一、实验目的
1、掌握查找的特点。
2、掌握折半查找的基本思想及其算法。
3、熟悉二叉排序树的特点,掌握二叉排序树的插入、删除操作。
二、实验内容
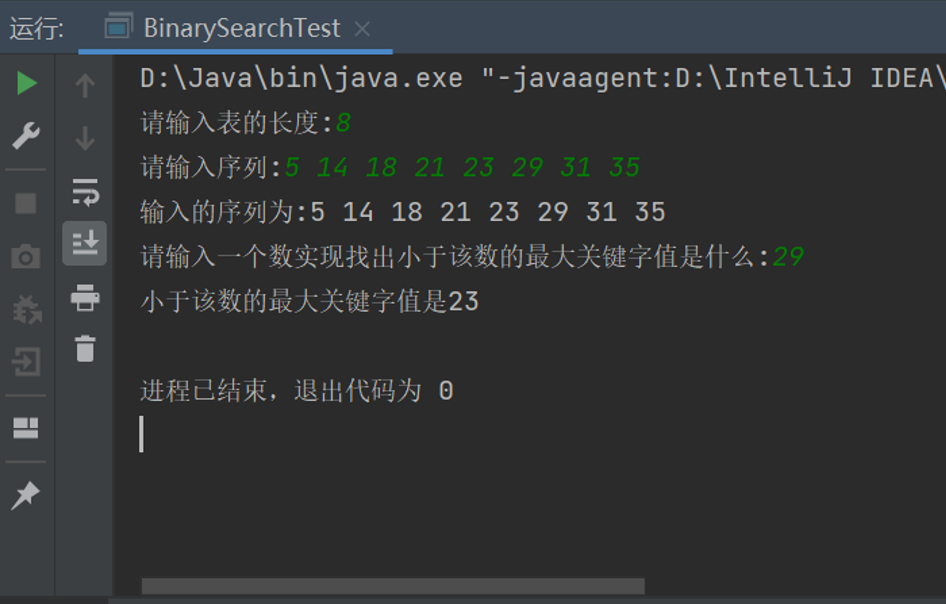
1、设有关键字序列k={ 5 ,14 ,18 ,21 ,23 ,29 ,31 ,35 },请找出小于29的最大关键字值是什么。
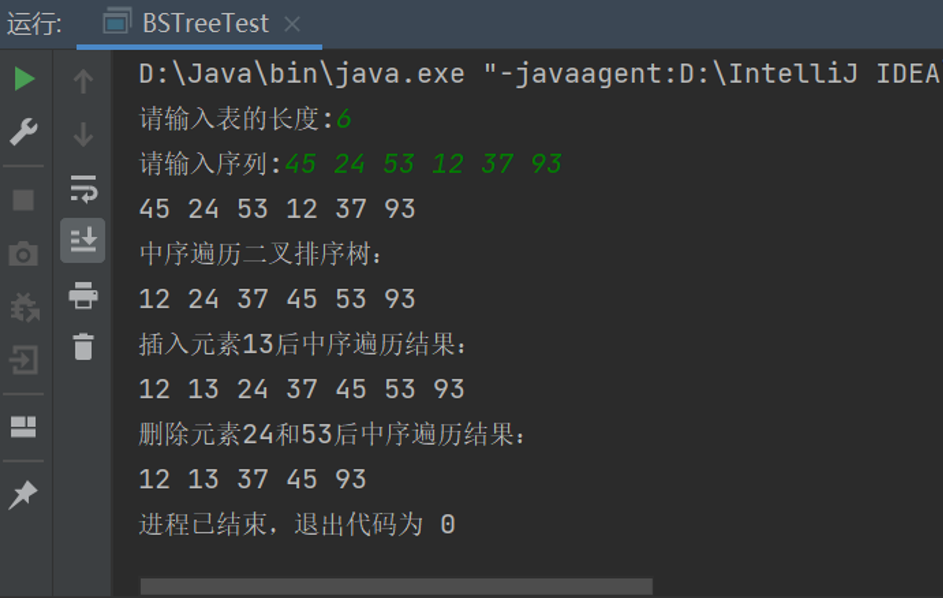
2、根据关键字序列{45、24、53、12、37、93}构造二叉排序树,并完成插入13删除关键字53和24的操作。
三、实验步骤
1、折半查找
(1)从键盘输入上述8个整数5 ,14,18 ,21 ,23 ,29 ,31 ,35,并输出其值检验输入是否正确。
(2)实现找出小于29的最大关键字值是什么的操作。
2、二叉排序树
(1)二叉排序树存储定义
(2)从键盘上输入六个整数45、24、53、12、37、93构造二叉排序树
(3)输出其中序遍历结果。
(4)插入数据元素13,输出其中序遍历结果。
(5)删除数据元素24和53,输出其中序遍历结果,注明:既有左子树又有右子树删除时利用中序遍历的前驱结点替换要删除的结点,然后删除其前驱结点。
四、代码及运行结果
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BinarySearchTest {
static SeqList ST=null;
public static void creatSearchList() throws Exception{
int maxSize=20;
ST=new SeqList(maxSize);
int curlen;
System.out.print("请输入表的长度:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
curlen=sc.nextInt();
KeyType[] k=new KeyType[curlen];
System.out.print("请输入序列:");
for(int i=0;i<curlen;i++) {
k[i]=new KeyType(sc.nextInt());
}
for(int i=0;i<curlen;i++) {
RecordNode r=new RecordNode(k[i]);
ST.insert(ST.curlen, r);
}
System.out.print("输入的序列为:");
for(int i=0;i<ST.curlen;i++) {
System.out.print(k[i]+" ");
}
System.out.println();
}
public static Comparable FindMax(SeqList ST, Comparable k){
int m = 0;
int n = ST.curlen - 1;
while(m < n){
int mid = (m + n + 1) / 2;
if(ST.r[mid].key.compareTo(k) <0 ) {
m = mid;
}else{
n= mid - 1;
}
}
if(ST.r[m].key.compareTo(k) >0 ) return -1;
return ST.r[m].key;
}
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception{
creatSearchList();
System.out.print("请输入一个数实现找出小于该数的最大关键字值是什么:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
int k=sc.nextInt();
KeyType key=new KeyType(k);
System.out.println("小于该数的最大关键字值是"+FindMax(ST, key));
}
}
public class BiTreeNode {
public Object data;
public BiTreeNode lchild,rchild;
public BiTreeNode(){
this(null);
}
public BiTreeNode(Object data){
this(data,null,null);
}
public BiTreeNode(Object data,BiTreeNode lchild,BiTreeNode rchild){
this.data=data;
this.lchild=lchild;
this.rchild=rchild;
}
}public class BSTree {
public BiTreeNode root;
public BSTree(){
root=null;
}
public void inOrderTraverse(BiTreeNode p){
if(p!=null){
inOrderTraverse(p.lchild);
System.out.print(((RecordNode)p.data).key.toString()+" ");
inOrderTraverse(p.rchild);
}
}
public Object removeBST(Comparable key) {
