JavaSE学习笔记-chapter06-常用类
学习资源:动力节点java学习
反编译Java字节码指令:javap -c ***.class 这会将Java编译后的字节码指令展示出来
javap:Java Class文件解析器, 能够解析已编译的Java类文件(即 .class 文件),并展示类的结构和内容
-c:告诉 javap 以字节码(bytecode)的形式显示方法体中的代码
第六章 常用类
文章目录
1. String类
1.1 初始String

package chapter.newversion.chapter06;
public class StringTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "hello";
String s2 = "hello";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
String s3 = "test";
String s4 = new String("test");
System.out.println(s3 == s4); // false
System.out.println(s3.equals(s4)); // true
}
}
1.2 String拼接

package chapter.newversion.chapter06;
public class StringTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 使用"+"进行拼接生成新的字符串不会被放到字符串常量池中(+两边至少有一个是变量)
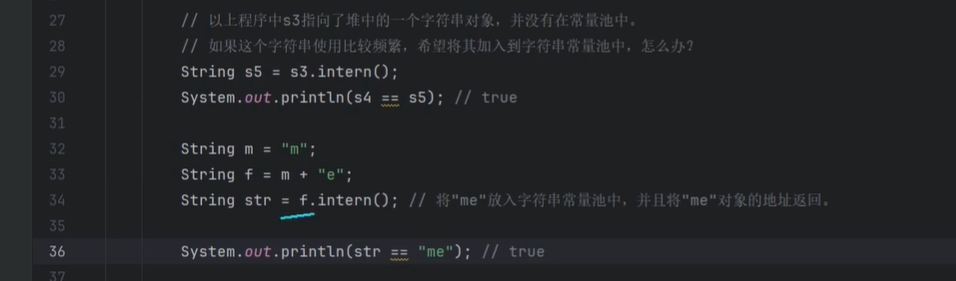
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "def";
String s3 = s1 + s2;
String s4 = "abcdef";
System.out.println(s3 == s4); // false
// 当+号两边都是字符串字面量时,编译器会进行自动优化,在编译阶段进行拼接
String s5 = "String" + "Test";
String s6 = "StringTest";
System.out.println(s5 == s6); // true
}
}
1.3 String的构造方法

package chapter.newversion.chapter06;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
/**
* String的构造方法
*/
public class StringTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
// char[] 字符数组
char[] c1 = {'1', '2', '3', '4', '5'};
String s1 = new String(c1);
System.out.println(s1); // 12345
String s2 = new String(c1, 0, 3);
System.out.println(s2); // 123
// byte[] 二进制数组
byte[] b1 = {97, 98, 99, 100};
String s3 = new String(b1);
System.out.println(s3); // abcd
String s4 = new String(b1, 0, 3);
System.out.println(s4); // abc
System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset()); // UTF-8
String s5 = new String(b1, Charset.defaultCharset());
System.out.println(s5); // abcd
String s6 = new String(b1, "UTF-8");
System.out.println(s6); // abcd
String s7 = new String(b1, StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
System.out.println(s7); // abcd
// java16对此构造方法添加了@IntrinicCandidate注解,表示是内在候选的方法,不建议使用了
// 这样写也就可以:String s8 = "zzy";,而且这样会少在堆中创建一个String对象
String s8 = new String("zzy");
}
}
1.4 String类的常用方法
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
public class Animal {
private String name;
private String age;
public Animal(String name, String age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.io.UnsupportedEncodingException;
import java.nio.charset.Charset;
import java.nio.charset.StandardCharsets;
import java.util.ArrayList;
import java.util.List;
/**
* String类常用方法单元测试
*/
public class StringMethodTest {
// 返回字符串指定索引的char值
@Test
public void testCharAt() {
String s1 = "abcdefg";
char c = s1.charAt(1);
System.out.println(c); // b
}
// 返回字符串长度
@Test
public void testLength() {
String s1 = "zzy";
System.out.println(s1.length()); // 3
}
// 判断字符串是否为空字符串,判读条件:长度为0就是空字符串
@Test
public void testIsEmpty() {
String s1 = "";
System.out.println(s1.isEmpty()); // true
String s2 = "zzy";
System.out.println(s2.isEmpty()); // false
String s3 = new String();
System.out.println(s3.isEmpty()); // true
// NullPointerException
// String s4 = null;
// System.out.println(s4.isEmpty());
}
// 判断两个字符串是否相等
@Test
public void testEquals() {
String s1 = new String("zzy");
String s2 = "zzy";
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
}
// 判断两个字符串是否相等,忽略大小写
@Test
public void testEqualsIgnoreCase() {
String s1 = "zzy";
String s2 = "Zzy";
System.out.println(s1.equalsIgnoreCase(s2)); // true
}
// 判断当前字符串中是否包含某个子字符串
@Test
public void testContains() {
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple".contains("https")); // true
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple".contains("zzy")); // false
}
// 判断当前字符串是否以某个子字符串开头
@Test
public void testStartsWith() {
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple".startsWith("https")); // true
}
// 判断当前字符串是否以某个字符串结尾
@Test
public void testEndsWith() {
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple".endsWith("simple")); // true
}
// 两个字符串按照字典顺序比较大小,返回值大于0即调用者大,相反调用者小,等于0则表示两个字符串大小相等
@Test
public void testCompareTo() {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "aba";
System.out.println(s1.compareTo(s2)); // 2
}
// 两个字符串按照字典顺序比较大小,比较时忽略大小写
@Test
public void testCompareToIgnoreCase() {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "ABC";
System.out.println(s1.compareToIgnoreCase(s2)); // 0
}
// 获取当前字符串中某个子字符串第一次出现处的下标
@Test
public void testIndexOf() {
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".indexOf("http")); // 0
// 从当前字符串的fromIndex下标开始向右搜索
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".indexOf("http", 8)); // 27
}
// 获取当前字符串中某个子字符串最后一次出现处的下标
@Test
public void testLastIndexOf() {
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".length()); // 50
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".lastIndexOf("http")); // 45
// 从当前字符串中的fromIndex下标开始向左搜索
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".lastIndexOf("http", 40)); // 27
}
// 将字符串转换成字节数组,本质上就是对字符串进行编码(按照系统默认的字符集)
@Test
public void testGetBytes() throws UnsupportedEncodingException {
String s1 = "abc";
byte[] bytes = s1.getBytes();
for (byte e : bytes) {
System.out.println(e);
}
// 按照指定的字符集进行编码
System.out.println(Charset.defaultCharset()); // UTF-8
byte[] bytes1 = s1.getBytes(Charset.defaultCharset());
for (byte e : bytes1) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("========");
byte[] bytes2 = s1.getBytes("UTF-8");
for (byte e : bytes2) {
System.out.println(e);
}
System.out.println("========");
byte[] bytes3 = s1.getBytes(StandardCharsets.UTF_8);
for (byte e : bytes3) {
System.out.println(e);
}
}
// 将字符串转化成字符数组
@Test
public void testToCharArray() {
char[] charArray = "zzy".toCharArray();
for (char c : charArray) {
System.out.println(c);
}
}
// 将字符串中所有字符转为小写
@Test
public void testToLowerCase() {
String lowerCase = "AbCdEfG".toLowerCase();
System.out.println(lowerCase); // abcdefg
}
// 将字符串中所有字符转为大写
@Test
public void testToUpperCase() {
String upperCase = "AbCdEfG".toUpperCase();
System.out.println(upperCase); // ABCDEFG
}
// 字符串的拼接方法
/*
concat()和'+'拼接字符串的区别:
1. concat()不会创建StringBuilder对象,'+'会创建StringBuilder对象
2. concat()拼接会有空指针异常风险,'+'没有空指针异常风险
3. concat()只能拼接两个字符串,'+'可以拼接还可以将字符串与其他数据类型进行拼接并自动转化为String类型
4. '+'使用居多,但对于大量的字符串拼接操作,以上两种方法都不推荐。而是采用StringBuilder(后面学习)
*/
@Test
public void testConcat() {
String s1 = "zzy";
String s2 = "Zeus";
String s3 = null;
System.out.println(s1.concat(s2)); // zzyZeus
// NullPointerException
// System.out.println(s1.concat(s3));
// s1.concat(999)
System.out.println(s1 + s3); // zzynull
String s4 = s1 + 999;
System.out.println(s4); // zzy999
System.out.println(s4 instanceof String); // true
}
// 从指定下标beginIndex开始截取子字符串
@Test
public void testSubstring() {
// ://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".substring(5));
// 从beginIndex开始,到endIndex结束
// ://py
System.out.println("https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttps".substring(5, 10));
}
// 去除字符串前后空白(只能去除ASCII码中的空白和制表符,不能去除全角空白,全角空白是\u3000)
/*
Java11新增String strip()去除字符串前后空白(支持所有编码形式的空白)
但平日使用较多的仍是trim(),因为不需要做判断,执行效率高
String stripLeading()去除字符串前面的空白
String stripTrailing()去除字符串后面的空白
*/
@Test
public void trim() {
String s1 = " \u3000z z y ";
System.out.println("===>" + s1 + "<===");
String s2 = s1.trim();
System.out.println("===>" + s2 + "<==="); // ===> z z y<===
}
// 返回字符串本身,而不是在虚拟机中的物理地址
@Test
public void testToString() {
String s1 = "zzy";
System.out.println(s1.toString()); // zzy
}
// 获取字符串常量池中的字符串,如果常量池没有,则将字符串加入常量池中并返回
@Test
public void testIntern() {
String s1 = "zzy";
String s2 = "zzy";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true
byte[] bytes = {97, 98, 99};
String s3 = new String(bytes);
String intern = s3.intern();
String s4 = "abc";
System.out.println(s3 == s4); // true
}
// 将多个字符串以某个分隔符连接
@Test
public void testJoin() {
// static String join(CharSequence d, CharSequence... elements)(java8新增)
System.out.println(String.join(", ", "java", "c", "python")); // java, c, python
List list = new ArrayList();
list.add("abc");
list.add("def");
list.add("xyz");
// static String join(CharSequence delimiter, Iterable<? extends CharSequence> elements)
System.out.println(String.join("-", list)); // abc-def-xyz
}
// 将其他数据类型转化为String类型
@Test
public void testValueOf() {
char[] c = {'a', 'b', 'c'};
System.out.println(String.valueOf(c)); // abc
Object obj1 = null;
// NullPointerException
// obj1.toString();
System.out.println(String.valueOf(obj1)); // null
Object obj2 = new Object();
System.out.println(String.valueOf(obj2)); // java.lang.Object@3ecd23d9
Animal animal = new Animal("cat", "9");
System.out.println(String.valueOf(animal)); // Animal{name='cat', age='9'}
}
}
1.5 初始正则表达式



