目录

一、文件的基本操作
创建文件对象和打开文件对象:open()
def my_write(): #(1)打开(创建)文件 file=open('Myqq.txt','w',encoding='utf-8') #如果文件不存在,则在当前目录下创建一个文件名字为Myqq.txt #(2)操作文件 file.write('我好爱她') #(3)关闭文件 file.close() #读取 def my_read(): #(1)打开(创建)文件 f=open('Myqq.txt','r',encoding='utf-8') s=f.read() print(type(s),s) f.close if __name__ == '__main__': my_write() my_read()
一、文件的状态和操作过程
文件没打开时是存储状态,使用open打开之后变成占用状态(其他程序不能占用)。
二、文件的操作
一、打开方式
a表示append。
r/w是文本方式打开,按照字符的方式读写。(而非字节流)
默认方式下文件是以读方式打开的:
file=open('a.txt') print(file)#<_io.TextIOWrapper name='a.txt' mode='r' encoding='cp936'> file.close()file=open('Myq.txt','r+') #表示有读写功能 file=open('Myq.txt','w+') #表示有读写功能,并且是覆盖写
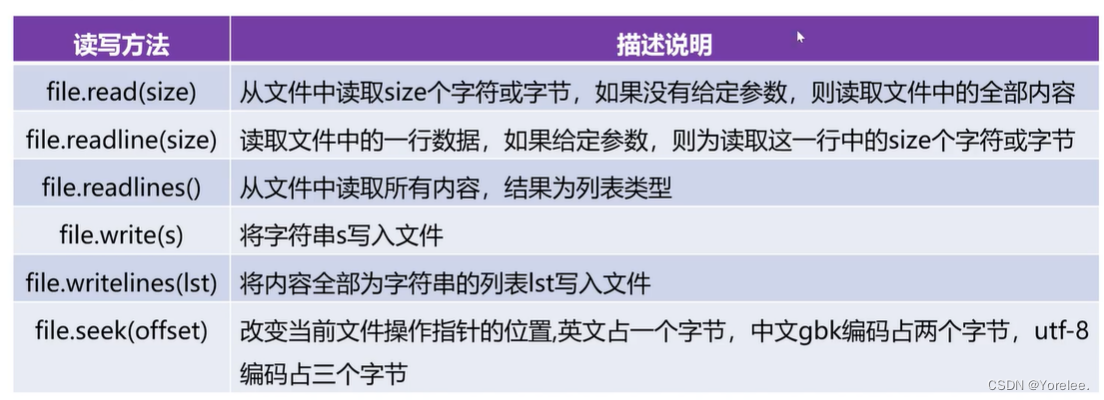
二、读写方式
offset是字节位置。
无论是read()还是readlines()等都从读写指针开始的。
file,readlines()每一行是列表中的一个元素
file=open('a.txt','w+',encoding='utf-8') lst=['北京','上海','天津'] file.writelines(lst) #直接将列表中的元素挨个写入file file.seek(0) for item in file: print(item) #北京上海天津 #相当于print(file.read()) file.close()def my_write(s): # (1)打开(创建文件)文件 file = open('myqq.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') file.write(s) file.write('\n') file.close() def my_write_list(file, lst): f = open(file, 'a', encoding='utf-8') f.writelines(lst) f.close() def my_read(filename): file=open(filename,'a+',encoding='utf-8') file.write('炙热的渴望是勇气') file.seek(0)#写指针导致读写指针指在最后,重置指针以便于从头读取 s=file.read(10)#读取10个字符,可能是10个汉字 s=file,readline() print(s) s=file.readline(2) print(s) file.close() if __name__ == '__main__': # my_write('她静悄悄地来过') # my_write('她慢慢带走沉默') # lst = ['从一个眼神\n', '一次谈心\n', '到变懂得变熟悉\n'] # my_write_list('myqq.txt', lst) my_read('myqq.txt')
三、文件的复制
def copy(src,new_path):#假如读取的是图片文件,用二进制读 #实际上就是边写边读 file1=open(src,'rb') file2=open(new_path,'wb') s=file1.read()#读取所有,返回的是二进制 file2.write(s)#写入所有 file2.close() file1.close() #先打开的后关,后打开的先关。 if __name__ == '__main__': src='./Myqq.jpg' #.代表的是当前目录 new_path='../Module/Myzwq.jpg' #..表示的是上级目录,相当于windows里的后退。后退一步的文件夹里必须有Module这个文件夹。 copy(src,new_path)
四、with语句
open()是打开文件的操作,as file是给该文件起个别名。在with语句的语句块中,不需要手动关闭文件。
print() with open('Myqq.txt', 'a', encoding='utf-8') as file: file.write('输了你!赢了世界又如何\n') print() #像for循环语句一样,这是一个顺序执行的def copy(src,new_file): with open(src,'r',encoding='utf-8'):#打开src文件 with open(new_file,'w',encoding=='utf-8'): #在src打开的过程中,再打开new_file,必须嵌套打开,src才保证一直打开着 new_file.write(src.read())
二、高维数据的存储和组织

