}
try {
PackageParser.Package newPackage = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,
System.currentTimeMillis(), user);
updateSettingsLI(newPackage, installerPackageName, null, null, res);
// delete the partially installed application. the data directory will have to be
// restored if it was already existing
if (res.returnCode != PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED) {
// remove package from internal structures. Note that we want deletePackageX to
// delete the package data and cache directories that it created in
// scanPackageLocked, unless those directories existed before we even tried to
// install.
deletePackageLI(pkgName, UserHandle.ALL, false, null, null,
dataDirExists ? PackageManager.DELETE_KEEP_DATA : 0,
res.removedInfo, true);
}
} catch (PackageManagerException e) {
res.setError("Package couldn’t be installed in " + pkg.codePath, e);
}
}
这个方法核心的步骤有两个:
PackageParser.Package newPackage = scanPackageLI(pkg, parseFlags, scanFlags,System.currentTimeMillis(), user);updateSettingsLI(newPackage, installerPackageName, null, null, res);
scanPackageLI负责安装,而updateSettingLI则是完成安装后的设置信息更新
2.4 scanPackageLI()
scanPackageLI()方法主要逻辑是由scanPackageDirtyLI()实现的,scanPackageDirtyLI()实在太长了,此处就不列出了,主要说下,这个方法实现了以下操作:
- 设置系统App的一些参数
- 校验签名
- 解析app的provider,校验是否与已有的provider冲突
- 32/64位abi的一些设置
- 四大组件的解析,注册
scanPackageDirtyLI()里面的操作确实是太多了,并不止这几点。如需更详细的信息还请查看源码。
另一方面,这个方法里,会调用到performDexOptLI(),其会去执行dexopt操作。
3. dexopt操作
Apk文件其实只是一个归档zip压缩包,而我们编写的代码最终都编译成了.dex文件,但为了提高运行性能,android系统并不会直接执行.dex,而是会在安装过程中执行dexopt操作来优化.dex文件,最终android系统执行的时优化后的’odex’文件(注意:这个odex文件的后缀也是.dex,其路径在data/dalvik-cache)。对于dalvik虚拟机,dexopt就是优化操作,而对于art虚拟机,dexopt执行的则是dex2oat操作,既将.dex文件翻译成oat文件。关于art和dex2oat的更多信息请看后文。
这里我们先来看看PMS的dexopt操作:
3.1 performDexOptLI()
这个方法的核心是
final int ret = mInstaller.dexopt(path, sharedGid, !isForwardLocked(pkg), pkg.packageName, dexCodeInstructionSet, vmSafeMode);
其作用就是调用PMS的mInstaller成员变量的dexopt操作。
3.2 Installer.dexopt
Installer类的dexopt方法又调用InstallerConnection类的dexopt方法,来看看这个方法:
public int dexopt(String apkPath, int uid, boolean isPublic, String pkgName,
String instructionSet, boolean vmSafeMode) {
StringBuilder builder = new StringBuilder(“dexopt”);
builder.append(’ ‘);
builder.append(apkPath);
builder.append(’ ‘);
builder.append(uid);
builder.append(isPublic ? " 1" : " 0");
builder.append(’ ‘);
builder.append(pkgName);
builder.append(’ ‘);
builder.append(instructionSet);
builder.append(’ ');
builder.append(vmSafeMode ? " 1" : " 0");
return execute(builder.toString());
}
public synchronized String transact(String cmd) {
if (!connect()) {
Slog.e(TAG, “connection failed”);
return “-1”;
}
if (!writeCommand(cmd)) {
/*
- If installd died and restarted in the background (unlikely but
- possible) we’ll fail on the next write (this one). Try to
- reconnect and write the command one more time before giving up.
