new ArrayList<Integer>();
for(int i=0;i<inst.data.size();i++){
al.add(i);
}
inst.buildDT("DecisionTree", "null", al, ll);
inst.writeXML("/home/orisun/test/dt.xml");
return;
}
//读取arff文件,给attribute、attributevalue、data赋值
public void readARFF(File file) {
try {
FileReader fr = new FileReader(file);
BufferedReader br = new BufferedReader(fr);
String line;
Pattern pattern = Pattern.compile(patternString);
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
Matcher matcher = pattern.matcher(line);
if (matcher.find()) {
attribute.add(matcher.group(1).trim());
String[] values = matcher.group(2).split(",");
ArrayList<String> al = new ArrayList<String>(values.length);
for (String value : values) {
al.add(value.trim());
}
attributevalue.add(al);
} else if (line.startsWith("@data")) {
while ((line = br.readLine()) != null) {
if(line=="")
continue;
String[] row = line.split(",");
data.add(row);
}
} else {
continue;
}
}
br.close();
} catch (IOException e1) {
e1.printStackTrace();
}
}
//设置决策变量
public void setDec(int n) {
if (n < 0 || n >= attribute.size()) {
System.err.println("决策变量指定错误。");
System.exit(2);
}
decatt = n;
}
public void setDec(String name) {
int n = attribute.indexOf(name);
setDec(n);
}
//给一个样本(数组中是各种情况的计数),计算它的熵
public double getEntropy(int[] arr) {
double entropy = 0.0;
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
sum += arr[i];
}
entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
entropy /= sum;
return entropy;
}
//给一个样本数组及样本的算术和,计算它的熵
public double getEntropy(int[] arr, int sum) {
double entropy = 0.0;
for (int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++) {
entropy -= arr[i] * Math.log(arr[i]+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
}
entropy += sum * Math.log(sum+Double.MIN_VALUE)/Math.log(2);
entropy /= sum;
return entropy;
}
public boolean infoPure(ArrayList<Integer> subset) {
String value = data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt];
for (int i = 1; i < subset.size(); i++) {
String next=data.get(subset.get(i))[decatt];
//equals表示对象内容相同,==表示两个对象指向的是同一片内存
if (!value.equals(next))
return false;
}
return true;
}
// 给定原始数据的子集(subset中存储行号),当以第index个属性为节点时计算它的信息熵
public double calNodeEntropy(ArrayList<Integer> subset, int index) {
int sum = subset.size();
double entropy = 0.0;
int[][] info = new int[attributevalue.get(index).size()][];
for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++)
info[i] = new int[attributevalue.get(decatt).size()];
int[] count = new int[attributevalue.get(index).size()];
for (int i = 0; i < sum; i++) {
int n = subset.get(i);
String nodevalue = data.get(n)[index];
int nodeind = attributevalue.get(index).indexOf(nodevalue);
count[nodeind]++;
String decvalue = data.get(n)[decatt];
int decind = attributevalue.get(decatt).indexOf(decvalue);
info[nodeind][decind]++;
}
for (int i = 0; i < info.length; i++) {
entropy += getEntropy(info[i]) * count[i] / sum;
}
return entropy;
}
// 构建决策树
public void buildDT(String name, String value, ArrayList<Integer> subset,
LinkedList<Integer> selatt) {
Element ele = null;
@SuppressWarnings("unchecked")
List<Element> list = root.selectNodes("//"+name);