def my_write(): # 一维数据 可以用字符串操作将列表转换成字符串 lst = ['输了你!', '我们的爱', '除了爱你还能爱谁'] with open('JJLin.txt', 'w', encoding='utf-8') as file: file.writelines(lst) def my_read(): with open('JJLin.txt', 'r', encoding='utf-8') as file: print(file.readlines()) my_write() my_read()def my_write_table(): #二维数据 lst=[ ['商品名称','单价','采购数量'], ['水杯','98.5','20'], ['鼠标','89','100'], ] with open('table.csv','w',encoding='utf-8') as file: for item in lst: line=','.join(item) file.write(line) file.write('\n') def my_read_table(): #二维数据 data=[] with open('table.csv','r',encoding='utf-8') as file: lst=file.readlines() #②每一行是列表中的一个元素 for item in lst:#③ new_lst=item[:len(item)-1].split(',') #④切掉\n,并以','切割 返回一个列表 data.append(new_lst)#④ my_write_table()#① my_read_table() ''' ①: 商品名称,单价,采购数量 水杯,98.5,20 鼠标,89,100 ② lst=['商品名称,单价,采购数量\n','水杯,98.5,20\n','鼠标,89,100\n'] ③ item='商品名称,单价,采购数量\n' 切片后:'商品名称,单价,采购数量' split()后:new_lst=['商品名称','单价','采购数量'] ④ data=[['商品名称','单价','采购数量']] 循环③ '''
高维数据:
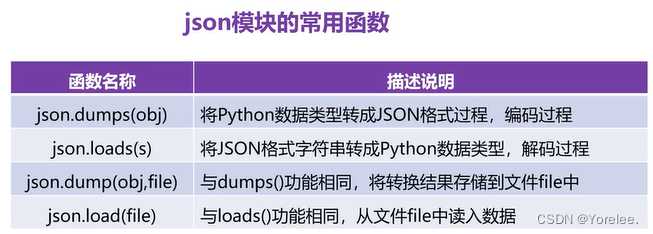
import json lst=[ {'name':'Zy','age':21,'score':97.9}, {'name':'Ly','age':21,'score':97.9}, {'name':'Lwq','age':21,'score':97.9} ] #编码 s=json.dumps(lst,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4) #ensure_ascii正常显示中文,indent缩进格式增加缩进 print(type(s))# list-->str ,列表中是字典 print(s) #解码 lst2=json.loads(s) print(type(lst2)) print(lst2) #编码到文件中 with open('student.txt','w') as file: json.dump(lst,file,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4) with open('student.txt','r') as file: json.load(lst,file,ensure_ascii=False,indent=4)
三、os模块中常用的函数
一、os模块
getcwd()返回的是字符串类型。
import os print('当前工作路径:',os.getcwd()) lst=os.listdir() print('当前路径下的所有目录及文件:',lst) print('D:\Program Files下的所有目录及文件:',os.listdir('D:\Program Files')) #创建文件夹 os.mkdir('好好学习') #已经存在不能创建 os.makedirs('./好好学习/aa/bb/cc/dd') #已经存在不能创建 #删除目录 os.rmdir('./好好学习/aa/bb/cc/dd') #./表示当前路径,当前路径可以不写 os.removedirs('好好学习/aa/bb/cc') #设置当前路径 os.chdir('D:\Program Files') #执行完这条语句之后,再写代码工作路径就是更改后的路径,但是本文件位置没变,运行路径变化 print('当前工作路径:',os.getcwd()) file=open('MMM.txt','w') file.close() #遍历目录树,递归遍历输出所有文件夹中的内容 