如果有正在学习计算机操作系统的小伙伴,可以通过此文章对 进程调度模拟程序,生产者――消费者问题算法的实现,银行家算法的实现更加清楚。
本人也只是一个学生,下面内容我主要整合了一些学习心得和成果,还有能够帮助自己快速掌握知识的视频,网站,链接。希望对你们有用。
1. 进程调度模拟程序
#include <algorithm>
#include <iostream>
#include <vector>
using namespace std;
struct PCB//类定义PCB表
{
string ID; //进程的名字
int arrive_time; //进入进程队列的时间
int CPUtime; //进程运行完需要的时间
int priority; //优先级
char status;//进程状态,"R"-运行态,"W"表示就绪态
};
vector<PCB> EnterReadyQueue;
//排序方式 按进入进程队列的时间先后排 时间相同则把运行时间长的放前面
bool cmp0(PCB a, PCB b) {
if (a.arrive_time == b.arrive_time) {
return a.CPUtime < b.CPUtime;
}
return a.arrive_time < b.arrive_time; //对时间进行排序。
}
//排序方式 按进入进程队列的优先级排 优先级相同则把进队时间先的放前面
bool cmp1(PCB a, PCB b) {
if (a.priority == b.priority) {
return a.arrive_time < b.arrive_time;
}
return a.priority > b.priority; //对时间进行排序。
}
void print_queue() { //打印当前就绪队列的情况。
cout << "<-------------------------------->" << endl;
cout << "进程名字 到达时间 需要运行的时间 优先数 进程状态" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < EnterReadyQueue.size(); i++) {
cout << EnterReadyQueue[i].ID << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].arrive_time << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].CPUtime << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].priority << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].status << endl;
}
cout << "<-------------------------------->" << endl << endl;
}
void Rprint_queue() { //打印当前就绪队列的情况。
cout << "<-------------------------------->" << endl;
cout << "进程名字 到达时间 需要运行的时间 进程状态" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < EnterReadyQueue.size(); i++) {
cout << EnterReadyQueue[i].ID << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].arrive_time << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].CPUtime << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[i].status << endl;
}
cout << "<-------------------------------->" << endl << endl;
}
void priority_way()//优先数算法的调用
{
int w_time = 0;
