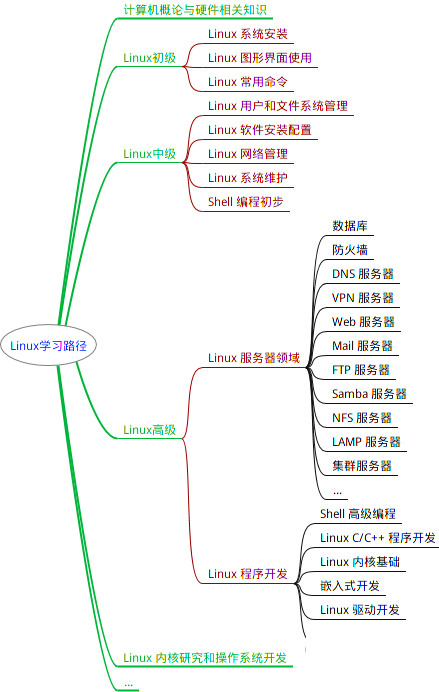
最全的Linux教程,Linux从入门到精通
======================
-
linux从入门到精通(第2版)
-
Linux系统移植
-
Linux驱动开发入门与实战
-
LINUX 系统移植 第2版
-
Linux开源网络全栈详解 从DPDK到OpenFlow

第一份《Linux从入门到精通》466页
====================
内容简介
====
本书是获得了很多读者好评的Linux经典畅销书**《Linux从入门到精通》的第2版**。本书第1版出版后曾经多次印刷,并被51CTO读书频道评为“最受读者喜爱的原创IT技术图书奖”。本书第﹖版以最新的Ubuntu 12.04为版本,循序渐进地向读者介绍了Linux 的基础应用、系统管理、网络应用、娱乐和办公、程序开发、服务器配置、系统安全等。本书附带1张光盘,内容为本书配套多媒体教学视频。另外,本书还为读者提供了大量的Linux学习资料和Ubuntu安装镜像文件,供读者免费下载。

本书适合广大Linux初中级用户、开源软件爱好者和大专院校的学生阅读,同时也非常适合准备从事Linux平台开发的各类人员。
需要《Linux入门到精通》、《linux系统移植》、《Linux驱动开发入门实战》、《Linux开源网络全栈》电子书籍及教程的工程师朋友们劳烦您转发+评论
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv4 = conv3x3(in_planes=64, out_channels=64, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv5 = conv1x1(in_planes =64,out_channels=80, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv6 = conv3x3(in_planes=80, out_channels=192, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv7 = conv3x3(in_planes=192, out_channels=256, stride=2, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x = self.maxpool(x)
x = self.conv4(x)
x = self.conv5(x)
x = self.conv6(x)
x = self.conv7(x)
return x
IR-A模块\*5:输入35\*35\*256,输出35\*35\*256.
class Inception_ResNet_A(nn.Module):
def init(self, input ):
super(Inception_ResNet_A, self).init()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes =input,out_channels=32,stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(in_planes=32, out_channels=32, stride=1, padding=1)
self.line = nn.Conv2d(96, 256, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c3 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c3", c3.shape)
c2_1 = self.conv2(c2)
# print("c2_1", c2_1.shape)
c3_1 = self.conv2(c3)
# print("c3_1", c3_1.shape)
c3_2 = self.conv2(c3_1)
# print("c3_2", c3_2.shape)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2_1, c3_2],dim=1)#torch.Size([4, 96, 15, 15])
# print("x",x.shape)
line = self.line(cat)
# print("line",line.shape)
out =x+line
out = self.relu(out)
return out
Reduction-A模块:输入35\*35\*256,输出17\*17\*896.
class Reduction_A(nn.Module):
def init(self, input,n=384,k=192,l=224,m=256):
super(Reduction_A, self).init()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv1 = conv3x3(in_planes=input, out_channels=n,stride=2,padding=0)
self.conv2 = conv1x1(in_planes=input, out_channels=k,padding=1)
self.conv3 = conv3x3(in_planes=k, out_channels=l,padding=0)
self.conv4 = conv3x3(in_planes=l, out_channels=m,stride=2,padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.maxpool(x)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c3 = self.conv2(x)
# print("c3", c3.shape)
c3_1 = self.conv3(c3)
# print("c3_1", c3_1.shape)
c3_2 = self.conv4(c3_1)
# print("c3_2", c3_2.shape)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2,c3_2], dim=1)
return cat
IR-B模块\*10:输入17\*17\*896,输出17\*17\*896.
