IMS初始化流程:
IMS启动流程:
IMS问题复盘:
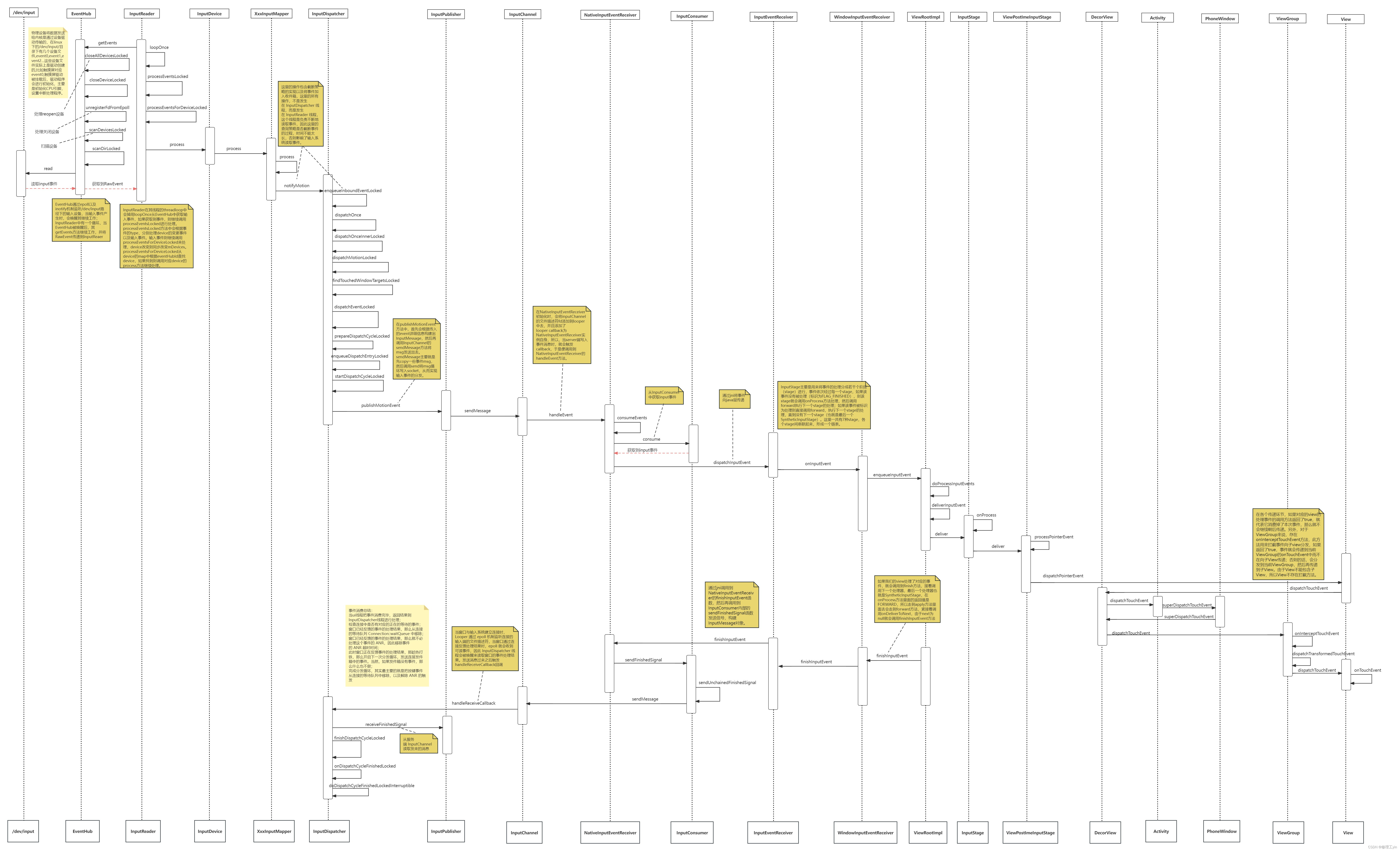
由于流程比较繁杂,这里可以先看下input事件分发时序图,了解下大致流程:
InputChannel创建时序图:

server端inputChannel注册时序图:
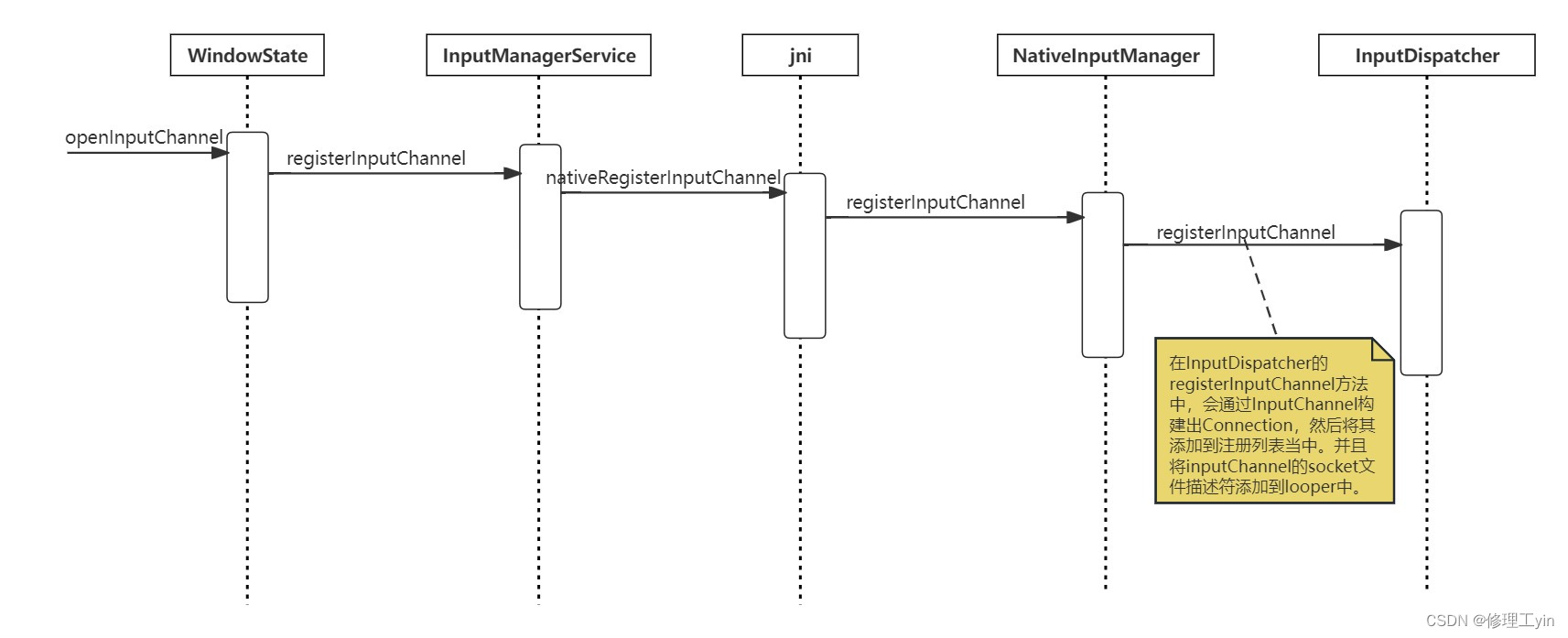
InputChannel的创建与初始化详细流程见第5节
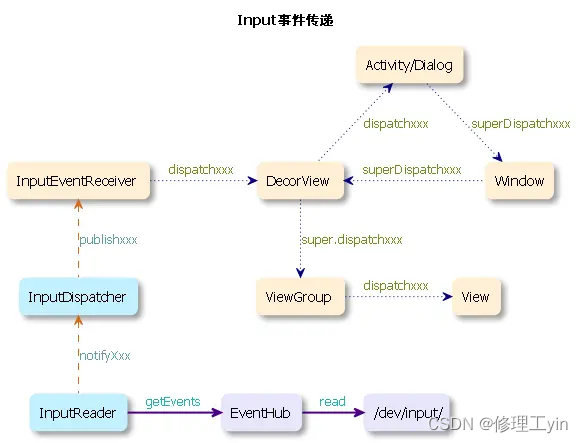
input事件分发流程
这里选择从底层开始分析,当手指放到屏幕上,硬件接收到电容信号,由kernel层去将这一系列的事件添加到/dev/input下作为不同的fd,再封装到eventhub库里面。
通过getevent命令我们也能看到/dev/input是否有对应的事件,或者dump input信息。
1. EventHub.getEvents获取事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/EventHub.cpp
ize_t EventHub::getEvents(int timeoutMillis, RawEvent* buffer, size_t bufferSize) {
..............
for (;;) {
nsecs_t now = systemTime(SYSTEM_TIME_MONOTONIC);
// Reopen input devices if needed.
if (mNeedToReopenDevices) {
mNeedToReopenDevices = false;
ALOGI("Reopening all input devices due to a configuration change.");
// 如果存在需要reopen的设备,则先关闭所有device
closeAllDevicesLocked();
// 然后设置需要scan设备的标识
mNeedToScanDevices = true;
break; // return to the caller before we actually rescan
}
// Report any devices that had last been added/removed.
// 如果存在需要关闭的设备,则遍历所有需要关闭的设备链表,
// 删除对应的device,并构建event
while (mClosingDevices) {
Device* device = mClosingDevices;
ALOGV("Reporting device closed: id=%d, name=%s\n", device->id, device->path.c_str());
mClosingDevices = device->next;
event->when = now;
event->deviceId = (device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId)
? ReservedInputDeviceId::BUILT_IN_KEYBOARD_ID
: device->id;
event->type = DEVICE_REMOVED;
event += 1;
delete device;
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
// 需要扫描device,则调用scanDevicesLocked方法扫描
// 最后更新device列表
if (mNeedToScanDevices) {
mNeedToScanDevices = false;
scanDevicesLocked();
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
}
//存在需要open的device,则更新mOpeningDevices链表
// 并构建event
while (mOpeningDevices != nullptr) {
Device* device = mOpeningDevices;
ALOGV("Reporting device opened: id=%d, name=%s\n", device->id, device->path.c_str());
mOpeningDevices = device->next;
event->when = now;
event->deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
event->type = DEVICE_ADDED;
event += 1;
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = true;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
// 需要scanFinish事件,则构建对应event
if (mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan) {
mNeedToSendFinishedDeviceScan = false;
event->when = now;
event->type = FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN;
event += 1;
if (--capacity == 0) {
break;
}
}
// Grab the next input event.
bool deviceChanged = false;
// 遍历需要处理的事件列表
while (mPendingEventIndex < mPendingEventCount) {
const struct epoll_event& eventItem = mPendingEventItems[mPendingEventIndex++];
// 如果是inotify事件,则修改对应标识,后面会扫描处理对于的变更
if (eventItem.data.fd == mINotifyFd) {
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
mPendingINotify = true;
} else {
ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for INotify.", eventItem.events);
}
continue;
}
// 管道事件,则设置wake为true,跳出循环继续执行
if (eventItem.data.fd == mWakeReadPipeFd) {
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
ALOGV("awoken after wake()");
// 标识被唤醒,后面epoll就不会进入wait状态
awoken = true;
char buffer[16];
ssize_t nRead;
do {
// 从管道中读取出消息内容
nRead = read(mWakeReadPipeFd, buffer, sizeof(buffer));
} while ((nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR) || nRead == sizeof(buffer));
} else {
ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for wake read pipe.",
eventItem.events);
}
continue;
}
...........................
// This must be an input event
// 真正的输入事件
if (eventItem.events & EPOLLIN) {
// 从device中读取出事件内容
int32_t readSize =
read(device->fd, readBuffer, sizeof(struct input_event) * capacity);
if (readSize == 0 || (readSize < 0 && errno == ENODEV)) {
// Device was removed before INotify noticed.
ALOGW("could not get event, removed? (fd: %d size: %" PRId32
" bufferSize: %zu capacity: %zu errno: %d)\n",
device->fd, readSize, bufferSize, capacity, errno);
// 出错,则关闭对应device,并标识设备发生变更
deviceChanged = true;
closeDeviceLocked(device);
} else if (readSize < 0) {
if (errno != EAGAIN && errno != EINTR) {
ALOGW("could not get event (errno=%d)", errno);
}
} else if ((readSize % sizeof(struct input_event)) != 0) {
ALOGE("could not get event (wrong size: %d)", readSize);
} else {
// 获取deviceId
int32_t deviceId = device->id == mBuiltInKeyboardId ? 0 : device->id;
// 遍历读取到的所有event,并构建出RawEvent
size_t count = size_t(readSize) / sizeof(struct input_event);
for (size_t i = 0; i < count; i++) {
struct input_event& iev = readBuffer[i];
event->when = processEventTimestamp(iev);
event->deviceId = deviceId;
event->type = iev.type;
event->code = iev.code;
event->value = iev.value;
event += 1;
capacity -= 1;
}
// 如果buffer满了,则break掉
if (capacity == 0) {
// The result buffer is full. Reset the pending event index
// so we will try to read the device again on the next iteration.
mPendingEventIndex -= 1;
break;
}
}
} else if (eventItem.events & EPOLLHUP) {
ALOGI("Removing device %s due to epoll hang-up event.",
device->identifier.name.c_str());
deviceChanged = true;
closeDeviceLocked(device);
} else {
ALOGW("Received unexpected epoll event 0x%08x for device %s.", eventItem.events,
device->identifier.name.c_str());
}
}
// readNotify() will modify the list of devices so this must be done after
// processing all other events to ensure that we read all remaining events
// before closing the devices.
if (mPendingINotify && mPendingEventIndex >= mPendingEventCount) {
// 标识已经处理过
mPendingINotify = false;
// 处理inotify事件
readNotifyLocked();
deviceChanged = true;
}
// Report added or removed devices immediately.
if (deviceChanged) {
continue;
}
// Return now if we have collected any events or if we were explicitly awoken.
if (event != buffer || awoken) {
break;
}
...............
// 开始wait时释放锁
mLock.unlock(); // release lock before poll
// epoll等待唤醒
int pollResult = epoll_wait(mEpollFd, mPendingEventItems, EPOLL_MAX_EVENTS, timeoutMillis);
// 唤醒开始执行时则加锁
mLock.lock(); // reacquire lock after poll
}
// All done, return the number of events we read.
return event - buffer;
}getEvents函数主要作用:
- 查看是否有需要reopen的device并进行处理,接着处理需要close的device,然后是判断是否需要扫描设备并进行device扫描。
- 处理新接入的设备,然后开始遍历待处理的事件,并分别处理inotify、管道以及真正的输入事件。
- 过程中如果有event被处理则就会break掉for循环继续进行下一次处理,如果所有事件都已处理完就会走到下面的epoll_wait进入wait状态等待唤醒
- 当driver向特定描述符写入事件后,会触发唤醒epoll起来工作,这时候eventHub通过read方法从描述符中读取原始事件,然后通过简单封装成rawEvent并传递给InputReader。
- 返回给InputReader的值就是event - buffer的差值,这个值就是rawEvent类型的。
2. InputReader处理事件
InputDispatcher中的事件是从InputReader中来的,InputReader从EventHub中获取到输入事件后,会通过调用InputDispatcher的notifyXxx方法来将事件传递到InuptDispatcher中。
InputReader在其线程的threadLoop中会调用loopOnce从EventHub中获取输入事件,如果获取到事件,则继续调用processEventsLocked进行处理。接着会调用到InputDevice -> InputMapper -> InputDispatcher(InputListenerInterface),在InputDispatcher中触发notifyXxx方法,从而将事件分发出去。
2.1 InputReader.loopOnce
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::loopOnce() {
int32_t oldGeneration;
int32_t timeoutMillis;
bool inputDevicesChanged = false;
std::vector<InputDeviceInfo> inputDevices;
...................
// 从EventHub中获取事件
size_t count = mEventHub->getEvents(timeoutMillis, mEventBuffer, EVENT_BUFFER_SIZE);
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(mLock);
mReaderIsAliveCondition.broadcast();
if (count) {
// 获取到输入事件则调用processEventsLocked进行处理
processEventsLocked(mEventBuffer, count);
}
..............
} // release lock
}
processEventsLocked方法中会根据事件的type,分别处理device的变更事件以及输入事件。输入事件则继续调用processEventsForDeviceLocked来处理,device改变则同步改变mDevices。
2.2 InputReader.processEventsLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsLocked(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count;) {
int32_t type = rawEvent->type;
size_t batchSize = 1;
if (type < EventHubInterface::FIRST_SYNTHETIC_EVENT) {
......................
#if DEBUG_RAW_EVENTS
ALOGD("BatchSize: %zu Count: %zu", batchSize, count);
#endif
// 这里事件类型如果不是device change事件则继续处理
processEventsForDeviceLocked(deviceId, rawEvent, batchSize);
} else {
switch (rawEvent->type) {
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_ADDED:
// device接入,将device添加到全局map中(mDevices)
addDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::DEVICE_REMOVED:// device断开
removeDeviceLocked(rawEvent->when, rawEvent->deviceId);
break;
case EventHubInterface::FINISHED_DEVICE_SCAN:
handleConfigurationChangedLocked(rawEvent->when);
break;
default:
ALOG_ASSERT(false); // can't happen
break;
}
}
count -= batchSize;
rawEvent += batchSize;
}
}processEventsForDeviceLocked中从device的map中根据eventHubId查找device,如果找到则调用对应device的process方法继续处理。
2.3 InputReader.processEventsForDeviceLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::processEventsForDeviceLocked(int32_t eventHubId, const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
// 通过eventHubId从map中查找InputDevice
auto deviceIt = mDevices.find(eventHubId);
if (deviceIt == mDevices.end()) {
// 没有对应的device则直接返回
ALOGW("Discarding event for unknown eventHubId %d.", eventHubId);
return;
}
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice>& device = deviceIt->second;
// device被忽略则返回
if (device->isIgnored()) {
// ALOGD("Discarding event for ignored deviceId %d.", deviceId);
return;
}
// 调用InputDevice的process继续处理事件
device->process(rawEvents, count);
}InputDevice的process中会遍历所有的event,并且根据event中的deviceId从mDevices中找到对应的device,然后遍历其所有的InputMapper,并调用mapper的process进行事件处理。
2.4 InputDevice.process
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputDevice.cpp
void InputDevice::process(const RawEvent* rawEvents, size_t count) {
// Process all of the events in order for each mapper.