w_time = EnterReadyQueue[0].arrive_time + EnterReadyQueue[0].CPUtime;
cout << "当前进程名字 进程到达时间 需要运行的时间 优先数" << endl;
cout << EnterReadyQueue[0].ID << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[0].arrive_time << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[0].CPUtime << " "
<< EnterReadyQueue[0].priority << endl;
cout << EnterReadyQueue[0].ID << "在第" << w_time << "秒运行结束"<< endl<< endl;
EnterReadyQueue.erase(EnterReadyQueue.begin());
sort(EnterReadyQueue.begin(), EnterReadyQueue.end(), cmp1); //重新排序
print_queue();
while(EnterReadyQueue.size() > 0)
{
PCB now = EnterReadyQueue.front();
w_time = w_time + now.CPUtime;
cout << "当前进程名字 进程到达时间 需要运行的时间 优先数" << endl;
cout << now.ID << " "
<< now.arrive_time << " "
<< now.CPUtime << " "
<< now.priority << endl;
cout << now.ID << "在第" << w_time << "秒运行结束"<< endl<< endl;
EnterReadyQueue.erase(EnterReadyQueue.begin());
if(EnterReadyQueue.size() != 0)
print_queue();
}
cout << "<-------- 就绪队列为空,调度进程结束 ---------->" << endl << endl;
cout << "进程总花费时间为 " << w_time << " 秒" << endl << endl;
}
void RR_way() // 时间片轮转算法的调用
{
int q; //时间片
cout <<"<-------- 请输入时间片 ---------->" << endl;
cin >> q;
while(EnterReadyQueue.size() > 0)
{
PCB now = EnterReadyQueue.front();
now.CPUtime = now.CPUtime - q;
if(now.CPUtime <= 0)
EnterReadyQueue.erase(EnterReadyQueue.begin());
else
{
EnterReadyQueue.push_back(now);
EnterReadyQueue.erase(EnterReadyQueue.begin());
}
if(EnterReadyQueue.size() != 0)
Rprint_queue();
}
cout << "<-------- 就绪队列为空,调度进程结束 ---------->" << endl << endl;
}
void m_priority()//优先数算法
{
int n;
cout << "请输入要运行的进程数量: ";
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
PCB Pro;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程的名字: ";
cin >> Pro.ID;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程的到达的时间: ";
cin >> Pro.arrive_time;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程预计需要运行的时间: ";
cin >> Pro.CPUtime;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程的优先级: ";