Iterator<Element> iter=list.iterator();
while(iter.hasNext()){
ele=iter.next();
if(ele.attributeValue("value").equals(value))
break;
}
if (infoPure(subset)) {
ele.setText(data.get(subset.get(0))[decatt]);
return;
}
int minIndex = -1;
double minEntropy = Double.MAX_VALUE;
for (int i = 0; i < selatt.size(); i++) {
if (i == decatt)
continue;
double entropy = calNodeEntropy(subset, selatt.get(i));
if (entropy < minEntropy) {
minIndex = selatt.get(i);
minEntropy = entropy;
}
}
String nodeName = attribute.get(minIndex);
selatt.remove(new Integer(minIndex));
ArrayList<String> attvalues = attributevalue.get(minIndex);
for (String val : attvalues) {
ele.addElement(nodeName).addAttribute("value", val);
ArrayList<Integer> al = new ArrayList<Integer>();
for (int i = 0; i < subset.size(); i++) {
if (data.get(subset.get(i))[minIndex].equals(val)) {
al.add(subset.get(i));
}
}
buildDT(nodeName, val, al, selatt);
}
}
// 把xml写入文件
public void writeXML(String filename) {
try {
File file = new File(filename);
if (!file.exists())
file.createNewFile();
FileWriter fw = new FileWriter(file);
OutputFormat format = OutputFormat.createPrettyPrint(); // 美化格式
XMLWriter output = new XMLWriter(fw, format);
output.write(xmldoc);
output.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
System.out.println(e.getMessage());
}
}
}最终生成的文件如下:
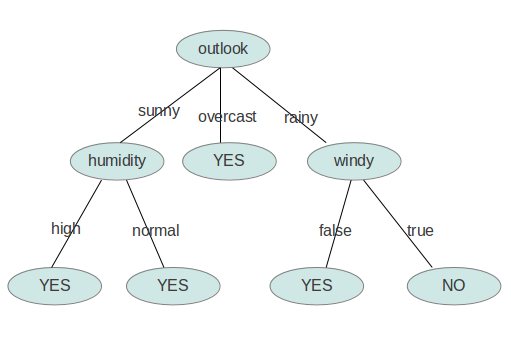
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?>
<root>
<DecisionTree value="null">
<outlook value="sunny">
<humidity value="high">no</humidity>
<humidity value="normal">yes</humidity>
</outlook>
<outlook value="overcast">yes</outlook>
<outlook value="rainy">
<windy value="TRUE">no</windy>
<windy value="FALSE">yes</windy>
</outlook>
</DecisionTree>
</root>用图形象地表示就是:
为便于比较,下面附上c++代码:
ID3.h
#ifndef _ID3_H_
#define _ID3_H_
#include <utility>
#include <list>
#include <map>
#define Type int //样本数据类型
#define Map1 std::map< int, Type > //定义一维map
#define Map2 std::map< int, Map1 > //定义二维map
#define Map3 std::map< int, Map2 > //定义三维map
#define Pair std::pair<int, Type>
#define List std::list< Pair > //一维list
#define SampleSpace std::list< List > //二维list 用于存放样本数据
#define Child std::map< int, Node* > //定义后继节点集合
#define CI const_iterator
/*
* 在ID3算法中,用二维链表存放样本,结构为list< list< pair<int, int> > >,简记为SampleSpace,取名样本空间
* 样本数据从根节点开始往下遍历。每一个节点的定义如下结构体
*/
struct Node
{
int index; //当前节点样本最大增益对应第index个属性,根据这个进行分类的
int type; //当前节点的类型
Child next; //当前节点的后继节点集合
SampleSpace sample; //未分类的样本集合
};
class ID3{
public:
ID3(int );
~ID3();
void PushData(const Type*, const Type); //将样本数据Push给二维链表
void Build(); //构建决策树
int Match(const Type*); //根据新的样本预测结果
void Print(); //打印决策树的节点的值
private:
void _clear(Node*);
void _build(Node*, int);
int _match(const int*, Node*);
void _work(Node*);
double _entropy(const Map1&, double);
int _get_max_gain(const SampleSpace&);
void _split(Node*, int);
void _get_data(const SampleSpace&, Map1&, Map2&, Map3&);
double _info_gain(Map1&, Map2&, double, double);
int _same_class(const SampleSpace&);
void _print(Node*);
private:
int dimension;
Node *root;
};
#endif // _ID3_H_
ID3.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <cassert>
#include <cmath>