// We cannot simply ask each mapper to process them in bulk because mappers may
// have side-effects that must be interleaved. For example, joystick movement events and
// gamepad button presses are handled by different mappers but they should be dispatched
// in the order received.
for (const RawEvent* rawEvent = rawEvents; count != 0; rawEvent++) {
.....................
if (mDropUntilNextSync) {
.............
// 从devices中找到对应的device,然后遍历其所有inputMapper,并调用其process方法进行处理
for_each_mapper_in_subdevice(rawEvent->deviceId, [rawEvent](InputMapper& mapper)
mapper.process(rawEvent);
});
}
--count;
}
}2.5 InputDevice.for_each_mapper_in_subdevice
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/include/InputDevice.h
// run a function against every mapper on a specific subdevice
inline void for_each_mapper_in_subdevice(int32_t eventHubDevice,
std::function<void(InputMapper&)> f) {
auto deviceIt = mDevices.find(eventHubDevice);
// 查找对应的device
if (deviceIt != mDevices.end()) {
auto& devicePair = deviceIt->second;
auto& mappers = devicePair.second;
// 遍历该device的所有InputMapper,并调用函数指针f
for (auto& mapperPtr : mappers) {
f(*mapperPtr);
}
}
}2.6 InputReader.addDeviceLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
void InputReader::addDeviceLocked(nsecs_t when, int32_t eventHubId) {
// 根据eventHubId查找device
if (mDevices.find(eventHubId) != mDevices.end()) {
ALOGW("Ignoring spurious device added event for eventHubId %d.", eventHubId);
return;
}
InputDeviceIdentifier identifier = mEventHub->getDeviceIdentifier(eventHubId);
// 创建device
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> device = createDeviceLocked(eventHubId, identifier);
device->configure(when, &mConfig, 0);
device->reset(when);
.................
}InputMapper在InputReader中处理device接入事件触发时会调用addDeviceLocked方法。
2.7 InputReader.createDeviceLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputReader.cpp
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> InputReader::createDeviceLocked(
int32_t eventHubId, const InputDeviceIdentifier& identifier) {
...................
std::shared_ptr<InputDevice> device;
if (deviceIt != mDevices.end()) {
// 如果device已经存在则直接返回
device = deviceIt->second;
} else {
// 否则创建出对应的InputDevice
int32_t deviceId = (eventHubId < END_RESERVED_ID) ? eventHubId : nextInputDeviceIdLocked();
device = std::make_shared<InputDevice>(&mContext, deviceId, bumpGenerationLocked(),
identifier);
}
// 调用addEventHubDevice,构建出相应的mapper
device->addEventHubDevice(eventHubId);
return device;
}调用到createDeviceLocked方法来创建出对应的InputDevice,创建出device后,便调用它的addEventHubDevice来创建出相应的InputMapper并添加到全局map中。
2.8 InputDevice.addEventHubDevice
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/InputDevice.cpp
void InputDevice::addEventHubDevice(int32_t eventHubId, bool populateMappers) {
if (mDevices.find(eventHubId) != mDevices.end()) {
return;
}
std::unique_ptr<InputDeviceContext> contextPtr(new InputDeviceContext(*this, eventHubId));
uint32_t classes = contextPtr->getDeviceClasses();
std::vector<std::unique_ptr<InputMapper>> mappers;
// Check if we should skip population
if (!populateMappers) {
mDevices.insert({eventHubId, std::make_pair(std::move(contextPtr), std::move(mappers))});
return;
}
// Switch-like devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_SWITCH) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<SwitchInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// Scroll wheel-like devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ROTARY_ENCODER) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<RotaryEncoderInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// Vibrator-like devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_VIBRATOR) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<VibratorInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// Keyboard-like devices.
uint32_t keyboardSource = 0;
int32_t keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_NON_ALPHABETIC;
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_KEYBOARD) {
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_KEYBOARD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_ALPHAKEY) {
keyboardType = AINPUT_KEYBOARD_TYPE_ALPHABETIC;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_DPAD) {
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_DPAD;
}
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_GAMEPAD) {
keyboardSource |= AINPUT_SOURCE_GAMEPAD;
}
if (keyboardSource != 0) {
mappers.push_back(
std::make_unique<KeyboardInputMapper>(*contextPtr, keyboardSource, keyboardType));
}
// Cursor-like devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_CURSOR) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<CursorInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// Touchscreens and touchpad devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH_MT) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<MultiTouchInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
} else if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_TOUCH) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<SingleTouchInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// Joystick-like devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_JOYSTICK) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<JoystickInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// External stylus-like devices.
if (classes & INPUT_DEVICE_CLASS_EXTERNAL_STYLUS) {
mappers.push_back(std::make_unique<ExternalStylusInputMapper>(*contextPtr));
}
// insert the context into the devices set
mDevices.insert({eventHubId, std::make_pair(std::move(contextPtr), std::move(mappers))});
}通过addEventHubDevice方法,可以看出针对不同的device类型,会构建出不同的mapper,最后将mapper数组添加到了mDevices的全局map中。
这里以对touch事件的处理为例,从上面的代码判断条件可以看出对于触摸类型的输入设备,如果设备支持多点触摸,它的触摸事件由 MultiTouchInputMapper 处理,而如果只支持单点触摸,它的触摸事件由 SingleTouchInputMapper 处理。现在的手机或者车机显示屏一般都是支持多点触摸的,所以直接看MultiTouchInputMapper 。
2.9 MultiTouchInputMapper.process
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/MultiTouchInputMapper.cpp
void MultiTouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
//调用父类处理同步事件(EV_SYN SYN_REPORT)
TouchInputMapper::process(rawEvent);
//使用累加器收集同步事件之前的每一个手指的触控点信息
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
}这里我们来看看一段在触摸屏上滑动手指所产生的触摸事件序列:
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 00000336
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 0000017f
/dev/input/event4: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 00000333
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000184
/dev/input/event4: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 0000032f
/dev/input/event4: EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000188
/dev/input/event4: EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000对于每一次的触摸事件,例如手指按下或者移动,驱动会先上报它的信息事件,例如 x, y 坐标事件,再加上一个同步事件(SYN_REPORT)。
对应的touch事件就会使用累加器MultiTouchMotionAccumulator 收集触摸事件的信息。
2.10 收集触摸事件信息
这里我们先理解下多点触摸协议是什么,多点触摸协议也就是 A / B 协议。A/B 协议也叫 slot 协议,下面简单介绍下这个协议。
当第一个手指按下时,会有如下事件序列:
//事件 ABS_MT_SLOT,表明触摸信息事件,是由哪个槽(slot)进行上报的。一个手指产生的触摸事件,只能由同一个槽进行上报。
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000000
//事件 ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID ,表示手指ID。手指 ID 才能唯一代表一个手指,槽的 ID 并不能代表一个手指。因为假如一个手指抬起,另外一个手指按下,这两个手指的事件可能由同一个槽进行上报,但是手指 ID 肯定是不一样的。
EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 00000000
//事件 ABS_MT_POSITION_X 和 ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 表示触摸点的 x, y 坐标值。
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 000002ea
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000534
//事件 SYN_REPORT 是同步事件,它表示系统需要同步并处理之前的事件。
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 当第一个手指移动时,会有如下事件:
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 000002ec
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000526
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 此时没有指定 ABS_MT_SLOT 事件和 ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 事件,默认使用前面的值,因为此时只有一个手指。
当第二个手指按下时,会有如下事件:
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000001
EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 00000001
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 00000470
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000475
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000第二个手指的事件,由另外一个槽进行上报。
当两个手指同时移动时,会有如下事件:
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000000
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 000004e0
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000001
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_X 0000046f
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 00000414
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 通过指定槽,就可以清晰看到事件由哪个槽进行上报,从而就可以区分出两个手指产生的事件。
当其中一个手指抬起时,会有如下事件:
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000000
// 注意,ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 的值为 -1
EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID ffffffff
EV_ABS ABS_MT_SLOT 00000001
EV_ABS ABS_MT_POSITION_Y 000003ee
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 当一个手指抬起时,ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 事件的值为 -1,也就是十六进制的 ffffffff。通过槽事件,可以知道是第一个手指抬起了。
如果最后一个手指也抬起了,会有如下事件:
EV_ABS ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID ffffffff
// 同步事件,不属于触摸事件
EV_SYN SYN_REPORT 00000000 通过 ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 事件可知,手指是抬起了,但是哪个手指抬起了呢?由于抬起的是最后一个手指,因此省略了槽事件。
现在让来看看累加器 MultiTouchMotionAccumulator 是如何收集这个协议上报的数据的:
2.10.1 MultiTouchMotionAccumulator.process
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/MultiTouchInputMapper.cpp
void MultiTouchMotionAccumulator::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
if (rawEvent->type == EV_ABS) {
bool newSlot = false;
if (mUsingSlotsProtocol) {
// slot协议,使用 ABS_MT_SLOT 事件获取索引
if (rawEvent->code == ABS_MT_SLOT) {
mCurrentSlot = rawEvent->value;
newSlot = true;
}
} else if (mCurrentSlot < 0) {
// 非slot协议 : 初始上报的事件,默认 slot 为 0
mCurrentSlot = 0;
}
if (mCurrentSlot < 0 || size_t(mCurrentSlot) >= mSlotCount) {
// ...
} else {
//根据索引,获取slot数组的元素,并填充信息
Slot* slot = &mSlots[mCurrentSlot];
if (!mUsingSlotsProtocol) {
slot->mInUse = true;
}
switch (rawEvent->code) {
case ABS_MT_POSITION_X:
slot->mAbsMTPositionX = rawEvent->value;
break;
case ABS_MT_POSITION_Y:
slot->mAbsMTPositionY = rawEvent->value;
break;
// ...
case ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID:
if (mUsingSlotsProtocol && rawEvent->value < 0) {
// The slot is no longer in use but it retains its previous contents,
// which may be reused for subsequent touches.
// slot协议: ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 事件的值小于0,表示当前 slot 不再使用。
slot->mInUse = false;
} else {
// slot协议 : ABS_MT_TRACKING_ID 事件的值为非负值,表示当前 slot 正在使用。
slot->mInUse = true;
slot->mAbsMTTrackingId = rawEvent->value;
}
break;
// ...
}
}
} else if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_MT_REPORT) {
// MultiTouch Sync: The driver has returned all data for *one* of the pointers.
// 非 slot协议 : EV_SYN + SYN_MT_REPORT 事件,分割手指的触控点信息
mCurrentSlot += 1;
}
}收集 slot 协议上报的数据的过程如下:
- 首先根据 ABS_MT_SLOT 事件,获取数组索引。如果上报的数据中没有指定 ABS_MT_SLOT 事件,那么默认用最近一次的 ABS_MT_SLOT 事件的值。
- 根据索引,从数组 mSlots 获取 Slot 元素,并填充数据。
就是用 Slot 数组的不同元素,收集不同手指所产生的事件信息。
2.11 TouchInputMapper.process处理同步事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::process(const RawEvent* rawEvent) {
//记录mouse或touch pad按键状态
mCursorButtonAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
//记录cursor scrolling motions
mCursorScrollAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
//记录touch、BTN_STYLUS、 tool buttons状态
mTouchButtonAccumulator.process(rawEvent);
// 处理同步事件
if (rawEvent->type == EV_SYN && rawEvent->code == SYN_REPORT) {
sync(rawEvent->when);
}
}
void TouchInputMapper::sync(nsecs_t when, nsecs_t readTime) {
// Push a new state.
// 添加一个空的元素
mRawStatesPending.emplace_back();
// 获取刚刚添加的元素
RawState& next = mRawStatesPending.back();
next.clear();
next.when = when;
next.readTime = readTime;
// ...
//同步累加器中的数据到 next 中
// syncTouch()由子类实现
syncTouch(when, &next);
// ...
// 处理数据
processRawTouches(false /*timeout*/);
}处理同步事件的过程如下:
- 调用 syncTouch() 把累加器收集到数据,同步到 mRawStatesPending 最后一个元素中。
- 同步过来的数据,基本上还是元数据,因此需要对它加工,最终要生成高级事件,并分发出去。
2.12 MultiTouchInputMapper.syncTouch
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/MultiTouchInputMapper.cpp
void MultiTouchInputMapper::syncTouch(nsecs_t when, RawState* outState) {
...........
for (size_t inIndex = 0; inIndex < inCount; inIndex++) {
// 从收集器中获取 Slot 数组的元素
const MultiTouchMotionAccumulator::Slot* inSlot =
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.getSlot(inIndex);
// 如果 tracking id 为负值,槽就会不再使用
if (!inSlot->isInUse()) {
continue;
}
.................
// 把累加器的Slot数组的数据同步到 RawState::rawPointerData 中
RawPointerData::Pointer& outPointer = outState->rawPointerData.pointers[outCount];
..................
// Assign pointer id using tracking id if available.
if (mHavePointerIds) {
int32_t trackingId = inSlot->getTrackingId();
int32_t id = -1;
// 把 tracking id 转化为 id
if (trackingId >= 0) {
// mPointerIdBits 保存的是手指的所有 id
// mPointerTrackingIdMap 是建立 id 到 trackingId 的映射
// 这里就是根据 trackingId 找到 id
for (BitSet32 idBits(mPointerIdBits); !idBits.isEmpty();) {
uint32_t n = idBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
if (mPointerTrackingIdMap[n] == trackingId) {
id = n;
}
}
// id < 0 表示从缓存中,根据 trackingId, 没有获取到 id
if (id < 0 && !mPointerIdBits.isFull()) {
// 从 mPointerIdBits 生成一个 id
id = mPointerIdBits.markFirstUnmarkedBit();
// mPointerTrackingIdMap 建立 id 到 trackingId 映射
mPointerTrackingIdMap[id] = trackingId;
}
}
// id < 0,表示手指抬起
if (id < 0) {
mHavePointerIds = false;
// 清除对应的数据
outState->rawPointerData.clearIdBits();
newPointerIdBits.clear();
} else { // 有 id
// 保存id
outPointer.id = id;
// 保存 id -> index 映射
// index 是数组 RawPointerData::pointers 的索引
outState->rawPointerData.idToIndex[id] = outCount;
outState->rawPointerData.markIdBit(id, isHovering);
newPointerIdBits.markBit(id);
}
}
outCount += 1;
}
// 保存手指的数量
outState->rawPointerData.pointerCount = outCount;
// 保存所有的手指 id
mPointerIdBits = newPointerIdBits;
// 对于 SLOT 协议,同步的收尾工作不做任何事
mMultiTouchMotionAccumulator.finishSync();
}累加器收集的数据是由驱动直接上报的元数据,这里把元数据同步到 RawState::rawPointerData,它的类型为 RawPointerData ,结构体定义如下:
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.h
/* Raw data for a collection of pointers including a pointer id mapping table. */
struct RawPointerData {
struct Pointer {
uint32_t id; // 手指的 ID
int32_t x;
int32_t y;
// ...
};
// 手指的数量
uint32_t pointerCount;
// 用 Pointer 数组保存触摸事件的所有信息
Pointer pointers[MAX_POINTERS];
// touchingIdBits 保存所有手指的ID
BitSet32 hoveringIdBits, touchingIdBits, canceledIdBits;
// 建立手指ID到数组索引的映射
uint32_t idToIndex[MAX_POINTER_ID + 1];
// ...
};这里需要注意的是:
- 只有手指 ID 才能唯一代表一个手指。
- index 只能作为数据的索引,来获取手指的触摸事件信息。
- 如果你知道了手指ID,那么就可以通过 idToIndex 获取索引,然后根据索引获取手指对应的触摸事件信息。
2.13 TouchInputMapper.processRawTouches处理同步后的数据
现在数据已经同步到 mRawStatesPending 最后一个元素中,但是这些数据基本上是元数据,是比较晦涩的,接下来看看如何处理这些数据:
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::processRawTouches(bool timeout) {
............
// 现在开始处理同步过来的数据
const size_t N = mRawStatesPending.size();
size_t count;
for (count = 0; count < N; count++) {
// 获取数据
const RawState& next = mRawStatesPending[count];
...
//mCurrentRawState 保存当前正在处理的元数据
mCurrentRawState.copyFrom(next);
if (mCurrentRawState.when < mLastRawState.when) {
mCurrentRawState.when = mLastRawState.when;
mCurrentRawState.readTime = mLastRawState.readTime;
}
//加工以及分发
cookAndDispatch(mCurrentRawState.when, mCurrentRawState.readTime);
}
// 成功处理完数据,就从 mRawStatesPending 从擦除
if (count != 0) {
mRawStatesPending.erase(mRawStatesPending.begin(), mRawStatesPending.begin() + count);
}
......
