目录
1.RestAPI
ES官方提供了各种不同语言的客户端,用来操作ES。这些客户端的本质就是组装DSL语句,通过http请求发送给ES。
官方文档地址:
Elasticsearch Clients | Elastic
由于ES目前最新版本是8.8,提供了全新版本的客户端,老版本的客户端已经被标记为过时。而我们采用的是7.12版本,因此只能使用老版本客户端:
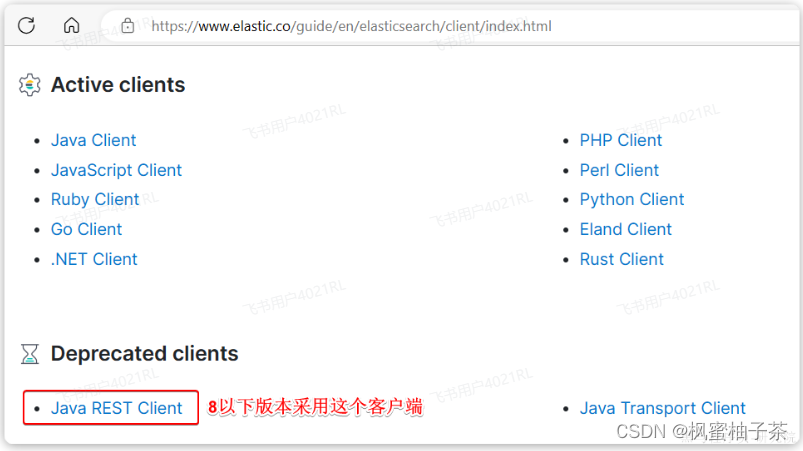
然后选择7.12版本,HighLevelRestClient版本:
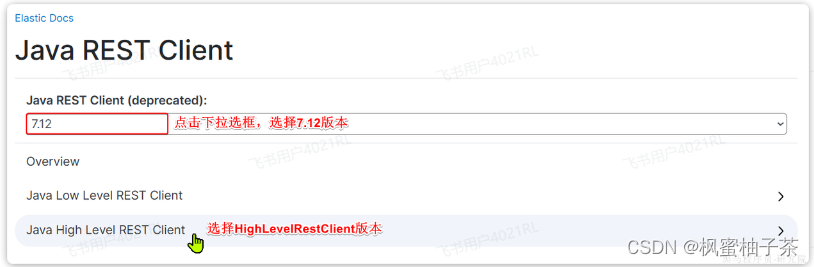
1.1.初始化RestClient
在elasticsearch提供的API中,与elasticsearch一切交互都封装在一个名为RestHighLevelClient的类中,必须先完成这个对象的初始化,建立与elasticsearch的连接。
分为三步:
1)在item-service模块中引入es的RestHighLevelClient依赖:
<dependency>
<groupId>org.elasticsearch.client</groupId>
<artifactId>elasticsearch-rest-high-level-client</artifactId>
</dependency>2)因为SpringBoot默认的ES版本是7.17.10,所以我们需要覆盖默认的ES版本:
<properties>
<maven.compiler.source>11</maven.compiler.source>
<maven.compiler.target>11</maven.compiler.target>
<elasticsearch.version>7.12.1</elasticsearch.version>
</properties>3)初始化RestHighLevelClient:
初始化的代码如下:
RestHighLevelClient client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));这里为了单元测试方便,我们创建一个测试类IndexTest,然后将初始化的代码编写在@BeforeEach方法中:
package com.hmall.item.es;
import org.apache.http.HttpHost;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestClient;
import org.elasticsearch.client.RestHighLevelClient;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.AfterEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.BeforeEach;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.IOException;
public class IndexTest {
private RestHighLevelClient client;
@BeforeEach
void setUp() {
this.client = new RestHighLevelClient(RestClient.builder(
HttpHost.create("http://192.168.150.101:9200")
));
}
@Test
void testConnect() {
System.out.println(client);
}
@AfterEach
void tearDown() throws IOException {
this.client.close();
}
}1.1.创建索引库
由于要实现对商品搜索,所以我们需要将商品添加到Elasticsearch中,不过需要根据搜索业务的需求来设定索引库结构,而不是一股脑的把MySQL数据写入Elasticsearch.
