探索开源项目:MiniShell
引言
在计算机编程的世界里,Shell 是一个至关重要的组成部分,它允许用户与操作系统交互,执行命令和程序。MiniShell 是一个简化版的 Shell 程序,通常用于教学和学习目的。在本文中,我们将深入分析一个 MiniShell 的实现代码,并探讨其功能和潜在的应用场景。
简单的命令解释器minishell
Minishell项目的功能,主要就是实现命令的运行。
涉及命令如下:
1,cp 复制文件 cp 1 2 把文件1复制成文件2
2,cat 查看文件 cat 1 查看文件到内容
3,cd 切换路径 cd 1 切换到目录1中 //chdir
4,ls 查看当前目录下到文件 ls 或 ls /home
5,ll 查看当前目录下到文件 ll 或 ll /home ls -l
6,touch 新建文件 touch 1 新建文件 1
7,rm删除文件
Minishell的业务流程:
-
运行程序 ,打印提示符
linux@ubuntu:~$
用户名@主机名:当前路径$
-
输入 要操作的命令
-
程序负责执行相关的命令
-
Exit 程序的退出
程序的实现流程:
-
运行程序 ,打印提示符 ---- 提示符打印
linux@ubuntu:~$
用户名@主机名:当前路径$ //getcwd -- sprintf(); //promt
-
输入 要操作的命令 ------ 解析命令
cd ..
ls
touch 1.txt
cat file
cp src.txt dest.txt
命令的格式:
<命令> [选项] [参数]
-
程序负责执行相关的命令 ---- 执行命令的功能
-
Exit 程序的退出
[开 始]
|
[打印提示符]
|
[等待用户输入] //fgets
|
[解析输入的命令]
|
[根据命令执行对应的操作]
|
[结束]
所有命令按照其指定格式运行。
利用Linux中IO接收实现MiniShell
Minishell框图:

Minishell流程图:
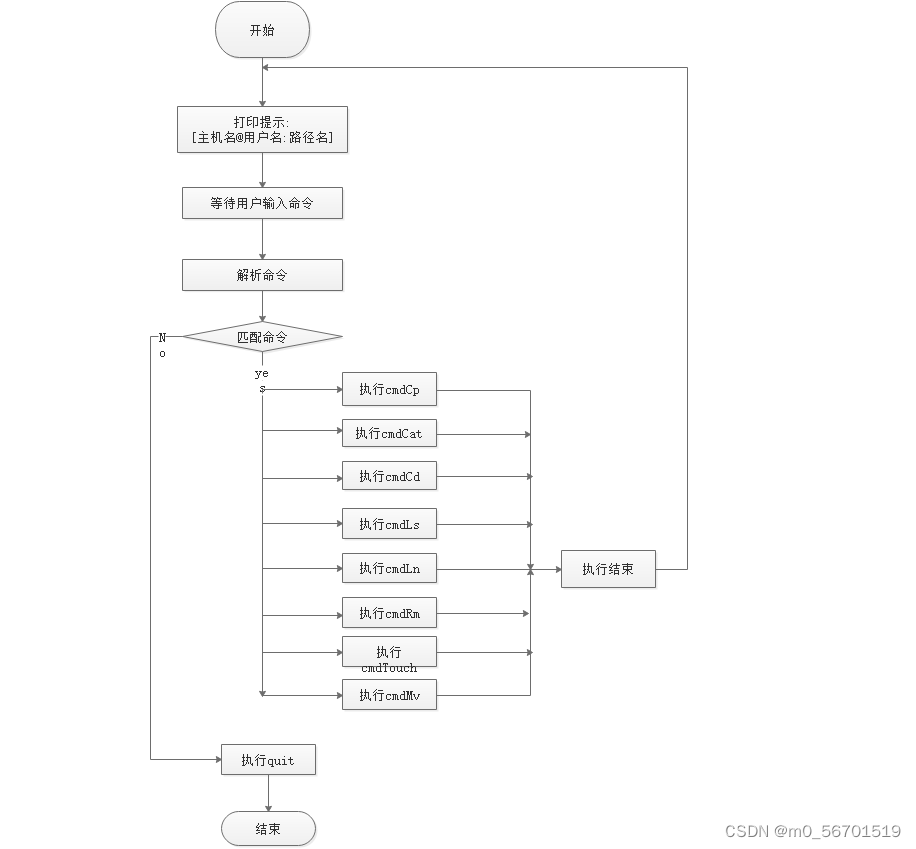
代码分析
包含的头文件
MiniShell 程序首先包含了多个头文件,这些头文件提供了对文件描述符、目录遍历、系统调用等功能的支持。
#include <stdio.h> #include <fcntl.h> #include <dirent.h> #include <sys/types.h> #include <sys/stat.h> #include <unistd.h> #include <pwd.h> #include <cstdlib> #include <ctime> #include <errno.h> #include <cstring> #include <limits.h>
辅助函数
程序定义了一个 location 函数,该函数根据给定的时间戳返回一个 tm 结构体指针,用于时间的本地化处理。
struct tm* location(const time_t *timer);
文件和目录列表显示
lsl 函数用于以 ls -l 的格式显示文件和目录的详细信息,包括类型、权限、链接数、所有者、组、大小、最后修改时间和文件名。
void lsl(const char *name) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
计算磁盘使用情况
total 函数计算当前目录下的总磁盘使用量,包括文件所占用的块数。
int total() { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
全部文件和目录的显示
lslall 函数结合了 total 和 lsl 函数,显示当前目录下所有文件和目录的详细信息,并显示总磁盘使用量。
void lslall() { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
显示所有文件和目录(包括隐藏文件)
ls_a 函数显示当前目录下的所有文件和目录,包括以点(.)开头的隐藏文件。
void ls_a() { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
搜索特定文件或目录
ls_f 函数搜索当前目录下与指定名称匹配的文件或目录,并显示其详细信息。
void ls_f(const char *filename) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
内容查看
cat 函数实现了内容查看功能,它打开指定的文件,并将其内容输出到标准输出。
int cat(const char* filename) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
当前目录显示
printdir 函数用于显示当前的工作目录,并在末尾添加 $ 提示符。
void printdir() { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
目录切换
change_directory 函数接受一个目录名参数,并尝试切换到该目录。
void change_directory(const char *dir_name) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
文件复制
do_cp_file 和 do_cp_dir 函数分别用于复制文件和目录。它们处理文件的打开、读取、写入和关闭。
int do_cp_file(const char *src, const char *dest) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... } int do_cp_dir(const char *dir_s, const char *dir_d) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