}开始处理元数据之前,首先使用 mCurrentRawState 复制了当前正在处理的数据,后面会使用它进行前后两次的数据对比,生成高级事件,例如 DOWN, MOVE, UP 事件。
2.14 TouchInputMapper.cookAndDispatch对数据进行加工和分发
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::cookAndDispatch(nsecs_t when, nsecs_t readTime) {
// 加工完的数据保存到 mCurrentCookedState
mCurrentCookedState.clear();
................
//加工事件
cookPointerData();
..........
// 此时的 device mode 为 DIRECT,表示直接分发
if (mDeviceMode == DeviceMode::POINTER) {
.....
} else {
updateTouchSpots();
if (!mCurrentMotionAborted) {
dispatchButtonRelease(when, readTime, policyFlags);
dispatchHoverExit(when, readTime, policyFlags);
//2. 分发触摸事件
dispatchTouches(when, readTime, policyFlags);
dispatchHoverEnterAndMove(when, readTime, policyFlags);
dispatchButtonPress(when, readTime, policyFlags);
}
........
}
.........
// 保存上一次的元数据和上一次的加工后的数据
mLastRawState.copyFrom(mCurrentRawState);
mLastCookedState.copyFrom(mCurrentCookedState);
}加工和分发事件的过程如下:
- 使用 cookPointerData() 进行加工事件。加工什么呢?例如,由于手指是在输入设备上触摸的,因此需要把输入设备的坐标转换为显示屏的坐标,这样窗口就能接收到正确的坐标事件。
- 使用 dispatchTouches() 进行分发事件。底层上报的数据毕竟晦涩难懂,因此需要包装成 DOWN/MOVE/UP 事件进行分发
2.15 TouchInputMapper.cookPointerData加工数据
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::cookPointerData() {
........
// Walk through the the active pointers and map device coordinates onto
// surface coordinates and adjust for display orientation.
for (uint32_t i = 0; i < currentPointerCount; i++) {
const RawPointerData::Pointer& in = mCurrentRawState.rawPointerData.pointers[i];
// Size
...
// Pressure
...
// Distance
...
// Coverage
...
// Adjust X,Y coords for device calibration
float xTransformed = in.x, yTransformed = in.y;
mAffineTransform.applyTo(xTransformed, yTransformed);
//把输入设备的坐标,转换为显示设备坐标
//转换后的坐标,保存到 xTransformed 和 yTransformed 中
rotateAndScale(xTransformed, yTransformed);
............省略若干代码...........
}
}加工的元数据保存到了 CookedState::cookedPointerData 中,它的类型为 CookedPointerData ,结构体定义如下:
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.h
struct CookedPointerData {
uint32_t pointerCount;
PointerProperties pointerProperties[MAX_POINTERS];
// 保存坐标数据
PointerCoords pointerCoords[MAX_POINTERS];
BitSet32 hoveringIdBits, touchingIdBits, canceledIdBits, validIdBits;
uint32_t idToIndex[MAX_POINTER_ID + 1];
...
};2.16 TouchInputMapper.rotateAndScale坐标点转换
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
// Transform raw coordinate to surface coordinate
void TouchInputMapper::rotateAndScale(float& x, float& y) {
// Scale to surface coordinate.
//根据x,y的缩放比例,计算触摸点在显示设备的缩放坐标
const float xScaled = float(x - mRawPointerAxes.x.minValue) * mXScale;
const float yScaled = float(y - mRawPointerAxes.y.minValue) * mYScale;
const float xScaledMax = float(mRawPointerAxes.x.maxValue - x) * mXScale;
const float yScaledMax = float(mRawPointerAxes.y.maxValue - y) * mYScale;
// Rotate to surface coordinate.
// 0 - no swap and reverse.
// 90 - swap x/y and reverse y.
// 180 - reverse x, y.
// 270 - swap x/y and reverse x.
// 根据旋转方向计算最终的显示设备的x,y坐标值
switch (mSurfaceOrientation) {
case DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_0:
x = xScaled + mXTranslate;
y = yScaled + mYTranslate;
break;
case DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_90:
y = xScaledMax - (mRawSurfaceWidth - mSurfaceRight);
x = yScaled + mYTranslate;
break;
case DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_180:
x = xScaledMax - (mRawSurfaceWidth - mSurfaceRight);
y = yScaledMax - (mRawSurfaceHeight - mSurfaceBottom);
break;
case DISPLAY_ORIENTATION_270:
y = xScaled + mXTranslate;
x = yScaledMax - (mRawSurfaceHeight - mSurfaceBottom);
break;
default:
assert(false);
}
}主要过程如下:
- 首先根据坐标轴的缩放比例 mXScale 和 mYScale,计算触摸屏的坐标点在显示屏的坐标系中的x, y轴的缩放值。
- 根据显示屏 x, y 轴的偏移量,以及旋转角度,最终计算出显示屏上的坐标点。
2.17 TouchInputMapper.dispatchTouches分发事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchTouches(nsecs_t when, nsecs_t readTime, uint32_t policyFlags) {
........
if (currentIdBits == lastIdBits) {
if (!currentIdBits.isEmpty()) {
// No pointer id changes so this is a move event.
// The listener takes care of batching moves so we don't have to deal with that here.
// 如果前后两次数据的手指数没有变化,并且当前的手指数不为0,那么此时事件肯定是移动事件,需要分发 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE 事件
dispatchMotion(when, readTime, policyFlags, mSource, AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE, 0, 0,
metaState, buttonState, AMOTION_EVENT_EDGE_FLAG_NONE,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex, currentIdBits, -1,
mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
}
} else { // 前后两次数据的手指数不相等
// There may be pointers going up and pointers going down and pointers moving
// all at the same time.
BitSet32 upIdBits(lastIdBits.value & ~currentIdBits.value);
BitSet32 downIdBits(currentIdBits.value & ~lastIdBits.value);
BitSet32 moveIdBits(lastIdBits.value & currentIdBits.value);
BitSet32 dispatchedIdBits(lastIdBits.value);
// Update last coordinates of pointers that have moved so that we observe the new
// pointer positions at the same time as other pointers that have just gone up.
// 参数 moveIdBits 表示有移动的手指,这里检测移动的手指,前后两次数据有变化,那么表示需要分发一个移动事件
bool moveNeeded =
updateMovedPointers(mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex, moveIdBits);
if (buttonState != mLastCookedState.buttonState) {
moveNeeded = true;
}
// Dispatch pointer up events.
while (!upIdBits.isEmpty()) {
........
// 有手指抬起,分发 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP 事件
dispatchMotion(when, readTime, policyFlags, mSource, AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP, 0,
isCanceled ? AMOTION_EVENT_FLAG_CANCELED : 0, metaState, buttonState, 0,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mLastCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex, dispatchedIdBits, upId,
mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
dispatchedIdBits.clearBit(upId);
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.canceledIdBits.clearBit(upId);
}
// Dispatch move events if any of the remaining pointers moved from their old locations.
// Although applications receive new locations as part of individual pointer up
// events, they do not generally handle them except when presented in a move event.
// 如果移动的手指前后两次数据有变化,那么分发移动事件
if (moveNeeded && !moveIdBits.isEmpty()) {
ALOG_ASSERT(moveIdBits.value == dispatchedIdBits.value);
dispatchMotion(when, readTime, policyFlags, mSource, AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE, 0, 0,
metaState, buttonState, 0,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex, dispatchedIdBits, -1,
mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
}
// Dispatch pointer down events using the new pointer locations.
while (!downIdBits.isEmpty()) {
uint32_t downId = downIdBits.clearFirstMarkedBit();
dispatchedIdBits.markBit(downId);
if (dispatchedIdBits.count() == 1) {
// First pointer is going down. Set down time.
mDownTime = when;
}
// 有手指按下,分发 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN
dispatchMotion(when, readTime, policyFlags, mSource, AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN,
0, 0, metaState, buttonState, 0,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerProperties,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.pointerCoords,
mCurrentCookedState.cookedPointerData.idToIndex, dispatchedIdBits,
downId, mOrientedXPrecision, mOrientedYPrecision, mDownTime);
}
}
}分发事件的过程,其实就是对比前后两次的数据,生成高级事件 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN, AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_MOVE, AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP,然后调用 dispatchMotion() 分发这些高级事件。
2.18 TouchInputMapper.dispatchMotion分发高级事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/reader/mapper/TouchInputMapper.cpp
void TouchInputMapper::dispatchMotion(nsecs_t when, nsecs_t readTime, uint32_t policyFlags,
uint32_t source, int32_t action, int32_t actionButton,
int32_t flags, int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState,
int32_t edgeFlags, const PointerProperties* properties,
const PointerCoords* coords, const uint32_t* idToIndex,
BitSet32 idBits, int32_t changedId, float xPrecision,
float yPrecision, nsecs_t downTime) {
..........
// action 添加索引
// action 中前8位表示手指索引,后8位表示ACTION
if (changedId >= 0 && id == uint32_t(changedId)) {
action |= pointerCount << AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_INDEX_SHIFT;
}
pointerCount += 1;
}
ALOG_ASSERT(pointerCount != 0);
// 当只有一个手指按下,发送 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN 事件。
// 但最后一个手指抬起时,发送 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_UP 事件。
if (changedId >= 0 && pointerCount == 1) {
// Replace initial down and final up action.
// We can compare the action without masking off the changed pointer index
// because we know the index is 0.
if (action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN) {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;
} else if (action == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP) {
if ((flags & AMOTION_EVENT_FLAG_CANCELED) != 0) {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_CANCEL;
} else {
action = AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_UP;
}
} else {
// Can't happen.
ALOG_ASSERT(false);
}
}
...............
// 把数据包装成 NotifyMotionArgs,并加入到 QueuedInputListener 队列
NotifyMotionArgs args(getContext()->getNextId(), when, readTime, deviceId, source, displayId,
policyFlags, action, actionButton, flags, metaState, buttonState,
MotionClassification::NONE, edgeFlags, pointerCount, pointerProperties,
pointerCoords, xPrecision, yPrecision, xCursorPosition, yCursorPosition,
downTime, std::move(frames));
getListener()->notifyMotion(&args);
}可以看到,数据最终被包装成 NotifyMotionArgs 分发到下一环 InputClassifier。
但是,在这之前,还对 action 做了如下处理:
- 为 action 添加一个 index。由于 index 是元数据数组的索引,因此 action 也就是绑定了触摸事件的数据。
- 如果是第一个手指按下,把 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN 转换为 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN。
- 如果是最后一个手指抬起,把 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_UP 转换成 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_UP。
2.19 小结
- 首先每次一个touchEvent获取Slot,在没有收到EV_SYN之前对应的Slot都是相同的,然后依次处理x,y,pressure,touch_major,这些值初始化slot的各个变量。
- 当收到ev.type== EV_SYN并且ev.code = SYN_MT_REPORT那么当前的slot的index加1,给下一次触摸事件去记录,同时sync函数处理这次触摸事件。
- 然后调用cookAndDispatch、cookPointerData进行加工和分发数据,对应的不同事件,调用dispatchMotion生成高级事件,数据最终被包装成 NotifyMotionArgs 分发到,分发到InputDispatcher的notifyMotion。
3. InputDispatcher分发事件
第二章说到了InputReader 对触摸事件的处理流程,最终的结果是把触摸事件包装成 NotifyMotionArgs,然后加入到 QueuedInputListener 的缓存队列,QueuedInputListener 会把缓存队列中的所有事件,分发给 InputClassifier。
3.1 InputDispatcher.notifyMotion收到触摸事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::notifyMotion(const NotifyMotionArgs* args) {
if (!validateMotionEvent(args->action, args->actionButton, args->pointerCount,
args->pointerProperties)) {
return;
}
uint32_t policyFlags = args->policyFlags;
//来自InputReader/InputClassifier的 motion 事件,都是受信任的
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED;
android::base::Timer t;
// 对触摸事件执行截断策略
// 触摸事件入队前,查询截断策略,查询的结果保存到参数 policyFlags
mPolicy->interceptMotionBeforeQueueing(args->displayId, args->eventTime, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
if (t.duration() > SLOW_INTERCEPTION_THRESHOLD) {
ALOGW("Excessive delay in interceptMotionBeforeQueueing; took %s ms",
std::to_string(t.duration().count()).c_str());
}
bool needWake;
{ // acquire lock
mLock.lock();
if (shouldSendMotionToInputFilterLocked(args)) {
...
}
// 包装成 MotionEntry
// Just enqueue a new motion event.
std::unique_ptr<MotionEntry> newEntry =
std::make_unique<MotionEntry>(args->id, args->eventTime, args->deviceId,
args->source, args->displayId, policyFlags,
args->action, args->actionButton, args->flags,
args->metaState, args->buttonState,
args->classification, args->edgeFlags,
args->xPrecision, args->yPrecision,
args->xCursorPosition, args->yCursorPosition,
args->downTime, args->pointerCount,
args->pointerProperties, args->pointerCoords, 0, 0);
//把触摸事件加入收件箱
needWake = enqueueInboundEventLocked(std::move(newEntry));
mLock.unlock();
} // release lock
//如果有必要,唤醒线程处理触摸事件
if (needWake) {
mLooper->wake();
}
}3.2 NativeInputManager.interceptMotionBeforeQueueing截断策略查询
/frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
void NativeInputManager::interceptMotionBeforeQueueing(const int32_t displayId, nsecs_t when,
uint32_t& policyFlags) {
bool interactive = mInteractive.load();
if (interactive) {
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_INTERACTIVE;
}
// 受信任,并且是非注入的事件
if ((policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_TRUSTED) && !(policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_INJECTED)) {
if (policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_INTERACTIVE) {
// 设备处于交互状态下,受信任且非注入的事件,直接发送给用户,而不经过截断策略处理
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER;
} else {
// 只有设备处于非交互状态,触摸事件才需要执行截断策略
JNIEnv* env = jniEnv();
jint wmActions = env->CallIntMethod(mServiceObj,
gServiceClassInfo.interceptMotionBeforeQueueingNonInteractive,
displayId, when, policyFlags);
if (checkAndClearExceptionFromCallback(env,
"interceptMotionBeforeQueueingNonInteractive")) {
wmActions = 0;
}
handleInterceptActions(wmActions, when, /*byref*/ policyFlags);
}
} else { // 注入事件,或者不受信任事件
// 只有在交互状态下,才传递给用户
// 注意,这里还有另外一层意思: 非交互状态下,不发送给用户
if (interactive) {
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER;
}
}
}
void NativeInputManager::handleInterceptActions(jint wmActions, nsecs_t when,
uint32_t& policyFlags) {
if (wmActions & WM_ACTION_PASS_TO_USER) {
policyFlags |= POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER;
}
}一个触摸事件,必须满足下面三种情况,才执行截断策略:
- 触摸事件是受信任的。来自输入设备的触摸事件都是受信任的。
- 触摸事件是非注入的。monkey 的原理就是注入触摸事件,因此它的事件是不需要经过截断策略处理的。
- 设备处于非交互状态。一般来说,非交互状态指的就是显示屏处于灭屏状态。
另外还需要关注的是,事件在什么时候是不需要经过截断策略,有两种情况:
- 对于受信任且非注入的触摸事件,如果设备处于交互状态,直接发送给用户。 也就是说,如果显示屏处于亮屏状态,输入设备产生的触摸事件一定会发送给窗口。
- 对于不受信任,或者注入的触摸事件,如果设备处于交互状态,也是直接发送给用户。也就是说,如果显示屏处于亮屏状态,monkey 注入的触摸事件,也是直接发送给窗口的。
最后还要注意一件事,如果一个触摸事件是不受信任的事件,或者是注入事件,当设备处于非交互状态下(通常指灭屏),那么它不经过截断策略,也不会发送给用户,也就是会被丢弃。
在实际工作中处理的触摸事件,通常都是来自输入设备,它肯定是受信任的,而且非注入的,因此它只有在设备处于非交互状态下(一般指灭屏)下,非会执行截断策略,而如果设备处于交互状态(通常指亮屏),会被直接分发给窗口。
3.2.1 PhoneWindowManager.interceptMotionBeforeQueueingNonInteractive截断策略实现
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/policy/PhoneWindowManager.java
public int interceptMotionBeforeQueueingNonInteractive(int displayId, long whenNanos,
int policyFlags) {
// 如果策略要求唤醒屏幕,那么截断这个触摸事件
// 一般来说,唤醒屏幕的策略取决于设备的配置文件
if ((policyFlags & FLAG_WAKE) != 0) {
if (wakeUp(whenNanos / 1000000, mAllowTheaterModeWakeFromMotion,
PowerManager.WAKE_REASON_WAKE_MOTION, "android.policy:MOTION")) {
// 返回 0,表示截断触摸事件
return 0;
}
}
// 判断非交互状态下,是否截断事件
if (shouldDispatchInputWhenNonInteractive(displayId, KEYCODE_UNKNOWN)) {
// 返回这个值,表示不截断事件,也就是事件分发给用户
return ACTION_PASS_TO_USER;
}
// 忽略 theater mode
if (isTheaterModeEnabled() && (policyFlags & FLAG_WAKE) != 0) {
wakeUp(whenNanos / 1000000, mAllowTheaterModeWakeFromMotionWhenNotDreaming,
PowerManager.WAKE_REASON_WAKE_MOTION, "android.policy:MOTION");
}
// 默认截断触摸事件
// 返回0,表示截断事件
return 0;
}
private boolean shouldDispatchInputWhenNonInteractive(int displayId, int keyCode) {
// Apply the default display policy to unknown displays as well.