*/
Slog.e(TAG, “write command failed? reconnect!”);
if (!connect() || !writeCommand(cmd)) {
return “-1”;
}
}
if (LOCAL_DEBUG) {
Slog.i(TAG, “send: '” + cmd + “'”);
}
final int replyLength = readReply();
if (replyLength > 0) {
String s = new String(buf, 0, replyLength);
if (LOCAL_DEBUG) {
Slog.i(TAG, “recv: '” + s + “'”);
}
return s;
} else {
if (LOCAL_DEBUG) {
Slog.i(TAG, “fail”);
}
return “-1”;
}
}
public int execute(String cmd) {
String res = transact(cmd);
try {
return Integer.parseInt(res);
} catch (NumberFormatException ex) {
return -1;
}
}
private boolean connect() {
if (mSocket != null) {
return true;
}
Slog.i(TAG, “connecting…”);
try {
mSocket = new LocalSocket();
LocalSocketAddress address = new LocalSocketAddress(“installd”,
LocalSocketAddress.Namespace.RESERVED);
mSocket.connect(address);
mIn = mSocket.getInputStream();
mOut = mSocket.getOutputStream();
} catch (IOException ex) {
disconnect();
return false;
}
return true;
}
由上面的几个方法可以知道,最终dexopt操作是通过socket的方式来跨进程通知守护进程installd,由其去执行dexopt操作。
3.3 commands::dexopt()
最终守护进程installd会调用Commands.c文件(位于/source/framework/native/cmds/installd)的dexopt方法。
int dexopt(const char *apk_path, uid_t uid, bool is_public,
const char *pkgname, const char *instruction_set,
bool vm_safe_mode, bool is_patchoat)
{
struct utimbuf ut;
struct stat input_stat, dex_stat;
char out_path[PKG_PATH_MAX];
char persist_sys_dalvik_vm_lib[PROPERTY_VALUE_MAX];
char *end;
const char *input_file;
char in_odex_path[PKG_PATH_MAX];
int res, input_fd=-1, out_fd=-1;
…
…
pid_t pid;
pid = fork();
if (pid == 0) {
/* child – drop privileges before continuing */
if (setgid(uid) != 0) {
ALOGE(“setgid(%d) failed in installd during dexopt\n”, uid);
exit(64);
}
if (setuid(uid) != 0) {
ALOGE(“setuid(%d) failed in installd during dexopt\n”, uid);
exit(65);
}
// drop capabilities
struct __user_cap_header_struct capheader;
struct __user_cap_data_struct capdata[2];
memset(&capheader, 0, sizeof(capheader));
memset(&capdata, 0, sizeof(capdata));
capheader.version = _LINUX_CAPABILITY_VERSION_3;
if (capset(&capheader, &capdata[0]) < 0) {
ALOGE(“capset failed: %s\n”, strerror(errno));
exit(66);
}
if (set_sched_policy(0, SP_BACKGROUND) < 0) {
ALOGE(“set_sched_policy failed: %s\n”, strerror(errno));
exit(70);
}
if (flock(out_fd, LOCK_EX | LOCK_NB) != 0) {
ALOGE(“flock(%s) failed: %s\n”, out_path, strerror(errno));
exit(67);
}
if (strncmp(persist_sys_dalvik_vm_lib, “libdvm”, 6) == 0) {
run_dexopt(input_fd, out_fd, input_file, out_path);
} else if (strncmp(persist_sys_dalvik_vm_lib, “libart”, 6) == 0) {
if (is_patchoat) {
run_patchoat(input_fd, out_fd, input_file, out_path, pkgname, instruction_set);
} else {
run_dex2oat(input_fd, out_fd, input_file, out_path, pkgname, instruction_set,
vm_safe_mode);
}
} else {
exit(69); /* Unexpected persist.sys.dalvik.vm.lib value /
}
exit(68); / only get here on exec failure */
} else {
res = wait_child(pid);
if (res == 0) {
ALOGV(“DexInv: — END ‘%s’ (success) —\n”, input_file);
} else {
ALOGE(“DexInv: — END ‘%s’ — status=0x%04x, process failed\n”, input_file, res);
goto fail;
}
}
ut.actime = input_stat.st_atime;
ut.modtime = input_stat.st_mtime;
utime(out_path, &ut);
close(out_fd);
close(input_fd);
return 0;
fail:
if (out_fd >= 0) {
close(out_fd);
unlink(out_path);
}
if (input_fd >= 0) {
close(input_fd);
}
return -1;
}
由上面的代码可以发现,installd在做了些操作后,fork出了一个新的进程,根据虚拟机的类型为libdvm或libart分别执行run_dexopt或run_dex2oat(如果为is_patchoat,则是run_patchoat)操作。
4. 更新权限信息
dexopt操作执行完后,installNewPackageLI()方法就会走到updateSettingsLI()来更新设置信息,而更新设置信息主要是权限信息,所以直接来看updatePermissionsLPw();
4.1 updatePermissionsLPw
private void updatePermissionsLPw(String changingPkg,
PackageParser.Package pkgInfo, int flags) {
// Make sure there are no dangling permission trees.