cin >> Pro.priority;
cout << endl;
Pro.status = 'W';
EnterReadyQueue.push_back(Pro); //加入进程就绪队列
}
sort(EnterReadyQueue.begin(), EnterReadyQueue.end(), cmp0); //对到来的时间排序
print_queue();
priority_way();
}
void m_RR()// 时间片轮转算法
{
int n;
cout << "请输入要运行的进程数量: ";
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
PCB Pro;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程的名字: ";
cin >> Pro.ID;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程的到达的时间: ";
cin >> Pro.arrive_time;
cout << "请输入第 " << i << " 个进程预计需要运行的时间: ";
cin >> Pro.CPUtime;
cout << endl;
Pro.status = 'W';
Pro.priority = 0;
EnterReadyQueue.push_back(Pro); //加入进程就绪队列
}
sort(EnterReadyQueue.begin(), EnterReadyQueue.end(), cmp0); //对到来的时间排序
Rprint_queue();
RR_way();
}
int main() {
int x;
cout << "<--------请选择使用哪一种算法 ---------->" << endl;
cout << "1:优先级调度算法 2:时间片轮转调度算法 " <<endl;
cin >> x;
switch(x){
case 1:m_priority();break;
case 2:m_RR();break;
}
return 0;
}
(1)使用优先级调度算法
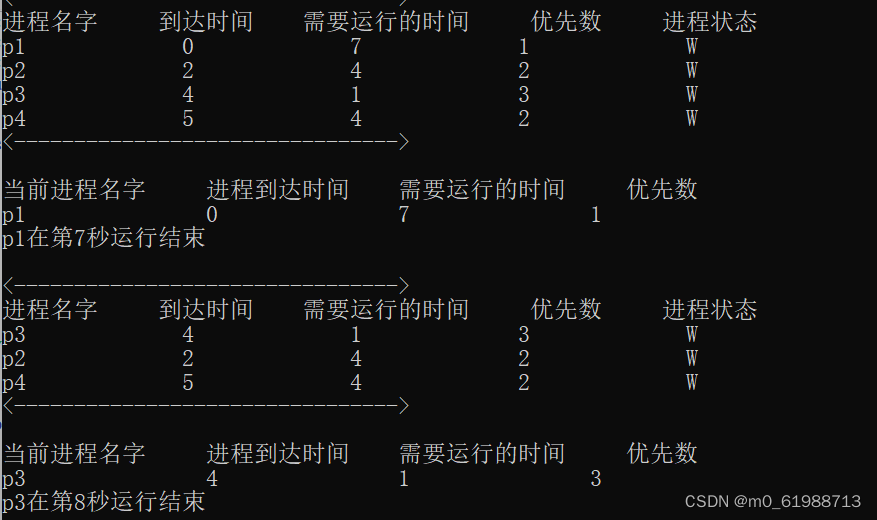

优先级调度算法可以通过https://mbd.baidu.com/ma/s/asLPWulS此链接先进行学习,了解优先级调度算法的具体内容,再自己进行算法的实现。书本也有算法的介绍,但是我觉得上面链接讲的更简洁明了。
(2)时间片轮转调度算法
时间片轮转算法相对简单,每次只要把第一个进程减去时间片,然后判断,如果减去之后小于0,那么说明该进程运行完毕,移除该进程,否则如果大于零说明载该时间片内未完成,那么将该进程移到末尾。课本上也讲的非常清楚。
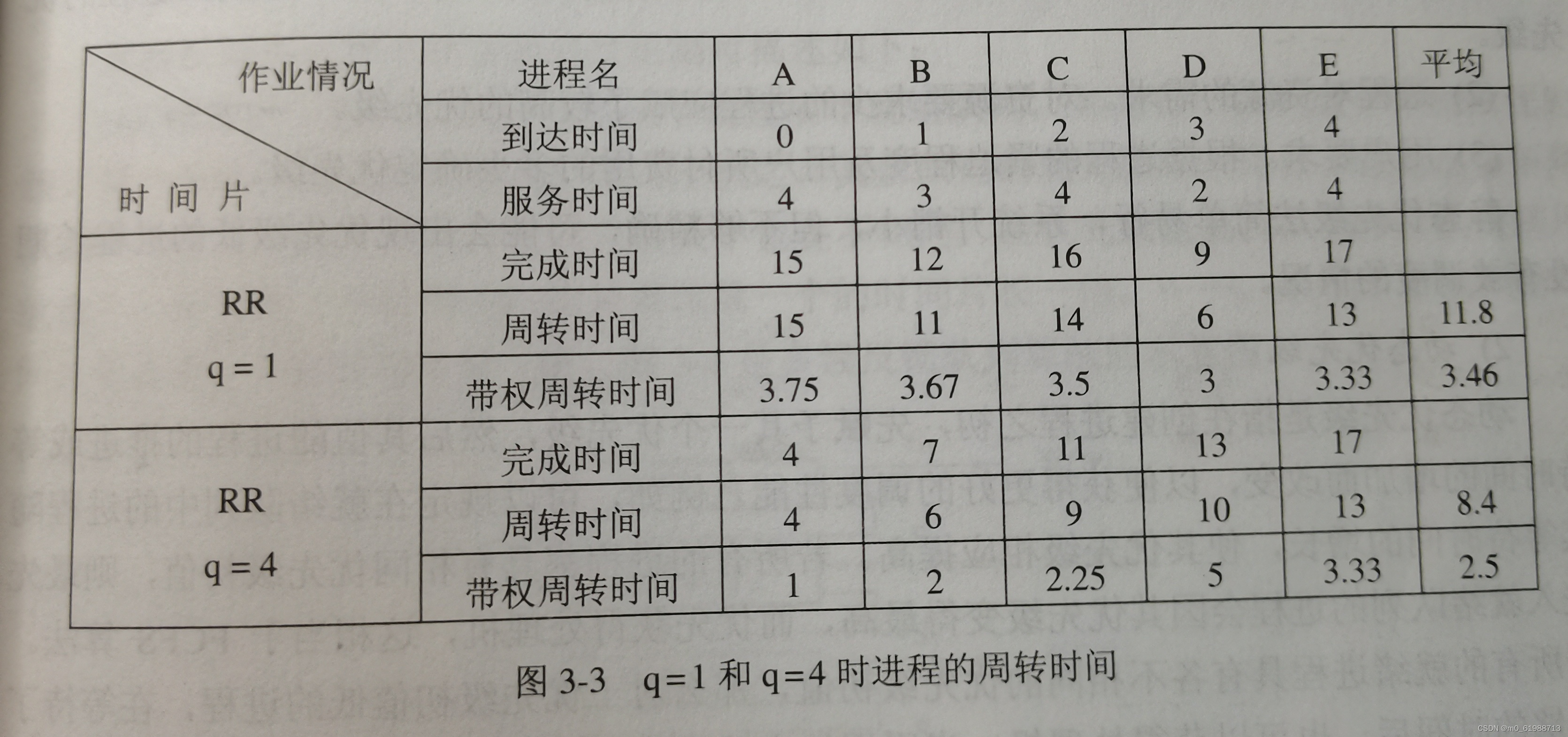
按照书上q = 4,的例子检验该代码可以得到下图:


2.生产者――消费者问题算法的实现
老规矩 先上代码
#include<iostream>
#include<windows.h>
#include<thread>
#include<mutex>
#include<random>
#include<time.h>
using namespace std;
#define N 5
int buffer[N]; //缓冲池
int rear; //指向缓冲池最末尾的产品
mutex mu; //互斥信号量
int empty; //空缓冲池区
int full; //满缓冲池区
void init(); //初始化
void insert(int item); //生产者生产产品
void consumer1(); //消费者1
void consumer2(); //消费者2
void consumer2(); //消费者3
//void remove(string name);
void display(); //显示情况
void init()
{
rear = -1;
empty = N;
full = 0;
}
void insert(int item)
{
do {
while (!empty)
{
//cout << "Producer is waiting for an empty slot..." << endl;
}
if(rear >= N-1)
{
cout <<"缓冲池已满" <<endl;
