1.栈
1.1 栈的定义
-
定义
stack,只允许在一端进行插入和删除的线性表。
-
重要术语:栈顶、栈底、空栈:
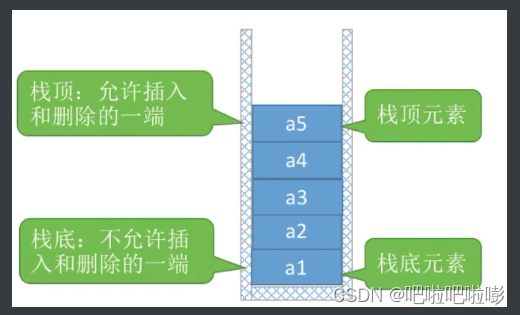
- 特点:后进先出
-
-
卡特兰数
当n个不同元素进栈时,出栈元素不同排序的个数为
$ \frac{1}{n+1}\quad C_{2n}^n$
1.2 顺序栈
1.2.1 初始化
- 定义
typedef struct{
ElemType data[MaxSize]; //静态数组存放在栈中元素
int top; //栈顶指针
}SqStack;
-
初始化
void InitStack(SqStack &S){ S.top=-1; } -
判空
bool StackEmpty(SqStack S){ if(S.top==-1) return true; else return false; }
1.2.2 进栈
bool Push(SqStack &S,ElemType x){
if(S.top==MaxSize-1)return false; //栈满报错
S.data[++S.top]=x; //增加top指针后,在top指针所指位置插入新元素x
return true;
}
1.2.3 出栈
bool Pop(SqStack &S,ElemType &x){
if(S.top==-1)return false; //空栈报错
x=S.data[S.top--]; //返回要删除的原栈顶元素后,top-1,把栈顶元素删除
return true;
}
1.2.4 读取栈顶元素
bool GetTop(SqStack S,ElemType &x){
if(S.top==-1)return false;
x=S.data[S.top]; //x记录栈顶元素
return true;
}
1.2.5 共享栈
-
顺序栈无法动态分配内存,会浪费部分内存。
-
所以可用两个top指针的共享栈:
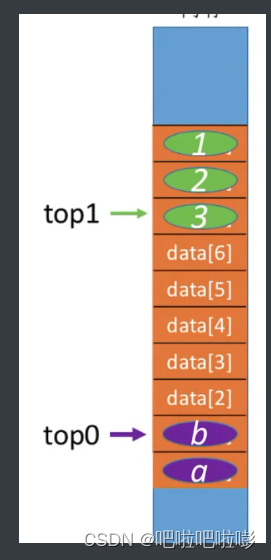
如图,top0从下往上存储,top1从上往下存储。
typedef struct{
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top0; //栈顶指针
int top1; //栈顶指针
}ShStack;
//初始化
void InitStack(ShStack &S){
S.top0=0; //从下往上存储
S.top1=MaxSize; //从上往下存储
}
//判满条件:
top0+1==top1;
*完整代码 顺序栈
#include<stdio.h>
#define MaxSize 99
#define ElemType int
typedef struct {
ElemType data[MaxSize];
int top;
}SqStack;
void InitStack(SqStack& S) {
S.top = -1;
}
bool StackEmpty(SqStack& S) {
if (S.top == -1)
return true;
else
return false;
}
bool Push(SqStack& S, ElemType x) {
if (S.top + 1 == MaxSize)return false;
S.data[++S.top] = x;
return true;
}
bool Pop(SqStack& S, ElemType& x) {
if (S.top == -1)return false;
x = S.data[S.top--];
return true;
}
bool GetTop(SqStack& S, ElemType& x) {
if (S.top == -1)return false;
x = S.data[S.top];
return true;
}
void PrintS(SqStack& S) {
int i = S.top;
while (i >=0) {
printf("%d\n", S.data[i--]);
}
printf("\n");
}
int main() {
SqStack S;
InitStack(S);
printf("入栈:\n");
Push(S, 2);
Push(S, 4);
Push(S, 5);
PrintS(S);
printf("出栈:\n");
int x;
Pop(S, x);
printf("出栈元素:%d\n", x);
PrintS(S);
GetTop(S, x);
printf("获取栈顶元素:%d",x );
}

1.3 链栈
-
定义
用链式存储的栈。
-
优点:便于多个栈共享存储空间,不存在栈满的情况。
-
实现:用单链表实现,且规定所有操作只能在单链表表头实现。
-
*完整代码 链栈
#define _CRT_SECURE_NO_WARNINGS
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define ElemType int
typedef struct LSnode{
ElemType data;//数据域
struct LSnode* next;//指针域
}LSnode, * LiStack;
//带头结点初始化
void InitStack(LiStack& S) {
S = (LSnode*)malloc(sizeof(LSnode));
S->next = NULL;
}
//相当于链表的头插法
void Push(LiStack& S, ElemType x) {
LSnode* q = (LSnode*)malloc(sizeof(LSnode));
q->data = x;
q->next = S->next;
S->next = q;
}
bool Pop(LiStack& S, ElemType& x) {
LSnode* q = S->next;
if (q == NULL)return false;
x = q->data;
S->next = q->next;
free(q);
return true;
}
bool GetItem(LiStack& S, ElemType& x) {
if (S->next == NULL)return false;
x= S->next->data;
return true;
}
void PrintS(LiStack& S) {
LSnode* p = S->next;
while (p != NULL) {
printf("%d\n", p->data);
p = p->next;
}
}
int main() {
LiStack S;
InitStack(S);
printf("入栈:\n");
Push(S, 1);
Push(S, 2);
Push(S, 3);
PrintS(S);
int x;
Pop(S, x);
printf("出栈元素为:%d\n", x);
PrintS(S);
GetItem(S, x);
printf("返回栈顶元素:%d\n", x);
}





 本文详细介绍了栈的基本概念、顺序栈(包括初始化、判空、进栈、出栈和读取栈顶元素)以及链栈(带头结点的实现)的定义、操作和代码示例。重点强调了顺序栈的局限性和链栈的优势。
本文详细介绍了栈的基本概念、顺序栈(包括初始化、判空、进栈、出栈和读取栈顶元素)以及链栈(带头结点的实现)的定义、操作和代码示例。重点强调了顺序栈的局限性和链栈的优势。
















 551
551

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








