本篇文章主要讲解string的用法。
目录
3.1 operator+=、append、push_back
1. 迭代器(Iterators)
- string 中的迭代器主要分为正向迭代器和反向迭代器,其中又可以细分为 const 和 非const类型的,这里主要讲解begin、end 和 rbegin、rend。

1.1 begin() 和 end()
- begin() & end() 有const 和 非const 类型,const类型主要就是不能修改。
- begin 指向的是首元素,end 指向的是最后一个元素的下一个位置。



void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello world");
string::iterator it = s0.begin();
while (it != s0.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
it = s0.begin();
while (it != s0.end())
{
*it += 3;
++it;
}
it = s0.begin();
while (it != s0.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
}
void string_test2()
{
const string s0("hello world");
string::const_iterator it = s0.begin();
while (it != s0.end())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
it = s0.begin();
//会报错
/*while (it != s0.end())
{
*it += 3;
++it;
}*/
}
int main()
{
string_test1();
string_test2();
return 0;
}
1.2 rbegin() 和 rend()
- rbegin() & rend() 是反向迭代器,也有const 和 非const 类型,const类型也是不能修改。
- rbegin 指向的是最后一个元素,rend 指向的是第一个元素的下一个。

void string_test3()
{
string s0("hello world");
string::reverse_iterator it = s0.rbegin();
while (it != s0.rend())
{
cout << *it << " ";
// 这里是++ ,不是--
++it;
}
cout << endl;
it = s0.rbegin();
// 可修改
while (it != s0.rend())
{
*it += 1;
++it;
}
it = s0.rbegin();
while (it != s0.rend())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
void string_test4()
{
const string s0("hello world");
string::const_reverse_iterator it = s0.rbegin();
// 只读,不可修改
while (it != s0.rend())
{
cout << *it << " ";
++it;
}
cout << endl;
}
2. 容量操作(capacity)
- 容量操作主要就是计算字符串长度、容量等,如下:

2.1 size()、length()、maxsize()
- size 和 length 都是返回字符串的长度,但是一般情况下都用size
- maxsize() 表示能接受最大的字符串长度。
void strint_test1()
{
string s0("hello world");
cout << s0.length() << endl;
cout << s0.size() << endl;
}
int main()
{
strint_test1();
return 0;
}
void strint_test1()
{
string s0("hello world");
// 不同编译器下可能不同
cout << "max_size() <:" << s0.max_size() << endl;
}
2.2 capacity()
- capacity 可以查看当前编译器为字符串已开辟的容量大小,咱们可以结合push_back()来查看string在vs环境下的扩容机制:
void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello world");
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
//查看扩容机制
cout << "开始时的capacity < :" << s0.capacity() << endl;
int newcapacity = s0.capacity();
for (size_t i = 0; i < 100; i++)
{
s0.push_back(' ');
if (newcapacity < s0.capacity())
{
newcapacity = s0.capacity();
cout << "扩容后的capacity < :" << newcapacity << endl;
}
}
}
- 可以看到最开始是两倍扩容,之后就是1.5倍扩容,那么在g++环境下呢?我们可以尝试一下在Linux环境下运行相同的代码,可以发现一直是二倍扩容:

2.3 empty()、clear()
- empty 是判断字符串是否为空,是返回1,否则返回0;
- clear 是清空字符串。


void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello world");
cout << s0.empty() << endl;
s0.clear();
cout << s0.empty() << endl;
}2.4 reserve()
- 如果说提前知道了字符串的长度,那么一直扩容的话编译器会有很多消耗,这个时候我们可以利用reserve() 提前开好空间,就不需要持续扩容了,减少了消耗。
- 但是并不是你要多大编译器就帮你开多大,他要根据内存对齐的原则,可能比你给的要大一些。
- 但是如果说你给的参数小于capacity(),编译器并不会帮你缩容,只有大于capacity的时候才会帮你扩容。

void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
s0.reserve(41);
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
} 
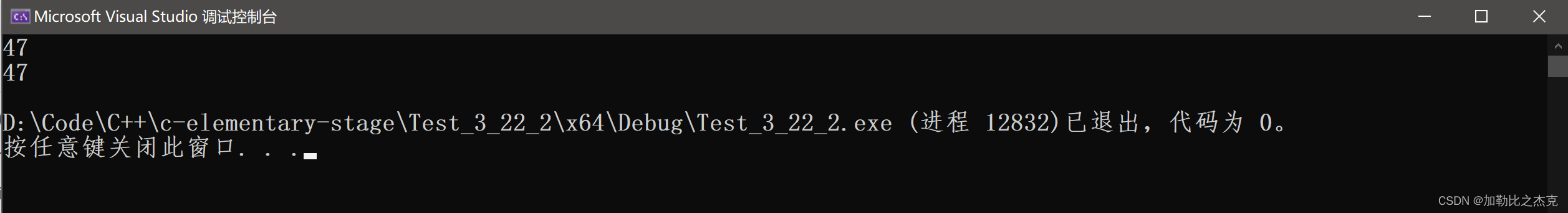
void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
s0.reserve(10);
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
}
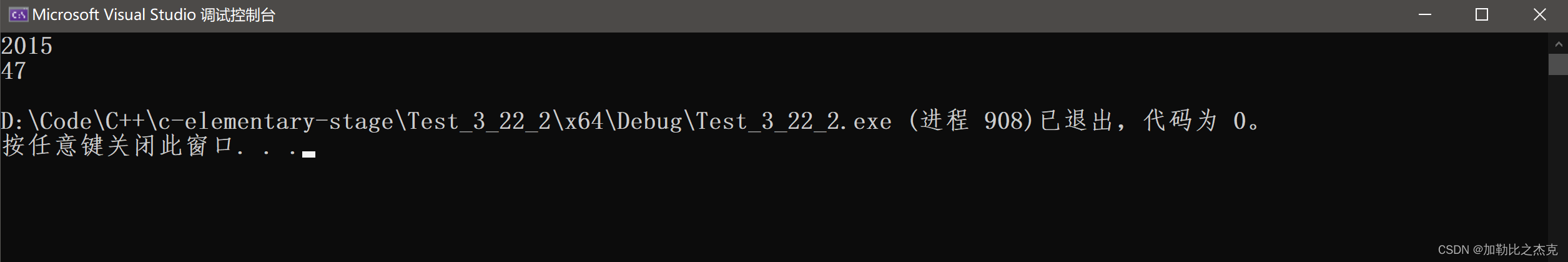
2.5 shrink_to_fit()
-
shring_to_fit() 就是缩容的意思,如果说你现在的容量大于size,他就会帮你缩容;
void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx");
s0.reserve(2000);
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
s0.shrink_to_fit();
cout << s0.capacity() << endl;
}
2.6 resize()
- resize() 是帮你调整大小的意思,当给的参数比size小,他会帮你删除元素;
- 当给的参数比size大,比capacity小,会帮你默认插入 '\0' 补齐;
- 当给的参数比capacity大,会帮你扩容,并默认插入 '\0'。
- 如果说也给了要以什么字符补齐,就会帮你用这个字符补齐。

