目录
类与对象
- 类就相当于是我们自定义的一个数据类型
- 类是属性和行为的集合
- 类创建的对象就是一个具体的实例(实例化)
- 创建对象:类名 对象名 = new 类名();
- 访问对象属性:对象名.属性名
- 属性也叫成员变量
- 属性可以是基本数据类型也可以是数组
- 属性如果不赋值,有默认值(见java入门第五天数组细节)
- Cat cat1 = new Cat();cat1是对象名,new Cat()创建的对象空间才是真正的对象
import java.util.*;
public class Object01{
public static void main(String []args) {
Cat cat1 = new Cat();
cat1.name = "大橘";
cat1.age = 2;
cat1.color = "橘色";
Cat cat2 = new Cat();
cat2.name = "牛奶";
cat2.age = 1;
cat2.color = "黑白";
System.out.println("第1只猫的名字:" + cat1.name + " 年龄:" + cat1.age + " 颜色:" + cat1.color);
System.out.println("第2只猫的名字:" + cat2.name + " 年龄:" + cat2.age + " 颜色:" + cat2.color);
}
}
class Cat{
String name;
int age;
String color;
}对象创建
- 直接创建 Cat cat = new Cat();
- 先声明再创建 Cat cat; cat = new Cat();
访问修饰符
访问修饰符 属性类型 属性名;
- public
- protected
- 默认(不写)
- private
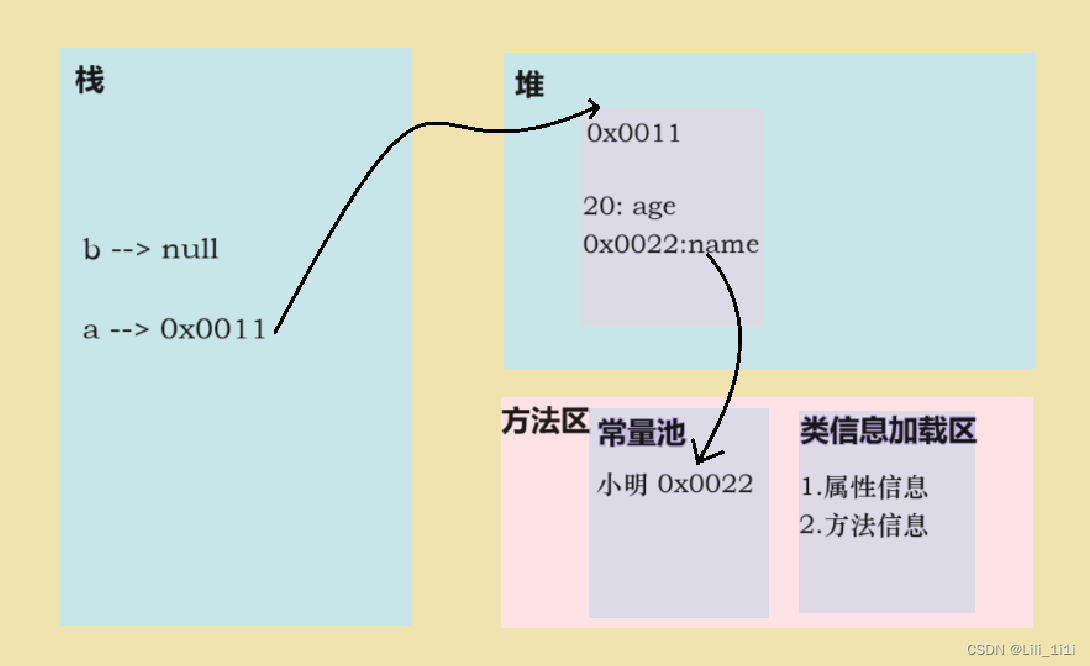
对象内存分配机制
看看下段代码会输出什么
![]()
Person a = new Person();
a.age = 10;
a.name = "小明";
Person b = a;
Syatem.out.println(b.name); //小明
b.age = 20;
b = null;
Syatem.out.println(a.age); //20 b不指向与a相同的空间了,b指向空
Syatem.out.println(b.age); //抛出异常,b已经不是一个对象了
class Person{
int age;
String name;
}
成员方法
- 访问修饰符 返回值类型 方法名(参数列表){
语句;
return 返回值;
}
- 调用方法:对象名.方法名(参数);
- 当程序执行到方法时,就会开辟一个独立的栈空间
- 方法执行完毕,或者执行到return,就会返回到调用方法的地方,开辟的栈空间被释放
- 返回后继续执行代码
- 返回数据类型
- 一个方法最多有一个返回值
- 返回类型可以是基本类型也可以是引用类型
- 如果方法是void,方法体中可以没有return语句
- 细节
- 方法体里不能有方法,即方法不能嵌套定义
- 同一个类中的方法直接调用,不需要创建对象
简单的小练习
import java.util.*;
public class MethodExercise01{
public static void main(String []args) {
Scanner scanner = new Scanner(System.in);
AA a = new AA();
System.out.println("请输入一个数,判断是否为奇数:");
int n = scanner.nextInt();
if(a.isOdd(n)){
System.out.println(n + "是奇数");
}else{
System.out.println(n + "不是奇数");
}