1.5.1 校验数字的表达式
1. 数字:^[0-9]*$
2. n位的数字:^\d{n}$
3. 至少n位的数字:^\d{n,}$
4. m-n位的数字:^\d{m,n}$
5. 零和非零开头的数字:^(0|[1-9][0-9]*)$
6. 非零开头的最多带两位小数的数字:^([1-9][0-9]*)+(.[0-9]{1,2})?$
7. 带1-2位小数的正数或负数:^(\-)?\d+(\.\d{1,2})?$
8. 正数、负数、和小数:^(\-|\+)?\d+(\.\d+)?$
9. 有两位小数的正实数:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{2})?$
10. 有1~3位小数的正实数:^[0-9]+(.[0-9]{1,3})?$
11. 非零的正整数:^[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^([1-9][0-9]*){1,3}$ 或 ^\+?[1-9][0-9]*$
12. 非零的负整数:^\-[1-9][]0-9"*$ 或 ^-[1-9]\d*$
13. 非负整数:^\d+$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*|0$
14. 非正整数:^-[1-9]\d*|0$ 或 ^((-\d+)|(0+))$
15. 非负浮点数:^\d+(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0$
16. 非正浮点数:^((-\d+(\.\d+)?)|(0+(\.0+)?))$ 或 ^(-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*))|0?\.0+|0$
17. 正浮点数:^[1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*$ 或 ^(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*))$
18. 负浮点数:^-([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*)$ 或 ^(-(([0-9]+\.[0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*\.[0-9]+)|([0-9]*[1-9][0-9]*)))$
19. 浮点数:^(-?\d+)(\.\d+)?$ 或 ^-?([1-9]\d*\.\d*|0\.\d*[1-9]\d*|0?\.0+|0)$
1.5.2 校验字符的表达式
1. 汉字:^[\u4e00-\u9fa5]{0,}$
2. 英文和数字:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[A-Za-z0-9]{4,40}$
3. 长度为3-20的所有字符:^.{3,20}$
4. 由26个英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Za-z]+$
5. 由26个大写英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Z]+$
6. 由26个小写英文字母组成的字符串:^[a-z]+$
7. 由数字和26个英文字母组成的字符串:^[A-Za-z0-9]+$
8. 由数字、26个英文字母或者下划线组成的字符串:^\w+$ 或 ^\w{3,20}$
9. 中文、英文、数字包括下划线:^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9_]+$
10. 中文、英文、数字但不包括下划线等符号:^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]+$ 或 ^[\u4E00-\u9FA5A-Za-z0-9]{2,20}$
11. 可以输入含有^%&',;=?$\"等字符:[^%&',;=?$\x22]+
12. 禁止输入含有~的字符:[^~\x22]+
1.5.3 特殊需求表达式
1. Email地址:^\w+([-+.]\w+)*@\w+([-.]\w+)*\.\w+([-.]\w+)*$
2. 域名:[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62}(/.[a-zA-Z0-9][-a-zA-Z0-9]{0,62})+/.?
3. InternetURL:[a-zA-z]+://[^\s]* 或 ^http://([\w-]+\.)+[\w-]+(/[\w-./?%&=]*)?$
4. 手机号码:^(13[0-9]|14[0-9]|15[0-9]|16[0-9]|17[0-9]|18[0-9]|19[0-9])\d{8}$ (由于工信部放号段不定时,所以建议使用泛解析 ^([1][3,4,5,6,7,8,9])\d{9}$)
5. 电话号码("XXX-XXXXXXX"、"XXXX-XXXXXXXX"、"XXX-XXXXXXX"、"XXX-XXXXXXXX"、"XXXXXXX"和"XXXXXXXX):^(\(\d{3,4}-)|\d{3.4}-)?\d{7,8}$
6. 国内电话号码(0511-4405222、021-87888822):\d{3}-\d{8}|\d{4}-\d{7}
7. 18位身份证号码(数字、字母x结尾):^((\d{18})|([0-9x]{18})|([0-9X]{18}))$
8. 帐号是否合法(字母开头,允许5-16字节,允许字母数字下划线):^[a-zA-Z][a-zA-Z0-9_]{4,15}$
9. 密码(以字母开头,长度在6~18之间,只能包含字母、数字和下划线):^[a-zA-Z]\w{5,17}$
10. 强密码(必须包含大小写字母和数字的组合,不能使用特殊字符,长度在8-10之间):^(?=.*\d)(?=.*[a-z])(?=.*[A-Z]).{8,10}$
11. 日期格式:^\d{4}-\d{1,2}-\d{1,2}
12. 一年的12个月(01~09和1~12):^(0?[1-9]|1[0-2])$
13. 一个月的31天(01~09和1~31):^((0?[1-9])|((1|2)[0-9])|30|31)$
14. xml文件:^([a-zA-Z]+-?)+[a-zA-Z0-9]+\\.[x|X][m|M][l|L]$
15. 中文字符的正则表达式:[\u4e00-\u9fa5]
16. 双字节字符:[^\x00-\xff] (包括汉字在内,可以用来计算字符串的长度(一个双字节字符长度计2,ASCII字符计1))
17. 空白行的正则表达式:\n\s*\r (可以用来删除空白行)
18. HTML标记的正则表达式:<(\S*?)[^>]*>.*?</\1>|<.*? /> (网上流传的版本太糟糕,上面这个也仅仅能部分,对于复杂的嵌套标记依旧无能为力)
19. 首尾空白字符的正则表达式:^\s*|\s*$或(^\s*)|(\s*$) (可以用来删除行首行尾的空白字符(包括空格、制表符、换页符等等),非常有用的表达式)
20. 腾讯QQ号:[1-9][0-9]{4,} (腾讯QQ号从10000开始)
21. 中国邮政编码:[1-9]\d{5}(?!\d) (中国邮政编码为6位数字)
22. IP地址:\d+\.\d+\.\d+\.\d+ (提取IP地址时有用)
23. IP地址:((?:(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|[01]?\\d?\\d)\\.){3}(?:25[0-5]|2[0-4]\\d|[01]?\\d?\\d))
1.6 String面试题
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
/*
String类常见面试题
*/
public class StringExam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
examDemo01();
examDemo02();
examDemo03();
examDemo04();
examDemo05();
examDemo06();
examDemo07(); // *
examDemo08(); // **
examDemo09(); // ***
examDemo10();
examDemo11(); // ***
}
public static void examDemo01() {
String s1 = new String("abc");
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println("=========");
}
public static void examDemo02() {
String s1 = "a" + "b" + "c";
String s2 = "abc";
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // true
System.out.println("=========");
}
public static void examDemo03() {
String s1 = "abc";
String s2 = "ab";
String s3 = s2 + "c";
System.out.println(s1 == s3); // false
System.out.println(s1.equals(s3)); // true
System.out.println("=========");
}
public static void examDemo04() {
// 创建了几个对象: 1
String s1 = "a" + "b";
}
public static void examDemo05() {
// 创建了几个对象: 5
String s1 = "a"; // 字符串常量池中1个
String s2 = new String("b"); // 字符串常量池中1个,堆中一个
String s3 = s1 + s2; // 堆两个(在使用'+'进行拼接的时候会自动创建一个StringBuilder对象,在调用toString()转化成String对象)
}
public static void examDemo06() {
// 创建了几个对象:6
String s1 = new String("a") + new String("b");
}
public static void examDemo07() {
String s1 = null;
// 底层调用valueOf不会出现空指针异常
String s2 = s1 + null;
System.out.println(s2); // nullnull
System.out.println("=========");
}
// *****
public static void examDemo08() {
String s1 = "a1";
String s2 = "a" + 1;
System.out.println(s1 == s2); // true 因为这里的1是字面量,是可以确定的值
System.out.println("=========");
}
// *********************
public static void examDemo09() {
String s1 = "ab";
final String s2 = "b";
String s3 = "a" + s2;
System.out.println(s1 == s3); // true
System.out.println("=========");
}
public static void examDemo10() {
String s1 = "abc";
StringBuilder s2 = new StringBuilder(s1);
System.out.println(s1.equals(s2)); // false
System.out.println("=========");
}
public static void examDemo11() {
String s1 = "ab";
final String s2 = getB();
String s3 = "a" + s2;
System.out.println(s1 == s3); // false
}
public static String getB() {
return "b";
}
}
1.7 其他面试题
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
/**
* 其他的面试题
*/
public class OtherExamTest {
@Test
public void test1() {
System.out.println(get()); // false
}
public boolean get() {
try{
return true;
} finally {
System.out.println("1");
return false;
}
}
// 就近原则
@Test
public void test2() {
m(null); // String...
}
public void m(Object obj) {
