for ((i=1;i<255;i++));do
ping -c 1 -w 1 10.0.0.$i &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "10.0.0.$i 可以ping通!" else echo "10.0.0.$i 不可以ping通!" fidone
wait
[root@shell day05]# sh for-ip.sh
10.0.0.1 可以ping通!
10.0.0.21 可以ping通!
^Z
[4]+ Stopped sh for-ip.sh
4、for循环打印99乘法表
[root@shell lianxi]# cat for99-1.sh #!/bin/bash #倒三角排序 for ((i=9 ;i>=1;i--));do for ((j=1;j<=i;j++));do echo -en "${j}x$i=$(($i\*$j))\t" #第一种方法计算 done echo done #正三角排序 for ((i=1;i<=9;i++));do for ((j=1;j<=i;j++));do echo -en "${j}x$i=`expr $i\*$j|bc`\t" #第二种方法计算 done echo done [root@shell lianxi]# sh for99-1.sh 1x9=9 2x9=18 3x9=27 4x9=36 5x9=45 6x9=54 7x9=63 8x9=72 9x9=81 1x8=8 2x8=16 3x8=24 4x8=32 5x8=40 6x8=48 7x8=56 8x8=64 1x7=7 2x7=14 3x7=21 4x7=28 5x7=35 6x7=42 7x7=49 1x6=6 2x6=12 3x6=18 4x6=24 5x6=30 6x6=36 1x5=5 2x5=10 3x5=15 4x5=20 5x5=25 1x4=4 2x4=8 3x4=12 4x4=16 1x3=3 2x3=6 3x3=9 1x2=2 2x2=4 1x1=1 1x1=1 1x2=2 2x2=4 1x3=3 2x3=6 3x3=9 1x4=4 2x4=8 3x4=12 4x4=16 1x5=5 2x5=10 3x5=15 4x5=20 5x5=25 1x6=6 2x6=12 3x6=18 4x6=24 5x6=30 6x6=36 1x7=7 2x7=14 3x7=21 4x7=28 5x7=35 6x7=42 7x7=49 1x8=8 2x8=16 3x8=24 4x8=32 5x8=40 6x8=48 7x8=56 8x8=64 1x9=9 2x9=18 3x9=27 4x9=36 5x9=45 6x9=54 7x9=63 8x9=72 9x9=81
5.给出一个网段,如10.0.0.0/24,如何判断网段内的所有ip是否能联通
[root@shell day05]# cat for-ip.sh #!/bin/bash ############################################################## # File Name: for\_ip.sh # Version: V1.0 # Author: lcx # Organization: www.oldboyedu.com ############################################################## #for i in 10.0.0.{1..254} #do # ping -c 2 -w 2 $i &>/dev/null # if [ $? -eq 0 ];then # echo $i 可以ping通! # else # echo $i 不可以ping通 &>/dev/null # fi #done for ((i=1;i<255;i++));do ping -c 1 -w 1 10.0.0.$i &>/dev/null if [ $? -eq 0 ];then echo "10.0.0.$i 可以ping通!" else echo "10.0.0.$i 不可以ping通!" fi done wait [root@shell day05]# sh for-ip.sh 10.0.0.1 可以ping通! 10.0.0.21 可以ping通! ^Z [4]+ Stopped sh for-ip.sh
2.循环的流程控制
break、continue、exit、return
2.1 break
[root@shell day05]# vim break.sh
1 #!/bin/bash
2 ##############################################################
3 # File Name: break.sh
4 # Version: V1.0
5 # Author: lcx
6 # Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
7 ##############################################################
8 for ((i=0;i<10;i++));do
9 echo $i
10 if [ $i -eq 3 ];then
11 break
12 fi
13 done
[root@shell day05]# sh break.sh
0
1
2
3
2.2 contunue
[root@shell day05]# cat break.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: break.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
##############################################################
for ((i=0;i<10;i++));do
echo $i
if [ $i -eq 3 ];then
continue
fi
done
echo "hello"
[root@shell day05]# sh break.sh
0
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
hello
流程控制的测试脚本
[root@shell day05]# vim for-bcer.sh
#!/bin/bash
##############################################################
# File Name: for-bcer.sh
# Version: V1.0
# Author: lcx
# Organization: www.oldboyedu.com
#############################################################
#循环流程控制break、continue、exit、return的区别和对比
if [ $# -ne 1 ];then
