1.拷贝构造函数
1.1拷贝构造函数是构造函数的一种重载形式
1.2不能使用常数 只能使用引用并加const(consy Complex &cdd)
2.构造函数中字符串的拷贝用strcpy_s(&目的字符串,长度,&源字符串)
3.三种引用方案
值传递
引用传递
常引用传递
4.局部对象只能以值的类型返回&&返回类型不允许是引用类型
#除非生存期不受函数影响
5.实现栈的深拷贝
//Mystack深拷贝函数
Mystack(const Mystack& s) {
_size = s._size;
_top = s._top;
data = new int[_size];
memmove(data, s.data, sizeof(int) * (_top + 1));
}#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Mystack {
enum { total_size = 10, nsize = 2 };
private:
int* data;
int _size;
int _top;
//增容
bool Capacity(int newSize) {
int* newdata = new int[newSize];
memmove(newdata, data, _size * sizeof(int));
delete[]data;//不可省略
data = newdata;
_size = newSize;
return true;
}
public:
Mystack() :data(nullptr), _size(total_size), _top(-1) {
data = new int[total_size];
}
Mystack(int t) :data(nullptr), _size(t), _top(-1) {
data = new int[total_size];
}
~Mystack() {
delete[]data;
data = nullptr;
_size = 0;
_top = -1;
}
//Mystack深拷贝函数
Mystack(const Mystack& s) {
_size = s._size;
_top = s._top;
data = new int[_size];
memmove(data, s.data, sizeof(int) * (_top + 1));
}
//判满 判空 入栈 出栈 获取栈元素 获取栈顶元素
bool Full() {
return (_top + 1) >= _size;
}
bool Empty() {
return (_top == -1);
}
bool Push(int val) {
if (Full() && !Capacity(nsize * _size)) return false;
_top += 1;
this->data[_top] = val;
cout << val << "已入栈" << endl;
return true;
}
bool Pop() {
if (Empty()) return false;
_top -= 1;
return true;
}
bool Get_Topvel(int& a) {
if (Empty()) return false;
a = this->data[_top];
return true;
}
bool Pop_val(int& a) {
if (Empty()) return false;
a = this->data[_top];
cout << a << "已出栈" << endl;
_top -= 1;
}
};
int main() {
Mystack s;
int c;
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++) {
s.Push(i);
}
Mystack s1(s);
cout << "s1" << endl;
while (!s1.Empty()) {
s1.Pop_val(c);
}
}6.实现字符串的深拷贝
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//字符串类
class Mystring {
private:
char* str;
public://有参 析构 拷贝
Mystring(const char *p=nullptr):str(nullptr) {
if (p != nullptr) {
int len = strlen(p) + 1;
str = new char[len];
strcpy_s(str, len, p);
}
}
~Mystring() {
if (str != nullptr) {
delete[]str;
}
str = nullptr;
}
Mystring(const Mystring &s) {
int n = strlen(s.str) + 1;
this->str = new char[n + 1];
strcpy_s(str, n , s.str );
}
/*Mystring(const Mystring& s) {
str = s.str;
}*/
//error
//打印
void Print_Str() {
cout << str << endl;
}
};
int main() {
Mystring ys("buling!");
Mystring ds(ys);
ys.Print_Str();
ds.Print_Str();
return 0;
}7.在使用字符串时,赋值或者拷贝函数应该先计算长度 然后new开辟空间
8.strcpy_s针对字符串赋值 mencpy针对整形赋值
9.在赋值函数中应该判断this指针的地址与&s的指针地址是否相等 以防自己给自己赋值
10.栈的赋值重载
Mystack& operator=(const Mystack& c) {
if (this != &c) {
delete[] data;
data = new int[_size];
memmove(data, c.data, sizeof(int) * (_top + 1));
_size = c._size;
_top = c._top;
}
}11.构造函数三特性 1.创建对象 2.创建对象 3.类型转换
12.后置++(int )
13.x+Int a
Int operator+(int x, const Int& a) {
return a + x;
}#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//整形类
class Int {
private:
int value;
public:
Int() :value(0) {
cout << "无参" << endl;
}
Int(int x) :value(x) {
cout << "有参" << endl;
}
~Int() {
cout << "析构" << endl;
}
Int(const Int& c) {
value = c.value;
}
//c = a + b; c=a+x c=x+a a.operator(x)
Int operator+(const Int& c) const{//运算符重载
int t = value + c.value;
return Int(t);
}
//a=a+b;
Int operator+=(const Int& c) {
value = value + c.value;
return *this;
}
//c=++a c=a a=a+1
//前置++
Int operator++() {
value += 1;
return *this;
}
//后置++
Int operator++(int) {
Int c;
c.value = value;
value += 1;
return c;
}
void Print() {
cout << "value= " << value << endl;
}
};
//Int c=x+a;
Int operator+(int x, const Int& a) {
return a + x;
}
int main() {
Int a{ 10 }, b{ 20 }, c{ 0 };
int x = 50;
c = a + b;
c.Print();
c = a + x;
c.Print();
c = x + a;
c.Print();
}14.大杂烩
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//整形类
class Int {
private:
int value;
public:
Int() :value(0) {
cout << "无参" << endl;
}
Int(int x) :value(x) {
cout << "有参" << endl;
}
~Int() {
cout << "析构" << endl;
}
Int(const Int& c) {
value = c.value;
}
//c = a + b; c=a+x c=x+a a.operator(x)
Int operator+(const Int& c) const {//运算符重载
int t = value + c.value;
return Int(t);
}
//c=a+x
Int &operator+(const int value ) {//运算符重载
this->value+=value;
return *this;
}
//a=a+b;
Int operator+=(const Int& c) {
value = value + c.value;
return *this;
}
//c=++a c=a a=a+1
//前置++
Int operator++() {
value += 1;
return *this;
}
//后置++
/*Int operator++(int) {
Int c;
c.value = value;
value += 1;
return c;
}*/
Int operator++(int) {
return Int (this->value ++);
}
void Print() {
cout << "value= " << value << endl;
}
int Value()const {
return value ;
}
//强转Int a ->int a
operator int() {
return this->value;
}
// c a
//bool operator<(const Int& a) {
// return this->value < a.value;
//}
c x
//bool operator<(const int x) {
// return this->value <x;
//}
};
//Int c=x+a;
Int operator+(int x, const Int& a) {
return a + x;
}
//x+=a; (x,&a)
int & operator+=(int &value, const Int & a) {
value=value+ a.Value();
return value;
}
//x c
//bool operator<(int& x, const Int& c) {
// return x < c.Value();
//}
//x y
int main() {
Int a{ 70 }, b{ 50 }, c{ 0 };
int x = 50,y=10;
int w = a;
cout << w << endl;
}
//#include <stddef.h>
//#include<string.h>
//#include<iostream>
//#include<string>
//using namespace std;
//class Mystring {
//private:
// char* str;
//public:
// Mystring(const char* p = nullptr) :str(nullptr) {
// if (p != nullptr) {
// size_t n = strlen(p) + 1;
// str = new char[n];
// strcpy_s(str, n, p);
// }
// }
// ~Mystring() {
// if (str != nullptr) {
// delete[]str;
// }
// str = nullptr;
// }
// //(&c,a)
// Mystring(const Mystring& c) {
// size_t n = strlen(c.str) + 1;
// this->str = new char[n];
// strcpy_s(str, n, c.str);
// }
// void Print_str() {
// cout << "str:" << str << endl;
// }
// //赋值重载函数c=a
// Mystring& operator=(const Mystring& s) {
// if (this != &s) {
// size_t n = strlen(str) + 1;
// delete[] str;
// str = new char[n];
// strcpy_s(str, n, s.str);