System.out.println("请输入要打印的图形的行数、列数以及符号:");
int row = scanner.nextInt();
int col = scanner.nextInt();
char c = scanner.next().charAt(0);
a.print(row,col,c);
}
}
class AA{
public boolean isOdd(int n){
return n%2 == 1;
}
public void print(int row,int col,char c){
for(int i = 0; i < row; i++){
for(int j = 0 ; j < col; j++){
System.out.print(c);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}成员方法传参机制
- 基本数据类型,传递的是值拷贝,形参的任何改变不影响实参
- 引用数据类型,传递的是地址,可以通过形参影响实参
![]()
![]()
public class MethodExercise01{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
p.age = 20;
B b = new B();
System.out.println(p.age); //20
//思考会输出什么?
b.test1(p);
System.out.println(p.age); //24
//再来,思考一下
b.test2(p);
System.out.println(p.age); //24 这里形参p指向了空,实参p还是指向那块空间
//这个呢?
b.test3(p);
System.out.println(p.age); //24
}
}
class Person{
int age;
String name;
}
class B{
public void test1(Person p){
p.age = 24;
}
public void test2(Person p){
p = null;
}
public void test3(Person p){
p = new Person(); //形参p指向一块新空间,与实参p所指空间不同了
p.age = 36;
}
}克隆对象
编写一个方法copyPerson,可以复制一个Person对象,返回复制的对象。
要求:得到的新对象和原来的对象是相互独立的,只是属性相同
public class MethodExercise02{
public static void main(String[] args){
Person p = new Person();
p.age = 20;
p.name = "小明";
MyTools tools = new MyTools();
Person p2 = tools.copyPerson(p);
//可以通过对象比较看看是否为一个对象
System.out.println(p == p2);
p2.name = "小明2号";
System.out.println("p的名字:" + p.name + "\t年龄:" + p.age);
System.out.println("p2的名字:" + p2.name + "\t年龄:" + p2.age);
}
}
class Person{
int age;
String name;
}
class MyTools{
public Person copyPerson(Person p){
Person p2 = new Person();
p2.age = p.age;
p2.name = p.name;
return p2;
}
}方法递归调用
(1)猴子吃桃子问题
有一堆桃子,猴子第一天吃了其中的一半,并再多吃了一个!
以后每天猴子都吃其中的一半,然后再多吃一个。
当第10天时想再吃,发现只有一个桃子了。
问:最初有多少个桃子?
