注意:所有链表问题,记得先在纸上或者画图把过程和逻辑理清楚来,不能凭空想象!
单链表和双链表
-
单链表
-
双链表
-
单双链表的反转
- 经典题目
- 给定一个单链表的头head,完成链表的逆序调整
- 给定一个双链表的头head,完成链表的逆序调整
- 单链表
- 双链表
- code
-
package class04; import java.util.ArrayList; import java.util.List; public class Code_ReverseList { // 定义单链表结点类 public static class Node { public int value; public Node next; public Node(int data) { value = data; } } // 定义双链表结点类 public static class DoubleNode { public int value; public DoubleNode last; public DoubleNode next; public DoubleNode(int data) { value = data; } } /* * 下面两个函数重点 * */ // 单链表逆序函数 public static Node reverseLinkedList(Node head) { // head怎么折腾,它的上游n1是不变的 Node pre = null; Node next = null; // 仔细注意以下边界 while (head != null) { // 满足head != null才进行。直到最后head是 null时,break next = head.next; // next这时在head的下一个位置 head.next = pre; // 因为是逆序,所以第一次头部的next指针指向null pre = head; // pre原本在null的位置,现在来到head的位置 head = next; // head就到next的位置了 // 不可以替换成,head=head.next,会出现,head.next指向null } return pre; // 返回 } // 双链表逆序函数 public static DoubleNode reverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) { DoubleNode pre = null; DoubleNode next = null; while (head != null) { next = head.next; // 记一下head.next的位置,方便后面更新head head.next = pre; // 第一次头部的next指针指向null head.last = next; // last一开始指向null,这时候要指向head.next位置 pre = head; // pre原本在null的位置,现在来到head的位置 head = next; // 更新head } return pre; } // ============================= // 单链表逆序函数另一种写法 public static Node testReverseLinkedList(Node head) { if (head == null) { // 边界条件 return null; } ArrayList<Node> list = new ArrayList<>(); while (head != null) { list.add(head); // list新增head head = head.next; // 更新head,直到最后head,next,指向null跳出 } list.get(0).next = null; // 定义初始0位置的next指针指向null int N = list.size(); for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) { list.get(i).next = list.get(i - 1); // 逆序处理 } return list.get(N - 1); // 返回最后head所在的地址 } // 双链表逆序函数另一种写法 public static DoubleNode testReverseDoubleList(DoubleNode head) { if (head == null) { // 边界条件 return null; } ArrayList<DoubleNode> list = new ArrayList<>(); while (head != null) { list.add(head); head = head.next; // 更新head } list.get(0).next = null; // 定义初始0位置的next指针指向null(重点) DoubleNode pre = list.get(0); int N = list.size(); for (int i = 1; i < N; i++) { DoubleNode cur = list.get(i); cur.last = null; // 定义cur.last是null,它会一直更新直到for循环结束到最后last是null cur.next = pre; // 更新next指针方向,指向左边 pre.last = cur; // 更新last指针方向,指向右边 pre = cur; // 更新pre的位置,方便下次继续以上操作 } return list.get(N - 1); // 返回最后head的地址 } // ========================== // for