public List< List< Integer> > levelOrder ( TreeNode root) {
List< List< Integer> > res = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return res;
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
int len = queue. size ( ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< len; i++ ) {
TreeNode temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
list. add ( temp. val) ;
if ( temp. left != null) queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
if ( temp. right != null) queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
}
res. add ( list) ;
}
return res;
}
public List< List< Integer> > levelOrder ( Node root) {
List< List< Integer> > res = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return res;
Queue< Node> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
int size = queue. size ( ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< size; i++ ) {
Node temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
list. add ( temp. val) ;
queue. addAll ( temp. children) ;
}
res. add ( list) ;
}
return res;
}
public List< List< Integer> > levelOrderBottom ( TreeNode root) {
LinkedList< List< Integer> > res = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return res;
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ; ;
int len = queue. size ( ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< len; i++ ) {
TreeNode temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
list. add ( temp. val) ;
if ( temp. left != null) queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
if ( temp. right != null) queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
}
res. addFirst ( list) ;
}
return res;
}
public List< List< Integer> > zigzagLevelOrder ( TreeNode root) {
List< List< Integer> > res = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return res;
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
boolean flag = true ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
LinkedList< Integer> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ; ;
int len = queue. size ( ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< len; i++ ) {
TreeNode temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
if ( flag) {
list. add ( temp. val) ;
} else {
list. addFirst ( temp. val) ;
}
if ( temp. left != null) queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
if ( temp. right != null) queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
}
flag = ! flag;
res. add ( list) ;
}
return res;
}
public boolean isCompleteTree ( TreeNode root) {
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
boolean flag = false ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
TreeNode temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
if ( temp == null) {
flag = true ;
continue ;
}
queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
}
return true ;
}
if ( temp == null) {
return false ;
}
queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
public List< Integer> rightSideView ( TreeNode root) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return res;
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
int len = queue. size ( ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< len; i++ ) {
TreeNode temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