if (root == null || key == null || !(key instanceof Comparable)) {
return null;
}
return removeBST(root, key, null);
}
public Object removeBST(BiTreeNode p,Comparable elemKey,BiTreeNode parent) {
if (p != null) {
if (elemKey.compareTo(((RecordNode) p.data).key) < 0)
return removeBST(p.lchild, elemKey, p);
else if (elemKey.compareTo(((RecordNode) p.data).key) > 0)
return removeBST(p.rchild, elemKey, p);
else if (p.lchild != null && p.rchild != null) {
BiTreeNode innext = p.rchild;
while (innext.lchild != null) {
innext = innext.lchild;
}
p.data = innext.data;
return removeBST(p.rchild, ((RecordNode) p.data).key, p);
} else {
if (parent == null) {
if (p.lchild != null) {
root = p.lchild;
} else {
root = p.rchild;
}
return p.data;
}
}
if (p == parent.lchild) {
if (p.lchild != null) {
parent.lchild = p.lchild;
} else {
parent.rchild = p.rchild;
}
} else if (p.lchild != null) {
parent.rchild = p.lchild;
} else {
parent.rchild = p.rchild;
}
return p.data;
}
return null;
}
public Object searchBST(Comparable key){//查找算法,封装
if(key==null||!(key instanceof Comparable)){
return null;
}
return searchBST(root,key);
}
private Object searchBST(BiTreeNode p,Comparable key){
if(p!=null){
if(key.compareTo(((RecordNode)p.data).key)==0) {
return p.data;
}
if(key.compareTo(((RecordNode)p.data).key)<0){
return searchBST(p.lchild,key);
}else{
return searchBST(p.rchild,key);
}
}
return null;
}
public boolean insertBST(Comparable key){
if(key==null||!(key instanceof Comparable)){
return false;
}
if(root==null){
root=new BiTreeNode(new RecordNode(key));
return true;
}
return insertBST(root,key);
}
private boolean insertBST(BiTreeNode p,Comparable key){
if(key.compareTo(((RecordNode)p.data).key)==0) {
return false;
}
if(key.compareTo(((RecordNode)p.data).key)< 0){
if(p.lchild==null){
p.lchild=new BiTreeNode(new RecordNode(key));
return true;
}else{
return insertBST(p.lchild,key);//递归的插入到左孩子
}
}else if(p.rchild==null){
p.rchild=new BiTreeNode(new RecordNode(key));
return true;
}else{
return insertBST(p.rchild,key);
}
}
}
import java.util.Scanner;
public class BSTreeTest {
public static void main(String[] args){
BSTree bsTree=new BSTree();
/*
int[] k={45,24,53,12,37,93};
KeyType[] key=new KeyType[k.length];
System.out.println("原序列");
for (int i=0;i<k.length;i++){
key[i]=new KeyType(k[i]);
if (bsTree.insertBST(key[i])){
System.out.print(key[i]+" ");