Iterator it = mSettings.mPermissionTrees.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BasePermission bp = it.next();
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
// We may not yet have parsed the package, so just see if
// we still know about its settings.
bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission tree: " + bp.name
- " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
it.remove();
} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {
if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission tree: " + bp.name - " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Make sure all dynamic permissions have been assigned to a package,
// and make sure there are no dangling permissions.
it = mSettings.mPermissions.values().iterator();
while (it.hasNext()) {
final BasePermission bp = it.next();
if (bp.type == BasePermission.TYPE_DYNAMIC) {
if (DEBUG_SETTINGS) Log.v(TAG, “Dynamic permission: name=”
- bp.name + " pkg=" + bp.sourcePackage
- " info=" + bp.pendingInfo);
if (bp.packageSetting == null && bp.pendingInfo != null) {
final BasePermission tree = findPermissionTreeLP(bp.name);
if (tree != null && tree.perm != null) {
bp.packageSetting = tree.packageSetting;
bp.perm = new PackageParser.Permission(tree.perm.owner,
new PermissionInfo(bp.pendingInfo));
bp.perm.info.packageName = tree.perm.info.packageName;
bp.perm.info.name = bp.name;
bp.uid = tree.uid;
}
}
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
// We may not yet have parsed the package, so just see if
// we still know about its settings.
bp.packageSetting = mSettings.mPackages.get(bp.sourcePackage);
}
if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Removing dangling permission: " + bp.name - " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
it.remove();
} else if (changingPkg != null && changingPkg.equals(bp.sourcePackage)) {
if (pkgInfo == null || !hasPermission(pkgInfo, bp.name)) {
Slog.i(TAG, "Removing old permission: " + bp.name - " from package " + bp.sourcePackage);
flags |= UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL;
it.remove();
}
}
}
// Now update the permissions for all packages, in particular
// replace the granted permissions of the system packages.
if ((flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_ALL) != 0) {
for (PackageParser.Package pkg : mPackages.values()) {
if (pkg != pkgInfo) {
grantPermissionsLPw(pkg, (flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_ALL) != 0,
changingPkg);
}
}
}
if (pkgInfo != null) {
grantPermissionsLPw(pkgInfo, (flags&UPDATE_PERMISSIONS_REPLACE_PKG) != 0, changingPkg);
}
}
private void grantPermissionsLPw(PackageParser.Package pkg, boolean replace,
String packageOfInterest) {
final PackageSetting ps = (PackageSetting) pkg.mExtras;
if (ps == null) {
return;
}
final GrantedPermissions gp = ps.sharedUser != null ? ps.sharedUser : ps;
HashSet origPermissions = gp.grantedPermissions;
boolean changedPermission = false;
if (replace) {
ps.permissionsFixed = false;
if (gp == ps) {
origPermissions = new HashSet(gp.grantedPermissions);
gp.grantedPermissions.clear();
gp.gids = mGlobalGids;
}
}
if (gp.gids == null) {
gp.gids = mGlobalGids;
}
final int N = pkg.requestedPermissions.size();
for (int i=0; i<N; i++) {
final String name = pkg.requestedPermissions.get(i);
final boolean required = pkg.requestedPermissionsRequired.get(i);
final BasePermission bp = mSettings.mPermissions.get(name);
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {
if (gp != ps) {
Log.i(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " checking " + name + ": " + bp);
}
}
if (bp == null || bp.packageSetting == null) {
if (packageOfInterest == null || packageOfInterest.equals(pkg.packageName)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Unknown permission " + name
- " in package " + pkg.packageName);
}
continue;
}
final String perm = bp.name;
boolean allowed;
boolean allowedSig = false;
if ((bp.protectionLevel&PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_FLAG_APPOP) != 0) {
// Keep track of app op permissions.