// return *this;
// }
// }
// //s3=s1+s21
// Mystring operator+(const Mystring& s) const {
// size_t n1 = strlen(str)+1;
// size_t n2 = strlen(s.str)+1;
// char* p = new char[n1 + n2 +3]; int i = 0, j = 0;
// for ( i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
// p[i] = str[i];
// }
// for ( j = 0; s.str[j] != '\0'; j++) {
// p[i] = s.str[j];
// i++;
// }
// p[i] = '\0';
// return Mystring(p);
// }
// //c=a+=b a=a+b
// Mystring& operator+=(const Mystring& s) {
// size_t n1= strlen(str) + 1;
// size_t n2 = strlen(s.str) + 1;
// char* p = new char[n1 + n2+3];
// int i = 0, j = 0;
// for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
// p[i] = str[i];
// }
// for (j = 0; s.str[j] != '\0'; j++) {
// p[i] = s.str[j];
// i++;
// }
// p[i] = '\0';
// delete[] str;
// strcpy_s(str, n1 + n2 , p);
// str = p;
// return *this;
// }
// //char ch = s3[1]; (s3,1) (&this,*( s3.str+1))
// char operator[](int index) {
// return *(str + 1);
// }
// //Mystring s4 = s1 + "newdata";
// Mystring operator+(const char* str1) {
// int n1 = strlen(str) + 1;
// int n2 = strlen(str1) + 1;
// char* p = new char[n1 + n2 + 3];
// int i = 0, j = 0;
// for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
// p[i] = str[i];
// }
// for (int j = 0; str1[j] != '\0'; j++) {
// p[i] = str1[j];
// i++;
// }
// return Mystring(p);
// }
//
//};
s5 ="newdata"+s1;
//Mystring operator+(const char*str1, const Mystring& s) {
//
//}
//int main() {
// Mystring s1{ "buling" };
//
// /*Mystring s2 = {" samrter!"};
// Mystring s3 = s1 + s2;*/
// //Mystring s4 = s1 + "newdata";
// /*char ch = s3[1];
// s3.Print_str();
// cout << ch << endl;*/
// Mystring s5 ="newdata"+s1;
// s5.Print_str();
//
// /*Mystring s6 = s1 += s2;*/
// //s1.Print_str();
// //s6.Print_str();
//
// /*s4.Print_str();
// s1.Print_str();
// s2.Print_str();
// s3.Print_str();*/
//}15.普通的友元函数
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//整形类
class Int {
private:
int value;
public:
Int(int x) :value(x) {
}
//友元函数
friend int operator+(int& x, const Int& a);
};
int operator+(int& x, const Int& a) {
return x + a.value;
}
int main() {
Int a{ 10 }, b{ 20 }, c{ 0 };
int x = 5;
x = x + a;
cout << x << endl;
}16.类友元
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//整形类
class Object;
class Int {
private:
int value;
public:
Int(int x) :value(x) {
}
void Print() {
cout << value << endl;
}
friend class Object;;
};
class Object {
public:
void fun(Int &it) {
it.value += 10;
}
};
int main() {
Int a{ 10 }, b{ 20 }, c{ 0 };
int x = 5;
Object obj;
obj.fun(a);
a.Print();
}17.另一个类中的一个函数定义为友元函数
注意一定要将calss Int的声明写到object前面
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
//整形类
class Int;
class Object {
public:
void fun(Int& it);
};
class Int {
private:
int value;
public:
Int(int x) :value(x) {
}
void Print() {
cout << value << endl;
}
friend void Object::fun(Int& it);
};
void Object::fun(Int& it) {
it.value += 10;
}
int main() {
Int a{ 10 }, b{ 20 }, c{ 0 };