test public static Node generateRandomLinkedList(int len, int value) { // 随机单链表的数组结点的生成 int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1)); // 随机数组大小 if (size == 0) { // 边界条件 return null; } size--; // 防止溢出 Node head = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1))); // 随机head结点值 Node pre = head; // 生成所有结点 while (size != 0) { Node cur = new Node((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1))); pre.next = cur; pre = cur; size--; } return head; // 返回 head } // for test public static DoubleNode generateRandomDoubleList(int len, int value) { // 随机双链表的结点的生成 int size = (int) (Math.random() * (len + 1)); // 随机数组大小 if (size == 0) { // 边界条件 return null; } size--; // 防止溢出 DoubleNode head = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1))); // 随机head结点值 DoubleNode pre = head; // 生成所有结点 while (size != 0) { DoubleNode cur = new DoubleNode((int) (Math.random() * (value + 1))); pre.next = cur; cur.last = pre; pre = cur; size--; } return head; // 返回 head } // for test public static List<Integer> getLinkedListOriginOrder(Node head) { // 单链表随机数组 List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); // 生成随机数组 while (head != null) { ans.add(head.value); head = head.next; } return ans; // 返回数组 } // for test public static boolean checkLinkedListReverse(List<Integer> origin, Node head) { // 单链表反转对数器 for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) { // 每个结点对应每个值,正确返回true,不正确返回false return false; } head = head.next; // 每遍历一次更新head结点 } return true; } // for test public static List<Integer> getDoubleListOriginOrder(DoubleNode head) { // 双链表随机数组 List<Integer> ans = new ArrayList<>(); // 随机数组生成 while (head != null) { ans.add(head.value); head = head.next; } return ans; // 返回随机数组 } // for test public static boolean checkDoubleListReverse(List<Integer> origin, DoubleNode head) { // 双链表反转对数器 DoubleNode end = null; for (int i = origin.size() - 1; i >= 0; i--) { if (!origin.get(i).equals(head.value)) { // 每个结点对应每个值,正确返回true,不正确返回false return false; } end = head; // 更新end值 head = head.next; } for (int i = 0; i < origin.size(); i++) { if (!origin.get(i).equals(end.value)) { // 因为双链表有next和end两个指针,所以需要都对比一下 return false; } end = end.last; } return true; } // for test public static void main(String[] args) { Node n1 = new Node(1); // 第一个结点 n1.next = new Node(2); // 第二个结点 n1.next.next = new Node(3); // 第三个结点 DoubleNode n2 = new DoubleNode(1); // 第一个结点 n2.next = new DoubleNode(2); // 第二个结点 n2.next.next = new DoubleNode(3); // 第三个结点 // reverseLinkedList(n1); // System.out.println(n1.value); // 这时n1的value还是1,它没变 n1 = reverseLinkedList(n1); // 重新定义n1,在调用方法后传进去新n1储存起来,接下来继续用 while (n1 != null) { System.out.print(n1.value + " "); // 3 2 1 n1 = n1.next; // 继续跳下一个结点 } System.out.print('\n' + "=================" + '\n'); // 测试 int len = 50; int value = 100; int testTime = 100000; System.out.println("test begin!"); for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { Node node1 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value); // 结点 List<Integer> list1 = getLinkedListOriginOrder(node1); // 数组 node1 = reverseLinkedList(node1); // 链表反转 if (!checkLinkedListReverse(list1, node1)) { // 测试是否有问题 System.out.println("Oops1!"); // 有问题则打印 } Node node2 = generateRandomLinkedList(len, value); List<Integer> list2 = getLinkedListOriginOrder(node2); node2 = testReverseLinkedList(node2); if (!checkLinkedListReverse(list2, node2)) { System.out.println("Oops2"); } DoubleNode node3 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value); List<Integer> list3 = getDoubleListOriginOrder(node3); node3 = reverseDoubleList(node3); if (!checkDoubleListReverse(list3, node3)) { System.out.println("Oops3"); } DoubleNode node4 = generateRandomDoubleList(len, value); List<Integer> list4 = getDoubleListOriginOrder(node4); node4 = testReverseDoubleList(node4); if (!checkDoubleListReverse(list4, node4)) { System.out.println("Oops4"); } } System.out.println("test finish"); } }
-
-
用单链表实现队列和栈
- 用单链表结构实现队列结构
- 用单链表结构实现栈结构
- 栈和队列
- 队列
- offer(V value)更新tail
- offer(V value)更新tail
- 栈

- code
-
package class04; import java.sql.SQLOutput; import java.util.LinkedList; import java.util.Queue; import java.util.Stack; public class Code_LinkedListToQueueAndStack { public static class Node<V> { // 指定为泛型 public V value; public Node<V> next; public Node(V v) { value = v; next = null; } } /* * 实现队列结构 * */ public static class MyQueue<V> { // 俩变量:头,尾 private Node<V> head; // 头 private Node<V> tail; // 尾 private int size; // size public MyQueue() { // 队列初始化的时候 head = null; tail = null; size = 0; } public boolean isEmpty() { // 判断队列里面是否有元素 return size == 0; } public int size() { // 返回加入了多少个元素 return size; } public void offer(V value) { // 接受某值以队列形式的值进入 Node<V> cur = new Node<V>(value); // 先建出一个结点 if (tail == null) { // 如果尾巴是null的 head = cur; // head指向这个结点 tail = cur; // tail也指向这个结点 } else { // tail!