ArraySet pkgs = mAppOpPermissionPackages.get(bp.name);
if (pkgs == null) {
pkgs = new ArraySet<>();
mAppOpPermissionPackages.put(bp.name, pkgs);
}
pkgs.add(pkg.packageName);
}
final int level = bp.protectionLevel & PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_MASK_BASE;
if (level == PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_NORMAL
|| level == PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_DANGEROUS) {
// We grant a normal or dangerous permission if any of the following
// are true:
// 1) The permission is required
// 2) The permission is optional, but was granted in the past
// 3) The permission is optional, but was requested by an
// app in /system (not /data)
//
// Otherwise, reject the permission.
allowed = (required || origPermissions.contains(perm)
|| (isSystemApp(ps) && !isUpdatedSystemApp(ps)));
} else if (bp.packageSetting == null) {
// This permission is invalid; skip it.
allowed = false;
} else if (level == PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_SIGNATURE) {
allowed = grantSignaturePermission(perm, pkg, bp, origPermissions);
if (allowed) {
allowedSig = true;
}
} else {
allowed = false;
}
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) {
if (gp != ps) {
Log.i(TAG, "Package " + pkg.packageName + " granting " + perm);
}
}
if (allowed) {
if (!isSystemApp(ps) && ps.permissionsFixed) {
// If this is an existing, non-system package, then
// we can’t add any new permissions to it.
if (!allowedSig && !gp.grantedPermissions.contains(perm)) {
// Except… if this is a permission that was added
// to the platform (note: need to only do this when
// updating the platform).
allowed = isNewPlatformPermissionForPackage(perm, pkg);
}
}
if (allowed) {
if (!gp.grantedPermissions.contains(perm)) {
changedPermission = true;
gp.grantedPermissions.add(perm);
gp.gids = appendInts(gp.gids, bp.gids);
} else if (!ps.haveGids) {
gp.gids = appendInts(gp.gids, bp.gids);
}
} else {
if (packageOfInterest == null || packageOfInterest.equals(pkg.packageName)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Not granting permission " + perm
- " to package " + pkg.packageName
- " because it was previously installed without");
}
}
} else {
if (gp.grantedPermissions.remove(perm)) {
changedPermission = true;
gp.gids = removeInts(gp.gids, bp.gids);
Slog.i(TAG, "Un-granting permission " + perm - " from package " + pkg.packageName
- " (protectionLevel=" + bp.protectionLevel
- " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(pkg.applicationInfo.flags)
- “)”);
} else if ((bp.protectionLevel&PermissionInfo.PROTECTION_FLAG_APPOP) == 0) {
// Don’t print warning for app op permissions, since it is fine for them
// not to be granted, there is a UI for the user to decide.
if (packageOfInterest == null || packageOfInterest.equals(pkg.packageName)) {
Slog.w(TAG, "Not granting permission " + perm - " to package " + pkg.packageName
- " (protectionLevel=" + bp.protectionLevel
- " flags=0x" + Integer.toHexString(pkg.applicationInfo.flags)
- “)”);
}
}
}
}
if ((changedPermission || replace) && !ps.permissionsFixed &&
!isSystemApp(ps) || isUpdatedSystemApp(ps)){
// This is the first that we have heard about this package, so the
// permissions we have now selected are fixed until explicitly
// changed.
ps.permissionsFixed = true;
}
ps.haveGids = true;
}
由上面两个方法可以看到,在apk的安装时PMS会将该app的所有权限都记录下来并更新到PMS的mAppOpPermissionPackages成员变量里面,并判定是否授予该app请求的权限。
4.2 完成安装
还记得前面说过的在processPendingInstall方法在执行installPackageLi后会执行以下语句
if (res.returnCode == PackageManager.INSTALL_SUCCEEDED && doRestore) {
// Pass responsibility to the Backup Manager. It will perform a
// restore if appropriate, then pass responsibility back to the
// Package Manager to run the post-install observer callbacks
// and broadcasts.
IBackupManager bm = IBackupManager.Stub.asInterface(
ServiceManager.getService(Context.BACKUP_SERVICE));
if (bm != null) {
if (DEBUG_INSTALL) Log.v(TAG, "token " + token
- " to BM for possible restore");
try {
bm.restoreAtInstall(res.pkg.applicationInfo.packageName, token);
} catch (RemoteException e) {
// can’t happen; the backup manager is local
} catch (Exception e) {
Slog.e(TAG, “Exception trying to enqueue restore”, e);
doRestore = false;
}
} else {
Slog.e(TAG, “Backup Manager not found!”);
doRestore = false;
}
}
我也不是很清楚为什么系统会调用IBackupManager的restoreAtInstall方法,不过发现在BackupManagerService的restoreAtInstall方法中会有以下代码:
…
if (skip) {
// Auto-restore disabled or no way to attempt a restore; just tell the Package
// Manager to proceed with the post-install handling for this package.