int x = 5;
Object obj;
obj.fun(a);
a.Print();
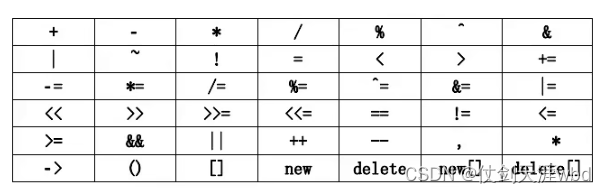
}18.C++中可以重载的符号
19.给贴贴汇报的作业152(Mystring)
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Mystring {
private:
char* str;
public:
Mystring(const char* p = nullptr) :str(nullptr) {
size_t n = strlen(p) + 1;
str = new char[n];
strcpy_s(str, n, p);
}
//(&c this ,s) c(s) c=s
Mystring(const Mystring& s) {
size_t n = strlen(s.str) + 1;
str = new char[n];
strcpy_s(str, n, s.str);
}
~Mystring() {
if (str != nullptr) {
delete[]str;
str = nullptr;
}
}
void Printf_str()
{
cout << this->str << endl;
}
/* Mystring operator+(const Mystring &s1) {
size_t n1 = strlen(str) + 1;
size_t n2 = strlen(s1.str) + 1;
char* p = new char[n1 + n2+3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
p[i] = str[i];
}
for (j = 0; s1.str[j] != '\0'; j++) {
p[i] = s1.str[j];
i++;
}
p[i] = '\0';
return Mystring(p);
}*/
//s3 = s1 +"hello";(&s1,const char*p)
Mystring operator+(const char* p) {
size_t n1 = strlen(this->str) + 1;
size_t n2 = strlen(p) + 1;
char* ps = new char[n1 + n2 + 3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
ps[i] = str[i];
}
for (j = 0; p[j] != '\0'; j++) {
ps[i] = p[j];
i++;
}
ps[i] = '\0';
return Mystring(ps);
}
char* Str() {
return (this->str);
}
//a1+=s2 a1.+=(s2)
Mystring& operator+=(const Mystring& s2) {
size_t n1 = strlen(this->str)+1;
size_t n2 = strlen(s2.str)+1;
char* p = new char[n1+n2+3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
p[i] = str[i];
}
for (j = 0; s2.str [j] != '\0'; j++)
{
p[i] = s2.str[j];
i++;
}
p[i] = '\0';
delete[]str;
str = p;
return *this;
}
//ch=s1[1]
char operator[](int index) {
return this->str[index];
}
//赋值运算符重载 s1=s2 s1.operator=(s2)
//operator=(&s1 this,s2);
Mystring operator=( Mystring& s2) {
if (this != &s2) {
delete[] str;
size_t n = strlen(s2.str ) ;
str = new char[n+1];
strcpy_s(str, n, s2.str);
}return *this;
}
/*Mystring& operator=(const Mystring& s) {
if (this != &s) {
size_t n = strlen(str) + 1;
delete[] str;
str = new char[n];
strcpy_s(str, n, s.str);
return *this;
}
}*/
// s1[0] = 'x'; s1.operator[](int index,)
//Mystring operator[]( int intdex, const char ch) {
//}
};
//s3 = "hello" + s1;
//_________________________________________________________________________________________
Mystring operator+(const char* p, Mystring& s)
{
size_t n1 = strlen(p) + 1;
size_t n2 = strlen(s.Str()) + 1;
char* ps = new char[n1 + n2 + 3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; p[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
ps[i] = p[i];
}
for (j = 0; s.Str()[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
ps[i] = s.Str()[j];
i++;
}
ps[i] = '\0';
return Mystring(ps);
}
int main() {
Mystring s1 = "jkfgfkd";
Mystring s2=s1;
s2.Printf_str();
// s1[0] = 'x';//s1.operator[](const char ch)
// s1.Printf_str();
//s2.Printf_str();
//char ch = s1[1];//s1.operator[](int index)
//cout << ch;
// Mystring s3 = s1 + s2;