=null tail.next = cur; // 更新tail.next tail = cur; // tail移到cur上 } size++; // 每进来一个结点,size都+1 } // C/C++需要做节点析构的工作 public V poll() { // 弹出的时候,先进来的先出去,从head开始弹出 V ans = null; // 先定义变量为null if (head != null) { ans = head.value; // ans抓住原head结点对应的值 head = head.next; // head结点next指针移动 size--; // size要-1 // 原head会被jvm释放,不可达 } if (head == null) { // 如果head是null(所有数都弹完了) tail = null; // 那么此时tail也要跟head一样,是null // 如果不做tail=null,那么tail对应结点的值不会被弹出 } return ans; // 返回head } public V peek() { // 此时要弹出的结点是什么,但是不真的弹出 V ans = null; if (head != null) { ans = head.value; // 抓住要弹出的值 } return ans; } } /* * 实现栈结构 * */ public static class MyStack<V> { private Node<V> head; private int size; public MyStack() { // 栈初始化 head = null; size = 0; } public boolean isEmpty() { // 判断队列里面是否有元素 return size == 0; } public int size() { // 返回加入了多少个元素 return size; } public void push(V value) { // 加入的时候 Node<V> cur = new Node<>(value); // 新建一个结点 if (head == null) { // 如果head等于努null head = cur; // cur就是头部 } else { //head!=null cur.next = head; // 指针指向老头 head = cur; // 更新 head } size++; // 每新增一个结点+1 } public V pop() { // 弹出 V ans = null; // 定义ans,为null if (head != null) { // 如果头部真有数据, ans = head.value; // ans抓住 head = head.next; // head.next更新下一个head size--; // -1 } return ans; // 返回 } public V peek() { return head != null ? head.value : null; } } // for test // 队列测试 public static void testQueue() { MyQueue<Integer> myQueue = new MyQueue<>(); Queue<Integer> test = new LinkedList<>(); int testTime = 5000000; int maxValue = 200000000; System.out.println("测试开始"); for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { if (myQueue.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } if (myQueue.size() != test.size()) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } double decide = Math.random(); if (decide < 0.33) { int num = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue); myQueue.offer(num); test.offer(num); } else if (decide > 0.66) { if (!myQueue.isEmpty()) { int num1 = myQueue.poll(); int num2 = test.poll(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } } else { if (!myQueue.isEmpty()) { int num1 = myQueue.peek(); int num2 = test.peek(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops"); } } } } if (myQueue.size() != test.size()) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } while (!myQueue.isEmpty()) { int num1 = myQueue.poll(); int num2 = test.poll(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } System.out.println("测试结束"); } // for test // 栈测试 public static void testStack() { MyStack<Integer> myStack = new MyStack<>(); Stack<Integer> test = new Stack<>(); int testTime = 5000000; int maxValue = 200000000; System.out.println("测试开始"); for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { if (myStack.