break;
}
empty--; //P(empty)
mu.lock(); //P(mutex)
cout << "生产的数为:" << item << endl;
buffer[++rear] = item; //产品放入缓冲区
display();
mu.unlock(); //V(mutex)
full++; //V(full)
break;
} while (1);
}
void display()
{
cout << "缓冲区:";
if (rear == -1)
cout << "空" << endl;
else {
for (int i = 0; i <= rear; i++)
cout << buffer[i] << " ";
cout << endl;
}
cout << endl;
}
void producer()
{
int item;
srand((unsigned int)time(NULL));
for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
{
item = rand() % 100 + 1;
int e = rand() % 500;
insert(item);
Sleep(e);
}
}
void consumer1()
{
//for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
while(1)
{
int e = rand() % 3000 ;
// p->remove("消费者1号");
int item;
do {
while (!full )
{
// cout << "Consumer is waiting for items..." << endl;
}
full--;
mu.lock();
if(rear != -1)
item = buffer[rear--]; //从缓冲区取出产品
cout << "消费者1号" << "消费的数为:" << item << endl;
display();
mu.unlock(); //V(mutex)
empty++; //V(empty)
break;
} while (1);
Sleep(e);
}
}
void consumer2()
{
//for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
while(1)
{
int e = rand() % 2000 ;
// p->remove("消费者1号");
int item;
do {
while (full <= 0)
{
// cout << "Consumer is waiting for items..." << endl;
}
full--;
mu.lock();
if(rear != -1)
item = buffer[rear--]; //从缓冲区取出产品
cout << "消费者2号" << "消费的数为:" << item << endl;
display();
mu.unlock(); //V(mutex)
empty++; //V(empty)
break;
} while (1);
Sleep(e);
}
}
void consumer3()
{
//for (int i = 0; i < 20; i++)
while(1)
{
int e = rand() % 2000 ;
// p->remove("消费者1号");
int item;
do {
while (full <= 0)
{
// cout << "Consumer is waiting for items..." << endl;
}
full--;
mu.lock();
if(rear != -1)
item = buffer[rear--]; //从缓冲区取出产品
cout << "消费者3号" << "消费的数为:" << item << endl;
display();
mu.unlock(); //V(mutex)
empty++; //V(empty)
break;
} while (1);
Sleep(e);
}
}
int main()
{
init();
thread pro(producer); //创建生产者子线程
thread con1(consumer1); //创建消费者子线程
thread con2(consumer2); //创建消费者子线程