System.out.println("Object...");
}
public void m(String s) {
System.out.println("String...");
}
static int a = getA();
static int b = 10;
public static int getA() {
return b;
}
@Test
public void test3() {
// 在a初始化的时候,b还未初始化getA()只能返回默认值0
System.out.println(a); // 0
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
public class Animal {
private String name;
private String age;
public Animal(String name, String age) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
}
public String getAge() {
return age;
}
public void setAge(String age) {
this.age = age;
}
@Override
public String toString() {
return "Animal{" +
"name='" + name + '\'' +
", age='" + age + '\'' +
'}';
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
/*
面试题:代码的执行顺序
*/
public class Exam {
public static void main(String[] args) {
new B();
}
}
class A {
private static A a = new B();
static {
System.out.println("A的静态代码块执行了");
}
{
System.out.println("A的构造代码块执行了");
}
public A() {
System.out.println("A的构造方法执行了");
}
}
class B extends A {
static {
System.out.println("B的静态代码块执行了");
}
{
System.out.println("B的构造代码块执行了");
}
public B() {
System.out.println("B的构造方法执行了");
}
}
1.8 String练习题
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
/*
获取指定字符串中大写字母、小写字母、数字的个数。
字符串的反转。
获取子字符串在整个字符串中出现的次数。
从身份证中读取信息,要求读取出这个人的生日以及性别
获取两个字符串中最大相同的子字符串。 StringTest07.java
*/
public class StringExercisesTest {
// 获取指定字符串中大写字母、小写字母、数字的个数。
@Test
public void test1() {
int number = 0;
int small = 0;
int big = 0;
String s = "Aa1Bb2Cc3dD###";
// 将字符串转化成字符数组
char[] sCharArray = s.toCharArray();
for (char c : sCharArray) {
String sTemp = String.valueOf(c);
if (sTemp.matches("\\d")) {
number++;
} else if (sTemp.matches("^[A-Z]+$")) {
big++;
}else if (sTemp.matches("^[a-z]+$")) {
small++;
}else {
continue;
}
}
System.out.println("该字符串中数字有" + number + "个,小写字母有" + small + "个,大写字母有" + big + "个");
}
// 字符串的反转 改进:StringTest04.java
@Test
public void test2() {
String s = "毅志张学大业工安西";
char[] sCharArray = s.toCharArray();
String result = "";
for (int i = sCharArray.length - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
result += sCharArray[i];
}
System.out.println(result);
}
// 获取子字符串在整个字符串中出现的次数 优化:StringTest05.java
@Test
public void test3() {
String s = "https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttpshttps";
int count = 0;
boolean control = true;
while (control){
// 未找到返回-1
int https = s.indexOf("https");
if (https != -1) {
count++;
if(https + "https".length() >= s.length()){
break;
}
s = s.substring(https + "https".length());
} else {
control = false;
}
}
System.out.println("https在字符串中出现的次数为:" + count + "次");
}
// 从身份证中读取信息,要求读取出这个人的生日以及性别 改进:StringTest06.java
/*
身份证18位
第1、2位数字表示:所在省份的代码
第3、4位数字表示:所在城市的代码
第5、6位数字表示:所在区县的代码
第7-14位数字表示:出生年、月、日(其中7、8、9、10位是年,11、12位是月,13、14位是日)
第15-17位都是同一地址辖区内的,以及同年同月同日出生人的顺序码
同时第17位兼具性别标识功能,男单女双(奇数包括1, 3, 5, 7, 9,而偶数包括0, 2, 4, 6, 8)
第18位数字是校检码:可以是0-9的数字,有时也用X表示
*/
@Test
public void test4() {
String idCard = "610122200112063713";
String y = idCard.substring(6, 10);
String m = idCard.substring(10, 12);
String d = idCard.substring(12, 14);
char c = idCard.charAt(16);
int sex = c - '0';
if (sex % 2 == 0) {
System.out.println("女");
}else {
System.out.println("男");
}
System.out.println(y + "年" + m + "月" + d + "日");
// System.out.println('1' + '0');
// System.out.println('1' - '0');
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
public class StringTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "hello";
String result = reserve(s);
System.out.println(s + "反转后为:" + result);
// 2
// System.out.println(5 / 2);
}
/**
* 反转数组
* @param s 原数组
* @return 原数组反转后的数组
*/
private static String reserve(String s) {
char[] sCharArray = s.toCharArray();
/*
数组长度为5: i < 3 length / 2
1 2 3 4 5
1 5
2 4
数组长度为4: i < 2 length / 2
1 2 3 4
1 4
2 3
*/
for (int i = 0; i < sCharArray.length / 2; i++) {
char temp = sCharArray[i];
sCharArray[i] = sCharArray[sCharArray.length - i - 1];
sCharArray[sCharArray.length - i - 1] = temp;
}
return new String(sCharArray);
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
public class StringTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s = "https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.httpsedu.cn/simplehttpshttps";
String son = "https";
int count = 0;
int index = 0;
while ((index = s.indexOf(son)) != -1) {
count++;
if(index + son.length() >= s.length()){
break;
}
s = s.substring(index + son.length());
}
System.out.println(son + "在字符串中出现的次数为:" + count + "次");
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
public class StringTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String idCard = "610122200112063713";
String y = idCard.substring(6, 10);
String m = idCard.substring(10, 12);
String d = idCard.substring(12, 14);
/*
'0' --> 48
'1' --> 49
'2' --> 50
*/
int sex = idCard.indexOf(16);
System.out.println(sex % 2 == 0 ? '女' : '男');
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.stringtest;
/*
获取两个字符串中最大相同的子字符串
*/
public class StringTest07 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
String s1 = "zicafzzyncasobvaohfzxeiowgn";
String s2 = "fafazzyfsayncsobvaohfzxeioyncafwf";
String maxString = maxSubString(s1, s2);
System.out.println(maxString);
}
/**
* 获取两个字符串中最大相同的子字符串
* @param s1 字符串1
* @param s2 字符串2
* @return 最大相同的子字符串
*/
private static String maxSubString(String s1, String s2) {
// 字符串长度
int l1 = s1.length();
int l2 = s2.length();
// 记录maxString长度和起始下标
int maxStringLen = 0;
int maxStringStart = 0;
// 遍历两个字符串
for (int i = 0; i < l1; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < l2; j++) {
// 记录相同子字符串的长度
int k = 0;
// 如果相等了就要继续比较下一个字符
while(i + k < l1 && j + k < l2 && s1.charAt(i + k) == s2.charAt(j + k)) {
k++;
}
// 更新maxString长度和起始下标
if(k > maxStringLen) {
maxStringLen = k;
maxStringStart = i;
}
}
}
return s1.substring(maxStringStart, maxStringStart + maxStringLen);
}
}
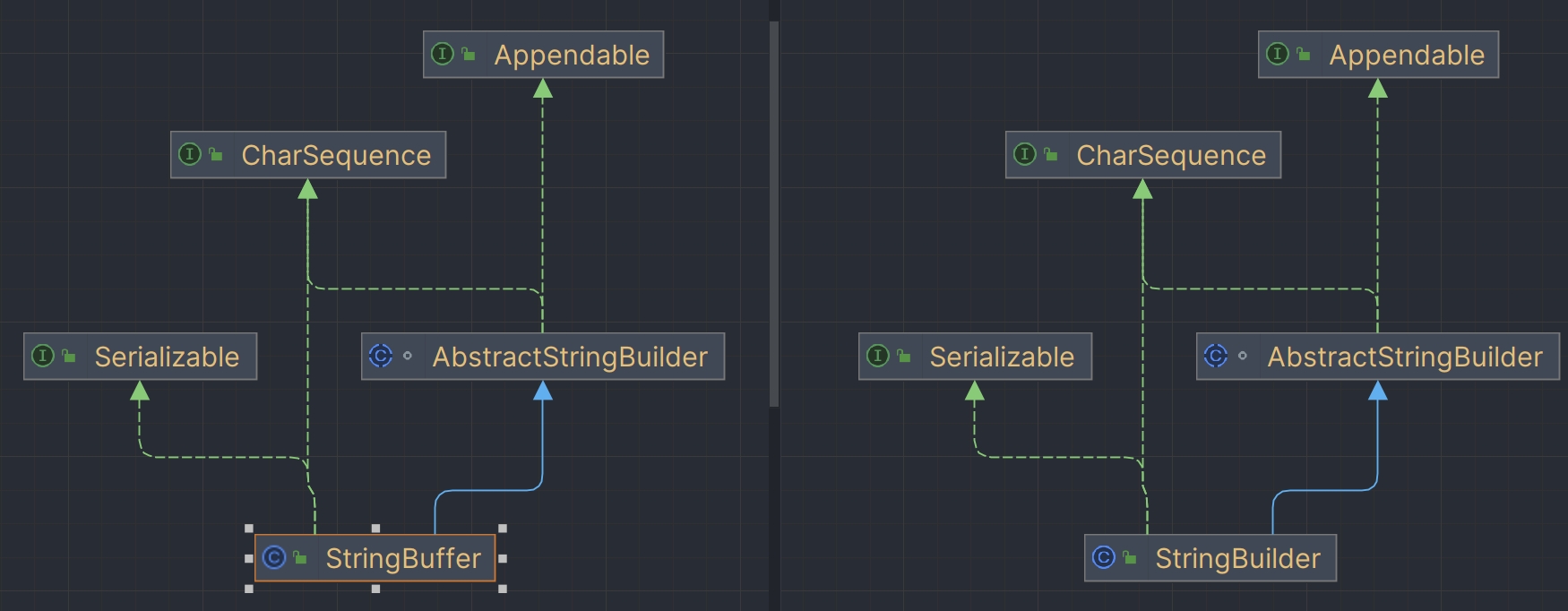
2. StringBuilder和StringBuffer
2.1 初始StringBuilder和StringBuffer