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } if (myStack.size() != test.size()) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } double decide = Math.random(); if (decide < 0.33) { int num = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue); myStack.push(num); test.push(num); } else if (decide < 0.66) { if (!myStack.isEmpty()) { int num1 = myStack.pop(); int num2 = test.pop(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } } else { if (!myStack.isEmpty()) { int num1 = myStack.peek(); int num2 = test.peek(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } } } if (myStack.size() != test.size()) { System.out.println("Oops1"); } while (!myStack.isEmpty()) { int num1 = myStack.pop(); int num2 = test.pop(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } System.out.println("测试结束"); } public static void main(String[] args) { testQueue(); testStack(); } }
-
-
用双链表实现双端队列
-
用双链表结构实现双端队列
- 双端队列
- 双链表实现双端队列
- code
-
package class04; import java.util.Deque; import java.util.LinkedList; //用双链表结构实现双端队列 public class Code_DoubleLinkedListToDeque { public static class Node<V> { public V value; // 双向链表,两个指针 public Node<V> last; public Node<V> next; public Node(V v) { value = v; last = null; next = null; } } public static class MyDeque<V> { // 定义双端链表类 private Node<V> head; // 头 private Node<V> tail; // 尾 private int size; public MyDeque() { head = null; tail = null; size = 0; } public boolean isEmpty() { return size == 0; } public int size() { return size; } public void pushHead(V value) { // 头部加 Node<V> cur = new Node<>(value); // 生成结点 if (head == null) { // 如果之前没有元素 head = cur; // 头指向该结点 tail = cur; // 尾指向该结点 } else { // head != null,就是再新增结点(之前有元素) cur.next = head; // 新进来的结点的next指针要指向头部 head.last = cur; // 老head的last指针要指向当前结点 head = cur; // head = cur,老head跳到当前结点做新头 } size++; // 每新增结点size+1 } public void pushTail(V value) { // 尾部加 Node<V> cur = new Node<>(value); // 生成结点 if (head == null) { // 如果之前没有元素 head = cur; // 头指向该结点 tail = cur; // 尾指向该结点 } else { // head!= null,就是再新增结点 tail.next = cur; // 尾部.next指向新结点 cur.last = tail; // 新结点的last指向的是tail tail = cur; // 更新tail的位置 } size++; } public V pollHead() { // 头部弹 V ans = null; // 先定义变量最后更新返回 if (head == null) { // 边界条件 return ans; } size--; // 返回了ans,size就要-1 ans = head.value; // 把ans设置成头结点的值 // 返回ans之前需要调整的东西 if (head == tail) { // 如果头和尾是一个元素,那么就一个玩意在盒子里,这时 head = null; // head指向null tail = null; // tail指向null } else { // 如果head != tail,头和尾不止一个元素 head = head.next; // 更新,head等于head的next head.last = null; // 此时,head.last一定要指向null,前一个元素才会被jvm释放, } return ans; // 返回头结点的值 } public V pollTail() { // 尾部弹 V ans = null; // 先定义变量最后更新返回 if (head == null) { // 边界条件 return ans; } size--; // 返回了ans,size就要-1 ans = tail.value; // 把ans设置成尾结点的值 if (head == tail) { // 如果头和尾是一个元素,那么就一个玩意在盒子里,这时 head = null; // head指向null tail = null; // tail指向null } else { // 如果head != tail,头和尾不止一个元素 tail = tail.last; // 更新,tail等于tail的last tail.next = null; // 此时,head.next一定要指向null,前一个元素才会被jvm释放, } return ans; // 返回头结点的值 } public V peekHead() { V ans = null; if (head != null) { ans = head.value; } return ans; } public V peekTail() { V ans = null; if (tail != null) { ans = tail.value; } return ans; } } // for test // 双链表结构实现双端队列测试 public static void testDeque() { MyDeque<Integer> myDeque = new MyDeque<>(); Deque<Integer> test = new LinkedList<>(); int testTime = 5000000; int maxValue = 200000000; System.out.println("测试开始"); for (int i = 0; i < testTime; i++) { if (myDeque.isEmpty() != test.isEmpty()) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } if (myDeque.size() != test.size()) { System.out.println("Oops"); } double decide = Math.random(); if (decide < 0.33) { int num = (int) (Math.random() * maxValue); if (Math.random() < 0.5) { myDeque.pushHead(num); test.addFirst(num); } else { myDeque.pushTail(num); test.addLast(num); } } else if (decide < 0.66) { if (!myDeque.isEmpty()) { int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; if (Math.random() < 0.5) { num1 = myDeque.pollHead(); num2 = test.pollFirst(); } else { num1 = myDeque.pollTail(); num2 = test.pollLast(); } if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } } else { //decide>0.66 if (!myDeque.isEmpty()) { int num1 = 0; int num2 = 0; if (Math.random() < 0.5) { num1 = myDeque.peekHead(); num2 = test.peekFirst(); } else { num1 = myDeque.peekTail(); num2 = test.peekLast(); } if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } } } if (myDeque.size() != test.size()) { int num1 = myDeque.pollHead(); int num2 = test.pollFirst(); if (num1 != num2) { System.out.println("Oops!"); } } System.out.println("测试结束"); } public static void main(String[] args) { testDeque(); } }
-
- 双端队列
-
- 经典题目
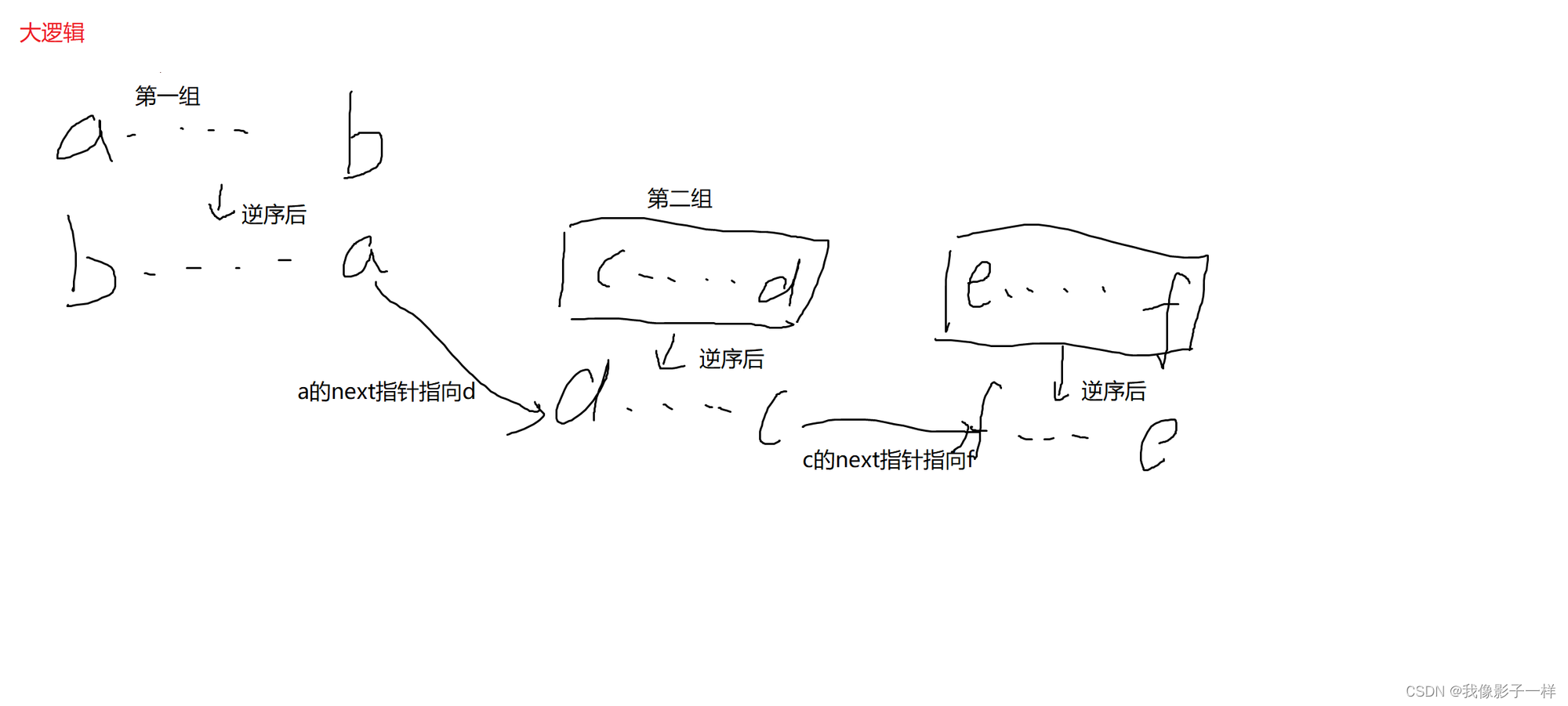
K个节点的组内逆序调整
- 给定一个单链表的头节点head,和一个正数k
- 实现k个节点的小组内部逆序,如果最后一组不够k个就不调整
-
例子
- 调整前:1->2->3->4->5->6->7-8,k=3
- 调整后:3->2->1->6->5->4->7->8
- 图

- 大逻辑
- getKGroupEnd(ListNode start, int k)