#include "ID3.h"
using namespace std;
//初始化ID3的数据成员
ID3::ID3(int dimension)
{
this->dimension = dimension;
root = new Node();
root->index = -1;
root->type = -1;
root->next.clear();
root->sample.clear();
}
//清空整个决策树
ID3::~ID3()
{
this->dimension = 0;
_clear(root);
}
//x为dimension维的属性向量,y为向量x对应的值
void ID3::PushData(const Type *x, const Type y)
{
List single;
single.clear();
for(int i = 0; i < dimension; i++)
single.push_back(make_pair(i + 1, x[i]));
single.push_back(make_pair(0, y));
root->sample.push_back(single);
}
void ID3::_clear(Node *node)
{
Child &next = node->next;
Child::iterator it;
for(it = next.begin(); it != next.end(); it++)
_clear(it->second);
next.clear();
delete node;
}
void ID3::Build()
{
_build(root, dimension);
}
void ID3::_build(Node *node, int dimension)
{
//获取当前节点未分类的样本数据
SampleSpace &sample = node->sample;
//判断当前所有样本是否是同一类,如果不是则返回-1
int y = _same_class(sample);
//如果所有样本是属于同一类
if(y >= 0)
{
node->index = -1;
node->type = y;
return;
}
//在_max_gain()函数中计算出当前节点的最大增益对应的属性,并根据这个属性对数据进行划分
_work(node);
//Split完成后清空当前节点的所有数据,以免占用太多内存
sample.clear();
Child &next = node->next;
for(Child::iterator it = next.begin(); it != next.end(); it++)
_build(it->second, dimension - 1);
}
//判断当前所有样本是否是同一类,如果不是则返回-1
int ID3::_same_class(const SampleSpace &ss)
{
//取出当前样本数据的一个Sample
const List &f = ss.front();
//如果没有x属性,而只有y,直接返回y
if(f.size() == 1)
return f.front().second;
Type y = 0;
//取出第一个样本数据y的结果值
for(List::CI it = f.begin(); it != f.end(); it++)
{
if(!it->first)
{
y = it->second;
break;
}
}
//接下来进行判断,因为list是有序的,所以从前往后遍历,发现有一对不一样,则所有样本不是同一类
for(SampleSpace::CI it = ss.begin(); it != ss.end(); it++)
{
const List &single = *it;
for(List::CI i = single.begin(); i != single.end(); i++)
{
if(!i->first)
{
if(y != i->second)
return -1; //发现不是同一类则返回-1
else
break;
}
}
}
return y; //比较完所有样本的输出值y后,发现是同一类,返回y值。
}
void ID3::_work(Node *node)
{
int mai = _get_max_gain(node->sample);
assert(mai >= 0);
node->index = mai;
_split(node, mai);
}
//获取最大的信息增益对应的属性
int ID3::_get_max_gain(const SampleSpace &ss)
{
Map1 y;
Map2 x;
Map3 xy;
_get_data(ss, y, x, xy);
double s = ss.size();
double entropy = _entropy(y, s); //计算熵值
int mai = -1;
double mag = -1;
for(Map2::iterator it = x.begin(); it != x.end(); it++)
{
double g = _info_gain(it->second, xy[it->first], s, entropy); //计算信息增益值
if(g > mag)
{
mag = g;
mai = it->first;
}
}
if(!x.size() && !xy.size() && y.size()) //如果只有y数据
return 0;
return mai;
}
//获取数据,提取出所有样本的y值,x[]属性值,以及属性值和结果值xy。
void ID3::_get_data(const SampleSpace &ss, Map1 &y, Map2 &x, Map3 &xy)
{
for(SampleSpace::CI it = ss.begin(); it != ss.end(); it++)
{
int c = 0;
const List &v = *it;
for(List::CI p = v.begin(); p != v.end(); p++)
{
if(!p->first)
{
c = p->second;
break;
}
}
++y[c];
for(List::CI p = v.begin(); p != v.end(); p++)
{
if(p->first)
{
++x[p->first][p->second];
++xy[p->first][p->second][c];
}
}
}
}
//计算熵值
double ID3::_entropy(const Map1 &x, double s)
{
double ans = 0;
for(Map1::CI it = x.begin(); it != x.end(); it++)
{
double t = it->second / s;
ans += t * log2(t);
}
return -ans;
}
//计算信息增益
double ID3::_info_gain(Map1 &att_val, Map2 &val_cls, double s, double entropy)
{
double gain = entropy;