StringBuilder和StringBuffer:可变长字符串
- StringBuffer是线程安全的,StringBuilder是不考虑线程安全的
2.2 继承结构(java8)
2.2 构造方法
 2
2
2.3 常用方法

package com.zeus.javase.stringbuildertest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
/**
* StringBuilder和StringBuffer的常用方法单元测试
*/
public class StringBuilderMethodTest {
// 给StringBuilder对象末尾添加序列
@Test
public void testAppend() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
s.append(true);
s.append(new Object());
s.append('a');
s.append(0.6);
System.out.println(s);
}
// 删除[start, end)的子序列
@Test
public void testDelete() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
s.append(true);
s.append(new Object());
s.append('a');
System.out.println(s);
s.delete(3, 7);
System.out.println(s);
}
// 删除指定索引的字符
@Test
public void testDeleteCharAt() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
s.append(true);
s.deleteCharAt(3);
System.out.println(s);
}
// 在指定索引处插入序列
@Test
public void testInsert() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
s.append(true);
s.append(new Object());
s.insert(3, false);
System.out.println(s);
s.insert(8, "Zeus");
System.out.println(s);
}
// 替换指定位置处的子序列,左闭右开
@Test
public void testReplace() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
s.append(true);
s.append(new Object());
System.out.println(s);
s.replace(3, 7, "false");
System.out.println(s);
}
// 翻转
@Test
public void testReverse() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("zzyZeus");
System.out.println(s);
s.reverse();
System.out.println(s);
}
// 设置指定索引处的字符
@Test
public void testSetCharAt() {
StringBuilder s = new StringBuilder();
s.append("abc");
s.append(true);
s.setCharAt(3, 'T');
System.out.println(s);
}
// 设置长度
@Test
public void testSetLength() {
StringBuilder stringBuilder = new StringBuilder();
stringBuilder.append("abc121654564566165");
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
stringBuilder.setLength(3);
System.out.println(stringBuilder);
}
}
2.4 字符串拼接性能比拼

