静态链表
用数组描述的链表叫做静态链表;让数组的元素由两个数据域组成,data和;数据域data,cur相当于单链表中的next指针,存放该元素的后继在数组中的下标。
由数组组成的静态链表:
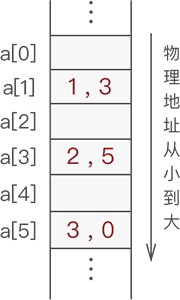
为了分辨数组中哪些量没有被使用,可以将所有没有被使用过的和被删除的量用游标链成一个备用链表。
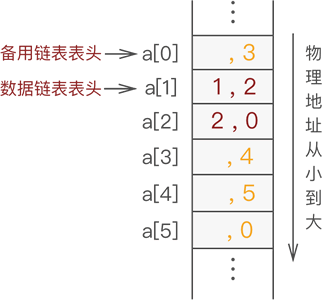
定义静态链表:
typedef struct
{
char data;
int next;
}*NodePtr,Node;
typedef struct
{
NodePtr node;
int *used;//判断地址是否有值,1代表有值,0代表无值
}*list,lnode;
初始化静态链表:
list initlist()
{
//temphead为指向整个静态链表的指针
list temphead=(list)malloc(sizeof(lnode)*initlen);
//将静态链表的空间分配给node数组和used数组
temphead->node=(NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node)*initlen);
temphead->used =(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*initlen);
//初始化头节点
temphead->node->date='\0';
temphead->node->next=-1;
temphead->used[0]=1;//头节点不能用来存放数据
int i;
for(i=1;i<initlen;i++)
{
temphead->used[i]=0;
}
return temphead;
}
静态链表的插入:
插入时可以从备用链表上获得第一个结点作为待插入的新结点
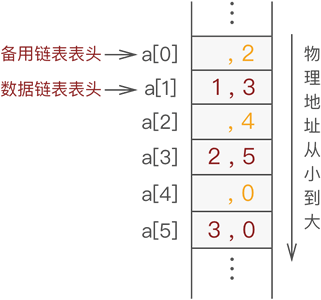
void insert(list parahead,char ch,int position)
{
int i;
int p=0;//从头结点开始
//1、找到插入位置前一个节点的下标
for(i=1;i<position;i++)
{
p=parahead->node[p].next;
if(p==-1)
{
printf("插入位置%d大于当前链表的长度\n",position);
return;
}
}
//2、查找当前链表中还有没有没用过的空间
int q=-1;
for(i=1;i<initlen;i++)
{
if(parahead->used[i]==0)
{
q=i;
parahead->used[q]=1;
break;
}
}
//3、如果没有多余的空间
if(q==-1)
{
printf("链表已满,不能插入元素\n");
return;
}
parahead->node[q].date =ch;
parahead->node[q].next=parahead->node[p].next ;
parahead->node[p].next=q;
}
静态链表的删除:
void deletenode1(list parahead,int position)
{
int i,p=0;
//判断删除位置的合法性
for(i=1;i<position;i++)
{
p=parahead->node[p].next ;
if(p==-1)
{
printf("删除位置大于当前链表的长度\n");
return;
}
}
int q=parahead->node[p].next ;
parahead->node[p].next =parahead->node[q].next ;
parahead->used[q]=0;
}
//删除指定元素的节点
void deletenode2(list parahead,char ch)
{
int p=0;
while(parahead->node[p].next !=-1&¶head->node[parahead->node[p].next ].date!=ch)
{
p=parahead->node[p].next ;
}
if(parahead->node[p].next ==-1)
{
printf("链表中没有%c,无法删除\n",ch);
return;
}
int q=parahead->node[p].next ;
parahead->node[p].next =parahead->node[q].next ;
parahead->used[q]=0;
}
全部代码:
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
#define initlen 10
typedef struct
{
char date;
int next;
}*NodePtr,Node;
typedef struct
{
NodePtr node;
int *used;//判断地址是否有值,1代表有值,0代表无值
}*list,lnode;
list initlist()
{
//temphead为指向整个静态链表的指针
list temphead=(list)malloc(sizeof(lnode)*initlen);
//将静态链表的空间分配给node数组和used数组
temphead->node=(NodePtr)malloc(sizeof(Node)*initlen);
temphead->used =(int*)malloc(sizeof(int)*initlen);
//初始化头节点
temphead->node->date='\0';
temphead->node->next=-1;
temphead->used[0]=1;//头节点不能用来存放数据
int i;
for(i=1;i<initlen;i++)
{
temphead->used[i]=0;
}
return temphead;
}
void printlist(list parahead)
{
int p=0;
while(p!=-1)
{
printf("%c",parahead->node[p].date );
p=parahead->node[p].next;
}
printf("\n");
}
void insert(list parahead,char ch,int position)
{
int i;
int p=0;//从头结点开始
//1、找到插入位置前的节点的下标
for(i=1;i<position;i++)
{
p=parahead->node[p].next;
if(p==-1)
{
printf("插入位置%d大于当前链表的长度\n",position);
return;
}
}
//2、查找当前链表中还有没有没用过的空间
int q=-1;
for(i=1;i<initlen;i++)
{
if(parahead->used[i]==0)
{
q=i;
parahead->used[q]=1;
break;
}
}
//3、如果没有多余的空间
if(q==-1)
{
printf("链表已满,不能插入元素\n");
return;
}
parahead->node[q].date =ch;
parahead->node[q].next=parahead->node[p].next ;
parahead->node[p].next=q;
}
void deletenode1(list parahead,int position)
{
int i,p=0;
for(i=1;i<position;i++)
{
p=parahead->node[p].next ;
if(p==-1)
{
printf("删除位置大于当前链表的实际长度\n");
return;
}
}
int q=parahead->node[p].next ;
parahead->node[p].next =parahead->node[q].next ;
parahead->used[q]=0;
}
//删除指定元素的节点
void deletenode2(list parahead,char ch)
{
int p=0;
while(parahead->node[p].next !=-1&¶head->node[parahead->node[p].next ].date!=ch)
{
p=parahead->node[p].next ;
}
if(parahead->node[p].next ==-1)
{
printf("链表中没有%c,无法删除\n",ch);
return;
}
int q=parahead->node[p].next ;
parahead->node[p].next =parahead->node[q].next ;
parahead->used[q]=0;
}
//测试
void test()
{
list tempList = initlist();
printlist(tempList);
//插入元素
insert(tempList, 'H', 1);
insert(tempList, 'e', 2);
insert(tempList, 'l', 3);
insert(tempList, 'l', 4);
insert(tempList, 'o', 5);
printlist(tempList);
//删除元素
printf("Deleting 'e'.\r\n");
deletenode2(tempList, 'e');
printf("Deleting 'a'.\r\n");
deletenode2(tempList, 'a');
printf("Deleting 'o'.\r\n");
deletenode2(tempList, 'o');
printlist(tempList);
printf("删除第2个元素\r\n");
deletenode1(tempList,2);
printf("删除第1个元素\r\n");
deletenode1(tempList,1);
printlist(tempList);
insert(tempList, 'x', 1);
printlist(tempList);
}
int main()
{
test();
return 0;
}
运行结果:
Hello
Deleting 'e'.
Deleting 'a'.
链表中没有a,无法删除
Deleting 'o'.
Hll
删除第2个元素
删除第1个元素
l
xl
总结:静态链表的优点:在进行插入和删除操作时,只需要改动游标,不需要移动元素,改进了在顺序存储结构中插入和删除元素时要移动大量元素的缺点
静态链表的缺点:没有解决连续存储分配带来的表长难以确定的问题(主要是太难理解了,人麻了,还好用的不多)





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