if ( temp. left != null) queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
if ( temp. right != null) queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
if ( i== len- 1 ) res. add ( temp. val) ;
}
}
return res;
}
public Node connect ( Node root) {
if ( root == null) return root;
if ( root. left != null) {
root. left. next = root. right;
if ( root. next != null) {
root. right. next = root. next. left;
}
}
connect ( root. left) ;
connect ( root. right) ;
return root;
}
public Node connect ( Node root) {
if ( root == null) return root;
if ( root. left != null && root. right != null) {
root. left. next = root. right;
}
if ( root. left != null && root. right == null) {
root. left. next = getNext ( root. next) ;
}
if ( root. right != null) {
root. right. next = getNext ( root. next) ;
}
connect ( root. right) ;
connect ( root. left) ;
return root;
}
public Node getNext ( Node root) {
if ( root == null) return null;
if ( root. left != null) return root. left;
if ( root. right != null) return root. right;
if ( root. next != null) return getNext ( root. next) ;
return null;
}
public boolean isSymmetric ( TreeNode root) {
if ( root== null) return true ;
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root. left) ;
queue. offer ( root. right) ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
TreeNode no1= queue. poll ( ) ;
TreeNode no2= queue. poll ( ) ;
if ( no1== null && no2== null) continue ;
if ( no1== null || no2== null || no1. val!= no2. val) return false ;
queue. offer ( no1. left) ;
queue. offer ( no2. right) ;
queue. offer ( no1. right) ;
queue. offer ( no2. left) ;
}
return true ;
}
public boolean isSameTree ( TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if ( p == null && q == null) return true ;
if ( p == null || q == null || p. val != q. val) {
return false ;
} else {
return isSameTree ( p. left, q. left) && isSameTree ( p. right, q. right) ;
}
}
public List< Double> averageOfLevels ( TreeNode root) {
List< Double> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return res;
Queue< TreeNode> = new LinkedList < > ( ) ;
queue. offer ( root) ;
while ( ! queue. isEmpty ( ) ) {
Double d = 0.0 ;
int len = queue. size ( ) ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< len; i++ ) {
TreeNode temp = queue. poll ( ) ;
d += temp. val;
if ( temp. left != null) queue. offer ( temp. left) ;
if ( temp. right != null) queue. offer ( temp. right) ;
}
res. add ( d/ len) ;
}
return res;
}
public List< Integer> preorderTraversal ( TreeNode root) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return list;
Stack< TreeNode> = new Stack < > ( ) ;
stack. push ( root) ;
while ( ! stack. isEmpty ( ) ) {
TreeNode temp = stack. pop ( ) ;
list. add ( Integer. valueOf ( temp. val) ) ;
if ( temp. right!= null) stack. push ( temp. right) ;
if ( temp. left!= null) stack. push ( temp. left) ;
}
return list;
}
public List< Integer> preorder ( Node root) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
if ( root == null) return list;
Stack< Node> = new Stack < > ( ) ;
stack. push ( root) ;
while ( ! stack. isEmpty ( ) ) {
Node temp = stack. pop ( ) ;
list. add ( temp. val) ;
for ( int i= temp. children. size ( ) - 1 ; i>= 0 ; i-- ) {
stack. push ( temp. children. get ( i) ) ;
}
}
return list;
}
