两个链表第一个公共子节点
-
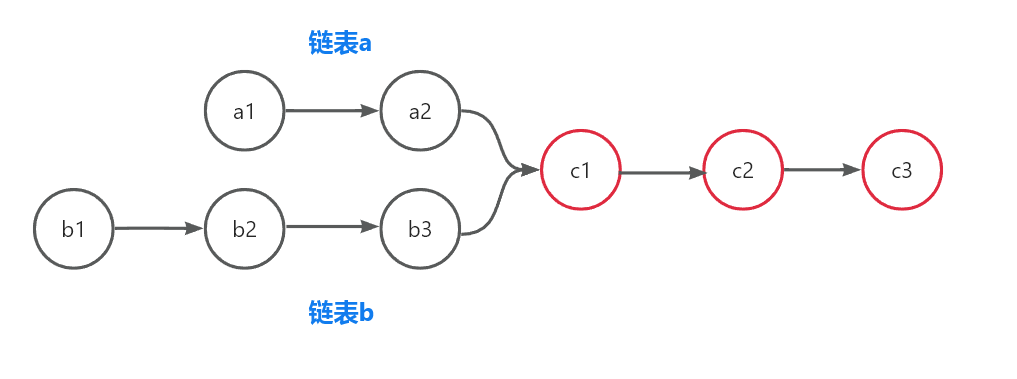
前情提要:什么情况下,两条链表存在公共子节点呢?如下图所示:
-
显而易见,c1、c2、c3均为两链表的公共子节点,且c1是两链表的第一个公共子节点
-
我们先废话少说,给出四种解题思路:
-
哈希和集合,代码如下:
-
/** * 方法1:通过Hash辅助查找 * * @param pHead1 链表a * @param pHead2 链表b * @return 第一个公共节点/null */ public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeByMap(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { // 1.判断链表是否为空 if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) { return null; } // 2.保存两链表头节点 ListNode current1 = pHead1; ListNode current2 = pHead2; // 3.通过Hash存储链表a的所有节点 HashMap<ListNode, Integer> hashMap = new HashMap<ListNode, Integer>(); while (current1 != null) { hashMap.put(current1, null); current1 = current1.next; } // 4.从头结点开始, 依次比较hash表中的节点与链表b的节点 while (current2 != null) { if (hashMap.containsKey(current2)) return current2; current2 = current2.next; } // 5.未发现公共节点 return null; } /** * 方法2:通过集合辅助查找 * * @param headA 链表a * @param headB 链表b * @return 第一个公共节点/null */ public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeBySet(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { // 1.通过Hash存储链表a的所有节点 Set<ListNode> set = new HashSet<>(); while (headA != null) { set.add(headA); headA = headA.next; } // 2.从头结点开始, 依次比较hash表中的节点与链表b的节点 while (headB != null) { if (set.contains(headB)) return headB; headB = headB.next; } // 3.未发现公共节点 return null; }
-
-
-
栈,代码如下:
-
/** * 方法3:通过栈 */ public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeByStack(ListNode headA, ListNode headB) { // 1.将两条链表从头节点开始, 分别压入栈中 Stack<ListNode> stackA = new Stack<>(); Stack<ListNode> stackB = new Stack<>(); while (headA != null) { stackA.push(headA); headA = headA.next; } while (headB != null) { stackB.push(headB); headB = headB.next; } // 2.两栈依次出栈, 当栈顶元素相同时, 保存该元素 ListNode preNode = null; while (stackB.size() > 0 && stackA.size() > 0) { if (stackA.peek() == stackB.peek()) { preNode = stackA.pop(); stackB.pop(); } else { break; } } // 3.返回第一个公共节点 return preNode; } -
两条链表拼接,代码如下:
/** * 方法4:通过序列拼接 */ public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeByCombine(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { // System.out.println("null == null" + (null == null)); // 1.判断链表是否为空 if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) { return null; } ListNode p1 = pHead1; ListNode p2 = pHead2; // 2.依次遍历两条链表 while (p1 != p2) { p1 = p1.next; p2 = p2.next; if (p1 != p2) {// 这个判断不能少 // 2.1.链表a遍历完, 切换遍历链表b if (p1 == null) { p1 = pHead2; } // 2.2.链表b遍历完, 切换遍历链表a if (p2 == null) { p2 = pHead1; } } } // 3.返回第一个公共节点 return p1; }-
差和双指针
/** * 方法5:通过差值来实现 * * @param pHead1 链表a * @param pHead2 链表b * @return */ public static ListNode findFirstCommonNodeBySub(ListNode pHead1, ListNode pHead2) { // 1.判断链表是否为空 if (pHead1 == null || pHead2 == null) { return null; } ListNode current1 = pHead1; ListNode current2 = pHead2; int l1 = 0, l2 = 0; // 2.分别拿到两链表的长度 while (current1 != null) { current1 = current1.next; l1++; } while (current2 != null) { current2 = current2.next; l2++; } current1 = pHead1; current2 = pHead2; // 3.计算两链表长度之差 int sub = l1 > l2 ? l1 - l2 : l2 - l1; // 4.长度较大的链表先遍历, 遍历次数即为长度之差 if (l1 > l2) { int a = 0; while (a < sub) { current1 = current1.next; a++; } } if (l1 < l2) { int a = 0; while (a < sub) { current2 = current2.next; a++; } } // 5.同时遍历两链表 while (current2 != current1) { current2 = current2.next; current1 = current1.next; } // 6.返回第一个公共节点 return current1; } -
-
上面代码里的注释,已经把解题思路解释的很清晰了
-
基于我个人的理解,下面讲解一下这些方法的共同点,也就是解题思路的形成过程:
我们的目标是:查出两条链表的第一个公共节点 公共节点是什么我们已经搞清楚了,那如何拿到第一个公共节点呢? 不论是分别正序/倒序遍历两条链表,我们的执行思路始终是: 从两链表的头节点/尾节点开始,分别依次向后遍历链表的每个节点,再比较两节点,判断它们是否相同,即是否为两链表的公共节点 我们能够判断出两链表的公共节点,那么第一个公共节点就好找了: 如果遍历顺序为正序,则选出第一组公共节点;如果遍历顺序为倒序,则选出最后一组公共节点 只需要根据正序/倒序遍历链表,选出第一组公共节点/最后一组公共节点,就找到了两链表的第一个公共节点 这里问题来了,我们要明确一点,即两链表的长度不一定相同 这就带来了问题: 我们上面查找两链表公共节点的思路,其实只有在两链表长度相同时,才行得通 那我们的目标就是,如何构造出两链表长度相同的环境: 哈希和集合:直接消除了链表长度带来的影响,通过开辟了新的空间,判断节点是否相等,进而查找出两链表的公共节点 栈、两链表拼接、差和双指针:本质上都是构造出两链表长度相同的环境,进而查找出两链表的公共节点
-
这就是查找两链表的第一个公共节点的解题思路了,希望对你有帮助






















 626
626











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