class Inception_ResNet_B(nn.Module):
def init(self, input):
super(Inception_ResNet_B, self).init()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes =input,out_channels=128,stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv1x7 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128,out_channels=128,kernel_size=(1,7), padding=(0,3))
self.conv7x1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128, out_channels=128,kernel_size=(7,1), padding=(3,0))
self.line = nn.Conv2d(256, 896, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c2_1 = self.conv1x7(c2)
# print("c2_1", c2_1.shape)
c2_1 = self.relu(c2_1)
c2_2 = self.conv7x1(c2_1)
# print("c2_2", c2_2.shape)
c2_2 = self.relu(c2_2)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2_2], dim=1)
line = self.line(cat)
out =x+line
out = self.relu(out)
# print("out", out.shape)
return out
Reduction-B模块:输入17\*17\*896,输出8\*8\*1792.
class Reduction_B(nn.Module):
def init(self, input):
super(Reduction_B, self).init()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=1)
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes=input, out_channels=256, padding=1)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(in_planes=256, out_channels=384, stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv3 = conv3x3(in_planes=256, out_channels=256,stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv4 = conv3x3(in_planes=256, out_channels=256, padding=1)
self.conv5 = conv3x3(in_planes=256, out_channels=256, stride=2, padding=0)
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.maxpool(x)
# print(“c1”, c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print(“c2”, c2.shape)
c3 = self.conv1(x)
# print(“c3”, c3.shape)
c4 = self.conv1(x)
# print(“c4”, c4.shape)
c2_1 = self.conv2(c2)
# print(“cc2_1”, c2_1.shape)
c3_1 = self.conv3(c3)
# print(“c3_1”, c3_1.shape)
c4_1 = self.conv4(c4)
# print(“c4_1”, c4_1.shape)
c4_2 = self.conv5(c4_1)
# print(“c4_2”, c4_2.shape)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2_1, c3_1,c4_2], dim=1)
# print(“cat”, cat.shape)
return cat
IR-C模块\*5:输入8\*8\*1792,输出8\*8\*1792.
class Inception_ResNet_C(nn.Module):
def init(self, input):
super(Inception_ResNet_C, self).init()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes=input, out_channels=192, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv1x3 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=192, kernel_size=(1, 3), padding=(0,1))
self.conv3x1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=192, out_channels=192, kernel_size=(3, 1), padding=(1,0))
self.line = nn.Conv2d(384, 1792, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.conv1(x)
# print("x", x.shape)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c2_1 = self.conv1x3(c2)
# print("c2_1", c2_1.shape)
c2_1 = self.relu(c2_1)
c2_2 = self.conv3x1(c2_1)
# print("c2_2", c2_2.shape)
c2_2 = self.relu(c2_2)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2_2], dim=1)
# print("cat", cat.shape)
line = self.line(cat)
out = x+ line
# print("out", out.shape)
out = self.relu(out)
return out
class Inception_ResNet(nn.Module):
def init(self,classes=2):
super(Inception_ResNet, self).init()
blocks = []
blocks.append(StemV1(in_planes=3))
for i in range(5):
blocks.append(Inception_ResNet_A(input=256))
blocks.append(Reduction_A(input=256))
for i in range(10):
blocks.append(Inception_ResNet_B(input=896))
blocks.append(Reduction_B(input=896))
for i in range(10):
blocks.append(Inception_ResNet_C(input=1792))
self.features = nn.Sequential(*blocks)
self.avepool = nn.AvgPool2d(kernel_size=3)
self.dropout = nn.Dropout(p=0.2)
self.linear = nn.Linear(1792, classes)
def forward(self,x):
x = self.features(x)
# print("x",x.shape)
x = self.avepool(x)
# print("avepool", x.shape)
x = self.dropout(x)
# print("dropout", x.shape)
x = x.view(x.size(0), -1)
x = self.linear(x)
return x
上述代码参考:[基于PyTorch实现 Inception-ResNet-v1\_NAND\_LU的博客-CSDN博客]( )
(2)Inception-Resnet-v2:
import torch
import torch.nn as nn
import torch.nn.functional as F
由于后面会经常用到,提前定义3×3卷积 和 1×1的卷积
class conv3x3(nn.Module):
def init(self, in_planes, out_channels, stride=1, padding=0):
super(conv3x3, self).init()
self.conv3x3 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_channels, kernel_size=3, stride=stride, padding=padding), # 卷积核为3x3
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels), # BN层,防止过拟合以及梯度爆炸
nn.ReLU() # 激活函数
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.conv3x3(input)
class conv1x1(nn.Module):
def init(self, in_planes, out_channels, stride=1, padding=0):
super(conv1x1, self).init()
self.conv1x1 = nn.Sequential(
nn.Conv2d(in_planes, out_channels, kernel_size=1, stride=stride, padding=padding), # 卷积核为1x1
nn.BatchNorm2d(out_channels),
nn.ReLU()
)
def forward(self, input):
return self.conv1x1(input)
stem模块:输入299\*299\*3,输出35\*35\*384.