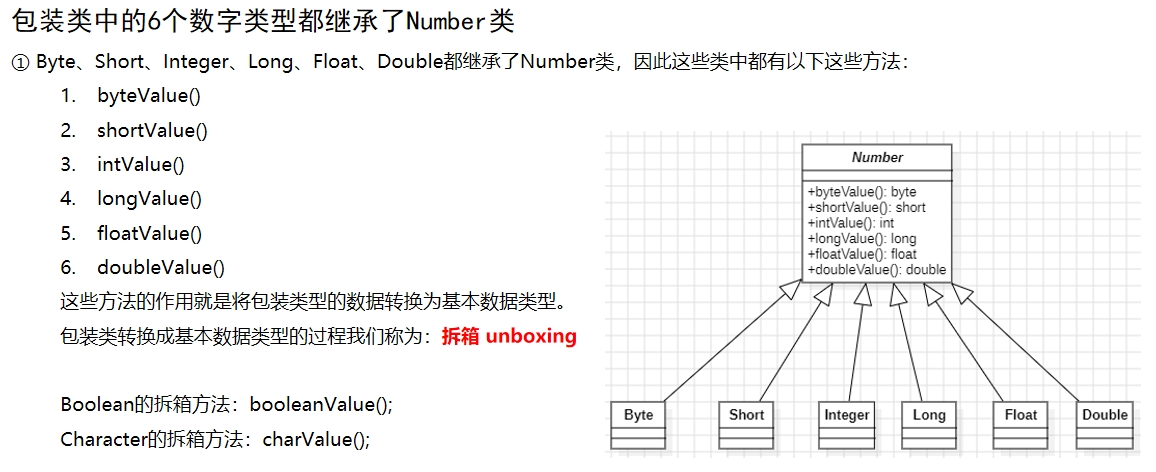
3. 包装类
3.1 初始包装类
目的:方便编程

3.2 装箱与拆箱
3.3 Integer的常量

public class IntegerTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(Integer.BYTES);
System.out.println(Integer.TYPE);
System.out.println(Integer.SIZE);
System.out.println(Integer.MAX_VALUE);
System.out.println(Integer.MIN_VALUE);
System.out.println(Boolean.TYPE);
System.out.println(Boolean.FALSE);
System.out.println(Boolean.TRUE);
}
}
3.4 Integer的构造方法

public class IntegerTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer i1 = new Integer(10);
Integer i2 = new Integer("10");
System.out.println(i1);
System.out.println(i2);
}
}
3.5 Integer的常用方法

