目录
前言
🌟在上一篇Java条件语句的介绍后就来到了我们的重点"循环语句"以及"循环控制"。在本篇文章中我将会带领大家学习并掌握循环语句以及循环控制的使用!
三、循环语句
循环语句类型有很多种:while循环、do…while、for循环
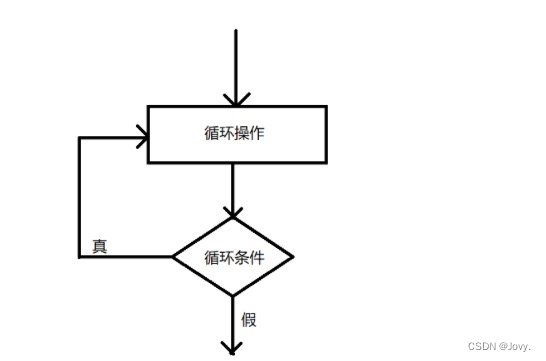
1.while循环语句
🧸whlie循环语句又称为条件判断语句
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int x = 10;
while( x < 20 ) {
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
x++;
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}以上代码运行结果如下
value of x : 10 value of x : 11 value of x : 12 value of x : 13 value of x : 14 value of x : 15 value of x : 16 value of x : 17 value of x : 18 value of x : 19
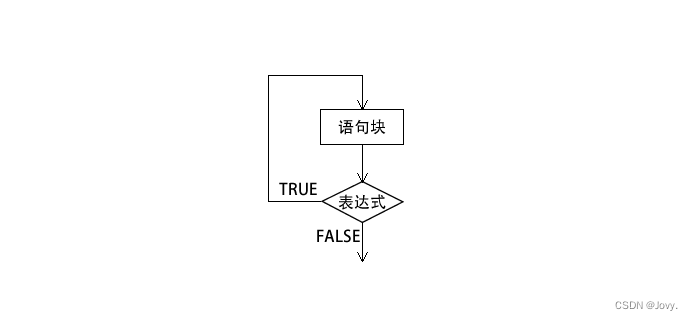
2.do…while循环
🌟do…while循环与while循环类似 区别在于:while循环是符合条件之后再执行循环体;而do…while循环是先执行一次,再判断是否符合条件最后决定是否执行循环体。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
int x = 10;
do{
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
x++;
System.out.print("\n");
}while( x < 20 );
}
}以上代码运行结果如下
value of x : 10 value of x : 11 value of x : 12 value of x : 13 value of x : 14 value of x : 15 value of x : 16 value of x : 17 value of x : 18 value of x : 19
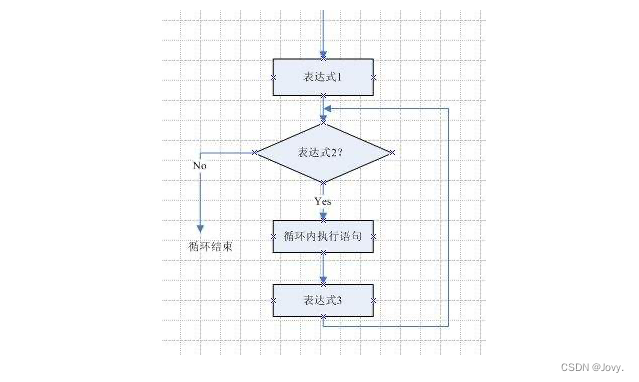
3.for循环
for循环是Java中最有用的循环语句之一,一个for循环可以用来重复执行某条语句,直到满足条件 for循环有两种语句一种是foreach语句,另一个就是传统的for语句
1.for循环
以下为代码演示
/*
for(初始化; 布尔表达式; 更新) {
//代码语句
}
*/
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int x = 10; x < 20; x = x+1) {
System.out.print("value of x : " + x );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}以上代码运行结果
value of x : 10 value of x : 11 value of x : 12 value of x : 13 value of x : 14 value of x : 15 value of x : 16 value of x : 17 value of x : 18 value of x : 19
2.foreach语句
foreach语句又称为增强for语句
以下为代码演示
/*for(声明语句 : 表达式)
{
//代码句子
}
*/
// 声明语句:声明新的局部变量,该变量的类型必须和数组元素的类型匹配。其作用域限定在循环语句块,其值与此时数组元素的值相等。
//表达式:表达式是要访问的数组名,或者是返回值为数组的方法。
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int x : numbers ){
System.out.print( x );
System.out.print(",");
}
System.out.print("\n");
String [] names ={"James", "Larry", "Tom", "Lacy"};
for( String name : names ) {
System.out.print( name );
System.out.print(",");
}
}
}运行结果如下
10,20,30,40,50, James,Larry,Tom,Lacy,
五、循环控制
1.break语句
break 主要用在循环语句或者 switch 语句中,用来跳出整个语句块
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int x : numbers ) {
// x 等于 30 时跳出循环
if( x == 30 ) {
break;
}
System.out.print( x );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}运行结果为10与20
break可以强制跳出循环或者是switch语句块!🙈
2.continue语句
continue语句的作用与break不同,他的作用就是强制跳过本次循环进入到下一次循环
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int [] numbers = {10, 20, 30, 40, 50};
for(int x : numbers ) {
if( x == 30 ) {
continue;
}
System.out.print( x );
System.out.print("\n");
}
}
}以上运行结果为10,20,40,50
六、结尾
这不仅仅是本篇的结尾,更是本章的结尾!
希望大家能支持一下博主的文章!























 14万+
14万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










