顺序表的原理

结构体定义
#define MAX_SIZE 100 struct _SqList{
ElemType *elems; // 顺序表的基地址
int length; // 顺序表的长度
int size; // 顺序表总的空间大小
}
顺序表的算法实现(顺序表的初始化)
| #define MAX_SIZE 100 typedef struct{ int *elems; // 顺序表的基地址 int length; // 顺序表的长度 int size; // 顺序表的空间 }SqList; bool initList(SqList &L) //构造一个空的顺序表L { L.elems=new int[MAX_SIZE]; //为顺序表分配Maxsize个空间 if(!L.elems) return false; //存储分配失败 L.length=0; //空表长度为0 L.size = MAX_SIZE; return true; } |

顺序表增加元素
| bool listAppend(SqList &L, int e) { if(L.length==MAX_SIZE) return false; //存储空间已满 L.elems[L.length] = e; L.length++; //表长增1 return true; } |

顺序表插入元素
| bool listInsert(SqList &L,int i, int e) { if(i<0 || i>=L.length)return false; //i值不合法 if(L.length==MAX_SIZE) return false; //存储空间已满 for(int j=L.length-1; j>=i; j--){ L.elems[j+1]=L.elems[j];//从最后一个元素开始后移,直到第i个元素后移 } L.elems[i]=e; //将新元素e放入第i个位置 L.length++; //表长增1 return true; } |
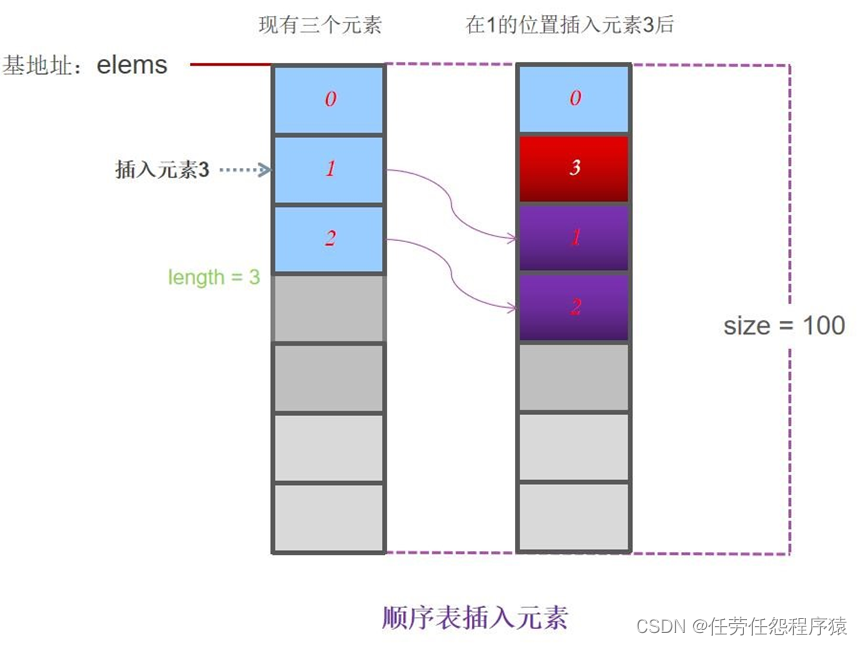
顺序表删除元素
| bool listDelete(SqList &L,int i) { if(i<0 || i>=L.length) return false; //不合法 if(i == L.length-1){//删除最后一个元素,直接删除 L.length--; return true; } for (int j=i; j<L.length-1; j++){ L.elems[j] =L.elems[j+1]; //被删除元素之后的元素前移 } L.length--; return true; } |
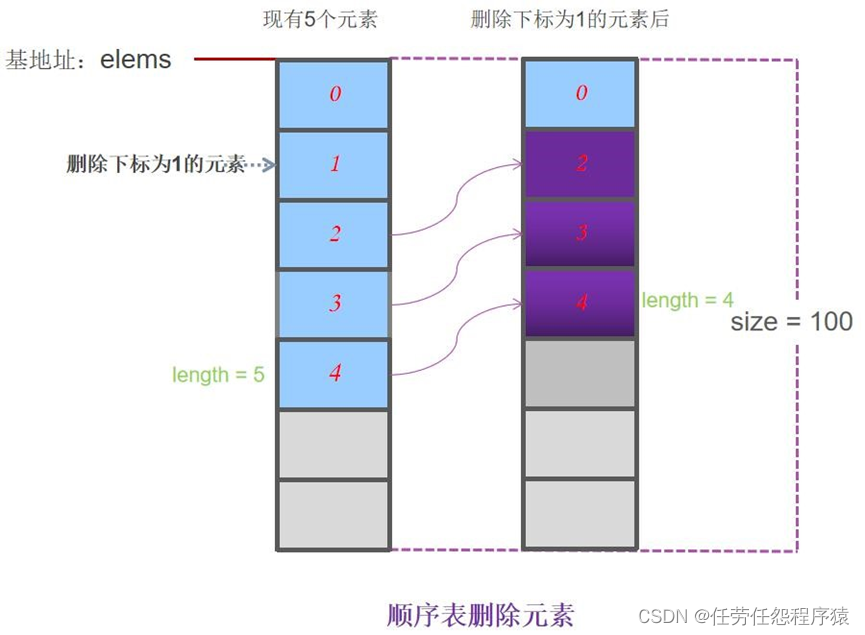
顺序表销毁
| void destroyList(SqList &L) { if (L.elems) delete []L.elems;//释放存储空间 L.length = 0; L.size = 0; } |
完整代码实现
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct
{
int* elems;
int length;
int size;
}SqList;
bool initList(SqList& L)
{
L.elems = new int[MAX_SIZE];
if (!L.elems)
{
return false;
}
L.size = MAX_SIZE;
L.length = 0;
return true;
}
bool AppendList(SqList& L, int z)
{
if (L.length == L.size)
{
return false;
}
L.elems[L.length] = z;
L.length += 1;
return true;
}
bool insertList(SqList& L, int z, int i)
{
if (L.length == L.size || i<0)
{
return false;
}
//插入的数在顺序表末尾
if (L.length - 1 == i)
{
L.elems[L.length] = z;
L.length += 1;
return true;
}
//插入的数没在顺序表末尾
for (int j = L.length - 1; i <= j; j--)
{
L.elems[j + 1] = L.elems[j];
}
L.elems[i] = z;
L.length += 1;
return true;
}
bool deleteList(SqList& L, int z, int i)
{
if (L.elems==NULL)
{
cout << "数据为空!" << endl;
return false;
}
for (int j = i; j <= L.length-2 ; j++)
