APEX是英伟达开源的,完美支持PyTorch框架,用于改变数据格式来减小模型显存占用的工具。其中最有价值的是amp(Automatic Mixed Precision),将模型的大部分操作都用Float16数据类型测试,一些特别操作仍然使用Float32。并且用户仅仅通过三行代码即可完美将自己的训练代码迁移到该模型。实验证明,使用Float16作为大部分操作的数据类型,并没有降低参数,在一些实验中,反而由于可以增大Batch size,带来精度上的提升,以及训练速度上的提升。
3.2.1 下载apex库
网址 https://github.com/NVIDIA/apex,下载到本地文件夹。解压后进入到apex的目录安装依赖。在执行命令;
cd C:\Users\WH\Downloads\apex-master #进入apex目录
pip install -r requirements.txt
3.2.2 安装apex库
依赖安装完后,打开cmd,cd进入到刚刚下载完的apex-master路径下,运行:
python setup.py install
然后跑了一堆东西,最后是这样的:
安装完成!
fvcore库的简介
fvcore是一个轻量级的核心库,它提供了在各种计算机视觉框架(如Detectron2)中共享的最常见和最基本的功能。这个库基于Python 3.6+和PyTorch。这个库中的所有组件都经过了类型注释、测试和基准测试。Facebook 的人工智能实验室即FAIR的计算机视觉组负责维护这个库。
github地址:https://github.com/facebookresearch/fvcore
执行命令
conda install -c fvcore -c iopath -c conda-forge fvcore
安装pycocotools
pip install pycocotools
安装cv2
pip install opencv-python
安装 antlr4
pip install antlr4-python3-runtime
安装future
pip install future
安装protobuf
pip install protobuf
安装absl
pip install absl-py
安装tensorboard
pip install tensorboard
安装pydot
pip install pydot
安装scipy
pip install scipy -i https://pypi.tuna.tsinghua.edu.cn/simple
进入Sparse R-CNN目录,目录根据自己的实际情况更改。
cd D:\SparseR-CNN-main
编译Detectron2和Sparse R-CNN
python setup.py build develop
看到如下信息,则表明安装完成,如果缺少库的情况,则需要安装库,再编译,直到编译成功!
=================================================================
新建input_img和output_img文件夹,imgs文件夹存放待测试的图片。
图片如下:

下载模型“r50_100pro_3x_model.pth”(注:如果不能下载,关注我的公众号获取连接。),将其放到“projects/SparseRCNN”目录下面。
执行命令:
python demo/demo.py --config-file projects/SparseRCNN/configs/sparsercnn.res50.100pro.3x.yaml --input imgs/*.jpg --output imgout --opts MODEL.WEIGHTS projects/SparseRCNN/r50_100pro_3x_model.pth
运行结果:
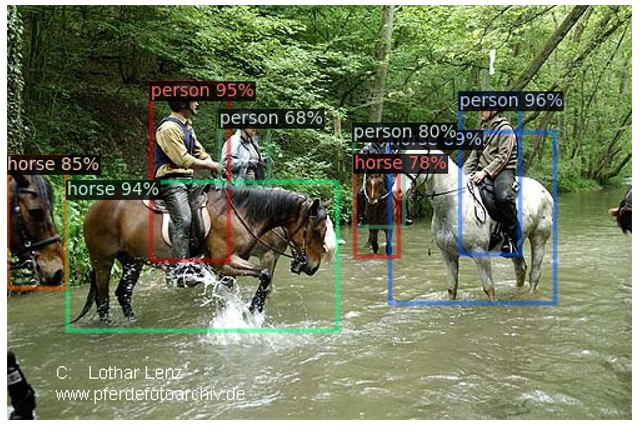
能够运行demo说明环境已经没有问题了。
==================================================================
本次采用的数据集是Labelme标注的数据集,地址:链接:https://pan.baidu.com/s/1nxo9-NpNWKK4PwDZqwKxGQ 提取码:kp4e,需要将其转为COCO格式的数据集。转换代码如下:
新建labelme2coco.py
import argparse
import json
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import skimage.io as io
import cv2
from labelme import utils
import numpy as np
import glob
import PIL.Image
REQUIRE_MASK = False
labels = {‘aircraft’: 1, ‘oiltank’: 2}
class labelme2coco(object):
def init(self, labelme_json=[], save_json_path=‘./new.json’):
‘’’
:param labelme_json: the list of all labelme json file paths
:param save_json_path: the path to save new json
‘’’
self.labelme_json = labelme_json
self.save_json_path = save_json_path
self.images = []
self.categories = []
self.annotations = []
self.data_coco = {}
self.label = []
self.annID = 1
self.height = 0
self.width = 0
self.require_mask = REQUIRE_MASK
self.save_json()
def data_transfer(self):
for num, json_file in enumerate(self.labelme_json):
if not json_file == self.save_json_path:
with open(json_file, ‘r’) as fp:
data = json.load(fp)
self.images.append(self.image(data, num))
for shapes in data[‘shapes’]:
print("label is ")
print(shapes[‘label’])
label = shapes[‘label’]
if label[1] not in self.label:
if label not in self.label:
print("find new category: ")
self.categories.append(self.categorie(label))
