目录
1. 计算各参数的梯度,要把前项运算的过程代码放入到"with tf.GradientTape() as tape:"中
2.要计算w,b的梯度,在定义w,b参数时,需用tf.Variable封装
1. 计算各参数的梯度,要把前项运算的过程代码放入到"with tf.GradientTape() as tape:"中
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # tf.Variable (关于计算梯度的代码,要放入“with tf.GradientTape() as tape”中)
# x: [b, 28*28]
# h1 = x@w1 + b1
# [b, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [b, 256]
h1 = x@w1 + tf.broadcast_to(b1, [x.shape[0], 256]) # 维度扩张
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) #添加非线性
# [b, 256] => [b, 128]
h2 = h1@w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2)
# [b, 128] => [b, 10]
out = h2@w3 + b3
# compute loss(计算损失函数)
# out: [b, 10]
# y: [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) #depth的值由最后的一层[b, 10]中的后者决定
#计算均方误差
# mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2)
# [b, 10]
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out)
# mean: scalar
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
2.要计算w,b的梯度,在定义w,b参数时,需用tf.Variable封装
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
# [dim_in, dim_out], [dim_out]
# [b, 784] => [b, 256]
# 要计算w,b的梯度,在定义w,b参数时,需用tf.Variable封装
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1)) #调节设置方差值可以解决梯度爆炸
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256]))
#[b, 256] => [b, 128]
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128]))
#[b, 128] => [b, 10]
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))3.计算梯度
# compute gradients(计算各参数([w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])的梯度)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]) #利用tensorflow计算各参数的梯度
# print(grads)
# w1 = w1 - lr * w1_grad
# lr 的定义见上面代码: lr = 1e-3
# 如下的索引lr * grads[0],lr * grads[1] 是因为 [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]
# assign_sub()的作用是原地更新
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1])
w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2])
b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3])
w3.assign_sub(lr * grads[4])
b3.assign_sub(lr * grads[5])
4. 完整代码:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import datasets #datasets提供数据集管理
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
# x: [60k, 28, 28],
# y: [60k] 表示的是lable
(x, y), _ = datasets.mnist.load_data() #自动加载数据集