final boolean isDefaultDisplay = displayId == DEFAULT_DISPLAY
|| displayId == INVALID_DISPLAY;
final Display display = isDefaultDisplay
? mDefaultDisplay
: mDisplayManager.getDisplay(displayId);
final boolean displayOff = (display == null
|| display.getState() == STATE_OFF);
if (displayOff && !mHasFeatureWatch) {
return false;
}
// displayOff 表示屏幕处于 off 状态,但是非 off 状态,并不表示一定是亮屏状态
// 对于 doze 状态,屏幕处于 on 状态,但是屏幕可能仍然是黑的
// 因此,只要屏幕处于 on 状态,并且显示了锁屏,触摸事件不会截断
if (isKeyguardShowingAndNotOccluded() && !displayOff) {
return true;
}
// 对于触摸事件,keyCode 的值为 KEYCODE_UNKNOWN
if (mHasFeatureWatch && (keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_BACK
|| keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_PRIMARY
|| keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_1
|| keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_2
|| keyCode == KeyEvent.KEYCODE_STEM_3)) {
return false;
}
// 对于默认屏幕,如果设备处于梦境状态,那么触摸事件不截断
// 因为 doze 组件需要接收触摸事件,可能会唤醒屏幕
if (isDefaultDisplay) {
IDreamManager dreamManager = getDreamManager();
try {
if (dreamManager != null && dreamManager.isDreaming()) {
return true;
}
} catch (RemoteException e) {
Slog.e(TAG, "RemoteException when checking if dreaming", e);
}
}
// Otherwise, consume events since the user can't see what is being
// interacted with.
return false;
} 截断策略是否截断触摸事件,取决于策略的返回值,有两种情况:
- 返回 0,表示截断触摸事件。
- 返回 ACTION_PASS_TO_USER ,表示不截断触摸事件,也就是把触摸事件分发给用户/窗口。
下面列举触摸事件截断与否的情况,但是要注意一个前提,设备处于非交互状态(一般就是指灭屏状态):
- 事件会被传递给用户,也就是不截断,情况如下:
- 有锁屏,并且显示屏处于非 off 状态。注意,非 off 状态,并不是表示屏幕处于 on(亮屏) 状态,也可能是 doze 状态(屏幕处于低电量状态),doze 状态屏幕也是黑的。
- 梦境状态。因为梦境状态下会运行 doze 组件。
- 事件被截断,情况如下:
- 策略标志位包含 FLAG_WAKE ,它会导致屏幕被唤醒,因此需要截断触摸事件。FLAG_WAKE 一般来自于输入设备的配置文件。
- 没有锁屏,没有梦境,也没有 FLAG_WAKE,默认就会截断。
从上面的分析可以总结出了两条结论:
- 如果系统有组件在运行,例如,锁屏、doze组件,那么触摸事件需要分发到这些组件,因此不会被截断。
- 如果没有组件运行,触摸事件都会被截断。触摸事件由于需要唤醒屏幕,而导致被截断,只是其中一个特例。
注意:这里的所有操作,不是发生在 InputDispatcher 线程,而是发生在 InputReader 线程,这个线程是负责不断地读取事件,因此这里的查询策略是否截断事件的过程,时间不能太长,否则影响了输入系统读取事件。
3.3 InputDispatcher.enqueueInboundEventLocked 收件箱接收事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::enqueueInboundEventLocked(EventEntry* entry) {
// mInboundQueue 队列为空,需要唤醒 InputDispatcher 线程来处理事件
bool needWake = mInboundQueue.empty();
// 加入到 mInboundQueue 中
mInboundQueue.push_back(entry);
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
switch (entry->type) {
..........
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
// 判断传入的动作事件之前的事件是否应该被丢弃
if (shouldPruneInboundQueueLocked(static_cast<MotionEntry&>(*entry))) {
mNextUnblockedEvent = entry;
needWake = true;
}
break;
}
...............
}
return needWake;
}InputDispatcher::mInboundQueue 是 InputDispatcher 的事件收件箱,所有的事件,包括注入事件,都会加入这个收件箱。就好像收件箱接收到"邮件"后,就需要唤醒 InputDispatcher 线程来处理"邮件"
3.4 InputDispatcher.dispatchOnce分发触摸事件
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnce() {
nsecs_t nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MAX;
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
mDispatcherIsAlive.notify_all();
if (!haveCommandsLocked()) {
// 分发一个触摸事件
dispatchOnceInnerLocked(&nextWakeupTime);
}
// 触摸事件的分发过程不会产生命令
if (runCommandsLockedInterruptible()) {
nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN;
}
// 计算线程下次唤醒的时间点,以便处理 anr
const nsecs_t nextAnrCheck = processAnrsLocked();
nextWakeupTime = std::min(nextWakeupTime, nextAnrCheck);
if (nextWakeupTime == LONG_LONG_MAX) {
mDispatcherEnteredIdle.notify_all();
}
} // release lock
// 线程休眠指定的时长
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
int timeoutMillis = toMillisecondTimeoutDelay(currentTime, nextWakeupTime);
mLooper->pollOnce(timeoutMillis);
}一次线程循环处理触摸事件的过程如下:
- 分发一个触摸事件。
- 当事件分发给窗口后,会计算一个窗口反馈的超时时间,利用这个时间,计算线程下次唤醒的时间点。
- 利用上一步计算出的线程唤醒的时间点,计算出线程最终需要休眠多长时间。当线程被唤醒后,会检查接收触摸时间的窗口,是否反馈超时,如果超时,会引发 ANR。
3.5 InputDispatcher.dispatchOnceInnerLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchOnceInnerLocked(nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
.............
// 这里是优化 app 切换的延迟
// mAppSwitchDueTime 是 app 切换的超时时间,如果小于当前时间,那么表明app切换超时了
// 如果app切换超时,那么在app切换按键事件之前的未处理的事件,都将会被丢弃
bool isAppSwitchDue = mAppSwitchDueTime <= currentTime;
if (mAppSwitchDueTime < *nextWakeupTime) {
*nextWakeupTime = mAppSwitchDueTime;
}
// mPendingEvent 表示正在处理的事件
if (!mPendingEvent) {
if (mInboundQueue.empty()) {
// ...
} else {
// 从收件箱队列中取出事件
mPendingEvent = mInboundQueue.front();
mInboundQueue.pop_front();
traceInboundQueueLengthLocked();
}
// 如果这个事件需要传递给用户,那么需要同上层的 PowerManagerService,此时有用户行为,这个作用就是延长亮屏的时间
if (mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER) {
pokeUserActivityLocked(*mPendingEvent);
}
}
ALOG_ASSERT(mPendingEvent != nullptr);
bool done = false;
// 检测丢弃事件的原因
DropReason dropReason = DropReason::NOT_DROPPED;
if (!(mPendingEvent->policyFlags & POLICY_FLAG_PASS_TO_USER)) {
// 被截断策略截断
dropReason = DropReason::POLICY;
} else if (!mDispatchEnabled) {
// 一般是由于系统正在系统或者正在关闭
dropReason = DropReason::DISABLED;
}
.....
switch (mPendingEvent->type) {
// ....
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
std::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> motionEntry =
std::static_pointer_cast<MotionEntry>(mPendingEvent);
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && isAppSwitchDue) {
// app 切换超时,导致触摸事件被丢弃
dropReason = DropReason::APP_SWITCH;
}
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && isStaleEvent(currentTime, *motionEntry)) {
// 10s 之前的事件,已经过期
dropReason = DropReason::STALE;
}
// 这里是优化应用无响应的一个措施,会丢弃mNextUnblockedEvent之前的所有触摸事件
if (dropReason == DropReason::NOT_DROPPED && mNextUnblockedEvent) {
dropReason = DropReason::BLOCKED;
}
// 分发触摸事件
done = dispatchMotionLocked(currentTime, motionEntry, &dropReason, nextWakeupTime);
break;
}
...
}
// 如果事件被处理,重置一些状态,例如 mPendingEvent
// 返回 true,就表示已经处理了事件
// 事件被丢弃,或者发送完毕,都会返回 true
// 返回 false,表示暂时不知道如何处理事件,因此线程会休眠
// 然后,线程再次被唤醒时,再来处理这个事件
if (done) {
if (dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
dropInboundEventLocked(*mPendingEvent, dropReason);
}
mLastDropReason = dropReason;
// 重置 mPendingEvent
releasePendingEventLocked();
// 立即唤醒,处理下一个事件
*nextWakeupTime = LONG_LONG_MIN; // force next poll to wake up immediately
}
}3.6 InputDispatcher.dispatchMotionLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
bool InputDispatcher::dispatchMotionLocked(nsecs_t currentTime, std::shared_ptr<MotionEntry> entry,
DropReason* dropReason, nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime) {
.........
// 触摸事件有原因需要丢弃,那么不走后面的分发流程
if (*dropReason != DropReason::NOT_DROPPED) {
setInjectionResult(*entry,
*dropReason == DropReason::POLICY ? InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED
: InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED);
return true;
}
bool isPointerEvent = entry->source & AINPUT_SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER;
std::vector<InputTarget> inputTargets;
bool conflictingPointerActions = false;
InputEventInjectionResult injectionResult;
if (isPointerEvent) {
// 寻找触摸的窗口,窗口保存到 inputTargets
// 为触摸事件,寻找触摸的窗口
// 触摸的窗口保存到 inputTargets 中
injectionResult =
findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(currentTime, *entry, inputTargets, nextWakeupTime,
&conflictingPointerActions);
} else {
...
}
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING) {
// 返回 false,表示暂时不知道如何处理这个事件,这会导致线程休眠
// 等线程下次被唤醒时,再来处理这个事件
return false;
}
// 走到这里,表示触摸事件已经被处理,因此保存处理的结果
// 只要返回的不是 InputEventInjectionResult::PENDING
// 都表示事件被处理,无论是权限拒绝还是失败,或是成功
setInjectionResult(*entry, injectionResult);
if (injectionResult == InputEventInjectionResult::PERMISSION_DENIED) {
ALOGW("Permission denied, dropping the motion (isPointer=%s)", toString(isPointerEvent));
return true;
}
if (injectionResult != InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED) {
CancelationOptions::Mode mode(isPointerEvent
? CancelationOptions::CANCEL_POINTER_EVENTS
: CancelationOptions::CANCEL_NON_POINTER_EVENTS);
CancelationOptions options(mode, "input event injection failed");
synthesizeCancelationEventsForMonitorsLocked(options);
return true;
}
// 走到这里,表示触摸事件已经成功找到触摸的窗口
// Add monitor channels from event's or focused display.
// 触摸事件找到了触摸窗口,在分发给窗口前,保存 global monitor 到 inputTargets 中
// 开发者选项中的 Show taps 和 Pointer location,利用的 global monitor
addGlobalMonitoringTargetsLocked(inputTargets, getTargetDisplayId(*entry));
if (isPointerEvent) {
// ... portal window 处理的代码
}
if (conflictingPointerActions) {
// ...
}
// 分发事件给 inputTargets 中的所有窗口
dispatchEventLocked(currentTime, entry, inputTargets);
return true;
}3.7 InputDispatcher.findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked寻找触摸的窗口
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
int32_t InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowTargetsLocked(
nsecs_t currentTime, const MotionEntry& entry, std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets,
nsecs_t* nextWakeupTime, bool* outConflictingPointerActions) {
...
// 对于非 DOWN 事件,获取已经 DOWN 事件保存的 TouchState
// TouchState 保存了接收 DOWN 事件的窗口
const TouchState* oldState = nullptr;
TouchState tempTouchState;
std::unordered_map<int32_t, TouchState>::iterator oldStateIt =
mTouchStatesByDisplay.find(displayId);
if (oldStateIt != mTouchStatesByDisplay.end()) {
oldState = &(oldStateIt->second);
tempTouchState.copyFrom(*oldState);
}
...
// 第一个条件 newGesture 表示第一个手指按下
// 后面一个条件,表示当前窗口支持 split motion,并且此时有另外一个手指按下
if (newGesture || (isSplit && maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_POINTER_DOWN)) {
/* Case 1: New splittable pointer going down, or need target for hover or scroll. */
// 触摸点的获取 x, y 坐标
int32_t x;
int32_t y;
int32_t pointerIndex = getMotionEventActionPointerIndex(action);
if (isFromMouse) {
// ...
} else {
x = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[pointerIndex].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_X));
y = int32_t(entry.pointerCoords[pointerIndex].getAxisValue(AMOTION_EVENT_AXIS_Y));
}
// 这里检测是否是第一个手指按下
bool isDown = maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN;
// 对于 DOWN 事件,根据触摸事件的x,y坐标,寻找触摸窗口
// 参数 addOutsideTargets 表示,只有在第一个手指按下时,如果没有找到触摸的窗口,
// 那么需要保存那些可以接受 OUTSIZE 事件的窗口到 tempTouchState
newTouchedWindowHandle =
findTouchedWindowAtLocked(displayId, x, y, &tempTouchState,
isDown /*addOutsideTargets*/, true /*addPortalWindows*/);
// ... 处理窗口异常的情况 ...
// 获取所有的 getsture monitor
const std::vector<TouchedMonitor> newGestureMonitors = isDown
? selectResponsiveMonitorsLocked(
findTouchedGestureMonitorsLocked(displayId, tempTouchState.portalWindows))
: tempTouchState.gestureMonitors;
// 既没有找到触摸点所在的窗口,也没有找到 gesture monitor,那么此次寻找触摸窗口的任务就失败了
if (newTouchedWindowHandle == nullptr && newGestureMonitors.empty()) {
ALOGI("Dropping event because there is no touchable window or gesture monitor at "
"(%d, %d) in display %" PRId32 ".",
x, y, displayId);
injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::FAILED;
goto Failed;
}
// 走到这里,表示找到了触摸的窗口,或者找到 gesture monitor
if (newTouchedWindowHandle != nullptr) {
// 马上要保存窗口了,现在获取窗口的 flag
int32_t targetFlags = InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS;
if (isSplit) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_SPLIT;
}
if (isWindowObscuredAtPointLocked(newTouchedWindowHandle, x, y)) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_OBSCURED;
} else if (isWindowObscuredLocked(newTouchedWindowHandle)) {
targetFlags |= InputTarget::FLAG_WINDOW_IS_PARTIALLY_OBSCURED;
}
// Update hover state.
if (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_HOVER_EXIT) {
newHoverWindowHandle = nullptr;
} else if (isHoverAction) {
newHoverWindowHandle = newTouchedWindowHandle;
}
// Update the temporary touch state.
// 如果窗口支持 split,那么用 tempTouchState 保存窗口的时候,要特别保存 pointer id
BitSet32 pointerIds;
if (isSplit) {
uint32_t pointerId = entry.pointerProperties[pointerIndex].id;
pointerIds.markBit(pointerId);
}
// tempTouchState 保存找到的触摸的窗口
// 如果是真的找到的触摸窗口,那么这里就是保存,如果是找到可以接受 OUTSIDE 的窗口,那么这里是更新
tempTouchState.addOrUpdateWindow(newTouchedWindowHandle, targetFlags, pointerIds);
} else if (tempTouchState.windows.empty()) {
// If no window is touched, set split to true. This will allow the next pointer down to
// be delivered to a new window which supports split touch.
tempTouchState.split = true;
}
if (isDown) {
// tempTouchState 保存所有的 gesture monitor
// 第一个手指按下时,tempTouchState 保存 gesture monitor
tempTouchState.addGestureMonitors(newGestureMonitors);
}
} else {
...
}
if (newHoverWindowHandle != mLastHoverWindowHandle) {
....
}
{
// 权限检测 ...
}
// 保存接收 AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_OUTSIDE 的窗口
if (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) {
// ...
}
// 第一个手指按下时,保存壁纸窗口
if (maskedAction == AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_DOWN) { //
// ...
}
// 走到这里,表示没有异常情况了
injectionResult = InputEventInjectionResult::SUCCEEDED;
// 把 tempTouchState 保存了触摸窗口和gesture monitor,保存到 inputTargets 中
for (const TouchedWindow& touchedWindow : tempTouchState.windows) {
addWindowTargetLocked(touchedWindow.windowHandle, touchedWindow.targetFlags,
touchedWindow.pointerIds, inputTargets);
}
for (const TouchedMonitor& touchedMonitor : tempTouchState.gestureMonitors) {
addMonitoringTargetLocked(touchedMonitor.monitor, touchedMonitor.xOffset,
touchedMonitor.yOffset, inputTargets);
}
// Drop the outside or hover touch windows since we will not care about them
// in the next iteration.
tempTouchState.filterNonAsIsTouchWindows();
Failed:
// ...
// 缓存 tempTouchState
if (maskedAction != AMOTION_EVENT_ACTION_SCROLL) {
if (tempTouchState.displayId >= 0) {
mTouchStatesByDisplay[displayId] = tempTouchState;
} else {
mTouchStatesByDisplay.erase(displayId);
}
}
return injectionResult;
}对于 DOWN 事件
- 根据 x,y 坐标寻找触摸的窗口。
- 获取所有的 gesture monitor 窗口 。
- 把触摸窗口保存到 tempTouchState 中。
- 把所有的 gesture monitor 窗口保存到 tempTouchState 中。
- 为 tempTouchState 保存所有窗口,创建 InputTarget 对象,并保存到参数 inputTargets 中。
- 使用 mTouchStatesByDisplay 缓存 tempTouchState。
gesture monitor 是为了实现手势功能而添加的一个窗口。什么是手势功能? 例如在屏幕的左边/右边,向屏幕中央滑动,会触发返回手势。
对于非 DOWN 事件,一般为 MOVE, UP 事件:
- 获取 DOWN 事件缓存的 tempTouchState。 因为 tempTouchState 保存了处理 DOWN 事件的触摸窗口和 gesture monitor,非 DOWN 事件,也会发送给这些窗口。
- 重复 DOWN 事件的第5步。
这个方法代码量很庞大,主要作用就是为触摸事件寻找触摸窗口,最终的结果就是把找到的窗口保存到参数 inputTargets 中,后面会把事件分发给 inputTargets 保存的窗口。
3.8 InputDispatcher.findTouchedWindowAtLocked根据坐标找到触摸窗口
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
// addOutsideTargets 在第一个手指按下是为 true
// addPortalWindows 值为 true
// ignoreDragWindow 默认为 false
sp<InputWindowHandle> InputDispatcher::findTouchedWindowAtLocked(int32_t displayId, int32_t x,
int32_t y, TouchState* touchState,
bool addOutsideTargets,
bool addPortalWindows,
bool ignoreDragWindow) {
if ((addPortalWindows || addOutsideTargets) && touchState == nullptr) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL(
"Must provide a valid touch state if adding portal windows or outside targets");
}
// Traverse windows from front to back to find touched window.