/*
day10: 1
day9: (1+1)*2=4
day8: (4+1)*2=10
...
dayn: (day(n+1)+1)*2
*/
public class Recursion01{
public static void main(String[] args){
T t = new T();
int day = 1;
int n = t.peach(day);
System.out.println("最初有" + n + "个桃子");
}
}
class T{
public int peach(int day){
if(day == 10){
return 1;
}else if(day >= 1 || day < 10){
return (peach(day+1)+1)*2;
}else{
System.out.println("输入的day应该在1-10");
return -1;
}
}
}(2)迷宫问题
![]()
用二维数组表示(8,7)的迷宫
从(1,1)走到(6,5)
红色表示障碍物,不能走
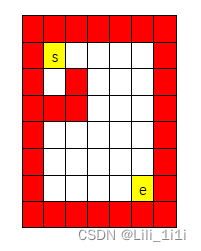
public class MiGong{
public static void main(String[] args){
int[][] map = new int[8][7];
//0表示可以走,1表示障碍物
for(int i = 0; i < 7; i++){
map[0][i] = 1;
map[7][i] = 1;
}
for(int i = 1; i < 7; i++){
map[i][0] = 1;
map[i][6] = 1;
}
map[3][1] = 1;
map[3][2] = 1;
map[2][2] = 1;
T t = new T();
t.findWay(map, 1, 1);
System.out.println("找路情况如下:");
for(int i = 0; i < 8; i++){
for(int j = 0; j < 7; j++){
System.out.print(map[i][j] + " ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
class T{
//0表示可以走,1表示障碍物,2表示走过且可以走,3表示走过但走不通
//找路策略:下-右-上-左
public boolean findWay(int[][] map, int i, int j){
if(map[6][5] == 2){
return true;
}else{
if(map[i][j] == 0){
map[i][j] = 2;
if(findWay(map, i+1, j)){
return true;
}else if(findWay(map, i, j+1)){
return true;
}else if(findWay(map, i-1, j)){
return true;
}else if(findWay(map, i, j-1)){
return true;
}else{
map[i][j] = 3;
return false;
}
}else{ //map[i][j]=1为障碍物不能走,map[i][j]=2以及走过了
return false;
}
}
}
}(3)汉诺塔问题
三根柱子有n个圆盘,大圆盘始终在下,小圆盘始终在上,从一根柱子全部移动到另一根柱子,一次只能移一个盘子,要怎么移动?
public class HanoiTower{
public static void main(String[] args){
Tower t = new Tower();
int num = 2;
t.move(num, 'A', 'B', 'C');
}
}
class Tower{
