《机器学习与数据挖掘》实验三
实验题目: 求解对数几率回归问题
实验目的: 掌握对数几率回归的基本原理与实现
实验环境(硬件和软件) Anaconda/Jupyter notebook/Pycharm
实验内容:
根据给定数据集(存放在data1.txt文件中,二分类数据),编码实现基于梯度下降的Logistic回归算法,并画出决策边界;
一、已经给定部分代码,补充完整的代码,需要补充代码的地方已经用红色字体标注,包括:
(1)#补充计算代价的代码;
(2)#补充参数更新代码;
(3)#补充画决策边界的代码;
二、提交的实验内容:(1)补充完整的代码;(也可以自己重写这部分的代码提交)(2)数据散点图,以及得到的决策边界;(3)梯度下降过程中损失的变化图;(4)基于训练得到的参数,输入新的样本数据,输出预测值;
import numpy as np
import matplotlib.pyplot as plt
import matplotlib as mpl
from sklearn.metrics import accuracy_score
def loaddata():
data = np.loadtxt('data/data1.txt',delimiter=',')
n = data.shape[1] - 1 # 特征数
X = data[:, 0:n]
y = data[:, -1].reshape(-1, 1)
return X, y
def plot(X,y):
pos = np.where(y==1)
neg = np.where(y==0)
plt.scatter(X[pos[0],0],X[pos[0],1],marker='x')
plt.scatter(X[neg[0], 0], X[neg[0], 1], marker='o')
plt.xlabel('Exam 1 score')
plt.ylabel('Exam 2 score')
plt.show()
X,y = loaddata()
plot(X,y)
print(X,y)
def sigmoid(z):
r = 1/(1+np.exp(-z))
return r
def hypothesis(X,theta):
z=np.dot(X,theta)
return sigmoid(z)
def computeCost(X,y,theta):
m = X.shape[0]
#补充计算代价的代码;
z=-1*y*np.log(hypothesis(X,theta))-(1-y)*np.log(1-hypothesis(X,theta))
return np.sum(z)/m
def gradientDescent(X,y,theta,iterations,alpha):
#取数据条数
m = X.shape[0]
#在x最前面插入全1的列
X = np.hstack((np.ones((m, 1)), X))
for i in range(iterations):
#补充参数更新代码;
for j in range(len(theta)):
theta[j]=theta[j]-(alpha/m)*np.sum((hypothesis(X,theta)-y)*X[:,j].reshape(-1,1))
theta = theta_temp
#每迭代1000次输出一次损失值
if(i%10000==0):
print('第',i,'次迭代,当前损失为:',computeCost(X,y,theta),'theta=',theta)
return theta
def predict(X):
# 在x最前面插入全1的列
c = np.ones(X.shape[0]).transpose()
X = np.insert(X, 0, values=c, axis=1)
#求解假设函数的值
h = hypothesis(X,theta)
#根据概率值决定最终的分类,>=0.5为1类,<0.5为0类
h[h>=0.5]=1
h[h<0.5]=0
return h
X,y = loaddata()
n = X.shape[1]#特征数
theta = np.zeros(n+1).reshape(n+1, 1)
# theta是列向量,+1是因为求梯度时X前会增加一个全1列
theta_temp = np.zeros(n+1).reshape(n+1, 1)
iterations = 250000
alpha = 0.008
theta = gradientDescent(X,y,theta,iterations,alpha)
print('theta=\n',theta)
def plotDescisionBoundary(X,y,theta):
cm_dark = mpl.colors.ListedColormap(['g', 'r'])
plt.xlabel('Exam 1 score')
plt.ylabel('Exam 2 score')
plt.scatter(X[:,0],X[:,1],c=np.array(y).squeeze(),cmap=cm_dark,s=30)
#补充画决策边界代码;
x1 = np.arange(min(X[:,0]),max(X[:,0]),0.1)
x2 = -(theta[1]*x1+theta[0]/theta[2])
plt.plot(x1,x2)
plt.show()
plotDescisionBoundary(X,y,theta)
实验结果:
代码内容补充见上图红色标记处;
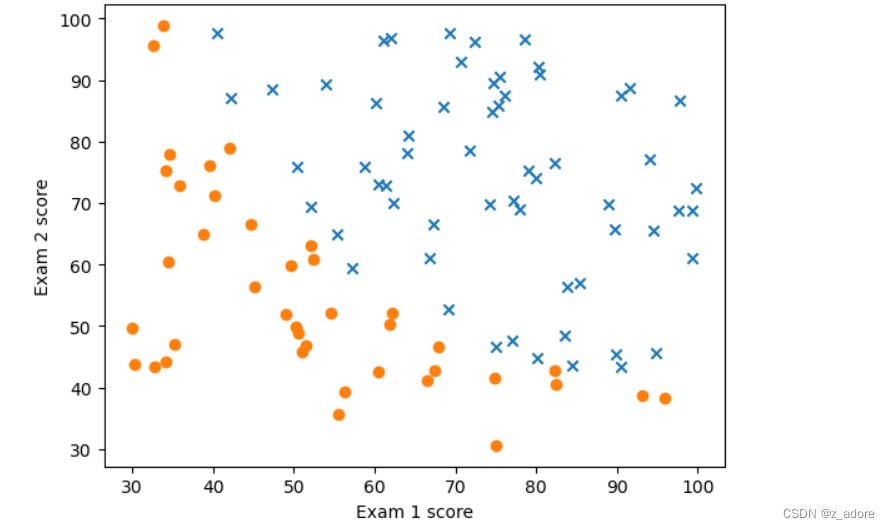 实验结果见如下:
实验结果见如下:
 部分数据显示:
部分数据显示:










 该实验旨在通过Python编程实现对数几率回归的梯度下降法,处理二分类数据集data1.txt。实验涉及数据加载、代价函数计算、参数更新、决策边界绘制以及预测功能。在实验过程中,还展示了损失函数随迭代次数的变化情况。
该实验旨在通过Python编程实现对数几率回归的梯度下降法,处理二分类数据集data1.txt。实验涉及数据加载、代价函数计算、参数更新、决策边界绘制以及预测功能。在实验过程中,还展示了损失函数随迭代次数的变化情况。

















 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