# 如果传参个数部位1,则打印下面的使用提示,提示四个命令作为参数
echo $"usage:$0 {break|continue|exit|return}"
exit 1 #退出脚本
fi
function test(){
for((i=0;i<5;i++));do
if [ $i -eq 3 ];then
$\*; #"$\*" 就是接收函数以外的参数,是{break|continue|exit|return}其中一个
fi
echo $i
done
echo "I am in func." #函数内循环外的输出提示
}
test $\* # 这里的$\*为参数的传参
func_ret=$? # 接收并测试函数返回值
if [ `echo $\*|grep return|wc -l` -eq 1 ];then # 如果传参中含有return
echo "return exit status: $func\_ret" # 则提示return退出的状态码
fi
echo "OK"
执行结果
[root@shell day05]# sh for-bcer.sh
usage:for-bcer.sh {break|continue|exit|return}
[root@shell day05]# sh for-bcer.sh break
0
1
2
I am in func.
OK
[root@shell day05]# sh for-bcer.sh continue
0
1
2
4
I am in func.
OK
[root@shell day05]# sh for-bcer.sh exit
0
1
2
[root@shell day05]# sh for-bcer.sh return
0
1
2
return exit status: 0
OK
3. 数组
普通数组:只能使用整数作为索引
关联数组:可以只用字符串作为数组索引
3.1 普通数组
[root@shell day05]# oldboy[2]=lcx
[root@shell day05]# oldboy[3]=gyj
[root@shell day05]# oldboy[4]=wx
[root@shell day05]# declare -a #查看数组
[root@shell day05]# echo $oldboy
ljg
[root@shell day05]# echo ${oldboy[3]}
gyj
[root@shell day05]# echo ${oldboy[4]}
wx
[root@shell day05]# echo ${oldboy[@]} #"@"和"\*"相同
ljg wd lcx gyj wx gds lfx hyj rh
[root@shell day05]# echo ${oldboy[\*]}
ljg wd lcx gyj wx gds lfx hyj rh
[root@shell day05]# echo ${!oldboy[\*]} #查看数组所有的索引下标
0 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8
[root@shell day05]# echo ${#oldboy[\*]} #查看数组元素个数
8
[root@shell day05]# oldboy=(ljg wd lcx gyj wx gds lfx hyj rh) #数组的批量赋值
[root@shell day05]# echo ${oldboy[\*]}
ljg wd lcx gyj wx gds lfx hyj rh
3.2 删除数组
[root@shell day05]# unset oldboy
[root@shell day05]# echo ${oldboy[@]}
[root@shell day05]# declare -a oldboy #定义空数组
[root@shell day05]# declare -a
declare -a BASH_ARGC='()'
declare -a BASH_ARGV='()'
declare -a BASH_LINENO='()'
declare -ar BASH_REMATCH='()'
declare -a BASH_SOURCE='()'
declare -ar BASH_VERSINFO='([0]="4" [1]="2" [2]="46" [3]="2" [4]="release" [5]="x86\_64-redhat-linux-gnu")'
declare -a DIRSTACK='()'
declare -a FUNCNAME='()'
declare -a GROUPS='()'
declare -a PIPESTATUS='([0]="0")'
declare -a oldboy='()' #定义成功的数组
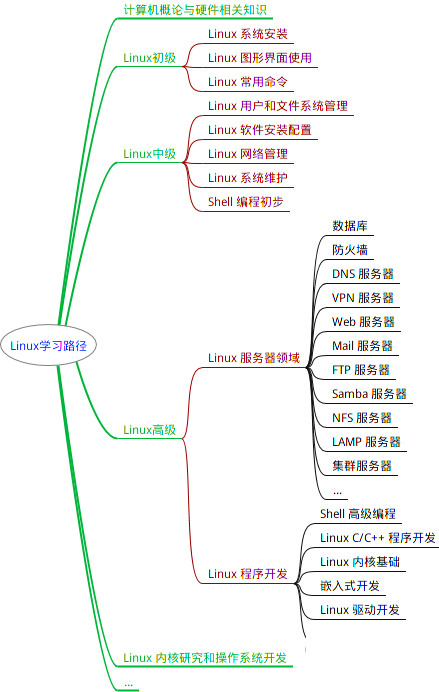
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通
======================
1. **linux从入门到精通(第2版)**
2. **Linux系统移植**
3. **Linux驱动开发入门与实战**
4. **LINUX 系统移植 第2版**
5. **Linux开源网络全栈详解 从DPDK到OpenFlow**

第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页
====================
内容简介
====
本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linux从入门到精通》的第2版**。本书第1版出版后曾经多次印刷,并被51CTO读书频道评为“最受读者喜爱的原创IT技术图书奖”。本书第﹖版以最新的Ubuntu 12.04为版本,循序渐进地向读者介绍了Linux 的基础应用、系统管理、网络应用、娱乐和办公、程序开发、服务器配置、系统安全等。本书附带1张光盘,内容为本书配套多媒体教学视频。另外,本书还为读者提供了大量的Linux学习资料和Ubuntu安装镜像文件,供读者免费下载。

**本书适合广大Linux初中级用户、开源软件爱好者和大专院校的学生阅读,同时也非常适合准备从事Linux平台开发的各类人员。**
> 需要《Linux入门到精通》、《linux系统移植》、《Linux驱动开发入门实战》、《Linux开源网络全栈》电子书籍及教程的工程师朋友们劳烦您转发+评论
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取!](https://bbs.csdn.net/topics/618542503)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**






















 3万+
3万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