定义stem模块
class StemV2(nn.Module):
def init(self, in_planes=3):
super(StemV2, self).init()
self.conv1 = conv3x3(in_planes =in_planes,out_channels=32,stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(in_planes=32, out_channels=32, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv3 = conv3x3(in_planes=32, out_channels=64, stride=1, padding=1)
self.maxpool1 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv4 = conv3x3(in_planes=64, out_channels=96, stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv5 = conv1x1(in_planes=160, out_channels=64, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv6 = conv3x3(in_planes=64, out_channels=96, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv7 = conv1x1(in_planes=160, out_channels=64, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv8 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=1, kernel_size=(1, 7), padding=(0, 3))
self.conv9 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=64, out_channels=64, stride=1, kernel_size=(7, 1), padding=(3, 0))
self.conv10 = conv3x3(in_planes=64, out_channels=96, stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv11 = conv3x3(in_planes=192, out_channels=192, stride=2, padding=0)
self.maxpool2 = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
x = self.conv1(x)
x = self.conv2(x)
x = self.conv3(x)
x1 = self.maxpool1(x)
x2 = self.conv4(x)
x = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1)
x1 = self.conv5(x)
x1 = self.conv6(x1)
x2 = self.conv7(x)
x2 = self.conv8(x2)
x2 = self.relu(x2)
x2 = self.conv9(x2)
x2 = self.relu(x2)
x2 = self.conv10(x2)
x = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1)
x1 = self.conv11(x)
x2 = self.maxpool2(x)
x = torch.cat([x1, x2], dim=1)
return x
IR-A模块\*5:输入35\*35\*384,输出35\*35\*256.
定义IR-A模块
class Inception_ResNet_A(nn.Module):
def init(self, input, scale=0.3):
super(Inception_ResNet_A, self).init()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes =input,out_channels=32,stride=1, padding=0)
self.conv2 = conv3x3(in_planes=32, out_channels=32, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv3 = conv3x3(in_planes=32, out_channels=48, stride=1, padding=1)
self.conv4 = conv3x3(in_planes=48, out_channels=64, stride=1, padding=1)
self.line = nn.Conv2d(128, 384, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
self.scale = scale
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c3 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c3", c3.shape)
c2_1 = self.conv2(c2)
# print("c2_1", c2_1.shape)
c3_1 = self.conv3(c3)
# print("c3_1", c3_1.shape)
c3_2 = self.conv4(c3_1)
# print("c3_2", c3_2.shape)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2_1, c3_2],dim=1)#torch.Size([4, 96, 15, 15])
# print("x",x.shape)
line = self.line(cat)
# print("line",line.shape)
out = self.scale*x+line
out = self.relu(out)
return out
Reduction-A模块:输入35\*35\*256,输出17\*17\*896.
定义Reduction-A模块
class Reduction_A(nn.Module):
def init(self, input, n=384, k=256, l=256, m=384, scale=0.3):
super(Reduction_A, self).init()
self.maxpool = nn.MaxPool2d(kernel_size=3, stride=2, padding=0)
self.conv1 = conv3x3(in_planes=input, out_channels=n, stride=2,padding=0)
self.conv2 = conv1x1(in_planes=input, out_channels=k, padding=1)
self.conv3 = conv3x3(in_planes=k, out_channels=l, padding=0)
self.conv4 = conv3x3(in_planes=l, out_channels=m, stride=2, padding=0)
self.scale =scale
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.maxpool(x)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c3 = self.conv2(x)
# print("c3", c3.shape)
c3_1 = self.conv3(c3)
# print("c3_1", c3_1.shape)
c3_2 = self.conv4(c3_1)
# print("c3_2", c3_2.shape)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2, c3_2], dim=1)
return cat
IR-B模块\*10:输入17\*17\*896,输出8\*8\*1792.