//num表示要移动的个数,a,b,c表示柱子
public void move(int num, char a, char b, char c){
if(num == 1){
System.out.println(a + "-->" + c);
}else{
//有多个盘,看成2个
move(num-1, a, c, b);
move(1, a, b, c);
move(num-1, b, a, c);
}
}
}方法重载
- 允许同一个类中,允许多个同名方法存在
- 要求形参列表不一样(形参类型或个数,参数名无要求)
- 返回类型无要求

answer

可变参数
- java允许将多个同名、同功能但参数个数不同的方法封装成一个方法
- 访问修饰符 返回类型 方法名(形参类型...形参名)
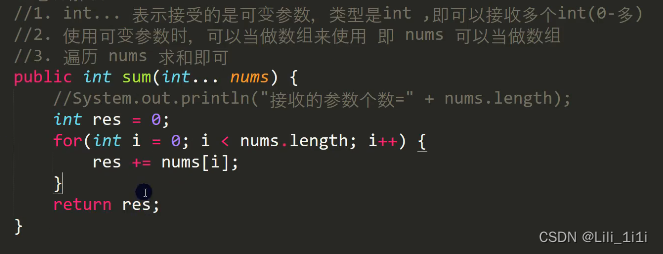
细节
- 可变参数的实参可以是0-多个
- 可变参数的实参可以是数组
- 可变参数的本质就是数组
- 可变参数可以和普通类型的参数放一起,但要求可变参数在最后
public void func(String str, int...nums){ } - 一个形参列表最多只能有一个可变参数
作用域
- java中主要的变量是属性(全局/成员变量)和局部变量
- 局部变量:除了属性之外的变量(一般是在成员方法中定义的变量)
- 属性的作用域为整个类
- 局部变量的作用域为定义它的代码块中
![]()
- 全局变量可以不赋值直接使用,因为属性有默认值
- 局部变量必须赋值后才能使用,局部变量没有默认值
![]()
- 属性和局部变量可以重名,使用时遵循就近原则
- 属性可以加访问修饰符,局部变量不能加修饰符
- 同一成员方法中的局部变量不能重名
- 属性生命周期较长随对象创建而创建,随对象销毁而销毁;局部变量随代码块执行而创建,随代码块结束而销毁
- 属性可以在本类直接使用,或者在其他类通过对象调用
- 局部变量只能在本类使用
构造器/方法(constructor)
- 想在创建对象时,直接给属性赋值,就可以用构造器
- 是类的一种特殊方法,完成对新对象的初始化
- 基本语法:【修饰符】方法名(形参列表){ 方法体; }
- 构造器的修饰符可以默认,也可以是public protected private
- 构造器没有返回值
- 方法名 和 类名 必须一样
- 参数列表 和 成员方法 一样的规则
- 构造器的调用由系统完成
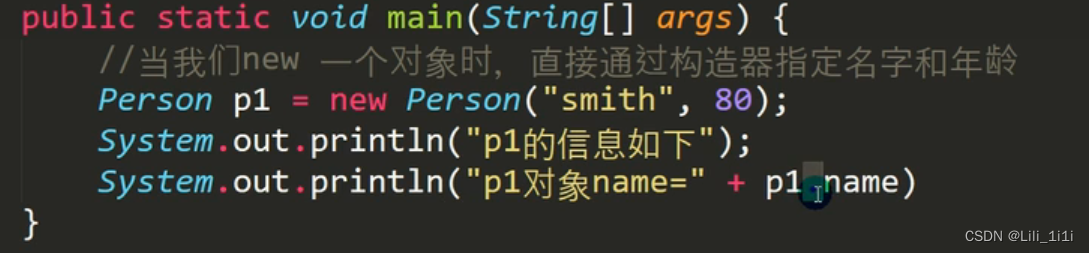

细节
- 一个类可以有多个构造器(构造器重载)
- 构造器名和类名相同
- 构造器没有返回值
- 构造器完成的是对象初始化,不是创建
- 构造器调用由系统完成
- 若未定义构造器,系统会给类自动生成一个默认无参构造器
- 一旦定义了自己的构造器,默认的构造器就被覆盖了,即不能再使用默认的无参构造器

javap反编译可以看到默认构造器 (由.class文件得到.java文件) 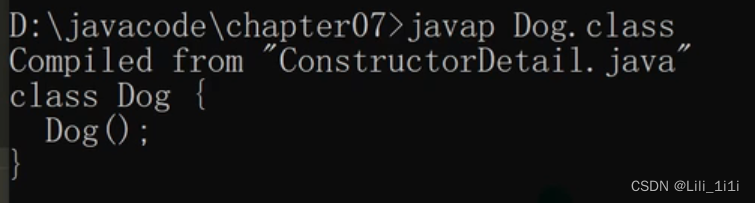
对象创建的流程分析(面试题)

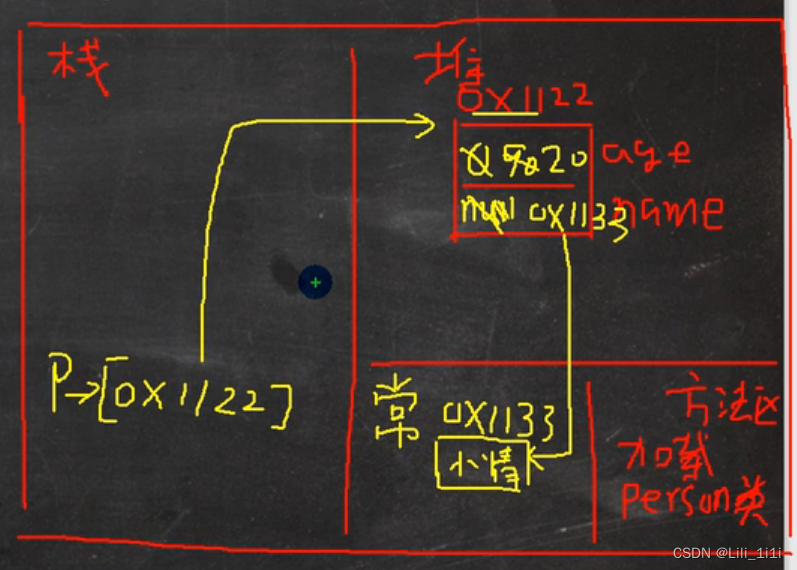
首先在方法区加载Person类信息;接着在堆中开辟一个对象空间,age是int型默认为0,name是String默认是null;然后看到age显性初始化为90;然后系统调用构造器,name赋值为“小倩”,在方法区常量池中为“小倩”开辟一个空间, name指向“小倩”,age赋值为20;最后在栈中p指向堆中的对象空间。

this
- this可以用来访问本类的属性、方法和构造器
- this用于区分当前类的属性和局部变量
- this相当于类的隐藏属性
- 哪个对象调用this,this就代表哪个对象
- 访问构造器:this(参数列表),只能在另一个构造器中使用,且必须位于第一句