}
}
*/
int curlen;
System.out.print("请输入表的长度:");
Scanner sc=new Scanner(System.in);
curlen=sc.nextInt();
KeyType[] k=new KeyType[curlen];
System.out.print("请输入序列:");
for(int i=0;i<curlen;i++) {
k[i] = new KeyType(sc.nextInt());
if (bsTree.insertBST(k[i])) {
System.out.print(k[i] + " ");
}
}
System.out.println("\n中序遍历二叉排序树:");
bsTree.inOrderTraverse(bsTree.root);
KeyType a=new KeyType();
a.key=13;
bsTree.insertBST(a);
System.out.println("\n插入元素13后中序遍历结果:");
bsTree.inOrderTraverse(bsTree.root);
KeyType b=new KeyType();
KeyType c=new KeyType();
b.key=24;
c.key=53;
bsTree.removeBST(b);
bsTree.removeBST(c);
System.out.println("\n删除元素24和53后中序遍历结果:");
bsTree.inOrderTraverse(bsTree.root);
}
}
public class KeyType implements Comparable<KeyType>{
public int key;
public KeyType(){
}
public KeyType(int key){
this.key=key;
}
public String toString(){
return key+"";
}
public int compareTo(KeyType another){
int thisVal=this.key;
int anotherVal=another.key;
return (thisVal<anotherVal?-1:(thisVal==anotherVal?0:1));
}
}
public class RecordNode {
public Comparable key;
public Object element;
public RecordNode(Comparable key) {
this.key=key;
}
public RecordNode(Comparable key,Object element) {
this.key=key;
this.element=element;
}
}public class SeqList {
public RecordNode[] r;
public int curlen;
public SeqList(int maxSize) {
this.r=new RecordNode[maxSize];
this.curlen=0;
}
public void insert(int i,RecordNode x)throws Exception{
if(curlen==r.length) {
throw new Exception("顺序表已满");
}
if(i<0||i>curlen) {
throw new Exception("插入位置不合理");
}
for(int j=curlen;j>i;j--) {
r[j]=r[j-1];
}
r[i]=x;
this.curlen++;
}
public int binarySearch(Comparable key){
if (curlen>0){
int low = 0,hight=curlen-1;
while (low<hight){
int mid=(low+hight)/2;
if (r[mid].key.compareTo(key)==0){
return mid;
}else if (r[mid].key.compareTo(key)>0){
hight=mid-1;
}else {
low=mid+1;
}
}
}
return -1;
}
}运行结果:
五、问题讨论
1、折半查找递归算法该怎么描述?
首先取整个有序表的中间记录的关键字值与给定值相比较,若相等,则查找成功;否则以位于中间位置的数据元素为分界点,将查找表分成左右两个子表,并判断待查找的关键字值key是在左子表还是在右子表,再在左或右子表中重复上述步骤,直到找到关键字值为key的记录或子表长度为0。
2、二叉排序树中序遍历结果有什么特点?
中序遍历一棵二叉排序树可得到一个关键字的有序序列。
3、在二叉树排序树中插入一个新结点,总是插入到叶结点下面吗?
新插入的结点一定是作为叶子节点添加的
4、在任意一棵非空二叉排序树中,删除某结点后又将其插入,则所得二排序叉树与原二排序叉树相同吗?
不一定相同,当删除的是叶子节点的情况下再将其插入所得二排序叉树与原二排序叉树才相同。





















 185
185











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








