- 在第 8 行,获取字符串 s 中从 1 开始、到 4 结束的字符串 ‘mooc’,使用 s [1:4] 表示该范围,注意该范围包括字符串的第 1 个字符、不包括第 4 个字符。
find()函数 与 index()函数
find() 函数与 index() 函数的功能:都是返回你想找的成员(元素)的位置
find() 函数的用法:str = string.finde(item) item:想要查询匹配的元素,返回一个整型
index() 函数的用法:str = string.index(item) item:想要查询匹配的元素,返回一个整型或者报错
附:字符串里的位置是从左向右从下标位[0]开始计算
find() 函数与 index() 函数的区别:
-
如果 find() 函数 找不到c成员(元素),会返回 -1
-
如果 index()函数 找不到成员(元素),会导致程序报错
info = “Python is good code”
print(info.find(“P”))
print(info.find(“good”))
print(info.find(“Java”))
>>> 0
>>> 10
>>> -1
info = “Python is good code”
print(info.index(“P”))
print(info.index(“good”))
print(info.index(“Java”)) # 直接报错(语法错误) ‘ValueError: substring not found’
>>> 0
>>> 10
startswith() 函数与 endswith() 函数
startswith() 函数的功能:判断字符串 开始位 是否是某成员(元素),可以指定统计的范围,[start,end) 左闭区间右开区间
startswith() 函数的用法:str = string.startswith(item) item:想要查询匹配的元素,返回一个布尔值
endswith() 函数的功能:判断字符串 结尾 是否是某成员(元素),可以指定统计的范围,[start,end) 左闭区间右开区间
startswith() 函数的用法:str = string.endswith(item) item:想要查询匹配的元素,返回一个布尔值
示例如下:
info = ‘Python is good’
print(info.startswith(‘Python’))
print(info.startswith(‘Java’))
print(info.endswith(‘good’))
print(info.endswith(‘bad’))
>>> True
>>> False
>>> True
>>> False
string_test = “this is string example”
print(string_test.startswith(‘this’)) # 字符串是否以 this 开头
print(string_test.startswith(‘string’, 8)) # 从第九个字符开始的字符串是否以 string 开头
print(string_test.startswith(‘this’, 2, 4)) # 从第2个字符开始到第四个字符结束的字符串是否以 this 开头
>>> True
>>> True
>>> False
capitalize () 函数
capitalize 的功能 : 将字符串的首字母大写
capitalize 的用法:str = string.capitalize() ;
示例如下:
str = ‘string’
str.capitalize()
‘String’
capitalize() 的注意事项:
-
只对首字母有效
-
只对字母有效
-
已经是大写,则无效
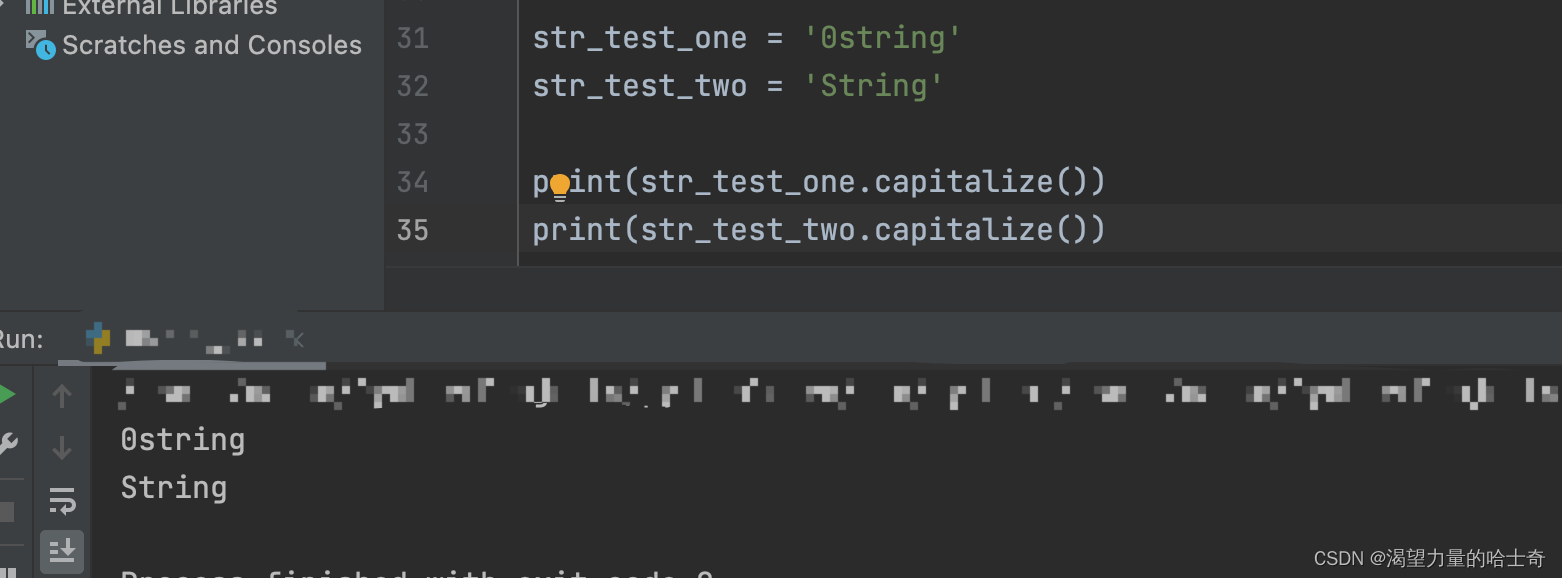
capitalize()函数小练习
将han meimei转换成规范的英文名字,打印实现姓、名首字母都是大写
name_1=“han”
name_2=“meimei”
print(name_1.capitalize() + ’ ’ +name_2.capitalize())
>>> 输出结果 ‘Han Meimei’
casefold()函数与lower()函数
casefold()函数与lower()函数 的功能 : 将字符串的全体字符小写
casefold()函数与lower()函数 的用法:str = string.casefold() , str = string.lower() ;
示例如下:
str_01 = ‘Hello’
str_01.casefold()
‘hello’
str_02 = ‘World’