public List< Integer> inorderTraversal ( TreeNode root) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
Stack< TreeNode> = new Stack < > ( ) ;
while ( root != null || ! stack. isEmpty ( ) ) {
while ( root != null) {
stack. push ( root) ;
root = root. left;
}
root = stack. pop ( ) ;
list. add ( root. val) ;
root = root. right;
}
return list;
}
class Solution {
public boolean isValidBST ( TreeNode root) {
return validate ( root, Long. MIN_VALUE, Long. MAX_VALUE) ;
}
public boolean validate ( TreeNode node, long min, long max) {
if ( node== null) return true ;
if ( node. val<= min || node. val>= max) return false ;
return validate ( node. left, min, node. val) && validate ( node. right, node. val, max) ;
}
}
TreeNode pre = null;
int res = Integer. MAX_VALUE;
public int minDiffInBST ( TreeNode root) {
dfs ( root) ;
return res;
}
public void dfs ( TreeNode root) {
if ( root == null) return ;
dfs ( root. left) ;
if ( pre != null) {
res = Math. min ( res, root. val- pre. val) ;
}
pre = root;
dfs ( root. right) ;
}
class Solution {
int count = 0 ;
int res;
public int kthSmallest ( TreeNode root, int k) {
dfs ( root, k) ;
return res;
}
public void dfs ( TreeNode root, int k) {
if ( root == null) return ;
dfs ( root. left, k) ;
count++ ;
if ( count == k) res = root. val;
dfs ( root. right, k) ;
}
}
public int findSecondMinimumValue ( TreeNode root) {
return helper ( root, root. val) ;
}
public int helper ( TreeNode root, int minVal) {
if ( root== null) {
return - 1 ;
}
if ( root. val> minVal) {
return root. val;
}
int l= helper ( root. left, minVal) ;
int r= helper ( root. right, minVal) ;
if ( l!= - 1 && r!= - 1 ) {
return Math. min ( l, r) ;
} else {
return Math. max ( l, r) ;
}
}
class Solution {
public TreeNode invertTree ( TreeNode root) {
if ( root == null) return null;
invertTree ( root. left) ;
TreeNode temp= root. right;
root. right = root. left;
root. left = temp;
invertTree ( root. left) ;
return root;
}
}
class Solution {
public List< Integer> postorderTraversal ( TreeNode root) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
last ( root, res) ;
return res;
}
public void last ( TreeNode root, List< Integer> ) {
if ( root== null) return ;
last ( root. left, res) ;
last ( root. right, res) ;
res. add ( root. val) ;
}
}
class Solution {
public List< Integer> postorderTraversal ( TreeNode root) {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
Stack< TreeNode> = new Stack < > ( ) ;
TreeNode cur= null;
while ( root!= null || ! stack. isEmpty ( ) ) {
while ( root!= null) {
stack. push ( root) ;
root= root. left;
}
root = stack. peek ( ) ;
if ( root. right== null || root. right== cur) {
res. add ( root. val) ;
cur= stack. pop ( ) ;
root= null;
} else {
root= root. right;
}
}
return res;
}
}
class Solution {
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
public List< Integer> postorder ( Node root) {
last ( root) ;
return res;
}
public void last ( Node root) {
if ( root == null) return ;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< root. children. size ( ) ; i++ ) {
last ( root. children. get ( i) ) ;
}
res. add ( root. val) ;
}
}
class Solution {
public boolean hasPathSum ( TreeNode root, int sum) {
if ( root== null) return false ;
if ( root. left== null && root. right== null) {
return sum== root. val;