package com.zeus.javase.integertest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
/**
* Integer的常用方法单元测试
*/
public class IntegerMethodTest {
// 比较两个int数据的大小
@Test
public void testCompare() {
System.out.println(Integer.compare(10, 5)); // 1
System.out.println(Integer.compare(3, 7)); // -1
System.out.println(Integer.compare(2, 2)); // 0
}
// 返回两个int数据的最大值/最小值
@Test
public void testMaxAndMin() {
System.out.println(Integer.max(10, 5)); // 10
System.out.println(Integer.min(10, 5)); // 5
}
// 将字符串数字转换成数字类型
@Test
public void testParseInt() {
int i = Integer.parseInt("100");
System.out.println(i);
// java.lang.NumberFormatException
// int i1 = Integer.parseInt("abc");
}
// 将int类型数字转化为十六、八、二进制字符串表示形式
@Test
public void testToJinZhi() {
String binaryString = Integer.toBinaryString(20);
System.out.println(binaryString);
String hexString = Integer.toHexString(20);
System.out.println(hexString);
String octalString = Integer.toOctalString(20);
System.out.println(octalString);
}
// 比较两个Integer对象的大小
@Test
public void testCompareTo() {
Integer i = new Integer(10);
Integer i1 = new Integer(20);
System.out.println(i.compareTo(i1)); // -1
}
// equals和toString方法
@Test
public void testEqualsAndToString() {
// 包装类都重写了equals方法和toString方法
Integer i = new Integer(10);
Integer i1 = new Integer(10);
System.out.println(i == i1); // false
System.out.println(i.equals(i1)); // true
System.out.println(i.toString());
}
// 拆箱:将包装类拆箱为基本数据类型
@Test
public void testIntValue() {
Integer i = new Integer(10);
int i1 = i.intValue();
System.out.println(i1);
}
// 将基本数据类型转化为字符串
@Test
public void testToString() {
String string = Integer.toString(10);
System.out.println(string);
}
// 将基本数据类型转化为Integer
@Test
public void testValueOf() {
Integer i = Integer.valueOf(10);
System.out.println(i);
Integer i1 = Integer.valueOf("100");
System.out.println(i1);
// java.lang.NumberFormatException
// Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf("abc");
// System.out.println(i2);
}
}
3.6 String、int、Integer相互转化
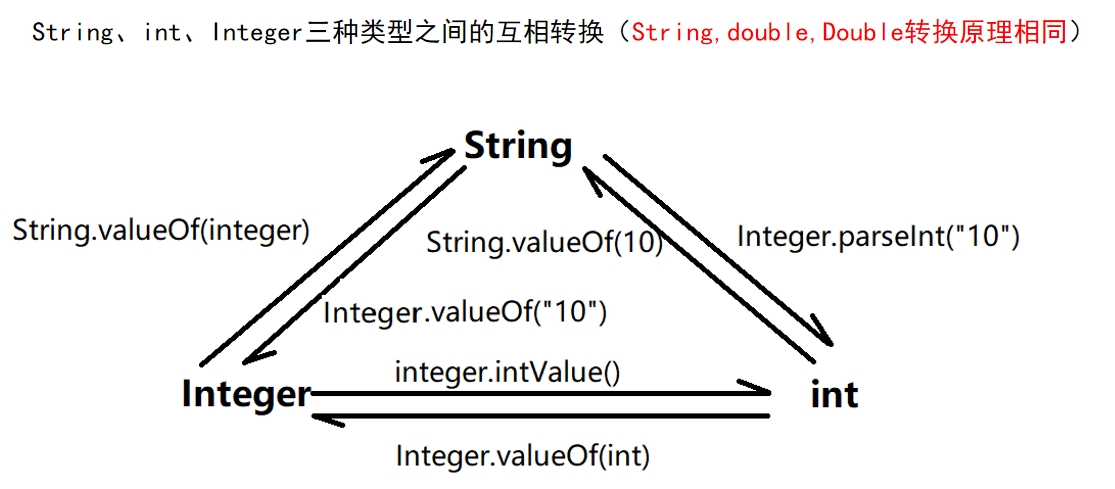
/**
* String int Integer之间相互转化
*/
public class IntegerTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// String --> int
int i = Integer.parseInt("10");
// int --> String
String s = Integer.toString(10);
String s1 = String.valueOf(10);
int i0 = 10;
String s0 = i + "";
String s2 = 10 + "";
// String --> Integer
Integer i1 = new Integer("10");
Integer i2 = Integer.valueOf("10");
// Integer --> String
Integer i3 = new Integer("10");
String s3 = i3.toString();
String s4 = String.valueOf(i3);
// int --> Integer
Integer i4 = new Integer(10);
Integer i5 = Integer.valueOf(10);
// Integer --> int
int i7 = i4.intValue();
}
}
3.7 自动装箱和自动拆箱(Java5新特性)
关于自动装箱和自动拆箱
- Java5新特性
- 自动装箱和自动拆箱属于编译阶段的功能
- 自动装箱:auto boxing
- 自动拆箱:auto unboxing
- 自动装箱和自动拆箱是为了方便写代码而存在的机制
- 装箱:int —> Integer
- 拆箱:Integer —> int

package com.zeus.javase.integertest;
/**
* 自动装箱与自动拆箱
*/
public class IntegerTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 自动装箱,底层:new Integer(10)
Integer i = 1000;
// 自动拆箱,底层i.intValue()
int i1 = i;
// 自动装箱
int i2 = 100;
m(i2);
// 注意空指针异常
i = null;
// NullPointerException
// int i3 = i;
m(null);
}
public static void m(Integer integer) {
// 排空
if(integer != null) {
// 自动拆箱
System.out.println(integer + 1);
}
}
}
3.8 面试题:整数型常量池
package com.zeus.javase.integertest;
/**
* 面试题:整数型常量池
* 为了提高效率,java提供了一个整数型常量池Integer[] integerCache
* 这个数组中存储了常用了256个Integer引用[-128, 127]
* 在这个范围内的数字,可以直接从整数型常量池中取,不需要新建Integer对象
*/
public class IntegerTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Integer a = 1000;
Integer b = 1000;
System.out.println(a == b); // false
Integer i1 = 127;
Integer i2 = 127;
System.out.println(i1 == i2); // true
}
}
3.9 大数字
1. BigInteger

package com.zeus.javase.bignumbertest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.math.BigInteger;
/**
* BigInteger常用方法单元测试
*/
public class BigIntegerMethodTest {
// 求和
@Test
public void testAdd() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
BigInteger result = i.add(i2);
System.out.println(result);
}
// 相减
@Test
public void testSubtract() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
BigInteger result = i.subtract(i2);
System.out.println(result);
}
// 乘积
@Test
public void testMultiply() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
BigInteger result = i.multiply(i2);
System.out.println(result);
}
// 商
@Test
public void testDivide() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
BigInteger result = i.divide(i2);
System.out.println(result);
}
// 比较
@Test
public void testCompareTo() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
System.out.println(i.compareTo(i2));
}
// 绝对值
@Test
public void testAbs() {
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("-5");
System.out.println(bigInteger.abs());
}
// 最大值
@Test
public void testMax() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
System.out.println(i.max(i2));
}
// 最小值
@Test
public void testMin() {
BigInteger i = new BigInteger("10");
BigInteger i2 = new BigInteger("5");
System.out.println(i.min(i2));
}
// 次幂
@Test
public void testPow() {
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("2");
System.out.println(bigInteger.pow(3)); // 8
}
// 平方根
@Test
public void testSqrt() {
BigInteger bigInteger = new BigInteger("9");
// java8中没有
// BigInteger bigInteger1 = bigInteger.sqrt();
// System.out.println(bigInteger1); // 3
}
}
2. BigDecimal