创建空文件
touch 函数用于创建一个空文件,如果文件已存在,则不进行任何操作。
void touch(const char* filename) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
删除文件
delete_file 函数尝试删除指定的文件,并在失败时打印错误信息。
int delete_file(const char *filename) { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
命令判断
judge 函数是 MiniShell 的核心,它读取用户输入的命令,并根据命令类型调用相应的函数。
int judge() { // ... 省略部分代码 ... }
主函数
调用命令判断函数并且打印相应内容
以下是我
#include <stdio.h>
#include<fcntl.h>
#include<dirent.h>
#include <sys/types.h>
#include <sys/stat.h>
#include <unistd.h>
#include <pwd.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<time.h>
#include<errno.h>
#include<string.h>
#include <limits.h>
struct tm*location(const time_t *timer);
void lsl(const char *name)
{
struct stat st;
if (stat(name,&st) < 0)
{
perror("stat fail");
}
switch (st.st_mode&S_IFMT)
{
case S_IFSOCK:
putchar('s');
break;
case S_IFLNK:
putchar('l');
break;
case S_IFREG:
putchar('-');
break;
case S_IFBLK:
putchar('b');
break;
case S_IFDIR:
putchar('d');
break;
case S_IFCHR:
putchar('c');
break;
case S_IFIFO:
putchar('p');
break;
}
st.st_mode&S_IRUSR?putchar('r'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IWUSR?putchar('w'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IXUSR?putchar('x'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IRGRP?putchar('r'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IWGRP?putchar('w'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IXGRP?putchar('x'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IROTH?putchar('r'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IWOTH?putchar('w'):putchar('-');
st.st_mode&S_IXOTH?putchar('x'):putchar('-');
printf(" ");
printf("%ld ",st.st_nlink);
printf("%s ",getpwuid(st.st_uid)->pw_name);
printf("%s ",getpwuid(st.st_gid)->pw_name);
printf("%ld\t",st.st_size);
struct tm* t = localtime(&st.st_mtime);
printf("%2d月 %2d %02d:%02d ", t->tm_mon+1, t->tm_mday, t->tm_hour, t->tm_min);
printf(" %s\n",name);
}
int total()
{
int t=0;
char buf[100];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
DIR *dir = opendir(buf);
struct dirent *pdir = NULL;
while (pdir = readdir(dir))
{
struct stat st;
if (stat(buf,&st) < 0)
{
perror("stat fail");
}
t=t+st.st_blocks/2;
}
return t+4;
}
void lslall()
{
char buf[100];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
DIR *dir = opendir(buf);
struct dirent *pdir = NULL;
printf("total %d\n",total());
while (pdir = readdir(dir))
{
if(pdir->d_name[0]!='.')
