目录
一、概念:
线程:进程内部的一条执行路径(序列)
进程:一个正在运行的程序
二、线程方式:

1.用户级线程:
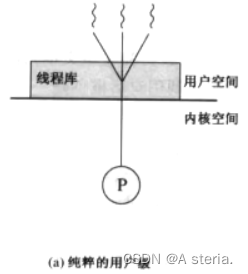
用户空间的代码管理线程的创建、调度等等,开销小但是由于是用户自己创建的与内核无关,所以内核无法感知到这类线程的存在,认为只有一个线程存在,无法利用多个处理器。
2.内核线程:
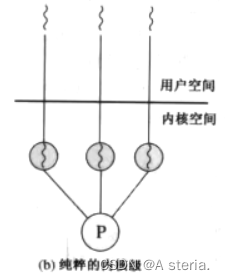
能够被调度到不同处理器上,使他们同时进行;开销相对于用户及线程大,可以利用多个处理器
3.组合线程:
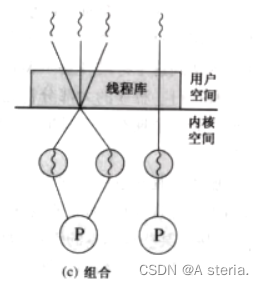
处于以上两者之间
三、线程在Linux中的实现

四、线程同步
1.信号量 :
//不随机打印,按照ABC的顺序打印
//接口

//代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
#include<semaphore.h>
sem_t sema;
sem_t semb;
sem_t semc;
void* funa(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
sem_wait(&sema);//ps1;
printf("A");
fflush(stdout);
sem_post(&semb);//vs2
}
}
void* funb(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
sem_wait(&semb);//psb;
printf("B");
fflush(stdout);
sem_post(&semc);//vsc
}
}
void * func(void *arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
sem_wait(&semc);
printf("C");
fflush(stdout);
sem_post(&sema);
}
}
int main()
{
sem_init(&sema,0,1);
sem_init(&semb,0,0);
sem_init(&semc,0,0);
pthread_t id1,id2,id3;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,funa,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,funb,NULL);
pthread_create(&id3,NULL,func,NULL);
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
pthread_join(id3,NULL);
sem_destroy(&sema);
sem_destroy(&semb);
sem_destroy(&semc);
exit(0);
}
//运行结果:

2.互斥锁:
能完成信号量的一个子集(信号量初始值为1的类型,有可能阻塞类似p操作为0)

//1.代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
void* fun1(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("A");//开始使用打印机
fflush(stdout);//标准输出,刷新
int n=rand()%3;//随即睡眠三秒以内的时间
sleep(n);
printf("A");//使用结束
fflush(stdout);
sleep(n)
}
}
void* fun2(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
printf("B");//开始使用打印机
fflush(stdout);//标准输出,刷新
int n=rand()%3;//随即睡眠三秒以内的时间
sleep(n);
printf("B");//使用结束
fflush(stdout);
sleep(n);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_t id1,id2;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,fun1,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,fun2,NULL);
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
}
//运行结果:
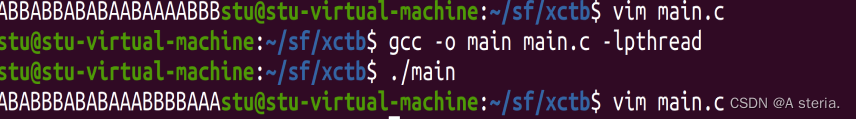
//如何让运行结果达到我们想要的成对出现?
//2.互斥锁接口:

//init
//lock、unlock
//destroy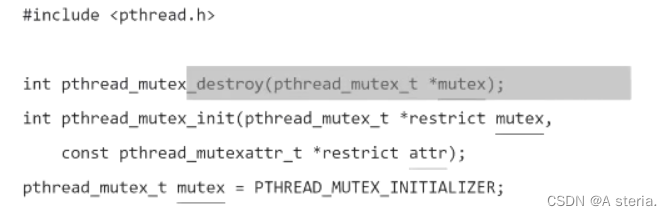
//3.加锁代码
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;//定义一个锁
void* fun1(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//可能阻塞
printf("A");//开始使用打印机
fflush(stdout);//标准输出,刷新
int n=rand()%3;//随即睡眠三秒以内的时间
sleep(n);
printf("A");//使用结束
n=rand()%3;
fflush(stdout);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//如果忘记解锁会一直阻塞
sleep(n);
}
}
void* fun2(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
printf("B");//开始使用打印机
fflush(stdout);//标准输出,刷新
int n=rand()%3;//随即睡眠三秒以内的时间
sleep(n);
printf("B");//使用结束
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
n=rand()%3;
sleep(n);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_mutex_init(&mutex,NULL);
pthread_t id1,id2;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,fun1,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,fun2,NULL);
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
exit(0);
}
//运行结果:
3.条件变量:
提供线程间的通知机制

//使用条件变量还需要互斥锁
//代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#include<unistd.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<pthread.h>
pthread_mutex_t mutex;
pthread_cond_t cond;
void*funa(void*arg)
{
char* s=(char*)arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);//上锁
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);//解锁,上锁
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);//解锁
if(strncmp(s,"end",3)==0)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("funa: %s\n",s);
}
}
}
void* funb(void* arg)
{
char* s=(char*) arg;
while(1)
{
pthread_mutex_lock(&mutex);
pthread_cond_wait(&cond,&mutex);
pthread_mutex_unlock(&mutex);
if(strncmp(s,"end",3)==0)
{
break;
}
else
{
printf("funb: %s\n",s);
}
}
}
int main()
{
char buff[128]={0};
pthread_t id1,id2;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,funa,(void*)buff);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,funb,(void*)buff);
while(1)
{
fgets(buff,128,stdin);
if(strncmp(buff,"end",3)==0)
{
pthread_cond_broadcast(&cond);//唤醒所有线程
break;
}
else
{
pthread_cond_signal(&cond);//唤醒一个线程
}
}
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
pthread_mutex_destroy(&mutex);
pthread_cond_destroy(&cond);
exit(0);
}//运行结果:
//ab交替读取,读到end,退出
4.读写锁:
对某个资源既有读也有写
//接口
// man pthread_rwlock_init

//其余接口

//代码
for(int i=0;i<10;i++)
{
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock);
printf("fun1 read start--\n");
sleep(1);
printf("fun1 read end--\n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);
sleep(1);
}
}
void* fun2(void* arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<5;i++);
{
pthread_rwlock_rdlock(&lock);
printf("fun2 read start--\n");
sleep(2);
printf("fun2 read end--\n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);
}
}
void* fun3(void*arg)
{
for(int i=0;i<3;i++)
{
pthread_rwlock_wrlock(&lock);
printf("fun3 write start--\n");
sleep(3);
printf("fun3 write end--\n");
pthread_rwlock_unlock(&lock);
}
}
int main()
{
pthread_rwlock_init(&lock,NULL);
pthread_t id1,id2,id3;
pthread_create(&id1,NULL,fun1,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,fun2,NULL);
pthread_create(&id2,NULL,fun3,NULL);
pthread_join(id1,NULL);
pthread_join(id2,NULL);
pthread_join(id3,NULL);
pthread_rwlock_destroy(&lock);
exit(0);
}
//运行结果
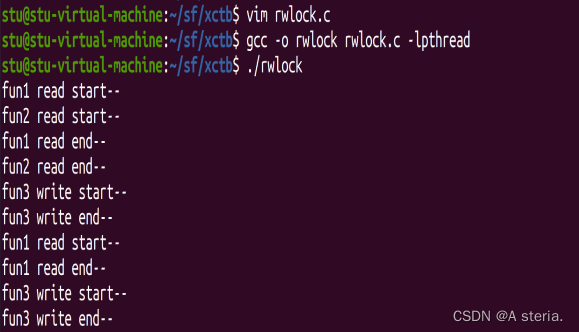
//两个读锁可以同时通过,一旦开始读不能写,一旦开始写不能读,
























 437
437











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