{
L.elems[j] = L.elems[j + 1];
}
L.length = L.length - 1;
return true;
}
bool destroyList(SqList& L)
{
if (L.elems)
{
delete[]L.elems;
}
L.length = 0;
L.size = 0;
return true;
}
void printList(SqList& L)
{
cout << "数据有:" << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
{
cout << L.elems[i] << " ";
}
}
int main1(void)
{
SqList list;
int x = 0;
//初始化顺序表
initList(list);
//追加数据
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
AppendList(list, i);
}
printList(list);
cout << endl;
cout << "请输入你要插入的数据和对应位置:";
insertList(list, 9, 3);
printList(list);
cout << "请输入你要删除的数据和对应位置:";
deleteList(list, 9, 3);
printList(list);
//销毁顺序表
cout << "请销毁顺序表:";
destroyList(list);
system("pause");
return 0;
}顺序表的企业级应用案例:
高并发 WEB 服务器中顺序表的应用
高性能的 web 服务器 Squid 每秒可处理上万并发的请求,从网络连接到服务器的客户端与服务器端在交互时会保持一种会话(和电话通话的场景类似)。服务器端为了管理好所有的客户端连接,给每个连接都编了一个唯一的整数编号,叫做文件句柄,简称 fd.
 为了防止某些恶意连接消耗系统资源,当某个客户端连接超时(在设定的一定时
为了防止某些恶意连接消耗系统资源,当某个客户端连接超时(在设定的一定时
间内没有发送数据)时,服务器就需要关闭这些客户端的连接具体
实现方案:
1. 当有新的请求连到服务器时,如果经过服务器频率限制模块判断,貌似恶意连接,则使用顺序表来保存此连接的超时数据,超时值使用时间戳来表示,时间戳是指格林威治时间 1970 年 01 月 01 日 00 时 00 分 00 秒(相当于北京时间 1970 年 01 月 01 日
08 时 00 分 00 秒)起至现在的总秒数,其结构体定义如下:
typedef struct {
int fd ;
time_t timeout; // 使用超时时刻的时间戳表示
}ConnTimeout;
2. 服务器程序每隔一秒钟扫描一次所有的连接,检查是否超时,如果存在超时的
连接,就关闭连接,结束服务,同时将顺序表中的记录清除!
代码如下:
webServer.cpp
#include <iostream>
#include <time.h>
#include <Windows.h>
#include "webServer.h"
using namespace std;
static void checkTimeouts(TimeoutSqList& list, time_t now);
int main(void)
{
time_t now, end;
time_t last_timeout;
TimeoutSqList list;
time(&now);
end = now + 60;
last_timeout = now;
initList(list);
//1.模拟频率限制模块通过判断分析,增加恶意连接到顺序表中
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
ConnTimeout e;
e.fd = i;
e.timeout = now + 5 + 2 * i;
AppendList(list, e);
}
printList(list);
do
{
if (last_timeout + 0.999 < now)
{
checkTimeouts(list, now);//检查超时的连接
last_timeout = now;
}
Sleep(10);//防止cpu空转
time(&now);
} while (now < end);
/*time_t now;
time(&now);
cout << "当前的时间戳 - timestamp:" << now << endl;
Sleep(2000);
time(&now);
cout << "两秒以后的时间戳 - timestamp:" << now << endl;*/
system("pause");
return 0;
}