print(self.categories)
self.label.append(label[1])
self.label.append(label)
points = shapes[‘points’]
self.annotations.append(self.annotation(points, label, num))
self.annID += 1
def image(self, data, num):
image = {}
img = utils.img_b64_to_arr(data[‘imageData’])
height, width = img.shape[:2]
img = None
image[‘height’] = height
image[‘width’] = width
image[‘id’] = num + 1
image[‘file_name’] = data[‘imagePath’].split(‘/’)[-1]
self.height = height
self.width = width
return image
def categorie(self, label):
categorie = {}
categorie[‘supercategory’] = label
categorie[‘supercategory’] = label
categorie[‘id’] = labels[label] # 0 默认为背景
categorie[‘name’] = label
return categorie
def annotation(self, points, label, num):
annotation = {}
print(points)
x1 = points[0][0]
y1 = points[0][1]
x2 = points[1][0]
y2 = points[1][1]
contour = np.array([[x1, y1], [x2, y1], [x2, y2], [x1, y2]]) # points = [[x1, y1], [x2, y2]] for rectangle
contour = contour.astype(int)
area = cv2.contourArea(contour)
print("contour is ", contour, " area = ", area)
annotation[‘segmentation’] = [list(np.asarray([[x1, y1], [x2, y1], [x2, y2], [x1, y2]]).flatten())]
[list(np.asarray(contour).flatten())]
annotation[‘iscrowd’] = 0
annotation[‘area’] = area
annotation[‘image_id’] = num + 1
if self.require_mask:
annotation[‘bbox’] = list(map(float, self.getbbox(points)))
else:
x1 = points[0][0]
y1 = points[0][1]
width = points[1][0] - x1
height = points[1][1] - y1
annotation[‘bbox’] = list(np.asarray([x1, y1, width, height]).flatten())
annotation[‘category_id’] = self.getcatid(label)
annotation[‘id’] = self.annID
return annotation
def getcatid(self, label):
for categorie in self.categories:
if label[1]==categorie[‘name’]:
if label == categorie[‘name’]:
return categorie[‘id’]
return -1
def getbbox(self, points):
polygons = points
mask = self.polygons_to_mask([self.height, self.width], polygons)
return self.mask2box(mask)
def mask2box(self, mask):
np.where(mask==1)
index = np.argwhere(mask == 1)
rows = index[:, 0]
clos = index[:, 1]
left_top_r = np.min(rows) # y
left_top_c = np.min(clos) # x
right_bottom_r = np.max(rows)
right_bottom_c = np.max(clos)
return [left_top_c, left_top_r, right_bottom_c - left_top_c, right_bottom_r - left_top_r]
def polygons_to_mask(self, img_shape, polygons):
mask = np.zeros(img_shape, dtype=np.uint8)
mask = PIL.Image.fromarray(mask)
xy = list(map(tuple, polygons))
PIL.ImageDraw.Draw(mask).polygon(xy=xy, outline=1, fill=1)
mask = np.array(mask, dtype=bool)
return mask
def data2coco(self):
data_coco = {}
data_coco[‘images’] = self.images
data_coco[‘categories’] = self.categories
data_coco[‘annotations’] = self.annotations
return data_coco
def save_json(self):
print(“in save_json”)
self.data_transfer()
self.data_coco = self.data2coco()
print(self.save_json_path)
json.dump(self.data_coco, open(self.save_json_path, ‘w’), indent=4)
labelme_json = glob.glob(‘LabelmeData/*.json’)
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
trainval_files, test_files = train_test_split(labelme_json, test_size=0.2, random_state=55)
import os