thread con3(consumer3);
pro.join(); //阻塞主线程
con1.join();
con2.join();
con3.join();
cout << "结束!" << endl;
return 0;
}
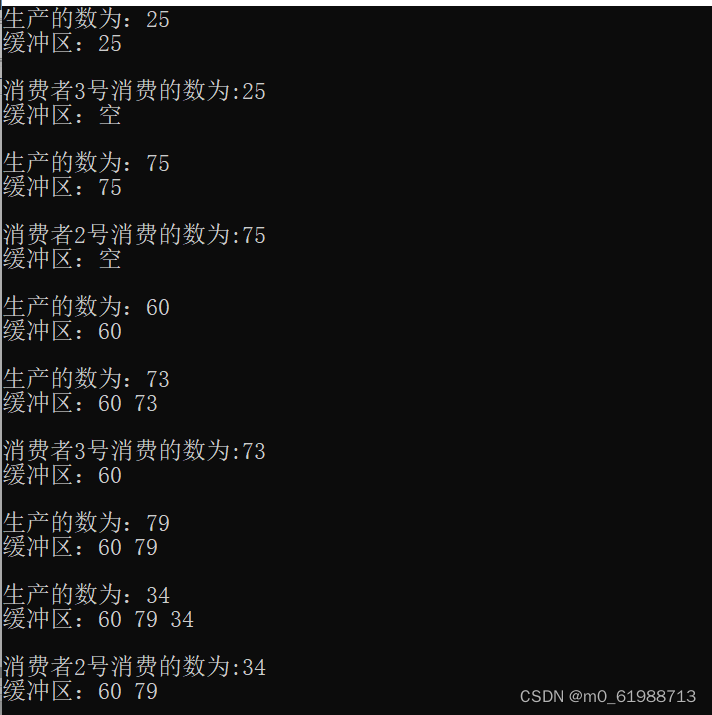
以上的例子可以先通过链接:https://mbd.baidu.com/ma/s/DhKQhJ7Q 进行学习,生产者消费者的问题其实很好理解,主要是代码实现不太容易。
上面链接主要写了如何创建线程,join和detach,传递参数,获取id和休眠,结束线程,并发访问,线程同步等,还有具体的例子。我觉得看完之后完全可以自己动手实现生产者――消费者问题算法。
下面是我补充的链接没有但是用的的知识。
(1)头文件的#include<mutex>
mutex互斥量是一个类,这个类有有一个lock()方法,和一个unlock()方法。 如果第一次运行了lock()这个方法,而没有运行unlock()这个方法,第二次再运行lock()这个方法时,程序就会卡停在这里,只有当运行了unlock()这个方法运行后,第二个lock()方法才会运行通过。就是运用这种“锁”的机制就可以保证两段代码独立运行。
(2) rand() % 100 + 1;
1到100的随机数,具体学习可以看https://www.bilibili.com/video/BV1et411b73Z?p=32。
我上面所写的和书上的有所不同,这里用到的是栈,每次从最后一位存取。而书上用的是循环队列,感兴趣的小伙伴可以自己试试修改一下。
3.银行家算法的实现
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
#define P 5 //进程数
#define R 3 //资源种类
int maxs[P][R] = {{7,5,3},{3,2,2},{9,0,2},{2,2,2},{4,3,3}};
int allocation[P][R] = {{0,1,0},{2,0,0},{3,0,2},{2,1,1},{0,0,2}}; //分配矩阵
int need[P][R] = {{7,4,3},{1,2,2},{6,0,0},{0,1,1},{4,3,1}}; //需求矩阵
int available[R] = {3,3,2}; //可用资源向量
int request[R]; //请求向量当前进程对各类资源的申请量,算法的入口参数
bool Finish[P];
int safeSeries[P]={0,0,0,0,0};//安全进程序列号
int num;
void showInfo()
{
cout <<"\n------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n" ;
cout <<"当前系统各类资源剩余:";
for(int j = 0; j < R; j++)
{
cout <<available[j] << " ";
}
cout <<"\n\n当前系统资源情况:\n";
cout <<" PID\t Max\t\tAllocation\t Need\n";
for(int i = 0; i < P; i++)
{
cout << "P" << i << "\t";
for(int j = 0; j < R; j++)
{
cout <<maxs[i][j] << " ";
}
cout <<"\t\t";
for(int j = 0; j < R; j++)
{
cout <<allocation[i][j] << " ";
}
cout <<"\t\t";
for(int j = 0; j < R; j++)
{
cout <<need[i][j] << " ";
}
cout <<"\n";
}
}
//打印安全检查信息
void SafeInfo(int *work, int i)
{
int j;
cout << "P" << i<< "\t";
//打印工作向量work
for(j = 0; j < R; j++)
cout <<work[j]<<" ";
cout <<"\t\t";
//打印需求矩阵need
for(j = 0; j < R; j++)
cout <<need[i][j]<<" ";;
cout <<"\t\t";
//打印可分配矩阵allocation