void checkTimeouts(TimeoutSqList& list, time_t now)
{
int fd, i;
cout << "检查超时fd……\n";
for (i = 0; i < list.length; i++)
{
if (list.elems[i].timeout > now)
{
continue;
}
//超时,清理连接
fd = list.elems[i].fd;
//关闭连接
printf("连接[fd=%d] 已经超时,关闭连接!\n", fd);
//删除顺序表中的元素
i--;
deleteList(list, i);
}
}TimeoutSqList.cpp
#include "webServer.h"
#include <iostream>
#include <Windows.h>
using namespace std;
bool initList(TimeoutSqList& L)
{
L.elems = new ConnTimeout[MAX_SIZE];
if (!L.elems)
{
return false;
}
L.size = MAX_SIZE;
L.length = 0;
return true;
}
bool AppendList(TimeoutSqList& L, ConnTimeout z)
{
if (L.length == L.size)
{
return false;
}
L.elems[L.length] = z;
L.length += 1;
return true;
}
bool insertList(TimeoutSqList& L, ConnTimeout z, int i)
{
if (L.length == L.size || i < 0)
{
return false;
}
//插入的数在顺序表末尾
if (L.length - 1 == i)
{
L.elems[L.length] = z;
L.length += 1;
return true;
}
//插入的数没在顺序表末尾
for (int j = L.length - 1; i <= j; j--)
{
L.elems[j + 1] = L.elems[j];
}
L.elems[i] = z;
L.length += 1;
return true;
}
bool deleteList(TimeoutSqList& L, int i)
{
if (L.elems == NULL)
{
cout << "数据为空!" << endl;
return false;
}
for (int j = i; j <= L.length - 2; j++)
{
L.elems[j] = L.elems[j + 1];
}
L.length = L.length - 1;
return true;
}
bool destroyList(TimeoutSqList& L)
{
if (L.elems)
{
delete[]L.elems;
}
L.length = 0;
L.size = 0;
return true;
}
void printList(TimeoutSqList& L)
{
cout << "当前:" << L.size << ",已保存元素的个数 length:" << L.length << endl;
for (int i = 0; i < L.length; i++)
{
cout << "fd:" << L.elems[i].fd << ",timeout:" << L.elems[i].timeout << endl;
}
}
webServer.h
#ifndef _WEB_SERVER_H_
#define _WEB_SERVER_H_
#include <time.h>
#define MAX_SIZE 100
typedef struct
{
int fd;
time_t timeout;//使用超时时刻的时间戳表示
}ConnTimeout;
typedef struct
{
ConnTimeout* elems; //顺序表的基地址
int length; //顺序表的长度
int size; //顺序表的大小
}TimeoutSqList;
//顺序表的接口
bool initList(TimeoutSqList& L);
bool AppendList(TimeoutSqList& L, ConnTimeout z);
bool deleteList(TimeoutSqList& L, int i);
bool destroyList(TimeoutSqList& L);
void printList(TimeoutSqList& L);
#endif






















 320
320











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