// Mystring s3 = s1 +"hello";
//Mystring s3 = "hello" + s1;
/* s1 += s2
s1.Printf_str();*/
//s3.Printf_str();
}20.浅赋值 浅拷贝
this.str=s1.str
21.在=运算符重载时应该判断this指针和&s地址是否相等
如:
if(this!=&s){
}
22.strcpy_s strcat_s
在写函数时,应注意区分它两的使用方法
strcpy_s(ps,len ,str)
strcat_s(ps,len ,p)
23.Mystring 作业
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Mystring {
private:
char* str;
public:
Mystring(const char* p = nullptr) :str(nullptr) {
size_t n = strlen(p) + 1;
str = new char[n];
strcpy_s(str, n, p);
}
//(&c this ,s) c(s) c=s
Mystring(const Mystring& s) {
size_t n = strlen(s.str) + 1;
str = new char[n];
strcpy_s(str, n, s.str);
}
~Mystring() {
if (str != nullptr) {
delete[]str;
str = nullptr;
}
}
void Printf_str()
{
cout << this->str << endl;
}
/* Mystring operator+(const Mystring &s1) {
size_t n1 = strlen(str) + 1;
size_t n2 = strlen(s1.str) + 1;
char* p = new char[n1 + n2+3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++) {
p[i] = str[i];
}
for (j = 0; s1.str[j] != '\0'; j++) {
p[i] = s1.str[j];
i++;
}
p[i] = '\0';
return Mystring(p);
}*/
//s3 = s1 +"hello";(&s1,const char*p)
Mystring operator+(const char* p) {
size_t len = strlen(this->str) +strlen(p) + 1;
char* ps = new char[len];
strcpy_s(ps, len, str);
strcat_s(ps, len, p);
return Mystring(ps);
}
char* Str() const {
return (this->str);
}
//a1+=s2 a1.+=(s2)
Mystring& operator+=(const Mystring& s2) {
size_t n1 = strlen(this->str)+1;
size_t n2 = strlen(s2.str)+1;
char* p = new char[n1+n2+3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; str[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
p[i] = str[i];
}
for (j = 0; s2.str [j] != '\0'; j++)
{
p[i] = s2.str[j];
i++;
}
p[i] = '\0';
delete[]str;
str = p;
return *this;
}
//ch=s1[1]
char &operator[](int index) {
return this->str[index];
}
//赋值运算符重载 s1=s2 s1.operator=(s2)
//operator=(&s1 this,s2);
Mystring operator=( Mystring& s2) {
if (this != &s2) {
delete[] str;
size_t n = strlen(s2.str ) ;
str = new char[n+1];
strcpy_s(str, n, s2.str);
}return *this;
}
/*Mystring& operator=(const Mystring& s) {
if (this != &s) {
size_t n = strlen(str) + 1;
delete[] str;
str = new char[n];
strcpy_s(str, n, s.str);
return *this;
}
}*/
// s1[0] = 'x'; s1.operator[](int index,)
//Mystring operator[]( int intdex, const char ch) {
//friend iostream& operator<<(iostream& out, const Mystring& s);
//}
};
//s3 = "hello" + s1;
//_________________________________________________________________________________________
Mystring operator+(const char* p, Mystring& s)
{
size_t n1 = strlen(p) + 1;
size_t n2 = strlen(s.Str()) + 1;
char* ps = new char[n1 + n2 + 3];
int i = 0, j = 0;
for (i = 0; p[i] != '\0'; i++)
{
ps[i] = p[i];
}
for (j = 0; s.Str()[j] != '\0'; j++)
{
ps[i] = s.Str()[j];
i++;
}
ps[i] = '\0';
return Mystring(ps);
}
//编写输出流函数
//cout<<s2<<endl;
//operstor<<(cout,const Mystring &s)
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Mystring& s) {
cout << s.Str();
return out;
}
//输入流重载 cin<<s2 (istream &input,const Mystring &s2)