lsl(pdir->d_name);
}
}
void ls_a()
{
char buf[100];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
DIR *dir = opendir(buf);
struct dirent *pdir = NULL;
while (pdir = readdir(dir))
{
printf("%s ",pdir->d_name);
}
printf("\n");
}
void ls_()
{
char buf[100];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
DIR *dir = opendir(buf);
struct dirent *pdir = NULL;
while (pdir = readdir(dir))
{
if(pdir->d_name[0]!='.')
printf("%s ",pdir->d_name);
}
printf("\n");
}
void ls_f(const char *filename)
{
char buf[1000];
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
DIR *dir = opendir(buf);
struct dirent *pdir = NULL;
while (pdir = readdir(dir))
{
if(strcmp(pdir->d_name,filename)==0&&pdir->d_type!=DT_DIR)
{
printf("%s ",pdir->d_name);
printf("\n");
}
if((strcmp(pdir->d_name,filename)==0)&&pdir->d_type==DT_DIR)
{
char buff[100];
getcwd(buff,sizeof(buff));
chdir(filename);
ls_();
chdir(buff);
break;
}
}
}
int cat(const char* filename) {
FILE *fp;
char buf[1000];
ssize_t bytes_read;
fp = fopen(filename, "r");
if (fp == NULL) {
perror("fopen");
return -1;
}
while ((bytes_read = fread(buf, 1, sizeof(buf), fp)) > 0) {
if (write(STDOUT_FILENO, buf, bytes_read) < 0) {
perror("write");
fclose(fp);
return -1;
}
}
if (bytes_read < 0) {
perror("fread");
fclose(fp);
return -1;
}
fclose(fp);
return 0;
}
void printdir()
{
char buf[1000];
fflush(stdout);
getcwd(buf,sizeof(buf));
//printf("%s$ ",buf);
int ret=strlen(buf);
buf[ret]='$';
buf[ret+1]=' ';
write(stdout->_fileno,buf,ret+2);
}
void change_directory(const char *dir_name) {
// 获取当前工作目录
char current_path[PATH_MAX];
if (getcwd(current_path, sizeof(current_path)) == NULL) {
perror("getcwd");
}
// 构建新的目录路径
char new_path[PATH_MAX];
if (dir_name[0] == '/') {
// 如果传入的目录名是绝对路径,直接使用它
snprintf(new_path, sizeof(new_path), "%s", dir_name);
} else {
// 如果传入的目录名是相对路径,将其与当前路径组合
snprintf(new_path, sizeof(new_path), "%s/%s", current_path, dir_name);
}
// 切换到新的目录
if (chdir(new_path) != 0) {
perror("chdir");
}
}
int do_cp_file(const char *src,const char *dest)
{
int fd_s = open(src,O_RDONLY);
int fd_d = open(dest,O_WRONLY|O_CREAT|O_TRUNC,0666);
if (fd_s < 0 || fd_d < 0)
{
perror("open fail");
return -1;
}
int ret = 0;
char buf[100] = {0};
while (ret = read(fd_s,buf,sizeof(buf)))
{
write(fd_d,buf,ret);
}
close(fd_s);
close(fd_d);
return 0;
}
void touch(const char* filename)
{
int fd=open(filename,O_RDWR|O_CREAT,0777);
if(fd<0)
{
perror("open fail");
}
}
int do_cp_dir(const char *dir_s,const char *dir_d)
{
if (mkdir(dir_d,0777) < 0 && errno!=EEXIST)
{
perror("mkdir fail");
return -1;
}
DIR *dir = opendir(dir_s);
if (dir == NULL)
{
perror("opendir fail");
return -1;
}
while (1)
{
struct dirent *pdir = readdir(dir);
char spath[512];
char dpath[512];
if (pdir == NULL)
break;
//dir_s
//dir_s/
if (pdir->d_name[0] != '.')