}
return hasPathSum ( root. left, sum- root. val) || hasPathSum ( root. right, sum- root. val) ;
}
}
public List< List< Integer> > pathSum ( TreeNode root, int targetSum) {
List< List< Integer> > res = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
List< Integer> = new ArrayList < > ( ) ;
dfs ( root, targetSum, res, list) ;
return res;
}
public static void dfs ( TreeNode root, int targetSum, List< List< Integer> > res, List< Integer> ) {
if ( root == null) return ;
list. add ( root. val) ;
if ( targetSum == root. val && root. left == null && root. right == null) {
res. add ( new ArrayList < > ( list) ) ;
list. remove ( list. size ( ) - 1 ) ;
return ;
}
dfs ( root. left, targetSum- root. val, res, list) ;
dfs ( root. right, targetSum- root. val, res, list) ;
list. remove ( list. size ( ) - 1 ) ;
}
HashMap< Integer, Integer> = new HashMap < > ( ) ;
int [ ] preorder;
public TreeNode buildTree ( int [ ] preorder, int [ ] inorder) {
this . preorder = preorder;
for ( int i= 0 ; i< inorder. length; i++ ) {
map. put ( inorder[ i] , i) ;
}
return buildTree ( 0 , preorder. length- 1 , 0 , inorder. length- 1 ) ;
}
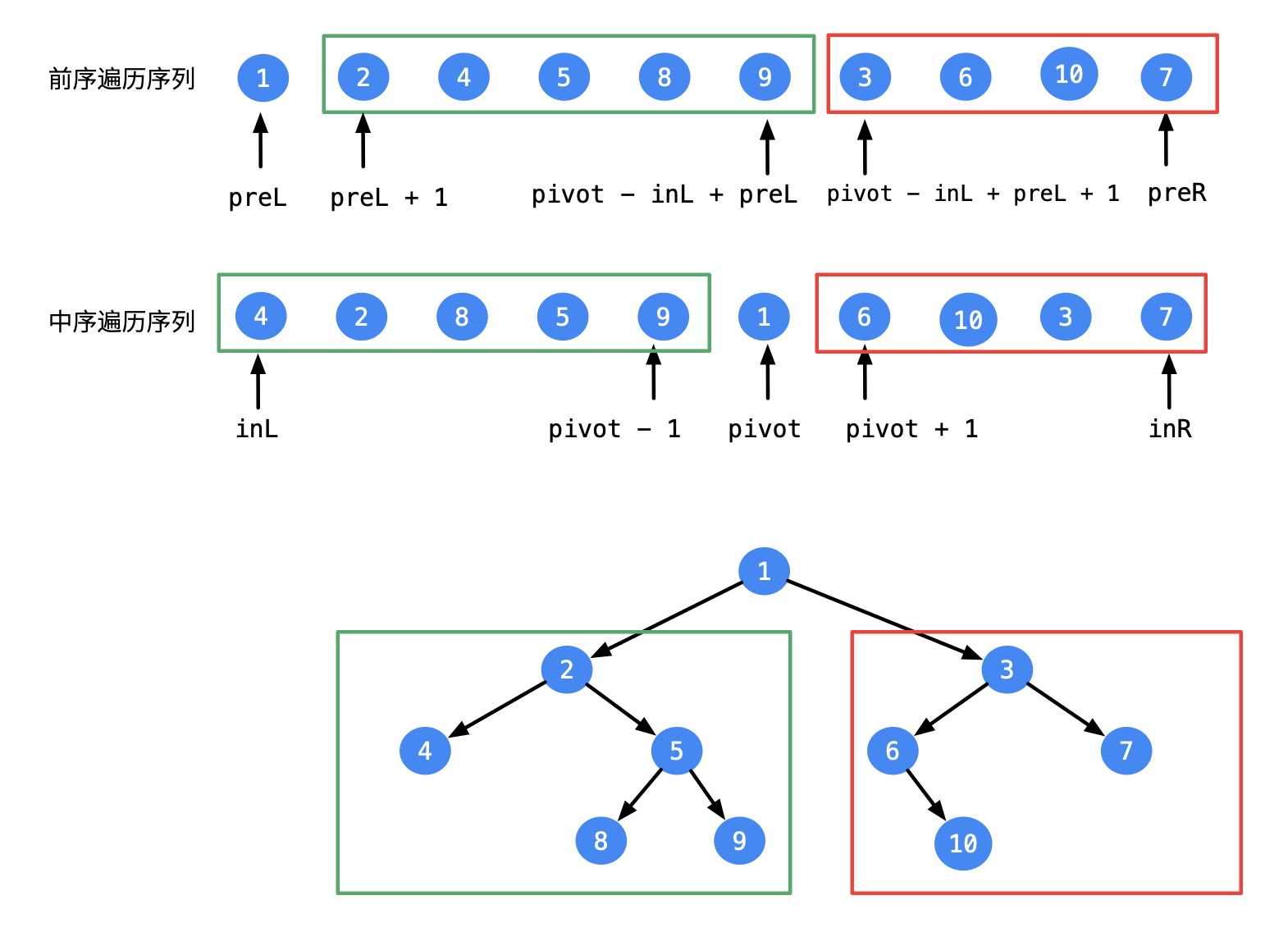
public TreeNode buildTree ( int preL, int preR, int inL, int inR) {
if ( preL> preR || inL> inR) {
return null;
}
int pivot = map. get ( preorder[ preL] ) ;
TreeNode root = new TreeNode ( preorder[ preL] ) ;
root. left = buildTree ( preL+ 1 , pivot- inL+ preL, inL, pivot- 1 ) ;
root. right = buildTree ( pivot- inL+ preL+ 1 , preR, pivot+ 1 , inR) ;
return root;
}
class Solution {
boolean res= true ;
public boolean isBalanced ( TreeNode root) {
recur ( root) ;
return res;
}
private int recur ( TreeNode root) {
if ( root== null) return 0 ;
int left= recur ( root. left) + 1 ;
int right= recur ( root. right) + 1 ;
if ( Math. abs ( left- right) > 1 ) res= false ;
return Math. max ( left, right) ;
}
}
TreeNode res;
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor ( TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
lca ( root, p, q) ;
return res;
}
public void lca ( TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if ( ( root. val- p. val) * ( root. val- q. val) <= 0 ) {
res = root;
} else if ( root. val- p. val < 0 && root. val- q. val < 0 ) {
lowestCommonAncestor ( root. right, p, q) ;
} else {
lowestCommonAncestor ( root. left, p, q) ;
}
}
public TreeNode lowestCommonAncestor ( TreeNode root, TreeNode p, TreeNode q) {
if ( root == null || root == p || root == q) return root;
TreeNode left = lowestCommonAncestor ( root. left, p, q) ;
TreeNode right = lowestCommonAncestor ( root. right, p, q) ;
if ( left == null) return right;
if ( right == null) return left;
return root;
}
class Solution {
public int maxDepth ( TreeNode root) {
if ( root== null) {
return 0 ;
} else {
int left= maxDepth ( root. left) ;
int right= maxDepth ( root. right) ;
return Math. max ( left, right) + 1 ;
}
}
}
class Solution {
public int minDepth ( TreeNode root) {
if ( root== null) {
return 0 ;
} else {
int left= minDepth ( root. left) ;
int right= minDepth ( root. right) ;
return root. left == null || root. right == null ? left + right + 1 : Math. min ( left, right) + 1 ;
}
}
}





















 456
456











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