str_02.lower()
‘world’
casefold()函数与lower()函数 的注意事项:
-
只对字符串的字母有效
-
已经是小写的字母无效
chinese = “你好,世界”
english = “Hello,World”
test_str = “test@1.com$OK”
print(chinese.casefold())
print(chinese.lower())
print(english.casefold())
print(english.lower())
print(test_str.casefold())
print(test_str.lower())
既然 casefold()函数与lower()函数 都可以将字符串的全体字符转为小写,那么又有什么区别呢?
其实还是有区别的,lower()函数是很早之前就存在的将字符串小写的方法,而casefold()函数则是 Python3.3版本之后才引入的小写方法。lower()函数是将英文字符进行小写,但是对德语等其他非英语字符就失去了效果,这个时候就是 casefold() 函数大显身手的时候了。
casefold()函数与lower()函数 小练习
将下列三个验证码全部转为 小写
str_1 = “NAh8”
str_2 = “Sn6H”
str_3 = “HKFM”
str_1 = “NAh8”
str_2 = “Sn6H”
str_3 = “HKFM”
print (str_1.lower())
print (str_2.casefold())
print (str_3.lower())
upper() 函数
upper() 函数的功能:将字符串全体大写
upper() 函数的用法:str = string.upper()
示例如下:
str = ‘string’
str.upper()
‘STRING’
capitalize 的注意事项:
-
只对字符串的字母有效
-
已经是大写的字母无效
str_test = ‘Hello World’
print(str_test.upper())
>>> ‘HELLO WORLD’
swapcase() 函数
swapcase() 函数的功能:将字符串中的字符进行大小写转换
swapcase() 函数的用法:str = string.swapcase()
swapcase() 函数的注意事项:只对字符串的字母有效
info_one = ‘Python is good’
info_two = ‘pthon web is so esay’
print(info_one.swapcase())
print(info_two.swapcase())
zfill() 函数
zfill() 函数的功能:为字符串定义长度,如果现有字符串长度不满足,缺少的部分自动用 0 补齐
zfill() 函数的用法:str = string.zfill(width) width:新字符串希望的长度
zfill() 函数的注意事项:与字符串的字符没有关系;如果定义的字符串长度小于当前字符串长度,则不会发生变化。
info = “Hello World”
print(info.zfill(10))
print(info.zfill(15))
print(info.zfill(20))
count() 函数
count() 函数的功能:统计字符串出现的次数;或者说返回当前字符串某个成员(元素)出现的次数
count() 函数的用法:str = string.zfill(item) item:查询个数/次数的元素
count() 函数的注意事项:如果查询的成员(元素)不存在,则返回 0
info = ‘’’
Please send this message to those people who mean something to you,to those who have touched your life in
one way or another,to those who make you smile when you really need it,to those that make you see the
brighter side of things when you are really down,to those who you want to let them know that you appreciate
their friendship. And if you don’t, don’t worry,nothing bad will happen to you,you will just miss out on the
opportunity to brighten someone’s day with this message.