// 从前到后,遍历窗口
const std::vector<sp<InputWindowHandle>>& windowHandles = getWindowHandlesLocked(displayId);
for (const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle : windowHandles) {
// ignoreDragWindow 默认为 false
if (ignoreDragWindow && haveSameToken(windowHandle, mDragState->dragWindow)) {
continue;
}
// 获取窗口信息
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
// 匹配属于特定屏幕的窗口
if (windowInfo->displayId == displayId) {
auto flags = windowInfo->flags;
// 窗口要可见
if (windowInfo->visible) {
// 窗口要可触摸
if (!flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCHABLE)) {
// 检测是否为触摸模型: 可获取焦点,并且不允许窗口之外的触摸事件发送到它后面的窗口
bool isTouchModal = !flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_FOCUSABLE) &&
!flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::NOT_TOUCH_MODAL);
// 窗口是触摸模型,或者触摸的坐标点落在窗口上
if (isTouchModal || windowInfo->touchableRegionContainsPoint(x, y)) {
int32_t portalToDisplayId = windowInfo->portalToDisplayId;
// 如果是 portal window
if (portalToDisplayId != ADISPLAY_ID_NONE &&
portalToDisplayId != displayId) {
if (addPortalWindows) {
// For the monitoring channels of the display.
// touchState 保存 portal window
touchState->addPortalWindow(windowHandle);
}
// 递归调用,获取 portal display id 下的触摸窗口
return findTouchedWindowAtLocked(portalToDisplayId, x, y, touchState,
addOutsideTargets, addPortalWindows);
}
// 不是 portal window,直接返回找到的窗口
return windowHandle;
}
}
// 走到这里,表示没有找到触摸窗口。也就是说,既没有找到触摸模型的窗口,也没有找到包含触摸点的窗口
// 当第一个手指按下是,addOutsideTargets 值为 true
// NOT_TOUCH_MODAL 和 WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH 一起使用,当第一个手指按下时,如果落在窗口之外
// 窗口会收到 MotionEvent.ACTION_OUTSIDE 事件
if (addOutsideTargets && flags.test(InputWindowInfo::Flag::WATCH_OUTSIDE_TOUCH)) {
touchState->addOrUpdateWindow(windowHandle,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE,
BitSet32(0));
}
}
}
}
return nullptr;
}寻找触摸点所在的窗口,其实就是从上到下遍历所有窗口,然后找到满足条件的窗口。
窗口首先要满足前置条件:
- 窗口要在指定屏幕上。
- 窗口要可见。
- 窗口要可触摸。
满足了所有的前置条件后,只要满足以下任意一个条件,那么就找到了触摸点所在的窗口:
- 是触摸模型的窗口: 可获取焦点,并且不允许窗口之外的触摸事件发送到它后面的窗口。
- 触摸点的 x,y 坐标落在窗口坐标系中。
3.9 InputDispatcher.addWindowTargetLocked保存窗口
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::addWindowTargetLocked(const sp<InputWindowHandle>& windowHandle,
int32_t targetFlags, BitSet32 pointerIds,
std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
std::vector<InputTarget>::iterator it =
std::find_if(inputTargets.begin(), inputTargets.end(),
[&windowHandle](const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
return inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken() ==
windowHandle->getToken();
});
const InputWindowInfo* windowInfo = windowHandle->getInfo();
// 创建 InputTarget,并保存到参数 inputTargets
if (it == inputTargets.end()) {
InputTarget inputTarget;
std::shared_ptr<InputChannel> inputChannel =
getInputChannelLocked(windowHandle->getToken());
if (inputChannel == nullptr) {
ALOGW("Window %s already unregistered input channel", windowHandle->getName().c_str());
return;
}
inputTarget.inputChannel = inputChannel;
inputTarget.flags = targetFlags;
inputTarget.globalScaleFactor = windowInfo->globalScaleFactor;
inputTarget.displaySize =
int2(windowHandle->getInfo()->displayWidth, windowHandle->getInfo()->displayHeight);
inputTargets.push_back(inputTarget);
it = inputTargets.end() - 1;
}
ALOG_ASSERT(it->flags == targetFlags);
ALOG_ASSERT(it->globalScaleFactor == windowInfo->globalScaleFactor);
// 保存 InputTarget 后,在保存窗口的坐标转换参数,
// 这个参数可以把显示屏的坐标,转换为窗口的坐标
it->addPointers(pointerIds, windowInfo->transform);
}
// InputDispatcher 保存 gesture monitor
void InputDispatcher::addMonitoringTargetLocked(const Monitor& monitor, float xOffset,
float yOffset,
std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
InputTarget target;
target.inputChannel = monitor.inputChannel;
target.flags = InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS;
ui::Transform t;
t.set(xOffset, yOffset);
target.setDefaultPointerTransform(t);
inputTargets.push_back(target);
}对于触摸事件,无论是触摸窗口,还是 gesture monitor,都会被转化为 InputTarget,然后保存到参数 inputTargets 中。当后面启动分发循环后,触摸事件就会发送到 inputTargets 保存的窗口中。
3.10 InputDispatcher.dispatchEventLocked分发事件给目标窗口
现在,处理触摸事件的焦点窗口已经找到,并且已经保存到 inputTargets,是时候来分发按键事件了:
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::dispatchEventLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const std::vector<InputTarget>& inputTargets) {
updateInteractionTokensLocked(*eventEntry, inputTargets);
pokeUserActivityLocked(*eventEntry);
for (const InputTarget& inputTarget : inputTargets) {
// 获取目标窗口的连接
sp<Connection> connection =
getConnectionLocked(inputTarget.inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
if (connection != nullptr) {
// 准备分发循环
prepareDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
} else {
if (DEBUG_FOCUS) {
ALOGD("Dropping event delivery to target with channel '%s' because it "
"is no longer registered with the input dispatcher.",
inputTarget.inputChannel->getName().c_str());
}
}
}
}焦点窗口只有一个,为何需要一个 inputTargets 集合来保存所有的目标窗口?因为根据前面的分析,除了焦点窗口以外,还有一个全局的监听事件的输入目标。
WindowManagerService 会在创建窗口时,创建一个连接,其中一端给窗口,另外一端给输入系统。当输入系统需要发送事件给窗口时,就会通过这个连接进行发送。
找到这个窗口的连接后,就准备分发循环 ? 问题来了,什么是分发循环 ? InputDispatcher 把一个事件发送给窗口,窗口处理完事件,然后返回结果为 InputDispatcher,这就是一个循环。但是注意,分发事件给窗口,窗口返回处理事件结果,这两个是互为异步过程。
3.11 InputDispatcher.prepareDispatchCycleLocked分发循环之前的准备
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::prepareDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
...
// 连接处理异常状态,丢弃事件
if (connection->status != Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dropping event because the channel status is %s",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), connection->getStatusLabel());
#endif
return;
}
// Split a motion event if needed.
// 针对触摸事件的split
if (inputTarget.flags & InputTarget::FLAG_SPLIT) {
...
}
// Not splitting. Enqueue dispatch entries for the event as is.
// 把事件加入到连接的发件箱中,然后启动分发循环
enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(currentTime, connection, eventEntry, inputTarget);
}
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntriesLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget) {
...
bool wasEmpty = connection->outboundQueue.empty();
// Enqueue dispatch entries for the requested modes.
// 保存事件到连接的发件箱 Connection::outboundQueue
// 注意最后一个参数,它的窗口的分发模式,定义了事件如何分发到指定窗口
// 根据前面的代码分析,目前保存的目标窗口的分发模式只支持下面列举的 InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS
// InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS 表示事件按照原样进行发送
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_OUTSIDE);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_HOVER_ENTER);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_EXIT);
enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(connection, eventEntry, inputTarget,
InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_SLIPPERY_ENTER);
// If the outbound queue was previously empty, start the dispatch cycle going.
// 连接的发件箱突然有事件了,那得启动分发循环,把事件发送到指定窗口
if (wasEmpty && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {
// 启动分发循环
startDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection);
}
}分发循环前的准备工作,其实就是根据窗口所支持的分发模式(dispatche mode),调用enqueueDispatchEntryLocked() 创建并保存事件到连接的收件箱。前面分析过,焦点窗口的的分发模式为 InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS | InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND,而此时只用到了InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS。
如果连接的收件箱之前没有事件,那么证明连接没有处于发送事件的状态中,而现在有事件了,那就启动分发循环来发送事件。
3.12 InputDispatcher.enqueueDispatchEntryLocked根据分发模式,添加事件到连接收件箱
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::enqueueDispatchEntryLocked(const sp<Connection>& connection,
std::shared_ptr<EventEntry> eventEntry,
const InputTarget& inputTarget,
int32_t dispatchMode) {
...
// 前面保存的 InputTarget,它的 flags 为 InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS
int32_t inputTargetFlags = inputTarget.flags;
// 窗口不支持请求的dispatcher mode,那么不添加事件到连接的发件箱中
// 对于按键事件,dispatchMode 只能是 InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS
if (!(inputTargetFlags & dispatchMode)) {
return;
}
// 为每一个窗口所支持的 dispatche mode,创建一个 DispatchEntry
inputTargetFlags = (inputTargetFlags & ~InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_MASK) | dispatchMode;
std::unique_ptr<DispatchEntry> dispatchEntry =
createDispatchEntry(inputTarget, eventEntry, inputTargetFlags);
// Use the eventEntry from dispatchEntry since the entry may have changed and can now be a
// different EventEntry than what was passed in.
EventEntry& newEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
// Apply target flags and update the connection's input state.
switch (newEntry.type) {
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
break;
}
}
...
}
// Remember that we are waiting for this dispatch to complete.
// 检测事件是否正在发送到前台窗应用,根据前面的代码分析,目标窗口的flags包括 FLAG_FOREGROUND
// 因此,条件成立
if (dispatchEntry->hasForegroundTarget()) {
// EventEntry::injectionState::pendingForegroundDispatches +1
incrementPendingForegroundDispatches(newEntry);
}
//把 DispatchEntry 加入到连接的发件箱中
connection->outboundQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry.release());
traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
}根据前面创建 InputTarget 的代码可知,InputTarget::flags 的值为 InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND | InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS。
InputTarget::FLAG_FOREGROUND 表明事件正在发送给前台应用,InputTarget::FLAG_DISPATCH_AS_IS 表示事件按照原样进行发送。
3.13 InputDispatcher.startDispatchCycleLocked启动分发循环
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::startDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection) {
...
// 遍历连接发件箱中的所有事件,逐个发送给目标窗口
while (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL && !connection->outboundQueue.empty()) {
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = connection->outboundQueue.front();
dispatchEntry->deliveryTime = currentTime;
// 计算事件分发的超时时间
const std::chrono::nanoseconds timeout =
getDispatchingTimeoutLocked(connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
dispatchEntry->timeoutTime = currentTime + timeout.count();
// Publish the event.
status_t status;
const EventEntry& eventEntry = *(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
switch (eventEntry.type) {
case EventEntry::Type::MOTION: {
MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(eventEntry);
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac = getSignature(keyEntry, *dispatchEntry);
....
// 1. 发送触摸事件
status = connection->inputPublisher
.publishMotionEvent(.......);
break;
}
...
}
// Check the result.
if (status) {
// 发送异常
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
...
}
return;
}
// 走到这里,表示事件发送成功
// 事件发送成功,那么从连接的发件箱中移除
connection->outboundQueue.erase(std::remove(connection->outboundQueue.begin(),
connection->outboundQueue.end(),
dispatchEntry));
traceOutboundQueueLength(*connection);
// 3把已经发送的事件,加入到连接的等待队列中 Connection::waitQueue
// 连接在等待什么呢?当然是等到窗口的处理结果
connection->waitQueue.push_back(dispatchEntry);
// 连接可响应,那么会记录事件处理的超时时间,一旦超时,会引发 ANR
// 因为我们不可能无限等待窗口处理完事件,后面还有好多事件要处理呢
// 用 AnrTracker 记录事件处理的超时时间
if (connection->responsive) {
mAnrTracker.insert(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime,
connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
}
traceWaitQueueLength(*connection);
}
}事件分发循环的过程如下:
- 通过窗口连接,把事件发送给窗口,并从连接的发件箱 Connection::outboundQueue 中移除。
- 把刚刚发送的事件,保存到连接的等待队列 Connection::waitQueue。连接在等待什么呢?当然是等到窗口的处理结果。
- 用 AnrTracker 记录事件处理的超时时间,如果事件处理超时,会引发 ANR。
3.14 InputPublisher.publishMotionEvent
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputPublisher::publishMotionEvent(
uint32_t seq, int32_t eventId, int32_t deviceId, int32_t source, int32_t displayId,
std::array<uint8_t, 32> hmac, int32_t action, int32_t actionButton, int32_t flags,
int32_t edgeFlags, int32_t metaState, int32_t buttonState,
MotionClassification classification, float xScale, float yScale, float xOffset,
float yOffset, float xPrecision, float yPrecision, float xCursorPosition,
float yCursorPosition, nsecs_t downTime, nsecs_t eventTime, uint32_t pointerCount,
const PointerProperties* pointerProperties, const PointerCoords* pointerCoords) {
...................
// 根据event信息构建InputMessage
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::MOTION;
msg.body.motion.seq = seq;
msg.body.motion.eventId = eventId;
msg.body.motion.deviceId = deviceId;
msg.body.motion.source = source;
msg.body.motion.displayId = displayId;
msg.body.motion.hmac = std::move(hmac);
msg.body.motion.action = action;
msg.body.motion.actionButton = actionButton;
msg.body.motion.flags = flags;
msg.body.motion.edgeFlags = edgeFlags;
msg.body.motion.metaState = metaState;
msg.body.motion.buttonState = buttonState;
msg.body.motion.classification = classification;
.................
// 通过InputChannel的sendMessage方法将event发送出去
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}3.15 InputChannel.sendMessage
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
const size_t msgLength = msg->size();
InputMessage cleanMsg;
// copy一份msg
msg->getSanitizedCopy(&cleanMsg);
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
// 通过socket循环写入msg
nWrite = ::send(mFd.get(), &cleanMsg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
..........
return OK;
}sendMessage主要就是先copy一份事件msg,然后调用send将msg循环写入socket,从而实现输入事件的分发。
3.16 小结
- InputReader 线程把事件加入到 InputDispatcher 的收件箱之前,会询问截断策略,如果策略截断了,那么事件最终不会发送给窗口。
- InputDispatcher 通过一次线程循环来发送事件
- 事件在发送之前,会循环分发策略。
- 如果截断策略和分发策略都不截断事件,那么会寻找能处理事件的焦点窗口。
- 焦点窗口找到了,那么会把事件加入到窗口连接的发件箱中。
- 执行分发循环,从窗口连接的发件箱中获取事件,然后发送给窗口。然后把事件从发件箱中移除,并加入到连接的等待队列中。最后,记录 ANR 时间。
- 窗口返回事件的处理结果,InputDispatcher 会读取结果,然后把事件从连接的等待队列中移除,然后解除 ANR 的触发。(这部分后面分析,应用进程处理完事件之后,也就是对应的view消费了事件之后会返回结果到inputDispatcher线程去处理)
- 继续发送连接中的事件,并重复上述过程,直至连接中没有事件为止。
4. InputChannel的创建与初始化
看完第三节的内容可以看到最后3.15小结会调用InputChannel里面的sendMessage会将消息发送给应用进程,里面的fd很关键,当fd 写入消息的时候,会唤醒处于epoll_wait 状态的线程(原理跟handler一样),接下来我们看看它是如何跟应用端的fd绑定的。
InputChannel会作为句柄传递到下层,后面分发事件的时候会通过它来进行。而且这里会创建出两个,一个作为server端注册到InputManagerService,最终会注册到InputDispatcher中去,另一个则作为client端来接收server端的事件。
4.1 ViewRootImpl.setView创建InputChannel
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public void setView(View view, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs, View panelParentView,
int userId) {
synchronized (this) {
if (mView == null) {
// .....
InputChannel inputChannel = null;
if ((mWindowAttributes.inputFeatures
& WindowManager.LayoutParams.INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0) {
inputChannel = new InputChannel();
}
// ...