- reverse(ListNode start, ListNode end)
- 功能
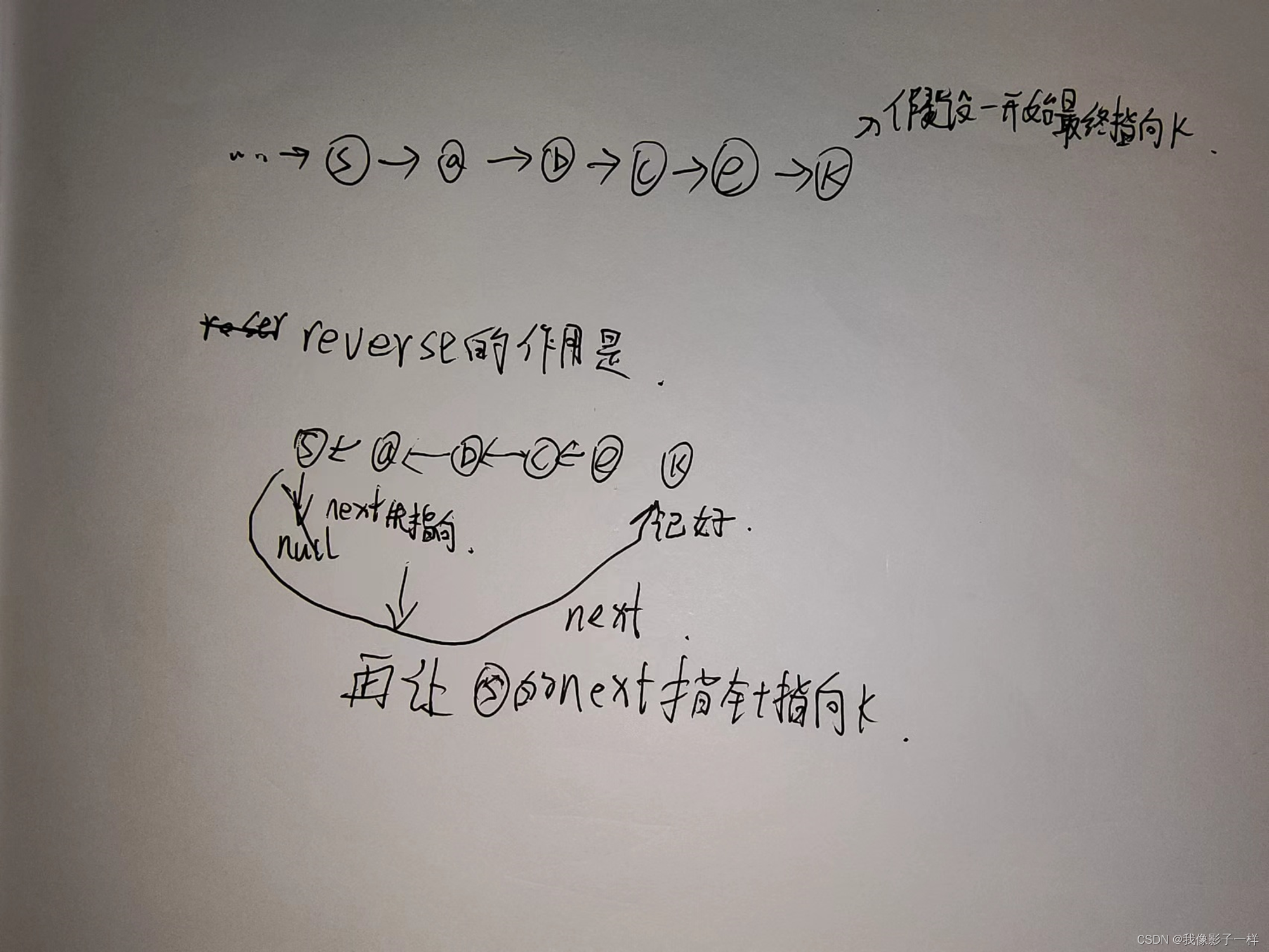
- 解析

- reverserKGroup(ListNode head, int k)
- code
-
package class04; // 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/reverse-nodes-in-k-group/ public class Code_ReverseNodesInKGroup { // leetcode不要提交这个类 public static class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; } public static ListNode reverseKGroup(ListNode head, int k) { ListNode start = head; // 一开始,让开始结点等于头 ListNode end = getKGroupEnd(start, k); // getKGroupEnd(start, k),从start开始,数够k个的那个点,返回 if (end == null) { // 如果end那个点是null,返回原先的head return head; } // 如果没有返回原先的head,说明第一组凑齐了! head = end; // 头部更新 reverse(start, end); // 逆序,开始结点的next要指向end.next // 上一组的结尾节点 ListNode lastEnd = start; while (lastEnd.next != null) { // 上一组的结尾节点的next指针不是空的就继续做,否则跳出循环 start = lastEnd.next; // 更新start的位置 end = getKGroupEnd(start, k); // 再从新start开始,数够k个的那个点,返回 if (end == null) { // 如果end那个点是null,返回原先的head return head; } reverse(start, end); // 逆序,开始结点的next要指向end.next lastEnd.next = end; // lastEnd的next指向end的位置,方便两组相连 lastEnd = start; // 更新lastEnd的位置 } return head; // 返回头部head } public static ListNode getKGroupEnd(ListNode start, int k) { // 给个开始结点,数够k个,把数到的结点返回 while (--k != 0 && start != null) { // --k != 0 ,一直做,直到--k=0时跳出循环,同时满足start!null=0,才满足条件 start = start.next; // 更新start,直至start.next指向null } return start; // 返回数到的结点 } public static void reverse(ListNode start, ListNode end) { // 给个开始结点和最后结点 end = end.next; // 结尾先往下跳一个 ListNode pre = null; // 定义pre为null ListNode cur = start; // 定义cur开始结点的位置 ListNode next = null; // 定义next为null while (cur != end) { // cur != end时,循环里才会做,而cur = end时会跳出循环,因为end.next前面几个都要干事情,所以才有了之前end = end.next; next = cur.next; // 记下一个环境 cur.next = pre; // cur的next指向null pre = cur; // 更新pre cur = next; // 更新cur } // while里一组逆序 start.next = end; // 逆序后开始结点的next要指向end.next } }
-
-
两个链表相加
- 给定两个链表的头节点head1和head2,认为从左到右是某个数字从低位到高位,返回相加之后的链表
-
例子 4->3->6 2->5->3
-
返回 6->8->9
-
解释 634 + 352 = 986
- 图
- code
-
package class04; // 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/add-two-numbers/ public class Code_AddTwoNumbers { // 不要提交这个类 public static class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; public ListNode(int val) { this.val = val; } public ListNode(int val, ListNode next) { this.val = val; this.next = next; } } public static ListNode addTwoNumbers(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { int len1 = listLength(head1); // 链表1的长度len1 int len2 = listLength(head2); // 链表2的长度len2 // 重定向 // l是长链表的头,s是短链表的头 ListNode l = len1 >= len2 ? head1 : head2; // 如果链表1长度大于链表2长度,那么链表1就是长链表,l就是他的头部head1,否则head2就是较长链表的 ListNode s = l == head1 ? head2 : head1; // 如果长链表的头部是head1.