- this只能在类定义的方法中使用,不能在类外部使用

练习题

public class Homework01{
public static void main(String[] args){
A01 a = new A01();
double arr[] = {12.0, -1.5, 6.8, 9.9, 100.1};
System.out.println(a.max(arr));
}
}
class A01{
public double max(double...nums){
//求double数组的最大值
int max = 0;
for(int i = 1; i < nums.length; i++){
if(nums[max] < nums[i]){
max = i;
}
}
return nums[max];
}
}public class Homework02{
public static void main(String[] args){
A02 a2 = new A02();
String strs[] = {"hello", "happy", "love", "lucky", "persistence"};
System.out.println(a2.find("persistence",strs));
System.out.println(a2.find("love",strs));
System.out.println(a2.find("haha",strs));
}
}
class A02{
public int find(String x,String...strs){
//String数组查找元素返回索引
for(int i = 0; i < strs.length; i++){
if(strs[i].equals(x)){
return i;
}
}
return -1;
}
}public class Homework03{
public static void main(String[] args){
Book HongLouMeng = new Book("红楼梦", 62.1);
HongLouMeng.updatePrice();
HongLouMeng.info();
}
}
class Book{
String title;
double price;
public Book(String title, double price){
this.title = title;
this.price = price;
}
public void updatePrice(){
//更改价格
if(this.price > 150){
this.price = price;
}else if(this.price > 100){
this.price = price;
}else{
return;
}
}
public void info(){
System.out.println("书名:" + this.title + ",价格:" + this.price);
}
} 
public class Homework04{
public static void main(String[] args){
A03 a3 = new A03();
int[] arr = {10, 20, 26, 42, 100, -1};
int[] newArr = a3.copyArr(arr);
System.out.println("arr是否等于newArr?" + (arr == newArr));
System.out.println("arr:");
for(int i = 0; i < arr.length; i++){
System.out.print(arr[i] + " ");
}