定义IR-B模块
class Inception_ResNet_B(nn.Module):
def init(self, input, scale=0.3):
super(Inception_ResNet_B, self).init()
self.conv1 = conv1x1(in_planes =input,out_channels=192,stride=0, padding=1)
self.conv2 = conv1x1(in_planes =input,out_channels=128,stride=0, padding=1)
self.conv1x7 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=128,out_channels=160,kernel_size=(1,7), padding=(0,3))
self.conv7x1 = nn.Conv2d(in_channels=160, out_channels=192,kernel_size=(7,1), padding=(3,0))
self.line = nn.Conv2d(384, 1152, 1, stride=1, padding=0, bias=True)
self.scale = scale
self.relu = nn.ReLU()
def forward(self, x):
c1 = self.conv1(x)
# print("c1",c1.shape)
c2 = self.conv2(x)
# print("c2", c2.shape)
c2_1 = self.conv1x7(c2)
# print("c2_1", c2_1.shape)
c2_1 = self.relu(c2_1)
c2_2 = self.conv7x1(c2_1)
# print("c2_2", c2_2.shape)
c2_2 = self.relu(c2_2)
cat = torch.cat([c1, c2_2], dim=1)
line = self.line(cat)
out =self.scale*x+line
out = self.relu(out)
# print("out", out.shape)
return out
Reduction-B模块:输入8\*8\*1792,输出8\*8\*1792.
为了做好运维面试路上的助攻手,特整理了上百道 **【运维技术栈面试题集锦】** ,让你面试不慌心不跳,高薪offer怀里抱!
这次整理的面试题,**小到shell、MySQL,大到K8s等云原生技术栈,不仅适合运维新人入行面试需要,还适用于想提升进阶跳槽加薪的运维朋友。**

本份面试集锦涵盖了
* **174 道运维工程师面试题**
* **128道k8s面试题**
* **108道shell脚本面试题**
* **200道Linux面试题**
* **51道docker面试题**
* **35道Jenkis面试题**
* **78道MongoDB面试题**
* **17道ansible面试题**
* **60道dubbo面试题**
* **53道kafka面试**
* **18道mysql面试题**
* **40道nginx面试题**
* **77道redis面试题**
* **28道zookeeper**
**总计 1000+ 道面试题, 内容 又全含金量又高**
* **174道运维工程师面试题**
> 1、什么是运维?
> 2、在工作中,运维人员经常需要跟运营人员打交道,请问运营人员是做什么工作的?
> 3、现在给你三百台服务器,你怎么对他们进行管理?
> 4、简述raid0 raid1raid5二种工作模式的工作原理及特点
> 5、LVS、Nginx、HAproxy有什么区别?工作中你怎么选择?
> 6、Squid、Varinsh和Nginx有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 7、Tomcat和Resin有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 8、什么是中间件?什么是jdk?
> 9、讲述一下Tomcat8005、8009、8080三个端口的含义?
> 10、什么叫CDN?
> 11、什么叫网站灰度发布?
> 12、简述DNS进行域名解析的过程?
> 13、RabbitMQ是什么东西?
> 14、讲一下Keepalived的工作原理?
> 15、讲述一下LVS三种模式的工作过程?
> 16、mysql的innodb如何定位锁问题,mysql如何减少主从复制延迟?
> 17、如何重置mysql root密码?
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取!](https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/4f45ff00ff254613a03fab5e56a57acb)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**
有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 7、Tomcat和Resin有什么区别,工作中你怎么选择?
> 8、什么是中间件?什么是jdk?
> 9、讲述一下Tomcat8005、8009、8080三个端口的含义?
> 10、什么叫CDN?
> 11、什么叫网站灰度发布?
> 12、简述DNS进行域名解析的过程?
> 13、RabbitMQ是什么东西?
> 14、讲一下Keepalived的工作原理?
> 15、讲述一下LVS三种模式的工作过程?
> 16、mysql的innodb如何定位锁问题,mysql如何减少主从复制延迟?
> 17、如何重置mysql root密码?
**网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。**
**[需要这份系统化的资料的朋友,可以点击这里获取!](https://bbs.csdn.net/forums/4f45ff00ff254613a03fab5e56a57acb)**
**一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!**






















 1311
1311

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