if not os.path.exists(“projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/annotations”):
os.makedirs(“projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/annotations/”)
if not os.path.exists(“projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/train2017”):
os.makedirs(“projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/train2017”)
if not os.path.exists(“projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/val2017”):
os.makedirs(“projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/val2017”)
labelme2coco(trainval_files, ‘projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/annotations/instances_train2017.json’)
labelme2coco(test_files, ‘projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/annotations/instances_val2017.json’)
import shutil
for file in trainval_files:
shutil.copy(os.path.splitext(file)[0] + “.jpg”, “projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/train2017/”)
for file in test_files:
shutil.copy(os.path.splitext(file)[0] + “.jpg”, “projects/SparseRCNN/datasets/coco/val2017/”)
===================================================================
在projects/SparseRCNN目录,新建change_model_size.py文件
import torch
import numpy as np
import pickle
num_class = 2
pretrained_weights = torch.load(‘r50_100pro_3x_model.pth’)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.0.class_logits.weight”].resize_(num_class,256)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.0.class_logits.bias”].resize_(num_class)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.1.class_logits.weight”].resize_(num_class,256)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.1.class_logits.bias”].resize_(num_class)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.2.class_logits.weight”].resize_(num_class,256)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.2.class_logits.bias”].resize_(num_class)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.3.class_logits.weight”].resize_(num_class,256)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.3.class_logits.bias”].resize_(num_class)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.4.class_logits.weight”].resize_(num_class,256)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.4.class_logits.bias”].resize_(num_class)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.5.class_logits.weight”].resize_(num_class,256)
pretrained_weights[“head.head_series.5.class_logits.bias”].resize_(num_class)
torch.save(pretrained_weights, “model_%d.pth”%num_class)
这个文件的目的是修改模型输出的size,numclass按照本次打算训练的数据集的类别设置。
文末有福利领取哦~
👉一、Python所有方向的学习路线
Python所有方向的技术点做的整理,形成各个领域的知识点汇总,它的用处就在于,你可以按照上面的知识点去找对应的学习资源,保证自己学得较为全面。
👉二、Python必备开发工具
👉三、Python视频合集
观看零基础学习视频,看视频学习是最快捷也是最有效果的方式,跟着视频中老师的思路,从基础到深入,还是很容易入门的。
👉 四、实战案例
光学理论是没用的,要学会跟着一起敲,要动手实操,才能将自己的所学运用到实际当中去,这时候可以搞点实战案例来学习。(文末领读者福利)
👉五、Python练习题
检查学习结果。

👉六、面试资料
我们学习Python必然是为了找到高薪的工作,下面这些面试题是来自阿里、腾讯、字节等一线互联网大厂最新的面试资料,并且有阿里大佬给出了权威的解答,刷完这一套面试资料相信大家都能找到满意的工作。
👉因篇幅有限,仅展示部分资料,这份完整版的Python全套学习资料已经上传
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!






















 1307
1307











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








