静态变量
- 用非访问控制修饰符static修饰的成员变量,称为静态成员变量,静态成员变量被所在类的所有实例对象所共享,所以也称为“类变量”。
- 静态变量不仅可以通过实例对象来进行访问,也可以使用“类名.变量名”来对其进行访问。
- 没有关键字static修饰的成员变量,称为非静态成员变量,由于非静态成员变量必须通过实例对象才能进行访问,因此也称为“实例变量”。
- 实例变量必须通过实例对象才能进行访问。
案例一:在Student类中定义一个静态成员变量schoolName和两个非静态成员变量name和age。
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student stu1 = new Student("林枫",19);
Student stu2 = new Student("叶凡",20);
Student.schoolName = "诸天";
stu1.show();
stu2.show();
}
}
class Student {
static String schoolName;
private String name;
private int age;
public Student(String name,int age){
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
}
public void show(){
System.out.println("我的地址是:"+schoolName+"\t我的名字:"+name+"\t我的年龄:"+age);
}
}
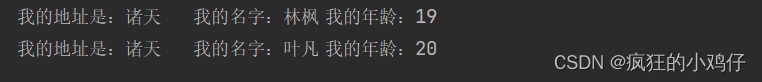
运行结果:
案例二
public class Student {
private static int age; //静态变量
private double score; //非静态变量
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student s1 = new Student();
System.out.println(Student.age);
System.out.println(s1.age);
System.out.println(s1.score);
}
}运行结果:

静态方法
- 在类中定义方法时,如果加上了关键字static, 则该方法称为静态方法。
- 静态方法与静态变量一样,被类中所有的实例对象共享,所以,静态方法可以通过实例对象访问,也可以通过类来进行访问,即“类名.方法名”。
class Student{
public static void introduce(){
System.out.println("我是小白");
}
}
public class Application {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student.introduce();
}
}运行结果:我是小白
案例三
public class Student {
private static int age;
private double score;
public void run(){
}
public static void go(){
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student.go();
// Student.run(); //会报错
//正确写法:new Student().run();
}
}案例四:静态方法中对静态成员的访问
public class Student {
private int a = 1;
public void method1(){
a++; //合法
}
public void method2(){
this.method1(); //合法
}
public static void method3(){
a++; //不合法,在静态方法中访问非静态变量
this.method1();//不合法,在静态方法中访问非静态方法
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
method3();//合法
method1();//不合法,在静态方法中访问非静态方法
System.out.println(a);//不合法,在静态方法中访问非静态变量
}静态代码块
- 用static 关键字修饰的代码块,称为静态代码块。
- 当类加载时,静态代码被执行。由于类只加载一次,因此静态代码块只执行一次。因此,可以用静态代码块对类成员变量进行初始化。
public class Student {
{
//代码块(匿名代码块)
}
static{
//静态代码块
}
}案例五:(拓展)
public class Student {
//加载顺序:静态代码块>匿名代码块 >构造函数
//2
{
System.out.println("匿名代码块");
}
//1
//只执行一次
static{
System.out.println("静态代码块");
}
//3
public Student(){
System.out.println("构造方法");
}
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student = new Student();
System.out.println("==================");
Student student2 = new Student();
}
}
案例六:随便输出一个数
//静态导入包
import static java.lang.Math.random;
public class Student {
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println(random());
}
}案例七:在学生类中创建一个静态代码块,完成类成员变量的初始化。
class Student{
static String schoolName;
static {
schoolName="诸天";
System.out.println("Student类的静态代码被执行");
}
}
public class Person {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1 = new Student();
Student student2 = new Student();
System.out.println("第一个地址:"+student1.schoolName);
System.out.println("第一个地址:"+student2.schoolName);
}
}运行结果:























 194
194











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