// 调用Session的addToDisplayAsUser方法来添加window,
// 会初始化InputChannel
res = mWindowSession.addToDisplayAsUser(mWindow, mSeq, mWindowAttributes,
getHostVisibility(), mDisplay.getDisplayId(), userId, mTmpFrame,
mAttachInfo.mContentInsets, mAttachInfo.mStableInsets,
mAttachInfo.mDisplayCutout, inputChannel,
mTempInsets, mTempControls);
// ...
if (inputChannel != null) {
if (mInputQueueCallback != null) {
mInputQueue = new InputQueue();
mInputQueueCallback.onInputQueueCreated(mInputQueue);
}
// 将InputChannel传入InputEventReceiver
// 创建app端监听,即WindowInputEventReceiver 作为事件的接收端
mInputEventReceiver = new WindowInputEventReceiver(inputChannel,
Looper.myLooper());
}
// ...
}
}
}4.2 Session.addToDisplayAsUser
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/Session.java
public int addToDisplayAsUser(IWindow window, int seq, WindowManager.LayoutParams attrs,
int viewVisibility, int displayId, int userId, Rect outFrame,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel,
InsetsState outInsetsState, InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls) {
// 直接调用WindowManagerService的addWindow方法
return mService.addWindow(this, window, seq, attrs, viewVisibility, displayId, outFrame,
outContentInsets, outStableInsets, outDisplayCutout, outInputChannel,
outInsetsState, outActiveControls, userId);
}4.3 WindowManagerService.addWindow
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowManagerService.java
public int addWindow(Session session, IWindow client, int seq,
LayoutParams attrs, int viewVisibility, int displayId, Rect outFrame,
Rect outContentInsets, Rect outStableInsets,
DisplayCutout.ParcelableWrapper outDisplayCutout, InputChannel outInputChannel,
InsetsState outInsetsState, InsetsSourceControl[] outActiveControls,
int requestUserId) {
// ...
final WindowState win = new WindowState(this, session, client, token, parentWindow,
appOp[0], seq, attrs, viewVisibility, session.mUid, userId,
session.mCanAddInternalSystemWindow);
// ...
final boolean openInputChannels = (outInputChannel != null
&& (attrs.inputFeatures & INPUT_FEATURE_NO_INPUT_CHANNEL) == 0);
if (openInputChannels) {
// 这里会调用WindowState的openInputChannel来打开inputChannel
win.openInputChannel(outInputChannel);
}
// ...
return res;
}addWindow方法中会调用WindowState打开InputChannel。
4.4 WindowState.openInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/wm/WindowState.java
void openInputChannel(InputChannel outInputChannel) {
if (mInputChannel != null) {
throw new IllegalStateException("Window already has an input channel.");
}
String name = getName();
// 通过openInputChannelPair方法创建出两个InputChannel
InputChannel[] inputChannels = InputChannel.openInputChannelPair(name);
mInputChannel = inputChannels[0];
mClientChannel = inputChannels[1];
// 注册server端的InputChannel到InputManagerService中
mWmService.mInputManager.registerInputChannel(mInputChannel);
mInputWindowHandle.token = mInputChannel.getToken();
if (outInputChannel != null) {
// 将client端的InputChannel设置到outInputChannel
mClientChannel.transferTo(outInputChannel);
mClientChannel.dispose();
mClientChannel = null;
} else {
// If the window died visible, we setup a dummy input channel, so that taps
// can still detected by input monitor channel, and we can relaunch the app.
// Create dummy event receiver that simply reports all events as handled.
mDeadWindowEventReceiver = new DeadWindowEventReceiver(mClientChannel);
}
mWmService.mInputToWindowMap.put(mInputWindowHandle.token, this);
}首先会通过调用InputChannel的静态方法openInputChannelPair来创建两个InputChannel,一个作为client一个作为server;然后还会调用InputManagerService的registerInputChannel来注册server端的InputChannel;最后将client端的InputChannel设置到outInputChannel中。
4.5 InputChannel.openInputChannelPair
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputChannel.java
public static InputChannel[] openInputChannelPair(String name) {
if (name == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("name must not be null");
}
if (DEBUG) {
Slog.d(TAG, "Opening input channel pair '" + name + "'");
}
// 继续调用natvie方法创建出两个InputChannel
return nativeOpenInputChannelPair(name);
}上述openInputChannelPair方法中会直接调用InputChannel的native方法nativeOpenInputChannelPair来创建出一对InputChannel。
4.6 android_view_InputChannel.android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputChannel.cpp
static jobjectArray android_view_InputChannel_nativeOpenInputChannelPair(JNIEnv* env,
jclass clazz, jstring nameObj) {
ScopedUtfChars nameChars(env, nameObj);
std::string name = nameChars.c_str();
sp<InputChannel> serverChannel;
sp<InputChannel> clientChannel;
// 创建出server端和client端的InputChannel
status_t result = InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(name, serverChannel, clientChannel);
// ...
// 添加到数组中,然后返回给上层
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 0, serverChannelObj);
env->SetObjectArrayElement(channelPair, 1, clientChannelObj);
return channelPair;
}jni方法nativeOpenInputChannelPair中会继续调用InputChannel的openInputChannelPair静态方法。然后将创建出的两个inputChannel分别添加到数组中,然后返回给上层。
4.7 InputChannel.openInputChannelPair
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::openInputChannelPair(const std::string& name,
sp<InputChannel>& outServerChannel, sp<InputChannel>& outClientChannel) {
int sockets[2];
// 创建一对相互连接的socket
if (socketpair(AF_UNIX, SOCK_SEQPACKET, 0, sockets)) {
status_t result = -errno;
// 创建失败做相应的处理
ALOGE("channel '%s' ~ Could not create socket pair. errno=%d",
name.c_str(), errno);
outServerChannel.clear();
outClientChannel.clear();
return result;
}
// 分别设置两个socket的可读可写buffer
int bufferSize = SOCKET_BUFFER_SIZE;
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[0], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_SNDBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
setsockopt(sockets[1], SOL_SOCKET, SO_RCVBUF, &bufferSize, sizeof(bufferSize));
sp<IBinder> token = new BBinder();
std::string serverChannelName = name + " (server)";
android::base::unique_fd serverFd(sockets[0]);
// 创建出server端InputChannel,并于socket关联
outServerChannel = InputChannel::create(serverChannelName, std::move(serverFd), token);
std::string clientChannelName = name + " (client)";
android::base::unique_fd clientFd(sockets[1]);
// 创建出client端InputChannel,并于socket关联
outClientChannel = InputChannel::create(clientChannelName, std::move(clientFd), token);
return OK;
}openInputChannelPair方法中会首先通过socketpair创建一对相互连接的套接字,然后分别给socket设置相应的选项值;然后通过InputChannel的create方法创建出两个分别与socket关联的inuptChannel。
4.8 InputChannel.create
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
sp<InputChannel> InputChannel::create(const std::string& name, android::base::unique_fd fd,
sp<IBinder> token) {
// 设置文件描述符fd的状态属性为O_NONBLOCK
const int result = fcntl(fd, F_SETFL, O_NONBLOCK);
if (result != 0) {
LOG_ALWAYS_FATAL("channel '%s' ~ Could not make socket non-blocking: %s", name.c_str(),
strerror(errno));
return nullptr;
}
// 创建出InputChannel并返回
return new InputChannel(name, std::move(fd), token);
}通过InputChannel的create方法构建出InputChannel并返回。
至此,InputChannel便创建并关联上socket上了。并且通过前面的介绍,我们知道了获取输入事件时是从client端的socket中读取消息并进行事件封装,然后传递到上层。但是这里我们发现有一个问题,就是client端socket中的数据是从哪里来的呢?我们继续看一下WindowState的openInputChannel方法。见4.4节
server端的InputChannel被注册到了InputManagerService中去了。
4.9 InputManagerService.registerInputChannel server端InputChannel的注册
/frameworks/base/services/core/java/com/android/server/input/InputManagerService.java
public void registerInputChannel(InputChannel inputChannel) {
if (inputChannel == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("inputChannel must not be null.");
}
// 调用native方法继续注册
nativeRegisterInputChannel(mPtr, inputChannel);
}在InputManagerService的registerInputChannel方法中直接调用了native方法nativeRegisterInputChannel。
4.10 com_android_server_input_ InputManagerService.nativeRegisterInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
static void nativeRegisterInputChannel(JNIEnv* env, jclass /* clazz */,
jlong ptr, jobject inputChannelObj) {
NativeInputManager* im = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputManager*>(ptr);
// 获取InputChannel
sp<InputChannel> inputChannel = android_view_InputChannel_getInputChannel(env,
inputChannelObj);
if (inputChannel == nullptr) {
throwInputChannelNotInitialized(env);
return;
}
// 将inputChannel注册到NativeInputManager中
status_t status = im->registerInputChannel(env, inputChannel);
// 设置dispose的callback,在inputChannel
// dispose之后会调用函数指针handleInputChannelDisposed
// 来调用NativeInputManager的unregisterInputChannel
// 解注册inputChannel
android_view_InputChannel_setDisposeCallback(env, inputChannelObj,
handleInputChannelDisposed, im);
}在native方法中,先调用了NativeInputManager的registerInputChannel方法注册inputChannel,然后会给inputChannel设置dispose callback,并且callback中执行了inputChannel的解注册。在NativeInputManager的registerInputChannel方法中,会获取InputDispatcher,并将inputChannel注册到其中去。
4.11 com_android_server_input_ InputManagerService.registerInputChannel
/frameworks/base/services/core/jni/com_android_server_input_InputManagerService.cpp
status_t NativeInputManager::registerInputChannel(JNIEnv* /* env */,
const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
ATRACE_CALL();
return mInputManager->getDispatcher()->registerInputChannel(inputChannel);
}4.12 InputDispatcher.registerInputChannel
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
#if DEBUG_REGISTRATION
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ registerInputChannel", inputChannel->getName().c_str());
#endif
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
// ...
// 创建connection并添加的注册列表中
sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, false /*monitor*/, mIdGenerator);
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd[fd] = connection;
mInputChannelsByToken[inputChannel->getConnectionToken()] = inputChannel;
// 将inputChannel的fd添加到looper中,并且对应的event是ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT
// 传入的looper callback为handleReceiveCallback方法,
// 因此当事件到来时,会触发此callback
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
} // release lock
// Wake the looper because some connections have changed.
mLooper->wake();
return OK;
}在InputDispatcher的registerInputChannel方法中,会通过InputChannel构建出Connection,然后将其添加到注册列表当中。
到了这里,server端的inputChannel最终被注册到了InputDispatcher的注册列表中去了,所以InputDispatcher中就可以通过向server端的socket中写入消息,然后client端就可以读取到了。但是这里还有一个问题,server端写入事件消息后,怎么通知到client去开始处理呢?这里我们回过头来看看4.1小结的内容,在setView方法中会创建app端的监听也就是WindowInputReceiver,并且把inputChannel传入进去。这里我们直接看WindowInputReceiver的父类,InputEventReceiver。
4.13 client端InputChannel读取事件并传递
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
public InputEventReceiver(InputChannel inputChannel, Looper looper) {
// ...
mInputChannel = inputChannel;
mMessageQueue = looper.getQueue();
// 将Java层的inputChannel向下层传递
mReceiverPtr = nativeInit(new WeakReference<InputEventReceiver>(this),
inputChannel, mMessageQueue);
mCloseGuard.open("dispose");
}在InputEventReceiver的构造方法中调用了native方法nativeInit进行native层的初始化
4.14 android_view_InputEventReceiver.nativeInit
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
static jlong nativeInit(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jobject receiverWeak,
jobject inputChannelObj, jobject messageQueueObj) {
// ...
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = new NativeInputEventReceiver(env,
receiverWeak, inputChannel, messageQueue);
// 初始化Receiver
status_t status = receiver->initialize();
// ...
return reinterpret_cast<jlong>(receiver.get());
}在NativeInputEventReceiver初始化时,会将inputChannel的文件描述符fd添加到looper中去,并且添加了looper callback为NativeInputEventReceiver实例自身,所以,当server端写入事件消息时,就会触发callback,于是便调用到NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent方法。
4.15 Looper.pollInner
/system/core/libutils/Looper.cpp
int Looper::pollInner(int timeoutMillis) {
....
int callbackResult = response.request.callback->handleEvent(fd, events, data);
if (callbackResult == 0) {
removeFd(fd, response.request.seq);
}
....
}looper callback为NativeInputEventReceiver实例自身,所以这里回调到NativeInputEventReceiver的handleEvent 方法。
4.16 android_view_InputEventReceiver.handleEvent
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
int NativeInputEventReceiver::handleEvent(int receiveFd, int events, void* data) {
// ...
// 接收添加的ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT事件
if (events & ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT) {
JNIEnv* env = AndroidRuntime::getJNIEnv();
// 调用consumeEvents方法处理事件
status_t status = consumeEvents(env, false /*consumeBatches*/, -1, nullptr);
mMessageQueue->raiseAndClearException(env, "handleReceiveCallback");
return status == OK || status == NO_MEMORY ? 1 : 0;
}
// ...
return 1;
}consumeEvents方法在其内部会通过jni的方式将事件向Java层传递到InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent,从而便实现了事件的分发。
4.17 小结
InputDispatcher是如果通过InputChannel将事件向上层进行分发的整个过程。首先是创建一对InputChannel,并且会开启一对相互连接的socket作为事件传递的媒介。server端的InputChannel会注册到InputDispatcher中去以完成事件的分发,并且会将其fd添加到looper中,而client端的InputChannel会在InputEventReceiver初始化时也会将其fd添加到looper中,并传入callback类接收server端写入的事件,这样整个过程便串联起来了。
5. InputConsumer处理事件
5.1 android_view_InputEventReceiver.consumeEvents
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::consumeEvents(JNIEnv* env,
bool consumeBatches, nsecs_t frameTime, bool* outConsumedBatch) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Consuming input events, consumeBatches=%s, frameTime=%" PRId64,
getInputChannelName().c_str(), toString(consumeBatches), frameTime);
}
// .....
// 这里通过InputConsumer的consume方法获取到inputevent
status_t status = mInputConsumer.consume(&mInputEventFactory,
consumeBatches, frameTime, &seq, &inputEvent,
&motionEventType, &touchMoveNum, &flag);
// 省略若干行
if (inputEventObj) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Dispatching input event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
// 此处通过jni调用InputEventReceiver的dispatchInputEvent方法进行事件的分发,
// 从而将input事件传递到java层
env->CallVoidMethod(receiverObj.get(),
gInputEventReceiverClassInfo.dispatchInputEvent, seq, inputEventObj);
if (env->ExceptionCheck()) {
ALOGE("Exception dispatching input event.");
skipCallbacks = true;
}
env->DeleteLocalRef(inputEventObj);
} else {
ALOGW("channel '%s' ~ Failed to obtain event object.",
getInputChannelName().c_str());
skipCallbacks = true;
}
if (skipCallbacks) {
mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal(seq, false);
}
}
consume方法中主要是从InputChannel获取输入事件的信息,然后根据消息中获取的事件类型构造出对应的event,并将消息中的事件信息赋值给event对象。在NativeInputEventReceiver的consumeEvents方法中,会循环调用InputConsumer的consume方法获取事件并进行处理。InputConsumer的consume方法中会通过InputChannel从socket中通过recv系统调用获取下层传递的事件,获取到事件后就会通过jni向Java层传递。
5.2 InputConsumer.consume
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputConsumer::consume(InputEventFactoryInterface* factory, bool consumeBatches,
nsecs_t frameTime, uint32_t* outSeq, InputEvent** outEvent,
int* motionEventType, int* touchMoveNumber, bool* flag) {
// ...
*outSeq = 0;
*outEvent = nullptr;
// Fetch the next input message.
// Loop until an event can be returned or no additional events are received.
while (!*outEvent) {
if (mMsgDeferred) {
// mMsg contains a valid input message from the previous call to consume
// that has not yet been processed.
mMsgDeferred = false;
} else {
// Receive a fresh message.
// 这里通过调用InputChannel的receiveMessage来获取消息
status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&mMsg);
// .....
}
// 根据消息的类型生成不同的Event
switch (mMsg.header.type) {
......
case InputMessage::Type::MOTION: {
// 构造一个MotionEvent
MotionEvent* motionEvent = factory->createMotionEvent();
if (!motionEvent) return NO_MEMORY;
updateTouchState(mMsg);
// 从msg中获取事件的各属性,并赋值给构造出的Event对象
initializeMotionEvent(motionEvent, &mMsg);
*outSeq = mMsg.body.motion.seq;
*outEvent = motionEvent;
if (DEBUG_TRANSPORT_ACTIONS) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' consumer ~ consumed motion event, seq=%u",
mChannel->getName().c_str(), *outSeq);
}
break;
}
// ....