System.out.println("\nnewArr:");
for(int i = 0; i < newArr.length; i++){
System.out.print(newArr[i] + " ");
}
}
}
class A03{
public int[] copyArr(int[] arr1){
int[] arr2 = new int[arr1.length];
for(int i = 0; i < arr2.length; i++){
arr2[i] = arr1[i];
}
return arr2;
}
}public class Homework05{
public static void main(String[] args){
Circle circle = new Circle(1);
circle.perimeter();
circle.area();
}
}
class Circle{
double radius;
public Circle(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
public void perimeter(){
//打印圆周长
System.out.println("圆的周长:" + (2*Math.PI*radius));
}
public void area(){
//打印圆面积
System.out.println("圆的面积:" + (Math.PI*radius*radius));
}
}public class Homework06{
public static void main(String[] args){
Cale c = new Cale(12, 6);
c.sum();
c.minus();
c.mul();
c.div();
System.out.println("===========");
Cale c2 = new Cale(99, 0);
c2.sum();
c2.minus();
c2.mul();
c2.div();
}
}
class Cale{
double a;
double b;
public Cale(double a, double b){
this.a = a;
this.b = b;
}
public void sum(){
System.out.println(a + " + " + b + " = " + (a + b));
}
public void minus(){
System.out.println(a + " - " + b + " = " + (a-b));
}
public void mul(){
System.out.println(a + " * " + b + " = " + (a*b));
}
public void div(){
if(b == 0){
System.out.println("除数不能为0");
}else{
System.out.println(a + " / " + b + " = " + (a/b));
}
}
} 
public class Homework07{
public static void main(String[] args){
Dog doggy = new Dog("圆圆", "白色", 2);
doggy.info();
}
}
class Dog{
String name;
String color;
int age;
public Dog(String name, String color, int age){
this.name = name;
this.color = color;
this.age = age;
}
public void info(){
System.out.println("狗狗的名字:" + name + " 颜色:" + color + " 年龄:" + age);
