Python自述:对大数据分析,人工智能中至关重要的机器学习、深度学习都提供了大力支持。背后有最庞大的‘代码库’,人们习惯称Python为胶水语言。
安装Python解释器:www.python.org
安装开发环境PyCharm:
http://www.jetbrains.com/pycharm/download/#section=windows
输出函数:
print('helloworld')
print(520)
print(1+1)
helloworld
520
2输出到文件中:
fp=open('D:/text.txt','a+')
print('hellowold',file=fp)
fp.close()不进行换行输出:
print('hello','world','python')
hello world python转义字符:
print('hello\nworld')#换行
print('hello\tworld')#一个\t是四个字符宽
print('hello\rworld')#回车,world给hello覆盖了
print('hello\bworld')#退一个格
hello
world
hello world
world
hellworld
print('http:\\www.baodu.com')
print('http:\\\\www.baodu.com')
http:\www.baidu.com
http:\\www.baidu.com
print('老巴说:\'学会python很重要\'')
老巴说:'学会python很重要'原字符(不希望字符串中转义字符起作用,就是用原字符):
print(r'hello\nworld')
hello\nworld
#最后一个字符不能是反斜杠,两个可以
print(r'hello\nworld\\')
hello\nworld\\内容介绍:
1、二进制与字符编码
2、Python中的标识符与保留字
3、Python中的变量与数据类型
4、Python中的注释
二进制与字符编码
#二进制需在前加‘0b’
print(chr(0b100111001011001))
print(ord('乙'))
乙
20057Python中的标识符与保留字
#查看系统保留字
import keyword
print(keyword.kwlist)
['False', 'None', 'True', 'and', 'as', 'assert', 'async', 'await', 'break', 'class',
'continue', 'def', 'del', 'elif', 'else', 'except', 'finally', 'for', 'from',
'global', 'if', 'import', 'in', 'is', 'lambda', 'nonlocal', 'not', 'or', 'pass',
'raise', 'return', 'try', 'while', 'with', 'yield']
)Python中的变量
name='ha哈'
print(name)
print('标识',id(name))
print('类型',type(name))
print('值',name)
ha哈
标识 2996988983888
类型 <class 'str'>
值 ha哈
#当多次赋值同一变量,变量名会指向新的空间(赋值)Python中的数据类型
整数型:int 93
浮点型:float 3.1415926
布尔型:bool True,False
字符串型:str '未来的老巴'
n1=98
n2=-1
n3=0
print(n1,type(n1),n2,type(n2),n3,type(n3))
98 <class 'int'> -1 <class 'int'> 0 <class 'int'>
print('二进制',0b10101010) #二进制已0b开头
print('八进制',0o7777777) #八进制已0o开头
print('十六进制',0x1EAF) #十六进制已0x开头
n1=1.1
n2=2.2
print(n1+n2)
from decimal import Decimal
print(Decimal('1.1')+Decimal('2.2'))
3.3000000000000003
3.3
print(True+1)
print(False+1)
2
1
str = """未来的老巴"""
print(str,type(str))
str1 = '''现在我
可以换行输出
了'''
print(str1)
未来的老巴 <class 'str'>
现在我
可以换行输出
了数据类型转换
在不同数据类型的数据拼接时需进行转换
name='未来的老巴'
age=20
print(type(name),type(age))
print(name+' '+str(age)+'岁') #int(),str(),float()
<class 'str'> <class 'int'>
未来的老巴 20岁
s1='3.14'
print(int(float(s1))) #str转换int类型,字符串为小数串先转换float型再转换int型
3Python中的注释
#单行注释
'''
print('未来的老巴')
多行注释'''
#下面是文档编码格式声明,需放在文档开头部分,加上#号注释
#coding:gbk
#coding:utf-8内容介绍
1、Python的输入函数input()
2、Python中的运算符
3、运算符的优先级
Python的输入函数input()
present=input('未来的老巴想要什么呢?')
print(present,type(present))
未来的老巴想要什么呢?钱喽
钱喽 <class 'str'>
a=input('请输入第一个数字')
b=input('请输入第二个数字')
print(a,b)
print(float(a)+float(b))#方式一,输出时转换类型
请输入第一个数字3
请输入第二个数字4
3 4
7.0
a=float(input('请输入第一个数字'))#方式二,输入时转换类型
b=float(input('请输入第二个数字'))
print(a+b)
请输入第一个数字3
请输入第二个数字4
7.0Python中的运算符
print(1+1)
print(1-1)
print(2*4)
print(1/2)
print(11//2)#整除
print(2**8)#幂运算
print(11%2)#取余运算 1
print(9//-4)
print(-9//4) # 一正一负整除,向下取整
print(9%-4)# 公式 余数=被除数-除数*商 9-(-4)*(-3) -3
print(-9%4)# 公式 余数=被除数-除数*商 -9-(4)*(-3) 3
#赋值运算符 运算顺序:从右到左
i=3+4
a=b=c=30 #链式赋值只有一个对象,但是有a,b,c三个引用
d=a+b+c
j,k,l=11,12,13
print(i,a,b,c,d,j,k,l)
7 30 30 30 90 11 12 13
a=20
a+=30#相当于a+30赋值给a a-=30 a*=30 a/=30 a//=2 a%=2
50
#交换两个变量的值
a,b=10,20
print(a,b)
a,b=b,a
print(a,b)
10 20
20 10
#比较运算符 > < <= >= != == 一个=是赋值运算符 两个==是比较运算符
a,b=10,20
print(a>b)
False
a,b=10,10
print(a==b) #说明a与b的值相等
print(a is b) #说明a与b的标识(id)相等
list1=[1,2,3,4]
list2=[1,2,3,4]
print(list1==list2)
print(list1 is list2)
print(id(list1),id(list2))
print(list1 is not list2)
True
True
True
False
2988171496640 2988171495680
True
#布尔运算符
a,b=1,2
print(a==1 and b==2) #True
print(a==2 and b==2) #False
print(a==2 and b==1) #False
print(a==1 or b==2) #True
print(a==2 or b==2) #True
print(a==2 or b==1) #False
print(not b==2) #False
print(not b==1) #True
list1=[1,2,3,4]
print(1 in list1) #True
print(5 in list1) #False
print(1 not in list1) #False
print(5 not in list1) #True
#位运算符
与:& 对应位都是1,结果数位才是1,否则为0
或:| 对应位都是0,结果数位才是0,否则为1
左移位:<< 左移一位相当于乘以2
右移位:>> 右移一位相当于除以2
print(4&8)
print(4|8)
0
12运算符的优先级
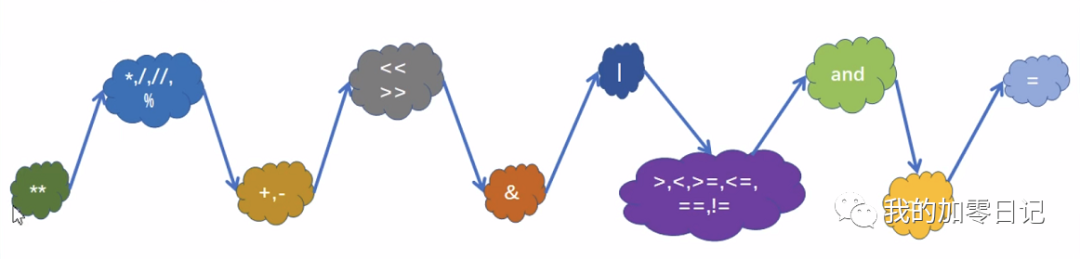






















 1180
1180











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