自我介绍一下,小编13年上海交大毕业,曾经在小公司待过,也去过华为、OPPO等大厂,18年进入阿里一直到现在。
深知大多数Android工程师,想要提升技能,往往是自己摸索成长或者是报班学习,但对于培训机构动则几千的学费,着实压力不小。自己不成体系的自学效果低效又漫长,而且极易碰到天花板技术停滞不前!
因此收集整理了一份《2024年Android移动开发全套学习资料》,初衷也很简单,就是希望能够帮助到想自学提升又不知道该从何学起的朋友,同时减轻大家的负担。

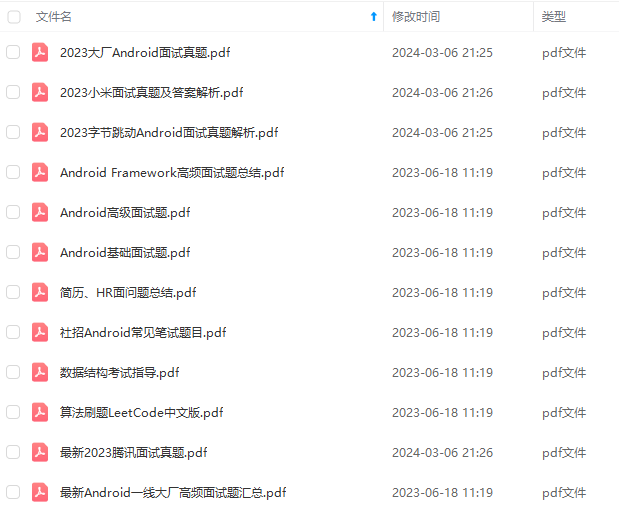
既有适合小白学习的零基础资料,也有适合3年以上经验的小伙伴深入学习提升的进阶课程,基本涵盖了95%以上Android开发知识点,真正体系化!
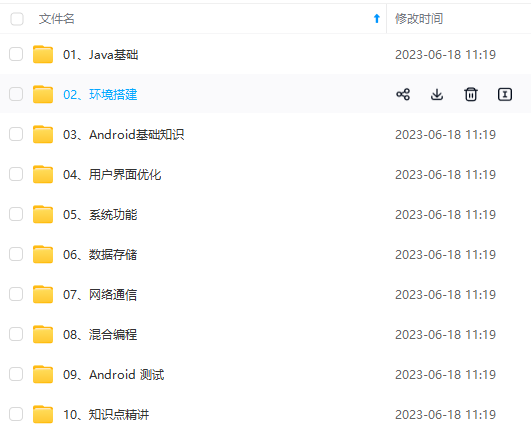
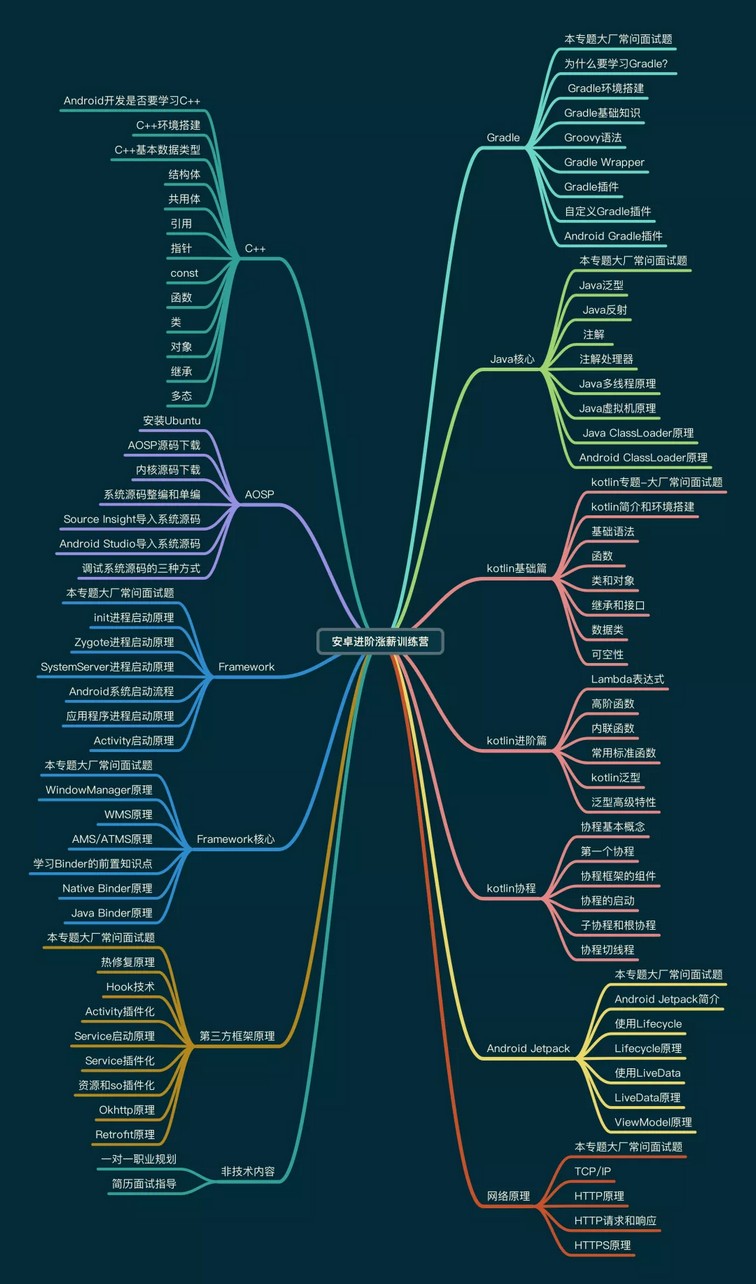
由于文件比较大,这里只是将部分目录大纲截图出来,每个节点里面都包含大厂面经、学习笔记、源码讲义、实战项目、讲解视频,并且后续会持续更新
如果你觉得这些内容对你有帮助,可以添加V:vip204888 备注Android获取(资料价值较高,非无偿)

最后
今天关于面试的分享就到这里,还是那句话,有些东西你不仅要懂,而且要能够很好地表达出来,能够让面试官认可你的理解,例如Handler机制,这个是面试必问之题。有些晦涩的点,或许它只活在面试当中,实际工作当中你压根不会用到它,但是你要知道它是什么东西。
最后在这里小编分享一份自己收录整理上述技术体系图相关的几十套腾讯、头条、阿里、美团等公司19年的面试题,把技术点整理成了视频和PDF(实际上比预期多花了不少精力),包含知识脉络 + 诸多细节,由于篇幅有限,这里以图片的形式给大家展示一部分。
还有 高级架构技术进阶脑图、Android开发面试专题资料,高级进阶架构资料 帮助大家学习提升进阶,也节省大家在网上搜索资料的时间来学习,也可以分享给身边好友一起学习。