那么短链表的头部就是head2,否则是head1. ListNode curL = l; // 长链表的当前结点 ListNode curS = s; // 短链表的当前结点 ListNode last = curL; // 第三结点产生进位信息不为0时,长链表的结点last int carry = 0; // 进位为0 int curNum = 0 ; // 当前数 // 第一阶段 while (curS != null) { // 短链表不为空 curNum = curL.val + curS.val + carry; // 长链表和短链表当前列结点和进位相加 curL.val = (curNum % 10); // 新长链表第一结点数更新 carry = curNum / 10; // 进位变化 last = curL; // last跟踪新长链表的结点 curL = curL.next; // 更新长链表下一结点 curS = curS.next; // 更新短链表下一结点 } // 第二阶段 while (curL != null) { // 长链表不为空 curNum = curL.val + carry; // 长链表结点和进位相加 curL.val = (curNum % 10); // 新长链表第一结点数更新 carry = curNum / 10; // 进位变化 last = curL; // last跟踪新长链表的结点 curL = curL.next; // 更新长链表下一结点 } // 第三阶段 if (carry != 0) { // 进位信息不为0时 last.next = new ListNode(1); // last.next。长链表的新结点 } return l; // 结果不额外生成链表,压到长链表里,最后返回 } // 求链表长度 public static int listLength(ListNode head) { int len = 0; // 初始长度为0 while (head != null) { // head不为空时 len++; // 长度+1 head = head.next; // 更新head,直到head.next=null为止 } return len; // 返回链表长度 } }
-
-
两个有序链表的合并
-
给定两个有序链表的头节点head1和head2,返回合并之后的大链表,要求依然有序
- 例子 1->3->3->5->7 2->2->3->3->7
- 返回 1->2->2->3->3->3->3->5->7
- 图
- code
-
package class04; // 测试链接:https://leetcode.com/problems/merge-two-sorted-lists public class Code_MergeTwoSortedLinkedList { // 不要提交这个类 public static class ListNode { public int val; public ListNode next; } public static ListNode mergeTwoLists(ListNode head1, ListNode head2) { // 链表head1和链表head2 if (head1 == null || head2 == null) { // 边界条件 return head1 == null ? head2 : head1; } ListNode head = head1.val <= head2.val ? head1 : head2; // 确定主链表的头结点(谁小就谁是) ListNode cur1 = head.next; //主链表的头结点的next指向下一个定义为cur1 ListNode cur2 = head == head1 ? head2 : head1; // 另外次链表的头结点定义为cur2 ListNode pre = head; // 准备好pre,它等于主链表的头结点 while (cur1 != null && cur2 != null) { // 范围条件 if (cur1.val <= cur2.val) { // 因为第一个最小的头结点定死了,所以先给cur1的值小于等于cur2的值的条件 pre.next = cur1; // cur1小于等于cur2时,pre的next指针指向cur1 cur1 = cur1.next; // 更新cur1的值 } else { pre.next = cur2; // cur1大于等于cur2时,pre的next指针指向cur2 cur2 = cur2.next; // 更新cur2的值 } pre = pre.next; //更新pre的值 } pre.next = cur1 != null ? cur1 : cur2; // cur1 == null 或者 cur2 == null时,跳出循环,这时,pre的next指针指向谁不为空的cur1或者cur2 return head; // 返回 } }
-


































 55
55











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