# x: [0~255] => [0~1.]
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32) # lable 1,2,3,4.... 所以使用int型
print(x.shape, y.shape, x.dtype, y.dtype)
print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x))
print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y))
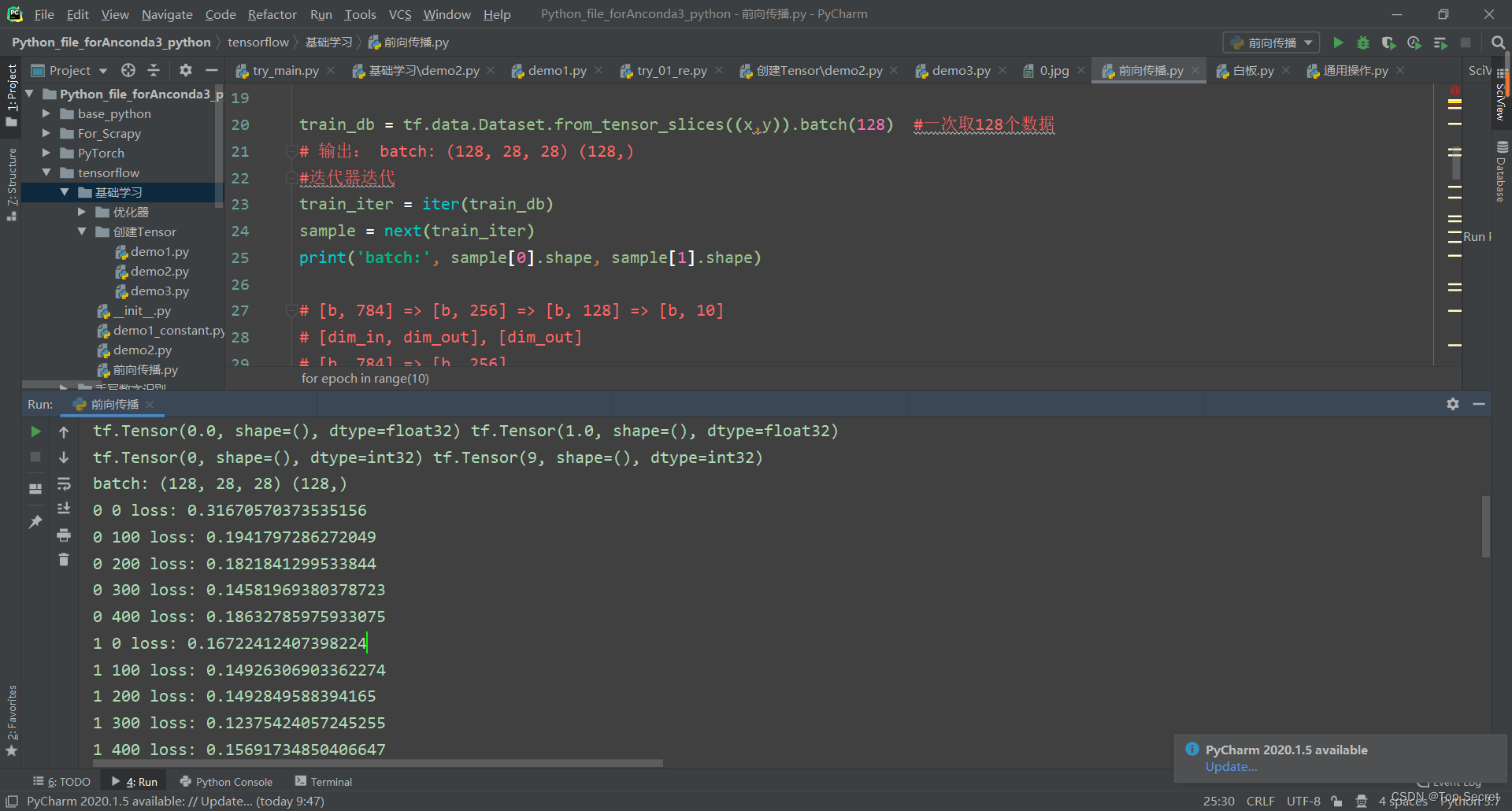
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y)).batch(128) #一次取128个数据
# 输出: batch: (128, 28, 28) (128,)
#迭代器迭代
train_iter = iter(train_db)
sample = next(train_iter)
print('batch:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
# [dim_in, dim_out], [dim_out]
# [b, 784] => [b, 256]
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256]))
#[b, 256] => [b, 128]
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128]))
#[b, 128] => [b, 10]
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
lr = 1e-3
# 前项运算
for epoch in range(10): # iterate db for 10
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): # for every batch
# x:[128, 28, 28]
# y: [128]
#维度变换
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # tf.Variable (关于计算梯度的代码,要放入“with tf.GradientTape() as tape”中)
# x: [b, 28*28]
# h1 = x@w1 + b1
# [b, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [b, 256]
h1 = x@w1 + tf.broadcast_to(b1, [x.shape[0], 256]) # 维度扩张
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1) #添加非线性
# [b, 256] => [b, 128]
h2 = h1@w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2)
# [b, 128] => [b, 10]
out = h2@w3 + b3
# compute loss(计算损失函数)
# out: [b, 10]
# y: [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10) #depth的值由最后的一层[b, 10]中的后者决定
#计算均方误差
# mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2)
# [b, 10]
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out)
# mean: scalar
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
# compute gradients(计算各参数([w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])的梯度)
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]) #利用tensorflow计算各参数的梯度
# print(grads)
# w1 = w1 - lr * w1_grad
# lr 的定义见上面代码: lr = 1e-3
# 如下的索引lr * grads[0],lr * grads[1] 是因为 [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1])
w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2])
b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3])
w3.assign_sub(lr * grads[4])
b3.assign_sub(lr * grads[5])
if step % 100 == 0:
print(epoch, step, 'loss:', float(loss))