}
}
return OK;
}5.3 event的构造和初始化
/frameworks/native/include/input/Input.h
class PreallocatedInputEventFactory : public InputEventFactoryInterface {
public:
PreallocatedInputEventFactory() { }
virtual ~PreallocatedInputEventFactory() { }
virtual KeyEvent* createKeyEvent() override { return &mKeyEvent; }
// 可以看到这里返回的是全局变量的地址
virtual MotionEvent* createMotionEvent() override { return &mMotionEvent; }
virtual FocusEvent* createFocusEvent() override { return &mFocusEvent; }
private:
// 这里定义不同类型的事件变量
KeyEvent mKeyEvent;
MotionEvent mMotionEvent;
FocusEvent mFocusEvent;
};5.3.1 event的初始化
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
// 对motion事件进行初始化
void InputConsumer::initializeMotionEvent(MotionEvent* event, const InputMessage* msg) {
// 省略若干行
event->initialize(msg->body.motion.eventId, msg->body.motion.deviceId, msg->body.motion.source,
msg->body.motion.displayId, msg->body.motion.hmac, msg->body.motion.action,
msg->body.motion.actionButton, msg->body.motion.flags,
msg->body.motion.edgeFlags, msg->body.motion.metaState,
msg->body.motion.buttonState, msg->body.motion.classification,
msg->body.motion.xScale, msg->body.motion.yScale, msg->body.motion.xOffset,
msg->body.motion.yOffset, msg->body.motion.xPrecision,
msg->body.motion.yPrecision, msg->body.motion.xCursorPosition,
msg->body.motion.yCursorPosition, msg->body.motion.downTime,
msg->body.motion.eventTime, pointerCount, pointerProperties, pointerCoords);
}这里主要是从msg中获取对应事件的详细信息然后赋值给对应的event对象上。
5.4 InputChannel.receiveMessage读取消息
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::receiveMessage(InputMessage* msg) {
ssize_t nRead;
do {
// 这里通过recv系统调用从socket中读取消息
nRead = ::recv(mFd.get(), msg, sizeof(InputMessage), MSG_DONTWAIT);
} while (nRead == -1 && errno == EINTR);
// .....
return OK;
}这个方法主要是从socket中读取消息,而socket的建立见第4节。
接收到消息之后我们回过头来看看5.1小结的内容,获取到消息之后通过jni调用InputEventReceiver中的dispatchInputEvent方法进行事件分发,从而将input事件传递到java层。
6. java层接收input事件进行分发
6.1 InputEventReceiver.dispatchInputEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
private void dispatchInputEvent(int seq, InputEvent event) {
mSeqMap.put(event.getSequenceNumber(), seq);
// 直接调用onInputEvent
onInputEvent(event);
}在InputEventReceiver中的dispatchInputEvent方法中会调用onInputEvent方法进行事件的处理,InputEventReceiver是抽象类,它的一个子类WindowInputEventReceiver是用来处理input事件的,WindowInputEventReceiver是frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java的内部类,它复写了onInputEvent方法,该方法中会调用enqueueInputEvent方法对事件进行入队。
6.2 WindowInputEventReceiver.onInputEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
@Override
public void onInputEvent(InputEvent event) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "processInputEventForCompatibility");
List<InputEvent> processedEvents;
try {
// 这块儿主要是对低版本进行兼容性处理
processedEvents =
mInputCompatProcessor.processInputEventForCompatibility(event);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
if (processedEvents != null) {
// 安卓M及以下版本,在这里处理
if (processedEvents.isEmpty()) {
// InputEvent consumed by mInputCompatProcessor
finishInputEvent(event, true);
} else {
for (int i = 0; i < processedEvents.size(); i++) {
enqueueInputEvent(
processedEvents.get(i), this,
QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_MODIFIED_FOR_COMPATIBILITY, true);
}
}
} else {
// 这里对事件进行入队
enqueueInputEvent(event, this, 0, true);
}
}onInputEvent方法中首先调用InputCompatProcessor的processInputEventForCompatibility方法对事件进行兼容性处理,这个方法中会判断应用的targetSdkVersion如果小于M并且是motion事件则进行兼容处理并返回,否则返回null;然后会调用enqueueInputEvent方法对事件进行入队。
6.3 InputCompatProcessor.processInputEventForCompatibility
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventCompatProcessor.java
public InputEventCompatProcessor(Context context) {
mContext = context;
// 获取应用的targetsdk版本
mTargetSdkVersion = context.getApplicationInfo().targetSdkVersion;
mProcessedEvents = new ArrayList<>();
}
public List<InputEvent> processInputEventForCompatibility(InputEvent e) {
// 小于M并且是motion事件则进行兼容处理
if (mTargetSdkVersion < Build.VERSION_CODES.M && e instanceof MotionEvent) {
mProcessedEvents.clear();
MotionEvent motion = (MotionEvent) e;
final int mask =
MotionEvent.BUTTON_STYLUS_PRIMARY | MotionEvent.BUTTON_STYLUS_SECONDARY;
final int buttonState = motion.getButtonState();
final int compatButtonState = (buttonState & mask) >> 4;
if (compatButtonState != 0) {
motion.setButtonState(buttonState | compatButtonState);
}
mProcessedEvents.add(motion);
return mProcessedEvents;
}
return null;
}6.4 转变事件类型并加入队列
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
void enqueueInputEvent(InputEvent event,
InputEventReceiver receiver, int flags, boolean processImmediately) {
// 转变为QueuedInputEvent
QueuedInputEvent q = obtainQueuedInputEvent(event, receiver, flags);
// 将事件插入到链表的末尾
QueuedInputEvent last = mPendingInputEventTail;
if (last == null) {
mPendingInputEventHead = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
} else {
last.mNext = q;
mPendingInputEventTail = q;
}
mPendingInputEventCount += 1;
Trace.traceCounter(Trace.TRACE_TAG_INPUT, mPendingInputEventQueueLengthCounterName,
mPendingInputEventCount);
if (processImmediately) {
// 调用doProcessInputEvents继续处理
doProcessInputEvents();
} else {
scheduleProcessInputEvents();
}
}此方法主要是将InputEvent转变为QueuedInputEvent并将其放到链表的末尾,然后调用doProcessInputEvents方法进行处理。
6.5 循环事件链并进行分发
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
void doProcessInputEvents() {
// 遍历整个链表,对事件进行分发
while (mPendingInputEventHead != null) {
QueuedInputEvent q = mPendingInputEventHead;
mPendingInputEventHead = q.mNext;
if (mPendingInputEventHead == null) {
mPendingInputEventTail = null;
}
q.mNext = null;
// .....
// 分发事件
deliverInputEvent(q);
}
}此方法中会遍历整个事件链表,对每个事件调用deliverInputEvent方法进行分发。
6.6 将事件分发到InputStage
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private void deliverInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
// .....
try {
// .....
InputStage stage;
if (q.shouldSendToSynthesizer()) {
// flag包含FLAG_UNHANDLED会走这里
stage = mSyntheticInputStage;
} else {
// 是否跳过输入法窗口进行分发
stage = q.shouldSkipIme() ? mFirstPostImeInputStage : mFirstInputStage;
}
// ............
if (stage != null) {
// 处理窗口焦点变更
handleWindowFocusChanged();
// 分发事件
stage.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
}此方法中会根据flag获取InputStage,然后调用InputStage的deliver方法分发事件,它主要是用来将事件的处理分成多个阶段进行。
6.6.1 InputStage是什么?
InputStage主要是用来将事件的处理分成若干个阶段(stage)进行,事件依次经过每一个stage,如果该事件没有被处理(标识为FLAG_FINISHED),则该stage就会调用onProcess方法处理,然后调用forward执行下一个stage的处理;如果该事件被标识为处理则直接调用forward,执行下一个stage的处理,直到没有下一个stage(也就是最后一个SyntheticInputStage)。这里一共有7种stage,各个stage间串联起来,形成一个链表,各个stage的处理过程大致如下图所示:
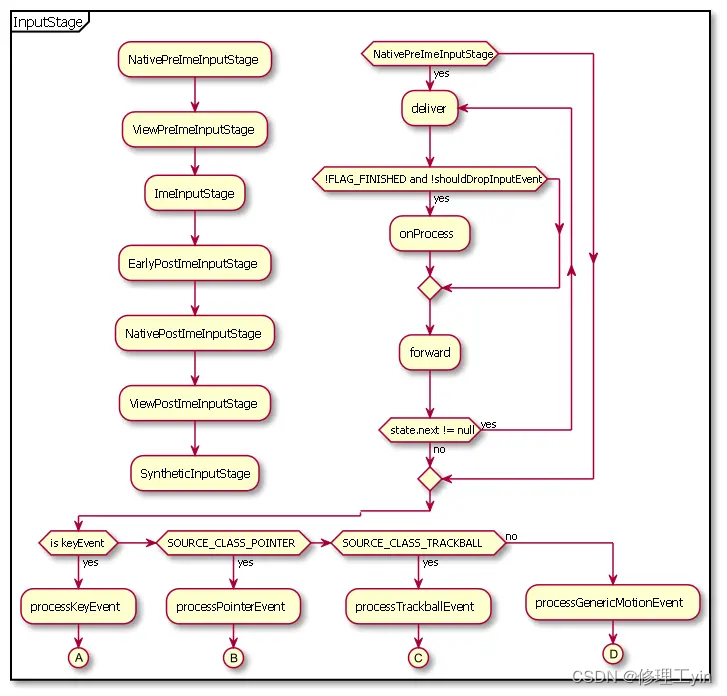
先来看下这些stage是如何串起来的,所有的Stage都继承于InputStage,而InputStage是抽象类,它的定义如下:
6.6.2 InputStage构造函数
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
abstract class InputStage {
private final InputStage mNext;
/**
* Creates an input stage.
* @param next The next stage to which events should be forwarded.
*/
public InputStage(InputStage next) {
// 从构成函数的定义能够看到,传入的next会赋值给当前实例的next,
// 因此,先插入的就会是最后一个节点(头插法),最终会形成一个链表
mNext = next;
}
}在ViewRootImpl的setView方法中有以下代码段:
6.6.3 ViewRootImpl.setView
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
// 如下创建出来的7个实例会串在一起形成一个链表,
// 链表的头是最后创建出来的nativePreImeStage,
// 链表的尾是首先构造出来的mSyntheticInputStage
// Set up the input pipeline.
mSyntheticInputStage = new SyntheticInputStage();
InputStage viewPostImeStage = new ViewPostImeInputStage(mSyntheticInputStage);
InputStage nativePostImeStage = new NativePostImeInputStage(viewPostImeStage,
"aq:native-post-ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage earlyPostImeStage = new EarlyPostImeInputStage(nativePostImeStage);
// 输入法对应的stage
InputStage imeStage = new ImeInputStage(earlyPostImeStage,
"aq:ime:" + counterSuffix);
InputStage viewPreImeStage = new ViewPreImeInputStage(imeStage);
InputStage nativePreImeStage = new NativePreImeInputStage(viewPreImeStage,
"aq:native-pre-ime:" + counterSuffix);
// 第一个处理事件的stage为NativePreImeInputStage
mFirstInputStage = nativePreImeStage;
mFirstPostImeInputStage = earlyPostImeStage;6.7 ViewRootImpl.deliver分发传递事件
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public final void deliver(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if ((q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED) != 0) {
// 调用next的deliver方法继续分发处理
forward(q);
} else if (shouldDropInputEvent(q)) {
finish(q, false);
} else {
traceEvent(q, Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
final int result;
try {
// 自身处理事件
result = onProcess(q);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
// 判断是否需要继续分发处理
apply(q, result);
}
}从native层的时候是以触摸事件展开分析,所以这里依然以触摸事件进行分析。
前面提到InputStage 是一个链表结构,内部采用拦截器模式来分发事件。
触摸事件会直接到ViewPostImeInputStage去进行拦截处理。
6.8 ViewPostImeInputStage.onProcess处理input事件
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (q.mEvent instanceof KeyEvent) {
// 处理key事件
return processKeyEvent(q);
} else {
final int source = q.mEvent.getSource();
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_POINTER) != 0) {
// 处理pointer事件
return processPointerEvent(q);
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_TRACKBALL) != 0) {
// 处理轨迹球事件
return processTrackballEvent(q);
} else {
// 处理一般的motion事件
return processGenericMotionEvent(q);
}
}
}6.9 ViewPostImeInputStage.processPointerEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
private int processPointerEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
final MotionEvent event = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
mAttachInfo.mUnbufferedDispatchRequested = false;
mAttachInfo.mHandlingPointerEvent = true;
// 调用view的dispatchPointerEvent来分发事件,此处的mView是decorview
boolean handled = mView.dispatchPointerEvent(event);
maybeUpdatePointerIcon(event);
maybeUpdateTooltip(event);
mAttachInfo.mHandlingPointerEvent = false;
if (mAttachInfo.mUnbufferedDispatchRequested && !mUnbufferedInputDispatch) {
mUnbufferedInputDispatch = true;
if (mConsumeBatchedInputScheduled) {
scheduleConsumeBatchedInputImmediately();
}
}
// 如果已经消费事件,就拦截事件,返回finish
return handled ? FINISH_HANDLED : FORWARD;
}这里的mView.dispatchPointerEvent会走到View.java里面的dispatchPointerEvent方法里面去,View.java属于DecorView的父类,具体实现逻辑由它的子类实现,所以这里又会走到DecorView 中的dispatchTouchEvent 方法去。
6.10 DecorView.dispatchTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/DecorView.java
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// 通过phineWindow获取callBack
final Window.Callback cb = mWindow.getCallback();
return cb != null && !mWindow.isDestroyed() && mFeatureId < 0
? cb.dispatchTouchEvent(ev) : super.dispatchTouchEvent(ev);
}这里的Window.Callback实际就是Activity的实例,Activity默认实现了Window.Callback接口的方法,这里就会将事件传递到Activity里。
6.11 Activity.dispatchTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/app/Activity.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN) {
onUserInteraction();
}
// getWindow返回的是PhoneWindow的实例
if (getWindow().superDispatchTouchEvent(ev)) {
return true;
}
return onTouchEvent(ev);
}getWindow返回的是PhoneWindow的实例,所以这里会调用到PhoneWindow中的superDispatchTouchEvent方法里面去了。
6.12 PhoneWindow.superDispatchTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/PhoneWindow.java
@Override
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
// 调用DecorView的同名方法
return mDecor.superDispatchTouchEvent(event);
}6.13 DecorView.superDispatchTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/com/android/internal/policy/DecorView.java
public boolean superDispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
return super.dispatchTouchEvent(event);
}这里会直接调用DecorView的父类的dispatchTouchEvent方法,这里开始执行一个事件传递到View树的过程。
6.14 ViewGroup.dispatchTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
@Override
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
// 检查是否拦截
final boolean intercepted;
if (actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
|| mFirstTouchTarget != null) { // 有触摸目标或者action为down
final boolean disallowIntercept = (mGroupFlags & FLAG_DISALLOW_INTERCEPT) != 0;
if (!disallowIntercept) {
intercepted = onInterceptTouchEvent(ev); // 判断是否拦截,默认false
ev.setAction(action);
}
} else {
// 没有触摸目标,此操作不是初始关闭,因此此视图组继续拦截触摸。
intercepted = true;
}
// 检查是否取消
final boolean canceled = resetCancelNextUpFlag(this)
|| actionMasked == MotionEvent.ACTION_CANCEL;
// 没有取消,也没有被拦截
if (!canceled && !intercepted) {
// 找一个可以接收事件的孩子。从前到后扫描mChildren。
final View[] children = mChildren;
for (int i = childrenCount - 1; i >= 0; i--) {
if (dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, false, child, idBitsToAssign)) {
// childView想在边界内接受触摸。
}
}
}
// 分发给触摸目标。
if (mFirstTouchTarget == null) {
// 没有触摸目标,因此请将其视为普通视图
handled = dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(ev, canceled, null,
TouchTarget.ALL_POINTER_IDS);
}
....
}6.15 ViewGroup.onInterceptTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
这个方法默认不做拦截:
public boolean onInterceptTouchEvent(MotionEvent ev) {
if (ev.isFromSource(InputDevice.SOURCE_MOUSE)
&& ev.getAction() == MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN
&& ev.isButtonPressed(MotionEvent.BUTTON_PRIMARY)
&& isOnScrollbarThumb(ev.getX(), ev.getY())) {
return true;
}
return false;
}6.16 ViewGroup.dispatchTransformedTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewGroup.java
这个方法负责将运动事件转换为特定子视图的坐标空间,如果子项为空, MotionEvent 将改为发送到此viewgroup,最后都会调用到view的dispatchTouchEvent去处理:
private boolean dispatchTransformedTouchEvent(MotionEvent event, boolean cancel,
View child, int desiredPointerIdBits) {
....
if (child == null) {
// 调用View的dispatchTouchEvent
handled = super.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
} else {
final float offsetX = mScrollX - child.mLeft;
final float offsetY = mScrollY - child.mTop;
transformedEvent.offsetLocation(offsetX, offsetY);
if (! child.hasIdentityMatrix()) {
transformedEvent.transform(child.getInverseMatrix());
}
// 调用子View的dispatchTouchEvent
handled = child.dispatchTouchEvent(transformedEvent);
}
return handled;
}6.17 View.dispatchTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public boolean dispatchTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
.....
if (onFilterTouchEventForSecurity(event)) {
// 如果有设置OnTouchListener,就先交给mOnTouchListener 处理
ListenerInfo li = mListenerInfo;
if (li != null && li.mOnTouchListener != null
&& (mViewFlags & ENABLED_MASK) == ENABLED
&& li.mOnTouchListener.onTouch(this, event)) {
result = true;
}
// 如果没有处理,交给onTouchEvent方法
if (!result && onTouchEvent(event)) {
result = true;
}
}
....
}6.18 View.onTouchEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/View.java
public boolean onTouchEvent(MotionEvent event) {
...........
// 如果设置了mTouchDelegate,就直接交给它处理
if (mTouchDelegate != null) {
if (mTouchDelegate.onTouchEvent(event)) {
return true;
}
}
// 如果可以点击或者支持在悬停或长按时显示工具提示。
if (clickable || (viewFlags & TOOLTIP) == TOOLTIP) {
switch (action) {
case MotionEvent.ACTION_UP:
....