package com.zeus.javase.bignumbertest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
/**
* BigDecimal常用方法单元测试
*/
public class BigDecimalMethodTest {
@Test
public void testAdd() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal.add(bigDecimal1);
System.out.println(result);
}
@Test
public void testSubtrahend() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal.subtract(bigDecimal1);
System.out.println(result);
}
@Test
public void testMultiplicand() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal.multiply(bigDecimal1);
System.out.println(result);
}
@Test
public void testDivisor() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal.divide(bigDecimal1);
System.out.println(result);
}
@Test
public void testMax() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal.max(bigDecimal1);
System.out.println(result);
}
@Test
public void testMin() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
BigDecimal bigDecimal1 = new BigDecimal("1.1");
BigDecimal result = bigDecimal.min(bigDecimal1);
System.out.println(result);
}
// 向左移动小数点
@Test
public void testMovePointLeft() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
System.out.println(bigDecimal.movePointLeft(2)); // 1.23123
}
// 向右移动小数点
@Test
public void testMovePointRight() {
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123.123");
System.out.println(bigDecimal.movePointRight(2)); // 12312.3
}
}
3. 数字格式化

package com.zeus.javase.bignumbertest;
import java.math.BigDecimal;
import java.text.DecimalFormat;
/**
* 数字格式化
*/
public class BigDecimalFormatTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 四舍六进五后非零则进一
DecimalFormat df = new DecimalFormat("###,###.##");
BigDecimal bigDecimal = new BigDecimal("123456789.1251");
String format = df.format(bigDecimal);
System.out.println(format); // 123,456,789.13
DecimalFormat df2 = new DecimalFormat("###,###.0000");
String format2 = df2.format(bigDecimal);
System.out.println(format2); // 123,456,789.1230
}
}
4. 日期API
4.1 不支持线程安全的


package com.zeus.javase.datetest;
import java.util.Date;
/*
java.util.Data日期类
*/
public class DateTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取系统当前时间对象
Date date = new Date();
// Fri May 24 14:56:04 CST 2024
System.out.println(date);
// 获取1970 1 1 0:0:0 + 1000ms的时间对象
Date date1 = new Date(1000);
// Thu Jan 01 08:00:01 CST 1970
System.out.println(date1);
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.datetest;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Date;
/**
* 日期格式化类
* Java.test.DateFormat
* java.text.SimpleDateFormat
*/
public class DateFormatTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
Date date = new Date();
System.out.println(date);
// Date ---> String
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss SSS");
String format = simpleDateFormat.format(date);
System.out.println(format); // 2024-05-24 03:05:05 813
// String ---> Date
String strDate = "2008-08-08 08:08:08 008";
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse(strDate);
System.out.println(parse); // Fri Aug 08 08:08:08 CST 2008
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.datetest;
import java.util.Calendar;
/**
* 日历类
*/
public class CalendarTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Calendar calendar = Calendar.getInstance();
System.out.println(calendar);
int year = calendar.get(Calendar.YEAR);
System.out.println(year);
int month = calendar.get(Calendar.MONTH);
System.out.println(month);
int week = calendar.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_WEEK);
System.out.println(week);
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.datetest;
import java.text.ParseException;
import java.text.SimpleDateFormat;
import java.util.Calendar;
import java.util.Date;
public class CalendarTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) throws ParseException {
// set()
Calendar c = Calendar.getInstance();
c.set(Calendar.YEAR, 2022);
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR));
c.set(2001, Calendar.DECEMBER, 6, 10, 21, 6);
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "-" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
// add()
c.add(Calendar.YEAR, 2);
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); // 2003
c.add(Calendar.YEAR, -1);
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR)); // 2002
// setTime()
String strDate = "2004-12-6 12:12:36";
SimpleDateFormat simpleDateFormat = new SimpleDateFormat("yyyy-MM-dd hh:mm:ss");
Date parse = simpleDateFormat.parse(strDate);
c.setTime(parse);
System.out.println(c.get(Calendar.YEAR) + "-" + (c.get(Calendar.MONTH) + 1) + "-" + c.get(Calendar.DAY_OF_MONTH));
// getTime()
c = Calendar.getInstance();
Date time = c.getTime();
System.out.println(time);
}
}
4.2 线程安全的(Java8)


package com.zeus.javase.java8datetest;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.LocalTime;
/**
* LocalDate
* LocalTime
* LocalDateTime
*/
public class DateTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// LocalDateTime:2024-05-25T15:51:03.231
System.out.println("LocalDateTime:" + now);
LocalDate now1 = LocalDate.now();
// LocalDate:2024-05-25
System.out.println("LocalDate:" + now1);
LocalTime now2 = LocalTime.now();
// LocalTime:15:51:03.232
System.out.println("LocalTime:" + now2);
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.java8datetest;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
/**
* LocalDateTime相关方法
*/
public class DateTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取当前时间
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
// 获取指定日期的时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2001, 10, 21, 18, 26, 36, 886);
System.out.println(localDateTime); // 2001-10-21T18:26:36.000000886
// 增加/减少时间
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = localDateTime.plusYears(1);
System.out.println(localDateTime1); // 2002-10-21T18:26:36.000000886
LocalDateTime localDateTime2 = localDateTime1.minusYears(2);
System.out.println(localDateTime2); // 2000-10-21T18:26:36.000000886
LocalDateTime localDateTime3 = localDateTime2.plusYears(24).minusMonths(5).plusDays(4).minusHours(3).plusMinutes(32);
System.out.println(localDateTime3); // 2024-05-25T15:58:36.000000886
// 获取年月日时分秒
System.out.println(localDateTime3.getYear());
System.out.println(localDateTime3.getMonth());
System.out.println(localDateTime3.getDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(localDateTime3.getHour());
System.out.println(localDateTime3.getMinute());
System.out.println(localDateTime3.getSecond());
}
}

package com.zeus.javase.java8datetest;
import java.time.Instant;
public class DateTest03 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 获取系统当前时间
Instant now = Instant.now();
System.out.println(now); // 2024-05-25T08:04:25.802Z
// 获取时间戳
long epochMilli = now.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(epochMilli); // 1716624348185
int count = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
count += i;
}
long epochMilli1 = now.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(epochMilli1); // 1716624348185
Instant now1 = Instant.now();
long epochMilli2 = now1.toEpochMilli();
System.out.println(epochMilli2); // 1716624399603
}
}


package com.zeus.javase.java8datetest;
import java.time.Duration;
import java.time.LocalDate;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.Period;
/**
* Duration计算时间间隔
* Period计算日期间隔
*/
public class DateTest04 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime localDateTime = LocalDateTime.of(2001, 1, 1, 1, 1, 1);
LocalDateTime localDateTime1 = LocalDateTime.of(2002, 2, 2, 2, 2, 2);
// Duration
Duration between = Duration.between(localDateTime, localDateTime1);
System.out.println(between.toDays()); // 397
System.out.println(between.toHours()); // 9529
LocalDate localDate = LocalDate.of(2001, 12, 1);
LocalDate localDate1 = LocalDate.of(2001, 11, 15);
// period
Period between1 = Period.between(localDate, localDate1);
System.out.println(between1.getYears()); // 0
System.out.println(between1.getMonths()); // 0
System.out.println(between1.getDays()); // -16
}
}