5.张量测试
5.1 载入了测试数据
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
# x: [60k, 28, 28], [10, 28, 28]
# y: [60k], [10k]
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
# x: [0~255] => [0~1.]
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32)
x_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_test, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(y_test, dtype=tf.int32)
print(x.shape, y.shape, x.dtype, y.dtype)
print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x))
print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y))
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y)).batch(128)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test,y_test)).batch(128)
train_iter = iter(train_db)
sample = next(train_iter)
print('batch:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)5.2 训练代码:
# test/evluation
# [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]
total_correct, total_num = 0, 0
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(test_db):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
h1 = tf.nn.relu(x@w1 + b1)
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h1@w2 + b2)
out = h2@w3 +b3
# out: [b, 10] ~ R
# prob: [b, 10] ~ [0, 1]
prob = tf.nn.softmax(out, axis=1)
# [b, 10] => [b]
# int64!!!
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# y: [b]
# [b], int32
# print(pred.dtype, y.dtype)
correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y), dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct)
total_correct += int(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]完整代码:
import tensorflow as tf
from tensorflow import keras
from tensorflow.keras import datasets
import os
os.environ['TF_CPP_MIN_LOG_LEVEL'] = '2'
# x: [60k, 28, 28], [10, 28, 28]
# y: [60k], [10k]
(x, y), (x_test, y_test) = datasets.mnist.load_data()
# x: [0~255] => [0~1.]
x = tf.convert_to_tensor(x, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y = tf.convert_to_tensor(y, dtype=tf.int32)
x_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(x_test, dtype=tf.float32) / 255.
y_test = tf.convert_to_tensor(y_test, dtype=tf.int32)
print(x.shape, y.shape, x.dtype, y.dtype)
print(tf.reduce_min(x), tf.reduce_max(x))
print(tf.reduce_min(y), tf.reduce_max(y))
train_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x,y)).batch(128)
test_db = tf.data.Dataset.from_tensor_slices((x_test,y_test)).batch(128)
train_iter = iter(train_db)
sample = next(train_iter)
print('batch:', sample[0].shape, sample[1].shape)