1.1.1.Mapping映射
搜索页面的效果如图所示:
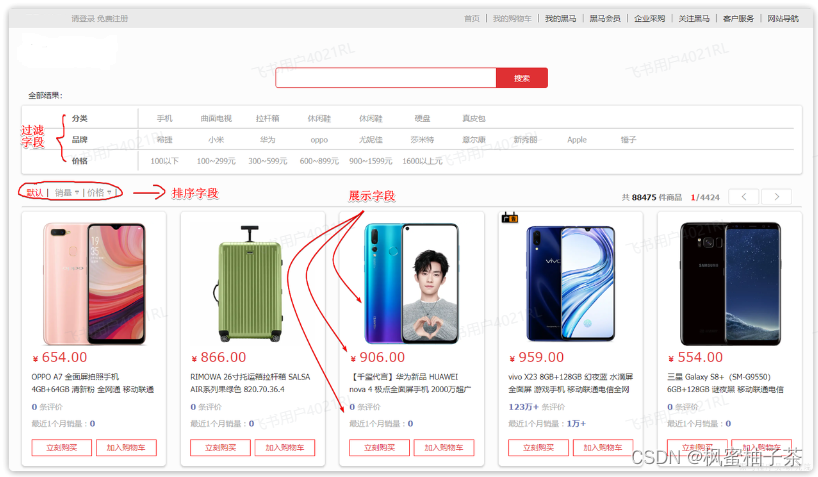
实现搜索功能需要的字段包括三大部分:
-
搜索过滤字段
-
分类
-
品牌
-
价格
-
-
排序字段
-
默认:按照更新时间降序排序
-
销量
-
价格
-
-
展示字段
-
商品id:用于点击后跳转
-
图片地址
-
是否是广告推广商品
-
名称
-
价格
-
评价数量
-
销量
-
对应的商品表结构如下,索引库无关字段已经划掉:
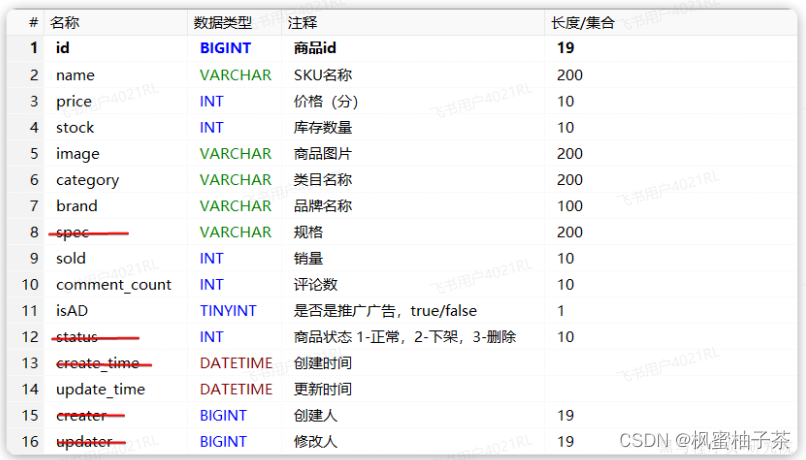
结合数据库表结构,以上字段对应的mapping映射属性如下:
| 字段名 | 字段类型 | 类型说明 | 是否 参与搜索 | 是否 参与分词 | 分词器 | |
| id |
| 长整数 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| name |
| 字符串,参与分词搜索 | ✔️ | ✔️ | IK | |
| price |
| 以分为单位,所以是整数 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| stock |
| 字符串,但需要分词 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| image |
| 字符串,但是不分词 | ❌ | ❌ | —— | |
| category |
| 字符串,但是不分词 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| brand |
| 字符串,但是不分词 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| sold |
| 销量,整数 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| commentCount |
| 评价,整数 | ❌ | ❌ | —— | |
| isAD |
| 布尔类型 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
| updateTime |
| 更新时间 | ✔️ | ❌ | —— | |
因此,最终我们的索引库文档结构应该是这样:
PUT /items
{
"mappings": {
"properties": {
"id": {
"type": "keyword"
},
"name":{
"type": "text",
"analyzer": "ik_max_word"
},
"price":{
"type": "integer"
},
"stock":{
"type": "integer"
},
"image":{
"type": "keyword",
"index": false
},
"category":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"brand":{
"type": "keyword"
},
"sold":{
"type": "integer"
},
"commentCount":{
"type": "integer",
"index": false
},
"isAD":{
"type": "boolean"
},
"updateTime":{
"type": "date"
}
}
}
}1.1.2.创建索引
创建索引库的API如下:
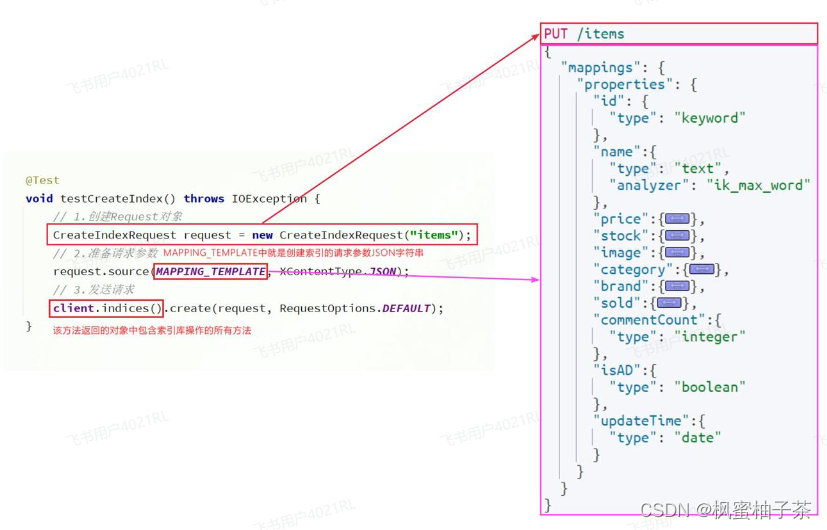
代码分为三步:
1)创建Request对象。
因为是创建索引库的操作,因此Request是
CreateIndexRequest。2)添加请求参数
其实就是Json格式的Mapping映射参数。因为json字符串很长,这里是定义了静态字符串常量
MAPPING_TEMPLATE,让代码看起来更加优雅。3)发送请求
client.indices()方法的返回值是IndicesClient类型,封装了所有与索引库操作有关的方法。例如创建索引、删除索引、判断索引是否存在等。
在item-service中的IndexTest测试类中,具体代码如下:
@Test
void testCreateIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
CreateIndexRequest request = new CreateIndexRequest("items");
// 2.准备请求参数
request.source(MAPPING_TEMPLATE, XContentType.JSON);
// 3.发送请求
client.indices().create(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}
static final String MAPPING_TEMPLATE = "{\n" +
" \"mappings\": {\n" +
" \"properties\": {\n" +