‘’’
this_count = info.count(‘this’)
you_count = info.count(‘you’)
love_count = info.count(‘love’)
print('"this"出现的次数为: ’ + str(this_count) + ‘次’)
>>> "this"出现的次数为: 2次
print('"you"出现的次数为: ’ + str(you_count) + ‘次’)
>>> "you"出现的次数为: 11次
print('"love"出现的次数为: ’ + str(love_count) + ‘次’)
>>> "maybe"出现的次数为: 0次
strip()函数
strip() 函数的功能 :去掉字符串两边的指定元素,默认是空格
strip() 函数的用法 :str = string.strip(item) ,括弧里传一个想要去掉的成员(元素),可以不填写
strip() 函数的拓展 :
-
传入的元素如果不在开头或者结尾则无效
-
lstrip 仅去掉字符串开头的指定元素或者是空格
-
rstrip 仅去掉字符串结尾的指定元素或者是空格
示例如下:
info = ’ Jack is a good boy ’
new_info_01 = info.strip()
print(new_info_01)
>>> Jack is a good boy
new_info_02 = info.strip(info)
print(new_info_02)
print(len(new_info_02))
>>> 实际上这里的 ‘new_info_02’ 已经北清空了
>>> 0 清空后的 ‘new_info_02’ 长度为0
text = ‘abcde’
text_lstrip = text.lstrip(‘a’)
print(text_lstrip)
>>> bcde
text_rstrip = text.rstrip(‘e’)
print(text_rstrip)
>>> abcd
replace()函数
replace()函数的功能:把字符串中的 old(旧字符串) 替换成 new(新字符串),并可以指定数量,默认 -1 代表替换全部
replace()函数的用法:str = string.replace(old, new, max)
-
old :被替换的元素
-
new:替换 old 的元素
-
max:可选,代表替换几个,默认替换掉全部匹配到的 old 。
示例如下:
info = “hello, Neo”
print(info.replace(“Neo”, “Jack”))
print(info.replace(" ", “*”, 1))
>>> hello, Jack
>>> hello,*Neo
info_test = “hello world !!!”
new_info_01 = info_test.replace(“h”, “H”)
new_info_02 = new_info_01.replace(“w”, “W”)
print(new_info_02.replace(‘!!!’, ‘Python’))
>>> Hello World Python
join() 函数
join()函数的功能:将序列中的元素以指定的字符连接生成一个新的字符串
join()函数的用法:str = "".join(lists)
示例如下:
lists = [“a”, “b”, “c”]
tuples = (“1”, “2”, “3”)
print("".join(lists)) # >>> ab*c
print(“@”.join(tuples)) # >>> 1@2@3
知识点
-
“”.join(lists) 是常见的将列表、元组转成字符串的写法
-
列表里面只能存放字符串元素,有其他类型的元素会报错 TypeError: sequence item 0: expected str instance, int found
最后
🍅 硬核资料:关注即可领取PPT模板、简历模板、行业经典书籍PDF。
🍅 技术互助:技术群大佬指点迷津,你的问题可能不是问题,求资源在群里喊一声。
🍅 面试题库:由技术群里的小伙伴们共同投稿,热乎的大厂面试真题,持续更新中。
🍅 知识体系:含编程语言、算法、大数据生态圈组件(Mysql、Hive、Spark、Flink)、数据仓库、Python、前端等等。
网上学习资料一大堆,但如果学到的知识不成体系,遇到问题时只是浅尝辄止,不再深入研究,那么很难做到真正的技术提升。
一个人可以走的很快,但一群人才能走的更远!不论你是正从事IT行业的老鸟或是对IT行业感兴趣的新人,都欢迎加入我们的的圈子(技术交流、学习资源、职场吐槽、大厂内推、面试辅导),让我们一起学习成长!








 本文详细介绍了Python字符串处理中的各种函数,如find()、index()、startswith()、endswith()、capitalize()、casefold()、lower()等,以及它们的用法、区别和注意事项。
本文详细介绍了Python字符串处理中的各种函数,如find()、index()、startswith()、endswith()、capitalize()、casefold()、lower()等,以及它们的用法、区别和注意事项。














 4万+
4万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