package com.zeus.javase.java8datetest;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.temporal.TemporalAdjusters;
/**
* 时间矫正器TemporalAdjusters
*/
public class DateTest05 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
System.out.println(now);
LocalDateTime with = now.with(TemporalAdjusters.lastDayOfMonth());
System.out.println(with);
}
}

package com.zeus.javase.java8datetest;
import java.time.LocalDateTime;
import java.time.format.DateTimeFormatter;
/**
* 日期格式化DateTimeFormatter
*/
public class DateTest06 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// LocalDateTime ---> String
LocalDateTime now = LocalDateTime.now();
DateTimeFormatter dtf = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
String format = dtf.format(now);
System.out.println(format); // 2024-05-25 04:21:37
// String ---> LocalDateTime
String srtLocalDateTime = "2023-01-09 19:26:36";
DateTimeFormatter dtf1 = DateTimeFormatter.ofPattern("yyyy-MM-dd HH:mm:ss");
LocalDateTime parse = LocalDateTime.parse(srtLocalDateTime, dtf1);
System.out.println(parse);
}
}
5. Math数学工具类

package com.zeus.javase.mathtest;
/**
* java.lang.Math类
*/
public class MathTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 绝对值
int abs = Math.abs(-10); // 10
System.out.println(abs);
// 常量:圆周率
System.out.println(Math.PI);
// 向上取整
System.out.println(Math.ceil(3.1));
// 向下取整
System.out.println(Math.floor(3.9));
// 最大值
System.out.println(Math.max(10, 20));
// 最小值
System.out.println(Math.min(8, 10));
// 随机数
double random = Math.random();
System.out.println(random);
// 四舍五入
System.out.println(Math.round(1.4));
System.out.println(Math.round(1.5));
// 平方根
System.out.println(Math.sqrt(4));
// 次幂
System.out.println(Math.pow(2, 3)); // 8.0
}
}
6. 枚举(Java5)

package com.zeus.javase.enumtest;
public enum Season {
SPRING, SUMMER, AUTUMN, WINTER
}
package com.zeus.javase.enumtest;
public class EnumTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Season season = getSeason();
switch (season) {
case SPRING:
System.out.println("春");
break;
case AUTUMN:
System.out.println("秋,autumn");
break;
case SUMMER:
System.out.println("夏天,summer");
break;
case WINTER:
System.out.println("冬天, winter");
break;
}
Season[] values = Season.values();
for (Season s : values) {
System.out.println(s);
}
}
public static Season getSeason() {
return Season.AUTUMN;
}
}

package com.zeus.javase.enumtest;
public enum Color implements Drawing{
BLUE("蓝色", "非常蓝"){
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println(BLUE.getName() + "绘画");
}
},
YELLOW("黄色", "非常黄"),
BLACK("黑色", "非常黑"),
RED("红色", "非常红"),
GREEN("绿色", "非常绿");
public String getDesc() {
return desc;
}
public String getName() {
return name;
}
private final String desc;
private final String name;
// 静态代码块
// static {
// System.out.println("Color的静态代码块");
// }
// 构造代码块
// {
// System.out.println("Color的构造代码块");
// }
private Color(String name, String desc) {
this.name = name;
this.desc = desc;
}
@Override
public void draw() {
System.out.println("绘画");
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.enumtest;
public class EnumTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Color color = getColor();
System.out.println(color.getName() + ", " + color.getDesc());
switch (color) {
case BLACK:
System.out.println("black");
break;
case BLUE:
System.out.println("blue");
break;
case RED:
System.out.println("red");
break;
case GREEN:
System.out.println("green");
break;
case YELLOW:
System.out.println("yellow");
break;
}
color.draw();
}
public static Color getColor() {
return Color.BLUE;
}
}
7. Radom随机数工具类

package com.zeus.javase.randomtest;
import java.util.Random;
public class RandomTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Random random = new Random();
// [-2147483648, 2147483647]
System.out.println(random.nextInt());
// [0, 11)
System.out.println(random.nextInt(11));
// [0.0, 1.0)
System.out.println(random.nextDouble());
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.randomtest;
import java.util.Random;
/**
* 生成5个不重复的随机数(0~10)
*/
public class RandomTest02 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 创建随机数生成器对象
Random random = new Random();
// 初始化长度为5的int类型数组
int[] randoms = {-1, -1, -1, -1, -1};
// for (int i = 0; i < randoms.length; i++) {
// int temp = random.nextInt(11);
//
// if(!checkContains(randoms, temp)) {
// randoms[i] = temp;
// } else{
// i--;
// }
// }
int index = 0;
while(index < randoms.length) {
int temp = random.nextInt(10);
if(!checkContains(randoms, temp)) {
randoms[index++] = temp;
}
}
for (int i : randoms) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
/**
* 判断生成的随机数是否已经在数组中
* @param ints 目标数组
* @param num 生成的数字
* @return 包含true, 不包含false
*/
public static boolean checkContains(int[] ints, int num) {
for (int i : ints) {
if(num == i) {
return true;
}
}
return false;
}
}
8. System系统类

package com.zeus.javase.systemtest;
import java.io.InputStream;
import java.io.PrintStream;
import java.util.Scanner;
public class SystemTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
PrintStream out = System.out;
out.println("PrintStream");
InputStream in = System.in;
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(in);
System.err.println("标准错误输出流");
}
}
package com.zeus.javase.systemtest;
import org.junit.jupiter.api.Test;
import java.util.Map;
import java.util.Properties;
/**
* System系统类常用方法单元测试
*/
public class SystemMethodTest {
@Test
public void testArrayCopy() {
int[] array1 = {1, 2, 3, 4, 5};
int[] array2 = new int[10];
System.arraycopy(array1, 0, array2, 0, array1.length);
for (int i : array2) {
System.out.println(i);
}
}
@Test
public void testExit() {
System.out.println("System.exit()执行");
System.exit(0);
}
@Test
public void testGc() {
System.out.println("建议启动垃圾回收器");
System.gc();
}
@Test
public void testCurrentTimeMillisAndNanoTime() {
// 获取自1970-1-1 0:0:0 000到系统当前时间的毫秒数
System.out.println(System.currentTimeMillis());
// 获取自1970-1-1 0:0:0 000到系统当前时间的纳秒数
System.out.println(System.nanoTime());
}
// 获取当前系统的环境变量
@Test
public void testGetenv() {
Map<String, String> getenv = System.getenv();
System.out.println(getenv);
}
// 获取当前系统的属性
@Test
public void testGetProperties() {
Properties properties = System.getProperties();
System.out.println(properties);
String property = System.getProperty("os.name");
System.out.println(property); // Windows 10
}
}
9. UUID

package com.zeus.javase.uuidtest;
import java.util.UUID;
// java.util.UUID
public class UUIDTest01 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 生成UUID
UUID uuid = UUID.randomUUID();
String stringUUID = uuid.toString();
System.out.println(stringUUID); // 6a88c810-b0df-453a-a7f1-4bac99869ce1
}
}






















 821
821

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