" \"id\": {\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"name\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"text\",\n" +
" \"analyzer\": \"ik_max_word\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"price\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"stock\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"image\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\",\n" +
" \"index\": false\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"category\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"brand\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"keyword\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"sold\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"commentCount\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"integer\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"isAD\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"boolean\"\n" +
" },\n" +
" \"updateTime\":{\n" +
" \"type\": \"date\"\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
" }\n" +
"}";1.2.删除索引库
删除索引库的请求非常简单
DELETE /hotel
与创建索引库相比:
-
请求方式从PUT变为DELTE
-
请求路径不变
-
无请求参数
所以代码的差异,注意体现在Request对象上。流程如下:
-
1)创建Request对象。这次是DeleteIndexRequest对象
-
2)准备参数。这里是无参,因此省略
-
3)发送请求。改用delete方法
在item-service中的IndexTest测试类中,编写单元测试,实现删除索引:
@Test
void testDeleteIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
DeleteIndexRequest request = new DeleteIndexRequest("items");
// 2.发送请求
client.indices().delete(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
}1.3.判断索引库是否存在
判断索引库是否存在,本质就是查询,对应的请求语句是:
GET /hotel
因此与删除的Java代码流程是类似的,流程如下:
-
1)创建Request对象。这次是GetIndexRequest对象
-
2)准备参数。这里是无参,直接省略
-
3)发送请求。改用exists方法
@Test
void testExistsIndex() throws IOException {
// 1.创建Request对象
GetIndexRequest request = new GetIndexRequest("items");
// 2.发送请求
boolean exists = client.indices().exists(request, RequestOptions.DEFAULT);
// 3.输出
System.err.println(exists ? "索引库已经存在!" : "索引库不存在!");
}1.4.总结
JavaRestClient操作elasticsearch的流程基本类似。核心是client.indices()方法来获取索引库的操作对象。
索引库操作的基本步骤:
-
初始化
RestHighLevelClient -
创建XxxIndexRequest。XXX是
Create、Get、Delete -
准备请求参数(
Create时需要,其它是无参,可以省略) -
发送请求。调用
RestHighLevelClient#indices().xxx()方法,xxx是create、exists、delete
























 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