istream& operator>>(istream& input, const Mystring& s2) {
cin >> s2.Str();
return input;
}
int main() {
const Mystring s1 = "jkfgfkd";
Mystring s2=" sjhf";
cin >> s2;
cout << s2;
// s1[0] = 'x';//s1.operator[](const char ch)
/* s1.Printf_str();
s1[0] = 'g';
s1.Printf_str();*/
//s2.Printf_str();
//s2.Printf_str();
//char ch = s1[1];//s1.operator[](int index)
//cout << ch;
// Mystring s3 = s1 + s2;
// Mystring s3 = s1 +"hello";
//Mystring s3 = "hello" + s1;
/* s1 += s2;
s1.Printf_str();*/
//s3.Printf_str();
}24.想要通过cahr ch='g'来改变对象s 的值,在返回类型前加一个&就好了
char &operator[](int index) {
return this->str[index];
}25.创建 输入输出流 注意是ostream
char* Str() const {
return (this->str);
}
//——————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————————
ostream& operator<<(ostream& out, const Mystring& s) {
cout << s.Str();
return out;
}26.新的 Mystring 类型
27.猫咪
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Cat {
private:
string _Owner;
string _Name;
static int num;
public:
Cat(const string &p,const string &ps) :_Owner(p), _Name(ps) {
cout << "构造" << " "<< ++num << endl;
}
Cat(const Cat& c) :_Owner(c._Owner ), _Name(c._Name ) {
cout<<"拷贝" << " " << ++num << endl;
}
~Cat() {
cout << "析构" << " " << --num << endl;
}
void Print_Cat() {
cout << "主人为" << this->_Owner <<endl<< "猫咪为" << this->_Name << endl << "num为" << this->num << endl;
}
};
int Cat::num = 0;
int main() {
Cat c1("xiao","fkhvn");
c1.Print_Cat();
}28.静态 成员
有以下几个特征:
(1)可以限制服务范围 如服务Cat类,并且存储在.data区中。
(2)不存在命名冲突,因为其是一个类中的变量,不具有透明性
(3)信息交流 如Cat类公用一个num
(4)常性+整形 可以直接在类中进行初始化(const + int char short long long)
(5)静态成员的目的:信息共享、信息交流
(6)静态成员为一个类共享,不属于某个具体的实例
(7)当静态成员为公有时,可在别的函数中使用,使用方法:Cat::num=0;
(8)可以在类体中定义一个static静态对象,但是要在类外进行初始化
29.Circle
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Circle {
private:
double r;
static double pi;
public:
Circle(double x) :r(x) { }
double Area() {
return r * r * pi;
}
void Print() {
cout << this->Area();
}
};
double Circle::pi = 3.14;
int main() {
Circle c1{ 3 };
c1.Print();
}30.类中不可定义一个对象
也不可以定义引用类型的对象
但是可以定义指针类型(如链表),以及静态类型(类中公用)
#include <stddef.h>
#include<string.h>
#include<iostream>
#include<string>
using namespace std;
class Int {
private:
int value;
Int* next;
public:
Int(int x) :value(value), next(nullptr) { }
Int(const Int& c) :value(c.value ),next(c.next ) {}
void Next( Int *p ) {
p = next;
}
};
int main() {
Int a{ 3};
Int b{ 4 };
b.Next(&a);
a.Next(nullptr);
}31.在静态成员方法调用时,静态方法里面没有this指针 因此,其只能调用静态变量
调用方法:
Object c1(6);
(1) c1.Show();
(2) Object :: Show();
32.静态方法 友元函数 普通方法
普通方法具有以下三种特征;
友元函数具有以下1特征;
静态方法具有以下1、2特征;
(1)访问类中的私有部分
(2)函数位于类的作用域中
(3)必须由一个类去激活
33.单例模式
有以下六步
(1)构造函数设为private
(2)删除 赋值重载 拷贝构造函数
(3)定义一个 静态对象
(4)在类外赋值
(5)写一个返回静态成员对象的方法
(6)建立一个对象,调用上一步写的方法 ,给新的对象赋值。
Int Int::a = 3;
static Int& Get_Static() {
return a;
}
int main() {
Int& tmp = Int::Get_Static();
}




















 1772
1772











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