for(Map1::CI it = att_val.begin(); it != att_val.end(); it++)
{
double r = it->second / s;
double e = _entropy(val_cls[it->first], it->second);
gain -= r * e;
}
return gain;
}
//对当前节点的sample进行划分
void ID3::_split(Node *node, int idx)
{
Child &next = node->next;
SampleSpace &sample = node->sample;
for(SampleSpace::iterator it = sample.begin(); it != sample.end(); it++)
{
List &v = *it;
for(List::iterator p = v.begin(); p != v.end(); p++)
{
if(p->first == idx)
{
Node *tmp = next[p->second];
if(!tmp)
{
tmp = new Node();
tmp->index = -1;
tmp->type = -1;
next[p->second] = tmp;
}
v.erase(p);
tmp->sample.push_back(v);
break;
}
}
}
}
int ID3::Match(const Type *x)
{
return _match(x, root);
}
int ID3::_match(const Type *v, Node *node)
{
if(node->index < 0)
return node->type;
Child &next = node->next;
Child::iterator p = next.find(v[node->index - 1]);
if(p == next.end())
return -1;
return _match(v, p->second);
}
void ID3::Print()
{
_print(root);
}
void ID3::_print(Node *node)
{
cout << "Index = " << node->index << endl;
cout << "Type = " << node->type << endl;
cout << "NextSize = " << node->next.size() << endl;
cout << endl;
Child &next = node->next;
Child::iterator p;
for(p = next.begin(); p != next.end(); ++p)
_print(p->second);
}
main.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include "ID3.cpp"
#include "ID3.h"
using namespace std;
enum outlook {SUNNY, OVERCAST, RAIN };
enum temp {HOT, MILD, COOL };
enum hum {HIGH, NORMAL };
enum windy {WEAK, STRONG };
int samples[14][4] =
{
{SUNNY , HOT , HIGH , WEAK },
{SUNNY , HOT , HIGH , STRONG},
{OVERCAST, HOT , HIGH , WEAK },
{RAIN , MILD, HIGH , WEAK },
{RAIN , COOL, NORMAL, WEAK },
{RAIN , COOL, NORMAL, STRONG},
{OVERCAST, COOL, NORMAL, STRONG},
{SUNNY , MILD, HIGH , WEAK },
{SUNNY , COOL, NORMAL, WEAK },
{RAIN , MILD, NORMAL, WEAK },
{SUNNY , MILD, NORMAL, STRONG},
{OVERCAST, MILD, HIGH , STRONG},
{OVERCAST, HOT , NORMAL, WEAK },
{RAIN , MILD, HIGH , STRONG}
};
int main()
{
ID3 Tree(4);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[0], 0);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[1], 0);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[2], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[3], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[4], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[5], 0);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[6], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[7], 0);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[8], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[9], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[10], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[11], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[12], 1);
Tree.PushData((int *)&samples[13], 0);
Tree.Build();
Tree.Print();
cout << endl;
for(int i = 0; i < 14; ++i)
cout << "predict value : " <<Tree.Match( (int *)&samples[i] ) << endl;
return 0;
}
参考博客:
http://blog.csdn.net/acdreamers/article/details/44661149
https://my.oschina.net/dfsj66011/blog/343647





















 3387
3387











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