for(j = 0; j < R; j++)
cout <<allocation[i][j]<<" ";;
cout <<"\t\t";
//打印work + allocation
for(j = 0; j < R; j++)
cout <<allocation[i][j]+work[j]<<" ";;
cout <<"\n";
}
//判断一个进程的所需资源是否全为零
bool isAllZero(int kang)
{
num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++ )
if(need[kang][i] == 0)
num ++;
if(num == R)
return true;
else
return false;
}
//安全检查
bool isSafe()
{
bool flag = true;
int safeIndex = 0; //安全进程个数
int allFinish = 0; //可需资源为0的进程数
//工作变量work:系统可提供给进程继续运行所需的各类资源数目
int work[R] = {0};
int r = 0; //进程序号
int temp = 0; //辅助判断所有进程是否全部分配完成
//预分配为了保护available
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++)
work[i] = available[i];
//把未完成进程置为false
for(int i = 0; i < P; i++)
{
bool result = isAllZero(i);
if(result == true)
{
Finish[i] = true;
allFinish++;
}
else
Finish[i] = false;
}
//预分配开始
while(allFinish != P)
{
num = 0;
//检测进程所需资源是否符合剩余资源
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++)
if(need[r][i] <= work[i] && Finish[r] == false)
num ++;
//符合
if(num == R)
{
if(flag)
{
flag = false;
cout << "\n系统安全情况分析:\n";
cout <<" PID\t Work\t\t Need\t \tAllocation\tWork+Allocation\n";
}
SafeInfo(work,r);
//释放资源
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++ )
work[i] = work[i] + allocation[r][i];
allFinish ++;
safeSeries[safeIndex] = r;
safeIndex ++;
Finish[r] = true;
}
r ++;
if(r >= P)
{
r = r % P;
if(temp == allFinish)
break;
temp = allFinish;
}
}
//判断系统是否安全
for(int i = 0; i < P; i++)
{
if(Finish[i] == false)
{
cout <<"\n当前系统不安全!\n\n";
return false;
}
}
//打印安全序列
cout <<"\n当前系统安全!\n\n安全序列为:";
//打印安全序列
for(int i = 0; i < allFinish; i++)
cout <<safeSeries[i];
return true;
}
int main()
{
//输入的进程序号
int curProcess = 0;
//用于控制输入内容的准确性(非字符)
int a = -1;
showInfo();
bool isStart = isSafe();
//用户输入或者预设系统资源分配合理才能继续进行进程分配工作
while(isStart)
{
//限制用户输入,以防用户输入大于进程数量的数字,以及输入其他字符(乱输是不允许的)
do
{
if(curProcess >= P || a < 0)
{
cout <<"\n请不要输入超出进程数量的值或者其他字符:\n";
while(getchar() != '\n');//清空缓冲区