- 比size小:
void string_test1() { string s0("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"); s0.resize(11); cout << s0 << endl; }
- 比size大,比capacity小:
void string_test1() { string s0("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"); // 默认用 '\0' 补齐 s0.resize(45); cout << s0 << endl; }
- 比capacity大:
void string_test1() { string s0("hello worldxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxxx"); // 用'D'补齐 s0.resize(100,'D'); cout << s0 << endl; }
3. 修改(Modifiers)
- 修改的主要功能是给字符串添加一个字符串或者字符,这里讲几个常用的。

3.1 operator+=、append、push_back
- push_back 就是尾插,但是只能一个字符一个字符插入;

void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello world");
s0.push_back(' ');
s0.push_back('d');
s0.push_back('d');
s0.push_back('d');
cout << s0 << endl;
}
- append用法有点多,可以加上 string类型、const char* 类型,甚至是迭代器:

void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello,");
string s1(" the humorous man");
s0.append(s1); //1
cout << s0 << endl;
s0.append(" handsome");//3
cout << s0 << endl;
s0.append(s1, 0, 4);//2
cout << s0 << endl;
s0.append(" the humorous man", 14);//4
cout << s0 << endl;
s0.append(10, 'x');//5
cout << s0 << endl;
s0.append(s1.begin(), s1.end() - 4);//6
cout << s0 << endl;
} 
- operator+=是一个运算符重载,可以加上string类型、char类型、cosnt char*类型

void string_test1()
{
string s0("hello,");
s0 += "humorous man";
cout << s0 << endl;
string s1("baby");
s0 += s1;
cout << s0 << endl;
s0 += 'I';
cout << s0 << endl;
}
3.2 assign()
-
string类的
assign函数会将指定的值赋给字符串,并覆盖原有的值。如果目标字符串比原字符串短,那么超出目标字符串长度的部分将会被删除。

#include <iostream>
#include <string>
int main() {
std::string s = "Hello";
s.assign("World");
std::cout << s << std::endl;
s.assign("Lorem ipsum", 5);
std::cout << s << std::endl;
s.assign(3, 'X');
std::cout << s << std::endl;
return 0;
}
3.3 insert()、erase()
-
insert() 就是在pos位置插入,可以是string、const char*、char;

int main()
{
string s = "Hello";
s.insert(5, 1, ' '); // 在位置 5 插入一个空格字符
cout << s << endl; // 输出:"Hello "
string s1 = "Hello";
string substring = " beautiful";
s1.insert(5, substring, 0, substring.length()); // 在位置 5 插入子字符串
cout << s1 << endl; // 输出:"Hello beautiful"
return 0;
}erase函数用于从字符串中删除字符或子字符串。它有以下几种用法:

int main()
{
string s = "Helloworld";
s.erase(6, 4); // 从位置 6 开始删除长度为 4 的子字符串
cout << s << endl; // 输出:"Hellow"
string s1 = "Hello";
s1.erase(s1.begin() + 2); // 删除第 2 个字符(索引位置为 2)
cout << s1 << endl; // 输出:"Helo"
}3.4 replace()
replace用于替换字符串中的字符或子字符串。

int main()
{
string s = "Hello World";
s.replace(6, 5, "Beautiful"); // 替换从位置 6 开始的 5 个字符为 "Beautiful"
cout << s << endl; // 输出:"Hello Beautiful"
string s1 = "Hello World";
s1.replace(s1.begin() + 2, s1.begin() + 5, "XYZ"); // 替换第 2 到第 5 个字符为 "XYZ"
cout << s1 << endl; // 输出:"HeXYZ World"
string s2 = "Hello World";
string substring = "Beautiful";
s2.replace(6, 5, substring, 0, 3); // 替换从位置 6 开始的 5 个字符为 substring 的前 3 个字符
cout << s2 << endl; // 输出:"Hello Bea"
string s3 = "Hello World";
s3.replace(6, 5, "Beautiful"); // 替换从位置 6 开始的 5 个字符为 "Beautiful"
cout << s3 << endl; // 输出:"Hello Beautiful"
}




















 919
919











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








