1、相对定位
(1)相对的是自身原有的位置
(2)相对定位移动后会保留原有的位置(可以使用定位占用,但普通写法时无法占用)
(3)不会影响文档流
position: relative; 开启相对定位
left:50px; 距离屏幕左侧50像素,即元素向右移动50px
top:50px; 距离屏幕上侧50像素,即元素向下移动50px
相对定位适用场景:
(1)小范围的移动使用
(2)移动后原有的位置不再使用
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>相对定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
.box1{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
background-color: red;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 50px;
}
.box2{
width: 200px;
height: 200px;
background-color: blue;
position: relative;
left: 50px;
top: 25px;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1"></div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>
2、绝对定位
(1)脱离当前文档流,使元素飘起来,父级无法获取自身的宽高;
(2)绝对定位的参考值:会去找具有相对定位属性的父元素,
如果没有给定它的父元素,则默认相对于html元素;
百分之九十以上的使用场景都需要相对定位来配合,
即“父相子绝(父级相对定位,子级绝对定位)”
position: absolute; 开启绝对定位
left:50px; 右移50px
top:50px; 下移50px
绝对定位适用场景:
(1)大,小范围移动都适用,但是需要其父元素的配合
(2)动态拖拽元素时,或者一些需要重叠的动画效果
调整当前定位元素的层级
z-index:数字; 设置z-index属性调整层级
注意:
(1)属性值没有单位,只写数字,比如 z-index:3;数字越大则层级越高;
(2)如果需要调整多个元素的层级时,需要将每个元素的层级都标清楚
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>绝对定位</title>
<style type="text/css">
.big>div{
width: 100px;
height: 100px;
border-radius: 50%;
}
.big{
position: relative;
}
.red{
background-color: red;
position: absolute;
top:55px;
left: 60px;
z-index: 1;
}
.blue{
background-color: blue;
position: absolute;
top: 100px;
left: 40px;
position: absolute;
z-index: 2;
}
.green{
background-color: green;
position: absolute;
top: 140px;
left: 60px;
z-index: 3;
}
.center{
background-color: yellow;
position: absolute;
top: 115px;
left: 120px;
z-index: 8;
}
#middle{
width: 50px;
height: 50px;
}
.pink{
background-color: pink;
position: absolute;
top: 150px;
left: 110px;
z-index:4;
}
.gray{
background-color: gray;
position: absolute;
top: 120px;
left: 150px;
z-index: 5;
}
.black{
background-color: black;
position: absolute;
top: 45px;
left: 110px;
z-index: 6;
}
.purple{
background-color: purple;
position: absolute;
top: 68px;
left: 145px;
z-index: 7;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="big">
<div class="black"></div>
<div class="red"></div>
<div class="blue"></div>
<div class="green"></div>
<div class="pink"></div>
<div class="gray"></div>
<div class="purple"></div>
<div class="center" id="middle"></div>
</div>
</body>
</html>
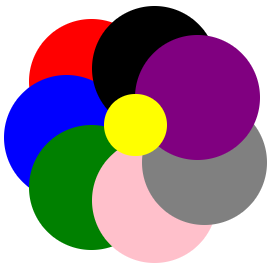
实力效果如下图:
注意:
(1)无论什么定位都要优先考虑它的参考对象
(2)left/top使用时,可以不紧跟着定位属性走,甚至写在不同选择器中,
但是一定要写开启定位,比如position:absolute表示元素开启绝对定位
(3)如果使用定位的元素较多时,会涉及到层级问题,这种情况下,
我们可以将层级设置大一些(根据实际情况,相对来说,也不用设太大),避免元素过多出现页面混乱。
3、固定定位
position:fixed; 开启固定定位
直接以浏览器窗口作为参考进行定位,它是浮动在页面中,元素位置不会随浏览器窗口的滚动条滚动而变化,除非你在屏幕中移动浏览器窗口的屏幕位置,或改变浏览器窗口的显示大小,因此固定定位的元素会始终位于浏览器窗口内视图的某个位置,不会受文档流影响。
<!DOCTYPE html>
<html>
<head>
<title>固定定位</title>
<style>
.box1{
width:120px;
height:120px;
text-align:center;
line-height:30px;
background-color:lightgray;
position:fixed;
}
.box2{
width:auto 0;
height:800px;
background-color:lightblue;
}
</style>
</head>
<body>
<div class="box1">
<p>锄禾日当午,</p>
<p>汗滴禾下土。</p>
<p>谁知盘中餐,</p>
<p>粒粒皆辛苦。</p>
</div>
<div class="box2"></div>
</body>
</html>






















 2418
2418











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