a = -1;
}
cout <<"\n------------------------------------------------------------------------------------\n";
cout <<"\n输入要分配的进程:";
cin >> curProcess;
a = curProcess;
cout <<"\n";
}while(curProcess >= P || a < 0);
//限制用户输入,此处只接受数字,以防用户输入其他字符(乱输是不允许的)
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++)
{
do
{
if(a < 0 )
{
cout << "\n请不要输入除数字以外的其他字符,请重新输入:\n";
while(getchar() != '\n');//清空缓冲区
a = -1;
}
cout <<"请输入要分配给进程 P" << curProcess << "的第 "<< i +1 << "类资源:";
cin >> request[i];
a = request[i];
}while( a < 0);
}
//判断用户输入的分配是否合理,如果合理,开始进行预分配
num = 0;
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++)
{
if(request[i] <= need[curProcess][i] && request[i] <= available[i])
num ++;
else
{
cout << "\n发生错误!可能原因如下:\n(1)您请求分配的资源可能大于该进程的某些资源的最大需要!\n(2)系统所剩的资源已经不足了!\n";
break;
}
}
//合理
if(num == R)
{
num = 0;
for(int j = 0; j < R; j++)
{
//分配资源
available[j] = available[j] - request[j];
allocation[curProcess][j] = allocation[curProcess][j] + request[j];
need[curProcess][j] = need[curProcess][j] - request[j];
//记录分配以后,是否该进程需要值为0了
if(need[curProcess][j] == 0)
num ++;
}
//如果分配以后出现该进程对所有资源的需求为0了,即刻释放该进程占用资源(视为完成)
if(num == R)
{
//释放已完成资源
for(int i = 0; i < R; i++ )
available[i] = available[i] + allocation[curProcess][i];
cout << "\n\n本次分配进程 P" << curProcess<< "完成,该进程占用资源全部释放完毕!\n";
}
else
//资源分配可以不用一次性满足进程需求
cout << "\n\n本次分配进程 P" << curProcess << "未完成!\n";
showInfo();
//预分配完成以后,判断该系统是否安全,若安全,则可继续进行分配,若不安全,将已经分配的资源换回来
if(!isSafe())
{
for(int j = 0; j < R; j++)
{
available[j] = available[j] + request[j];
allocation[curProcess][j] = allocation[curProcess][j] - request[j];
need[curProcess][j] = need[curProcess][j] +request[j];
}
cout <<"资源不足,等待中...\n\n分配失败!\n";
}
}
}
}
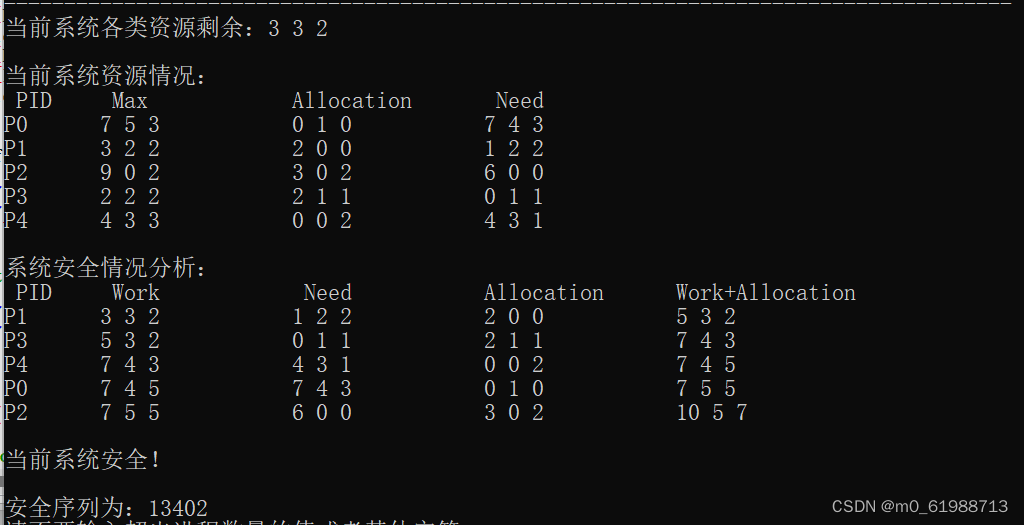



银行家算法主要的原理也不是很难,书上也有给出银行家算法中的数据结构,银行家算法,安全性算法。认真阅读书本上的内容再结合代码就很容易理解。
最后,希望这篇文章能够对你们有帮助!




















 982
982











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