【Android核心高级技术PDF文档,BAT大厂面试真题解析】

【算法合集】

【延伸Android必备知识点】

【Android部分高级架构视频学习资源】
**Android精讲视频领取学习后更加是如虎添翼!**进军BATJ大厂等(备战)!现在都说互联网寒冬,其实无非就是你上错了车,且穿的少(技能),要是你上对车,自身技术能力够强,公司换掉的代价大,怎么可能会被裁掉,都是淘汰末端的业务Curd而已!现如今市场上初级程序员泛滥,这套教程针对Android开发工程师1-6年的人员、正处于瓶颈期,想要年后突破自己涨薪的,进阶Android中高级、架构师对你更是如鱼得水,赶快领取吧!
里以图片的形式给大家展示一部分。
还有 高级架构技术进阶脑图、Android开发面试专题资料,高级进阶架构资料 帮助大家学习提升进阶,也节省大家在网上搜索资料的时间来学习,也可以分享给身边好友一起学习。
【Android核心高级技术PDF文档,BAT大厂面试真题解析】
[外链图片转存中…(img-9cgi6jBW-1711593176228)]
【算法合集】
[外链图片转存中…(img-u9Smqoyx-1711593176229)]
【延伸Android必备知识点】
[外链图片转存中…(img-Tu6xChXS-1711593176229)]
【Android部分高级架构视频学习资源】
**Android精讲视频领取学习后更加是如虎添翼!**进军BATJ大厂等(备战)!现在都说互联网寒冬,其实无非就是你上错了车,且穿的少(技能),要是你上对车,自身技术能力够强,公司换掉的代价大,怎么可能会被裁掉,都是淘汰末端的业务Curd而已!现如今市场上初级程序员泛滥,这套教程针对Android开发工程师1-6年的人员、正处于瓶颈期,想要年后突破自己涨薪的,进阶Android中高级、架构师对你更是如鱼得水,赶快领取吧!






















 4350
4350











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