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
# [dim_in, dim_out], [dim_out]
w1 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([784, 256], stddev=0.1))
b1 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([256]))
w2 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([256, 128], stddev=0.1))
b2 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([128]))
w3 = tf.Variable(tf.random.truncated_normal([128, 10], stddev=0.1))
b3 = tf.Variable(tf.zeros([10]))
lr = 1e-3
for epoch in range(100): # iterate db for 10
for step, (x, y) in enumerate(train_db): # for every batch
# x:[128, 28, 28]
# y: [128]
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
with tf.GradientTape() as tape: # tf.Variable
# x: [b, 28*28]
# h1 = x@w1 + b1
# [b, 784]@[784, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [256] => [b, 256] + [b, 256]
h1 = x@w1 + tf.broadcast_to(b1, [x.shape[0], 256])
h1 = tf.nn.relu(h1)
# [b, 256] => [b, 128]
h2 = h1@w2 + b2
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h2)
# [b, 128] => [b, 10]
out = h2@w3 + b3
# compute loss
# out: [b, 10]
# y: [b] => [b, 10]
y_onehot = tf.one_hot(y, depth=10)
# mse = mean(sum(y-out)^2)
# [b, 10]
loss = tf.square(y_onehot - out)
# mean: scalar
loss = tf.reduce_mean(loss)
# compute gradients
grads = tape.gradient(loss, [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3])
# print(grads)
# w1 = w1 - lr * w1_grad
w1.assign_sub(lr * grads[0])
b1.assign_sub(lr * grads[1])
w2.assign_sub(lr * grads[2])
b2.assign_sub(lr * grads[3])
w3.assign_sub(lr * grads[4])
b3.assign_sub(lr * grads[5])
if step % 100 == 0:
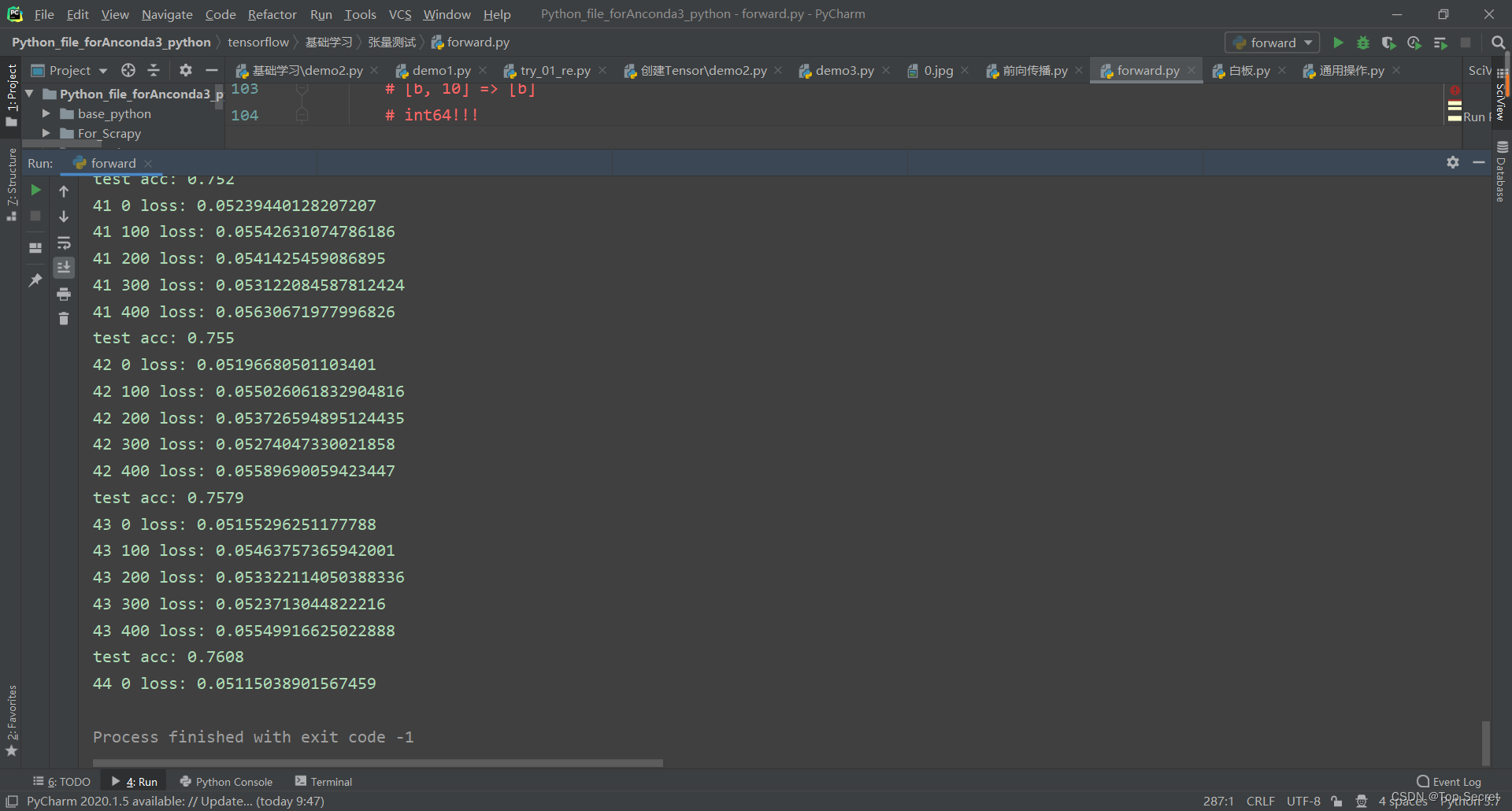
print(epoch, step, 'loss:', float(loss))
# test/evluation
# [w1, b1, w2, b2, w3, b3]
total_correct, total_num = 0, 0
for step, (x,y) in enumerate(test_db):
# [b, 28, 28] => [b, 28*28]
x = tf.reshape(x, [-1, 28*28])
# [b, 784] => [b, 256] => [b, 128] => [b, 10]
h1 = tf.nn.relu(x@w1 + b1)
h2 = tf.nn.relu(h1@w2 + b2)
out = h2@w3 +b3
# out: [b, 10] ~ R
# prob: [b, 10] ~ [0, 1]
prob = tf.nn.softmax(out, axis=1)
# [b, 10] => [b]
# int64!!!
pred = tf.argmax(prob, axis=1)
pred = tf.cast(pred, dtype=tf.int32)
# y: [b]
# [b], int32
# print(pred.dtype, y.dtype)
correct = tf.cast(tf.equal(pred, y), dtype=tf.int32)
correct = tf.reduce_sum(correct)
total_correct += int(correct)
total_num += x.shape[0]
acc = total_correct / total_num
print('test acc:', acc)






















 263
263











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










