桥接模式可以减少类的创建
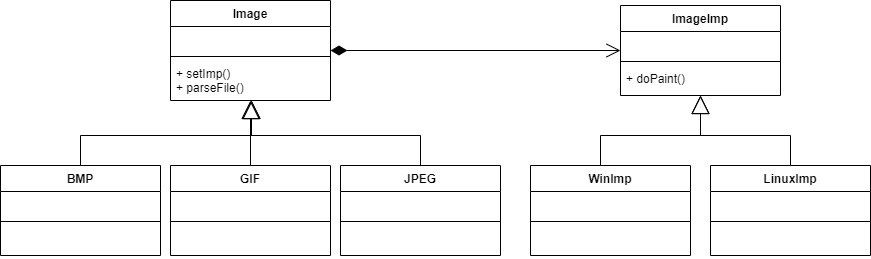
矩阵类
public class Matrix {
private String fileName;
public Matrix(String fileName) {
this.fileName = fileName;
}
public String getFileName() {
return fileName;
}
}图片抽象类
public abstract class Image {
protected ImageImp imp;
public void setImp(ImageImp imp) {
this.imp = imp;
}
public abstract void parseFile(String fileName);
}BMP类
public class BMP extends Image {
@Override
public void parseFile(String fileName) {
imp.doPaint(new Matrix(fileName));
}
}GIF类
public class GIF extends Image {
@Override
public void parseFile(String fileName) {
imp.doPaint(new Matrix(fileName));
}
}JPEG类
public class JPEG extends Image {
@Override
public void parseFile(String fileName) {
imp.doPaint(new Matrix(fileName));
}
}图片实现抽象类
public abstract class ImageImp {
public abstract void doPaint(Matrix matrix);
}Windows实现类
public class WinImp extends ImageImp {
@Override
public void doPaint(Matrix matrix) {
System.out.println("调用Windows系统的算法绘制像素矩阵:"+matrix.getFileName());
}
}Linux实现类
public class LinuxImp extends ImageImp {
@Override
public void doPaint(Matrix matrix) {
System.out.println("调用Linux系统的算法绘制像素矩阵:"+matrix.getFileName());
}
}演示类
public class Demo {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Image image1 = new BMP();
ImageImp imageImp1 = new WinImp();
image1.setImp(imageImp1);
image1.parseFile("demo.bmp");
}
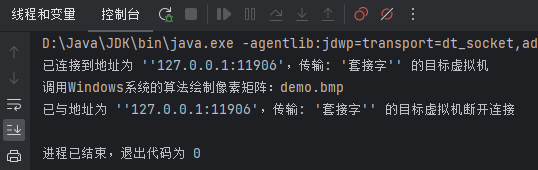
}演示结果






















 516
516











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