{
dir_s[strlen(dir_s)-1]=='/'?sprintf(spath,"%s%s",dir_s,pdir->d_name):sprintf(spath,"%s/%s",dir_s,pdir->d_name); //"dir_s/1.txt"
dir_d[strlen(dir_d)-1]=='/'?sprintf(dpath,"%s%s",dir_d,pdir->d_name):sprintf(dpath,"%s/%s",dir_d,pdir->d_name); //"dir_s/1.txt"
if (pdir->d_type == DT_DIR)
{
do_cp_dir(spath,dpath);
}else
{
do_cp_file(spath,dpath);
}
}
}
closedir(dir);
return 0;
}
int delete_file(const char *filename) {
if (remove(filename) != 0) {
perror("remove");
return -1; // 删除失败
}
return 0; // 删除成功
}
int judge()
{
char buf[100];
fflush(stdin);
int ret = read(stdin->_fileno,buf,sizeof(buf));
buf[ret-1]='\0';
if(strcmp(buf,"ls -l")==0)
lslall();
if(strncmp(buf,"ls ",3)==0&&buf[3]!='-'&&buf[4]!='l')
{
char buff[100];
char temp[100];
if(buf[3]!='/')
{
char *arg = buf + 3;// 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
ls_f(arg);
}
else
{
printf("here");
char *arg = buf + 3;
getcwd(buff,sizeof(buff));
change_directory(arg);
getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp));
ls_();
change_directory(buff);
}
}
if(strcmp(buf,"ls")==0)
ls_();
if(strcmp(buf,"ls -a")==0)
ls_a();
if(strncmp(buf,"ls -l ",6)==0)
{
char buff[100];
char temp[100];
char bufff[1000];
getcwd(bufff,sizeof(bufff));
DIR *dir = opendir(bufff);
struct dirent *pdir = NULL;
char *arg = buf + 6;
int t=0;
while(pdir=readdir(dir))
{
if(strcmp(pdir->d_name,arg)==0&&pdir->d_type!=DT_DIR)
t=1;
}
if(t)
{
lsl(arg);
}
else
{
getcwd(buff,sizeof(buff));
change_directory(arg);
getcwd(temp,sizeof(temp));
lslall(temp);
change_directory(buff);
}
}
if(strncmp(buf,"cat ",4)==0)
{
char *arg = buf + 4; // 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
cat(arg);
}
if(strncmp(buf,"cd ",3)==0)
{
char *arg = buf + 3; // 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
change_directory(arg);
}
if(strncmp(buf,"cp ",3)==0)
{
char *arg = buf + 3; // 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
char *source = strtok(arg, " "); // 使用空格分割字符串,获取源文件名
char *destination = strtok(NULL, " "); // 继续分割,获取目标路径
do_cp_dir(source,destination);
}
if(strncmp(buf,"rm ",3)==0)
{
char *arg = buf + 3; // 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
delete_file(arg);
}
if(strncmp(buf,"touch ",6)==0)
{
char *arg = buf + 6; // 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
touch(arg);
}
if(strncmp(buf,"exit",4)==0)
{
char *arg = buf + 4; // 跳过 "ls -l " 前缀
return -1;
}
return 0;
}
int main(int argc, const char *argv[])
{
while(1)
{
printdir();
if(judge()==-1)
break;
}
return 0;
}
MiniShell 是一个用 C 语言实现的轻量级 Shell 程序,它模拟了 UNIX Shell 的一些基本功能,如文件列表显示、内容查看、目录切换、文件复制、文件删除和创建空文件等。通过分析 MiniShell 的代码,我们可以深入了解 Shell 程序的工作原理,以及操作系统中文件和目录操作的底层实现。
MiniShell 的设计简洁,易于理解,适合作为学习材料,帮助初学者掌握系统编程和 Shell 脚本编写的基础知识。同时,MiniShell 也可以作为开发更高级 Shell 程序的基础框架,通过扩展和定制,实现更多复杂的功能。
总的来说,MiniShell 虽然功能有限,但它提供了一个很好的起点,让我们能够探索和学习 Shell 编程的核心概念。随着技术的不断进步和创新,我们可以期待 MiniShell 以及类似的工具在未来发挥更大的作用,帮助更多的人掌握计算机编程的精髓。





















 319
319











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