}
}⭐⭐
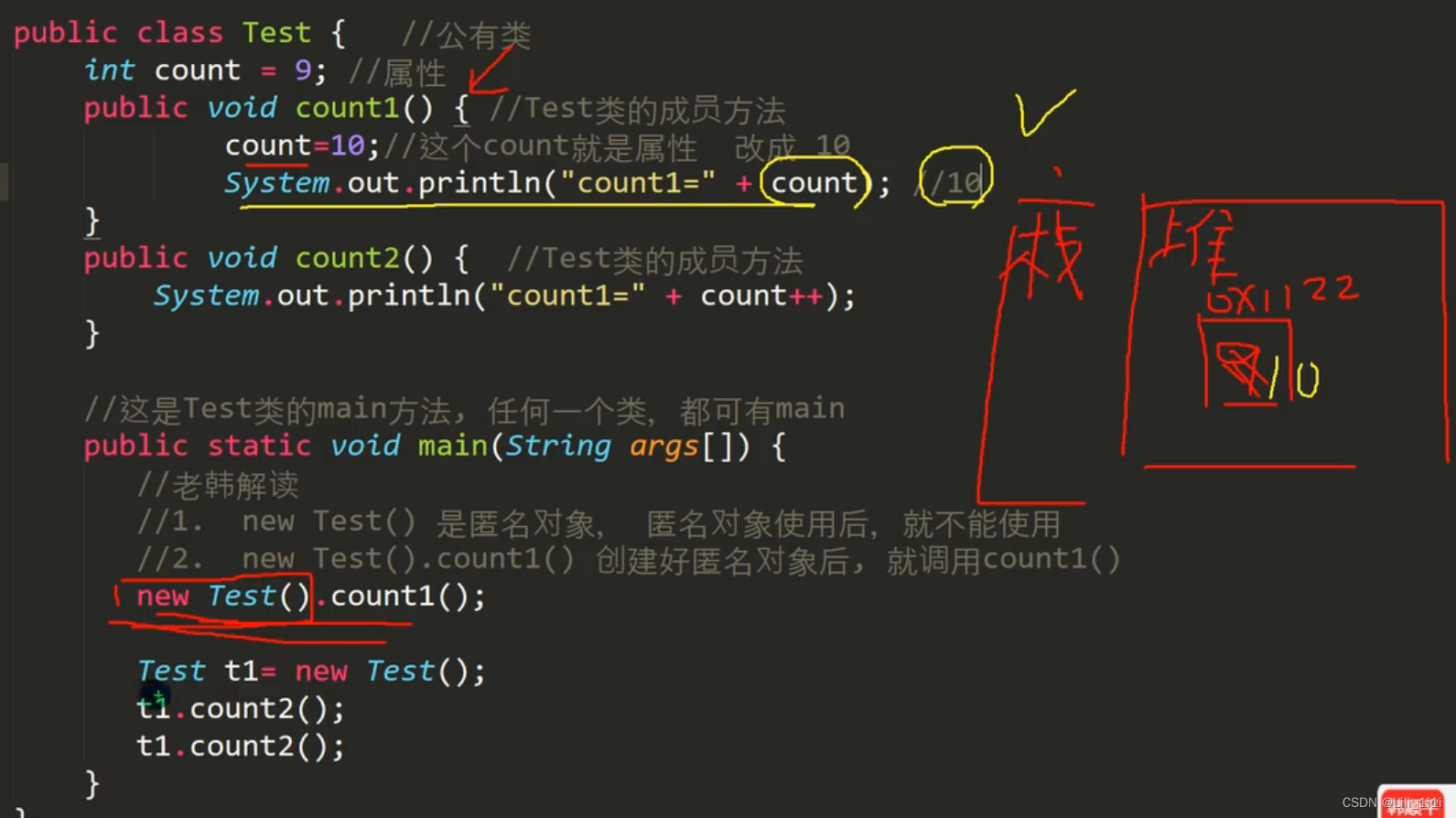
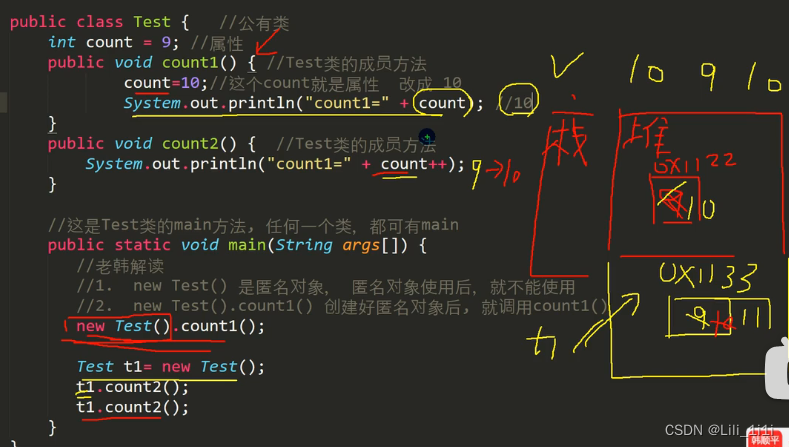
8、answer:输出10、9、10
t1对象的count属性最后为11

public class Homework09{
public static void main(String[] args){
Music music = new Music("雨天", 3.14);
music.play();
music.getInfo();
}
}
class Music{
String name;
double times;
public Music(String name, double times){
this.name = name;
this.times = times;
}
public void play(){
System.out.println("你能体谅 我有雨天~");
}
public void getInfo(){
System.out.println("音乐名:" + name + " 时长:" + times);
}
} 

11. answer: public double method(double d1, double d2){...}
class Employee{
String name;
char gender;
int age;
String occupation;
double sal;
public Employee(String name, char gender, int age){
this.name = name;
this.gender = gender;
this.age = age;
}
public Employee(String occupation, double sal){
this.occupation = occupation;
this.sal = sal;
}
public Employee(String name, char gender, int age, String occupation, double sal){
this(name, gender, age);
this.occupation = occupation;
this.sal = sal;
}
}
public class Homework13{
public static void main(String[] args){
PassObject p = new PassObject();
Circle c = new Circle();
p.printAreas(c, 5);
}
}
class Circle{
double radius;
public double findArea(){
return Math.PI*radius*radius;
}
public void updateRadius(double radius){
this.radius = radius;
}
}
class PassObject{
public void printAreas(Circle c, int times){
System.out.println("Radiius\t面积");
for(int i = 1; i <= times; i++){
c.updateRadius(i);
System.out.println(i + "\t" + c.findArea());
}
}
}
扩展题可以尝试自己做做~























 1万+
1万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