for dirs,dirlst,filelst in os.walk('D:\Program Files'): print(dirs) print(dirlst) print(filelst) print('-'*20) #删除指定的文件 os.remove('MMM.txt') #删除当前路径下的MMM.txt文件,注意当前路径之前被更改过 #os.remove('C:\\Users\Administrator\Desktop\pythonProject\\text.txt') #'\t'需要转义字符\\t #缘神启动! os.startfile("E:\Program Files\腾讯游戏\WeGame\wegame.exe")
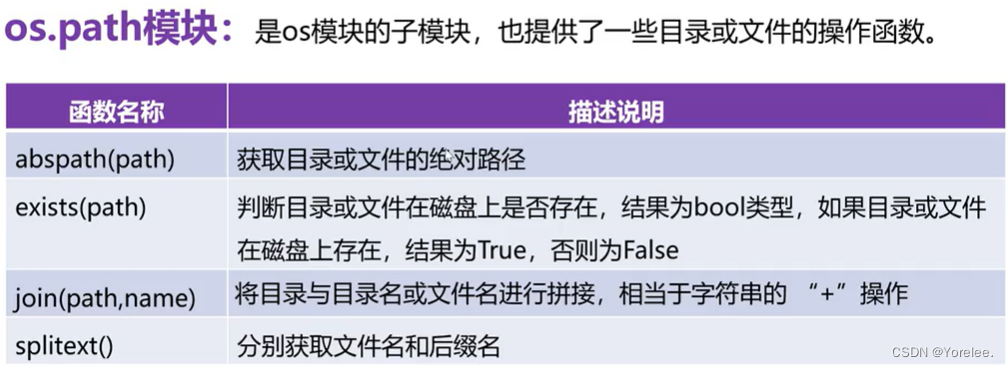
二、os.path子模块
exists(path)的使用可以避免使用同一个操作重复创建文件。
比如 if os.path.exists(path_to_file):
f=open(file)
import os.path as op print('获取目录或文件的绝对路径',op.abspath('./JJLin.txt'))#必须给参数 #绝对路径指的是从盘符开始的 print('判断目录或文件在磁盘上是否存在',op.exists('JJLin.txt')) #相对路径 print('判断目录或文件在磁盘上是否存在',op.exists('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher\launcher.exe')) print('分割文件的名和文件后缀名:',op.splitext('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher\launcher.exe')) print('提取文件名:',op.basename('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher\launcher.exe')) print('提取路径:',op.dirname('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher\launcher.exe')) print('是否是有效路径(文件夹):',op.isdir('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher')) #判断文件夹! print('是否是有效路径(文件夹):',op.isdir('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher\launcher.exe')) #判断文件夹! print('是否是有效文件:',op.isfile('E:\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher\launcher.exe')) #判断文件夹! ''' 获取目录或文件的绝对路径 C:\Users\Administrator\Desktop\pythonProject\JJLin.txt 判断目录或文件在磁盘上是否存在 True 判断目录或文件在磁盘上是否存在 True 分割文件的名和文件后缀名: ('E:\\WeGameApps\\rail_apps\\无畏契约(2001715)\\WeGameLauncher\\launcher', '.exe') 提取文件名: launcher.exe 提取路径: E:\WeGameApps\rail_apps\无畏契约(2001715)\WeGameLauncher 是否是有效路径(文件夹): True 是否是有效路径(文件夹): False 是否是有效文件: True '''








 本文详细介绍了Python中文件的基本操作,如文件状态管理、打开方式、读写方法、文件复制、with语句的使用,以及高维数据的存储和处理,同时涵盖了os模块和os.path子模块的常用函数,包括文件路径处理和检查文件类型。
本文详细介绍了Python中文件的基本操作,如文件状态管理、打开方式、读写方法、文件复制、with语句的使用,以及高维数据的存储和处理,同时涵盖了os模块和os.path子模块的常用函数,包括文件路径处理和检查文件类型。





























 3626
3626

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