// 仅当我们处于按下状态时才执行单击操作
if (!focusTaken) {
if (mPerformClick == null) {
mPerformClick = new PerformClick();
}
if (!post(mPerformClick)) {
performClickInternal();
}
}
break;
case MotionEvent.ACTION_DOWN:
// 对于滚动容器内的视图,将按下的反馈延迟一小段时间,以防这是滚动。
if (isInScrollingContainer) {
mPrivateFlags |= PFLAG_PREPRESSED;
if (mPendingCheckForTap == null) {
mPendingCheckForTap = new CheckForTap();
}
mPendingCheckForTap.x = event.getX();
mPendingCheckForTap.y = event.getY();
postDelayed(mPendingCheckForTap, ViewConfiguration.getTapTimeout());
} else {
// 不在滚动容器内,因此立即显示反馈
setPressed(true, x, y);
// 检查是否长按
checkForLongClick(0, x, y);
}
break;
}
return false;
}这个方法里面在action_down的时候,会延迟检查是否发生长按事件,执行相应的performLongClick方法。
在action_up的时候,会post一个PerformClick,执行相应的单击事件的方法。
6.19 小结
通过以上分析,我们便了解了input事件从Native层传递到Java层,然后继续传递到View树上的整个过程。需要注意的是,在各个传递环节,如果调用方法返回了true,就代表它消费掉了本次事件,那么就不会继续朝后传递。另外,对于ViewGroup来说,存在onInterceptTouchEvent方法,此方法用来拦截事件向子view分发,如果返回了true,事件就会传递到当前ViewGroup的onTouchEvent中而不在向子View传递;否则的话,会分发到当前ViewGroup,然后再传递到子View。由于View不能包含子View,所以View不存在拦截方法。
7. 事件确认
在ViewPostImeInputStage 中,如果我们的view处理了对应的事件,就会调用到finish方法,接着调用下一个处理器:
7.1 ViewRootImpl.finish
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
protected void apply(QueuedInputEvent q, int result) {
if (result == FORWARD) {
forward(q);
} else if (result == FINISH_HANDLED) {
finish(q, true);
} else if (result == FINISH_NOT_HANDLED) {
finish(q, false);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid result: " + result);
}
}
protected void finish(QueuedInputEvent q, boolean handled) {
q.mFlags |= QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED;
if (handled) {
q.mFlags |= QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED_HANDLED;
}
forward(q);
}
// 调用下一个处理器
protected void forward(QueuedInputEvent q) {
onDeliverToNext(q);
}由6.6.3小结可知,下一个处理器是SyntheticInputStage,在onProcess方法里面的返回值是FORWARD,所以走到apply方法里面去会走到forward方法,紧接着调用onDeliverToNext,由于next为null就会调用finishInputEvent方法:
7.2 ViewRootImpl.onDeliverToNext
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
final class SyntheticInputStage extends InputStage {
public SyntheticInputStage() {
super(null);
}
@Override
protected int onProcess(QueuedInputEvent q) {
q.mFlags |= QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_RESYNTHESIZED;
if (q.mEvent instanceof MotionEvent) {
final MotionEvent event = (MotionEvent)q.mEvent;
final int source = event.getSource();
// 是轨迹球
if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_TRACKBALL) != 0) {
mTrackball.process(event);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
// 是操纵杆
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_CLASS_JOYSTICK) != 0) {
mJoystick.process(event);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
// 是摸导航
} else if ((source & InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCH_NAVIGATION)
== InputDevice.SOURCE_TOUCH_NAVIGATION) {
mTouchNavigation.process(event);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
} else if ((q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_UNHANDLED) != 0) {
mKeyboard.process((KeyEvent)q.mEvent);
return FINISH_HANDLED;
}
return FORWARD;
}
}
..........................
protected void apply(QueuedInputEvent q, int result) {
if (result == FORWARD) {
forward(q);
} else if (result == FINISH_HANDLED) {
finish(q, true);
} else if (result == FINISH_NOT_HANDLED) {
finish(q, false);
} else {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("Invalid result: " + result);
}
}
.......................
protected void forward(QueuedInputEvent q) {
onDeliverToNext(q);
}
......................
protected void onDeliverToNext(QueuedInputEvent q) {
if (mNext != null) {
mNext.deliver(q);
} else {
finishInputEvent(q);
}
}
.........7.3 ViewRootImpl.finishInputEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/ViewRootImpl.java
public InputEventReceiver mReceiver;
...........
private void finishInputEvent(QueuedInputEvent q) {
Trace.asyncTraceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "deliverInputEvent",
q.mEvent.getId());
if (q.mReceiver != null) {
boolean handled = (q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_FINISHED_HANDLED) != 0;
boolean modified = (q.mFlags & QueuedInputEvent.FLAG_MODIFIED_FOR_COMPATIBILITY) != 0;
if (modified) {
Trace.traceBegin(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW, "processInputEventBeforeFinish");
InputEvent processedEvent;
try {
processedEvent =
mInputCompatProcessor.processInputEventBeforeFinish(q.mEvent);
} finally {
Trace.traceEnd(Trace.TRACE_TAG_VIEW);
}
if (processedEvent != null) {
q.mReceiver.finishInputEvent(processedEvent, handled);
}
} else {
q.mReceiver.finishInputEvent(q.mEvent, handled);
}
} else {
q.mEvent.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();
}
/ 回收队列中的输入事件
recycleQueuedInputEvent(q);
}7.4 InputEventReceiver.finishInputEvent
/frameworks/base/core/java/android/view/InputEventReceiver.java
public final void finishInputEvent(InputEvent event, boolean handled) {
if (event == null) {
throw new IllegalArgumentException("event must not be null");
}
if (mReceiverPtr == 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event but the input event "
+ "receiver has already been disposed.");
} else {
int index = mSeqMap.indexOfKey(event.getSequenceNumber());
if (index < 0) {
Log.w(TAG, "Attempted to finish an input event that is not in progress.");
} else {
int seq = mSeqMap.valueAt(index);
mSeqMap.removeAt(index);
// 调用naive接口通知事件是否已经消费
nativeFinishInputEvent(mReceiverPtr, seq, handled);
}
}
event.recycleIfNeededAfterDispatch();
}7.5 android_view_InputEventReceiver.nativeFinishInputEvent
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
static void nativeFinishInputEvent(JNIEnv* env, jclass clazz, jlong receiverPtr,
jint seq, jboolean handled) {
sp<NativeInputEventReceiver> receiver = reinterpret_cast<NativeInputEventReceiver*>(receiverPtr);
status_t status = receiver->finishInputEvent(seq, handled);
.....
}7.6 NativeInputEventReceiver.finishInputEvent
/frameworks/base/core/jni/android_view_InputEventReceiver.cpp
status_t NativeInputEventReceiver::finishInputEvent(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Finished input event.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
// mInputConsumer是InputConsumer的实例
status_t status = mInputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal(seq, handled);
if (status) {
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
if (kDebugDispatchCycle) {
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ Could not send finished signal immediately. "
"Enqueued for later.", getInputChannelName().c_str());
}
Finish finish;
finish.seq = seq;
finish.handled = handled;
mFinishQueue.add(finish);
if (mFinishQueue.size() == 1) {
setFdEvents(ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT | ALOOPER_EVENT_OUTPUT);
}
return OK;
}
ALOGW("Failed to send finished signal on channel '%s'. status=%d",
getInputChannelName().c_str(), status);
}
return status;
}7.7 InputConsumer.sendFinishedSignal
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputConsumer::sendFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
if (seqChainCount) {
....
while (!status && chainIndex > 0) {
chainIndex--;
status = sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(chainSeqs[chainIndex], handled);
}
....
}
// 为批次中的最后一条消息发送完成信号。
return sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(seq, handled);
}7.8 InputConsumer.sendUnchainedFinishedSignal
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputConsumer::sendUnchainedFinishedSignal(uint32_t seq, bool handled) {
InputMessage msg;
msg.header.type = InputMessage::Type::FINISHED;
msg.body.finished.seq = seq;
msg.body.finished.handled = handled ? 1 : 0;
return mChannel->sendMessage(&msg);
}这里通过InputChannel 发送完成信号。
前面第4节已经说过InputChannel的创建与初始化,包括client与server端的注册。
当窗口与输入系统建立连接时,Looper 通过 epoll 机制监听连接的输入端的文件描述符,当窗口通过连接反馈处理结果时,epoll 就会收到可读事件,因此 InputDispatcher 线程会被唤醒来读取窗口的事件处理结果。
发送消息过来之后触发handleReceiveCallback回调:
7.9 InputChannel发送消息到inputDispatcher线程handleReceiveCallback回调
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputChannel::sendMessage(const InputMessage* msg) {
const size_t msgLength = msg->size();
InputMessage cleanMsg;
// copy一份msg
msg->getSanitizedCopy(&cleanMsg);
ssize_t nWrite;
do {
// 通过socket循环写入msg
nWrite = ::send(mFd.get(), &cleanMsg, msgLength, MSG_DONTWAIT | MSG_NOSIGNAL);
} while (nWrite == -1 && errno == EINTR);
..........
return OK;
}
..........
frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
status_t InputDispatcher::registerInputChannel(const sp<InputChannel>& inputChannel) {
#if DEBUG_REGISTRATION
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ registerInputChannel", inputChannel->getName().c_str());
#endif
{ // acquire lock
std::scoped_lock _l(mLock);
// ...
// 创建connection并添加的注册列表中
sp<Connection> connection = new Connection(inputChannel, false /*monitor*/, mIdGenerator);
int fd = inputChannel->getFd();
mConnectionsByFd[fd] = connection;
mInputChannelsByToken[inputChannel->getConnectionToken()] = inputChannel;
// 将inputChannel的fd添加到looper中,并且对应的event是ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT
// 传入的looper callback为handleReceiveCallback方法,
// 因此当事件到来时,会触发此callback
mLooper->addFd(fd, 0, ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT, handleReceiveCallback, this);
} // release lock
// Wake the looper because some connections have changed.
mLooper->wake();
return OK;
}7.10 InputDispatcher.handleReceiveCallback
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
int InputDispatcher::handleReceiveCallback(int fd, int events, void* data) {
InputDispatcher* d = static_cast<InputDispatcher*>(data);
{ // acquire lock
AutoMutex _l(d->mLock);
ssize_t connectionIndex = d->mConnectionsByFd.indexOfKey(fd);
if (connectionIndex < 0) {
ALOGE("Received spurious receive callback for unknown input channel. "
"fd=%d, events=0x%x", fd, events);
return 0; // remove the callback
}
bool notify;
sp<Connection> connection = d->mConnectionsByFd.valueAt(connectionIndex);
if (!(events & (ALOOPER_EVENT_ERROR | ALOOPER_EVENT_HANGUP))) {
if (!(events & ALOOPER_EVENT_INPUT)) {
ALOGW("channel '%s' ~ Received spurious callback for unhandled poll event. "
"events=0x%x", connection->getInputChannelName(), events);
return 1;
}
nsecs_t currentTime = now();
bool gotOne = false;
status_t status;
// 通过一个无限循环读取,尽可能读取所有的反馈结果
for (;;) {
uint32_t seq;
bool handled;
// 接收消息
status = connection->inputPublisher.receiveFinishedSignal(&seq, &handled);
if (status) {
break;
}
// 调用 InputDispatcher 类 finishDispatchCycleLocked 方法
d->finishDispatchCycleLocked(currentTime, connection, seq, handled);
gotOne = true;
}
if (gotOne) {
// 调用 runCommandsLockedInterruptible 执行命令(Commond)
d->runCommandsLockedInterruptible();
if (status == WOULD_BLOCK) {
return 1;
}
}
......
} else {
......
}
......
} // release lock
}主要作用:
- mConnectionsByFd 取出 Connection
- 调用 Connection 类成员变量 inputPublisher 的 receiveFinishedSignal 方法接收消息
- 调用 InputDispatcher 类 finishDispatchCycleLocked 方法
- 调用 runCommandsLockedInterruptible 执行命令(Commond)
7.11 InputPublisher.receiveFinishedSignal
/frameworks/native/libs/input/InputTransport.cpp
status_t InputPublisher::receiveFinishedSignal(uint32_t* outSeq, bool* outHandled) {
......
InputMessage msg;
status_t result = mChannel->receiveMessage(&msg);
if (result) {
*outSeq = 0;
*outHandled = false;
return result;
}
if (msg.header.type != InputMessage::TYPE_FINISHED) {
ALOGE("channel '%s' publisher ~ Received unexpected message of type %d from consumer",
mChannel->getName().string(), msg.header.type);
return UNKNOWN_ERROR;
}
*outSeq = msg.body.finished.seq;
*outHandled = msg.body.finished.handled;
return OK;
}从服务端 InputChannel 读取发来的消息。
7.12 InputDispatcher.finishDispatchCycleLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::finishDispatchCycleLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq,
bool handled) {
#if DEBUG_DISPATCH_CYCLE
ALOGD("channel '%s' ~ finishDispatchCycle - seq=%u, handled=%s",
connection->getInputChannelName().c_str(), seq, toString(handled));
#endif
if (connection->status == Connection::STATUS_BROKEN ||
connection->status == Connection::STATUS_ZOMBIE) {
return;
}
// Notify other system components and prepare to start the next dispatch cycle.
// // 通知其他系统组件并准备开始下一个调度周期
onDispatchCycleFinishedLocked(currentTime, connection, seq, handled);
}7.13 InputDispatcher.onDispatchCycleFinishedLocked
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::onDispatchCycleFinishedLocked(nsecs_t currentTime,
const sp<Connection>& connection, uint32_t seq,
bool handled) {
// 创建命令并加入到命令队列 mCommandQueue 中
// 当命令调用时,会执行 doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible 函数
std::unique_ptr<CommandEntry> commandEntry = std::make_unique<CommandEntry>(
&InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible);
commandEntry->connection = connection;
commandEntry->eventTime = currentTime;
commandEntry->seq = seq;
commandEntry->handled = handled;
postCommandLocked(std::move(commandEntry));
}7.14 InputDispatcher.doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible
/frameworks/native/services/inputflinger/dispatcher/InputDispatcher.cpp
void InputDispatcher::doDispatchCycleFinishedLockedInterruptible(CommandEntry* commandEntry) {
sp<Connection> connection = commandEntry->connection;
const nsecs_t finishTime = commandEntry->eventTime;
uint32_t seq = commandEntry->seq;
const bool handled = commandEntry->handled;
// Handle post-event policy actions.
// 根据序号seq,从连接的等待队列中获取事件
std::deque<DispatchEntry*>::iterator dispatchEntryIt = connection->findWaitQueueEntry(seq);
if (dispatchEntryIt == connection->waitQueue.end()) {
return;
}
// 获取对应的事件
DispatchEntry* dispatchEntry = *dispatchEntryIt;
// 如果事件处理的有一点点慢,但是没超过超时事件,那么这里会给一个警告
// 这也说明,窗口处理事件,不要执行耗时的代码
const nsecs_t eventDuration = finishTime - dispatchEntry->deliveryTime;
if (eventDuration > SLOW_EVENT_PROCESSING_WARNING_TIMEOUT) {
ALOGI("%s spent %" PRId64 "ms processing %s", connection->getWindowName().c_str(),
ns2ms(eventDuration), dispatchEntry->eventEntry->getDescription().c_str());
}
reportDispatchStatistics(std::chrono::nanoseconds(eventDuration), *connection, handled);
bool restartEvent;
if (dispatchEntry->eventEntry->type == EventEntry::Type::KEY) {
KeyEntry* keyEntry = static_cast<KeyEntry*>(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
restartEvent =
afterKeyEventLockedInterruptible(connection, dispatchEntry, keyEntry, handled);
} else if (dispatchEntry->eventEntry->type == EventEntry::Type::MOTION) {
MotionEntry* motionEntry = static_cast<MotionEntry*>(dispatchEntry->eventEntry);
restartEvent = afterMotionEventLockedInterruptible(connection, dispatchEntry, motionEntry,
handled);
} else {
restartEvent = false;
}
// Dequeue the event and start the next cycle.
// Because the lock might have been released, it is possible that the
// contents of the wait queue to have been drained, so we need to double-check
// a few things.
dispatchEntryIt = connection->findWaitQueueEntry(seq);
if (dispatchEntryIt != connection->waitQueue.end()) {
dispatchEntry = *dispatchEntryIt;
// 从 Connection::waitQueue 中移除等待反馈的事件
connection->waitQueue.erase(dispatchEntryIt);
// 既然事件处理结果已经反馈了,那么就不用再记录它的处理超时时间了
mAnrTracker.erase(dispatchEntry->timeoutTime,
connection->inputChannel->getConnectionToken());
// 连接从无响应变为可响应,那么停止 ANR
if (!connection->responsive) {
connection->responsive = isConnectionResponsive(*connection);
}
traceWaitQueueLength(connection);
if (restartEvent && connection->status == Connection::STATUS_NORMAL) {
connection->outboundQueue.push_front(dispatchEntry);
traceOutboundQueueLength(connection);
} else {
releaseDispatchEntry(dispatchEntry);
}
}
// Start the next dispatch cycle for this connection.
// 既然通过连接收到反馈,那趁这个机会,如果发件箱还有事件,继续启动分发循环来发送事件
startDispatchCycleLocked(now(), connection);
}7.15 小结
- 检查连接中是否有对应的正在的等待的事件。
- 窗口已经反馈的事件的处理结果,那么从连接的等待队列 Connection::waitQueue 中移除。
- 窗口已经反馈的事件的处理结果,那么就不必处理这个事件的 ANR,因此移除事件的 ANR 超时时间。
- 此时窗口正在反馈事件的处理结果,那趁热打铁,那么开启下一次分发循环,发送连接发件箱中的事件。当然,如果发件箱没有事件,那么什么也不做。
完成分发循环,其实最主要的就是把按键事件从连接的等待队列中移除,以及解除 ANR 的触发。






















 3829
3829











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








