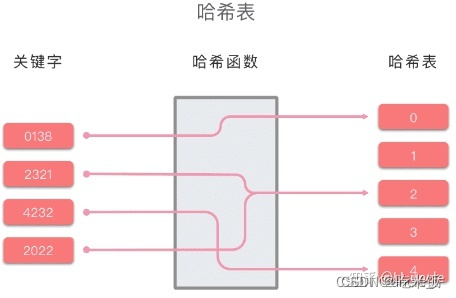
哈希表:也叫做散列表。是根据关键字和值(Key-Value)直接进行访问的数据结构。也就是说,它通过关键字 key 和一个映射函数 Hash(key) 计算出对应的值 value,然后把键值对映射到表中一个位置来访问记录,以加快查找的速度。这个映射函数叫做哈希函数(散列函数),用于存放记录的数组叫做 哈希表(散列表)。 哈希表的关键思想是使用哈希函数,将键 key 和值 value 映射到对应表的某个区块中。可以将算法思想分为两个部分:
向哈希表中插入一个关键字:哈希函数决定该关键字的对应值应该存放到表中的哪个区块,并将对应值存放到该区块中
在哈希表中搜索一个关键字:使用相同的哈希函数从哈希表中查找对应的区块,并在特定的区块搜索该关键字对应的值
哈希表的原理示例图如下所示:
哈希函数:将哈希表中元素的关键键值映射为元素存储位置的函数。一般来说,哈希函数会满足以下几个条件:
哈希函数应该易于计算,并且尽量使计算出来的索引值均匀分布,这能减少哈希冲突
哈希函数计算得到的哈希值是一个固定长度的输出值
如果 Hash(key1) 不等于 Hash(key2),那么 key1、key2 一定不相等
如果 Hash(key1) 等于 Hash(key2),那么 key1、key2 可能相等,也可能不相等(会发生哈希碰撞)
在哈希表的实际应用中,关键字的类型除了数字类型,还有可能是字符串类型、浮点数类型、大整数类型,甚至还有可能是几种类型的组合。一般会将各种类型的关键字先转换为整数类型,再通过哈希函数,将其映射到哈希表中。 而关于整数类型的关键字,通常用到的哈希函数方法有:直接定址法、除留余数法、平方取中法、基数转换法、数字分析法、折叠法、随机数法、乘积法、点积法等。
哈希冲突处理
哈希冲突:不同的关键字通过同一个哈希函数可能得到同一哈希地址,即 key1 ≠ key2,而 Hash(key1) = Hash(key2),这种现象称为哈希冲突。
开放地址法
开放地址法:指的是将哈希表中的「空地址」向处理冲突开放。当哈希表未满时,处理冲突时需要尝试另外的单元,直到找到空的单元为止。H(i) = (Hash(key) + F(i)) \% m,i = 1, 2, 3, ..., n (n ≤ m - 1)
H(i) 是在处理冲突中得到的地址序列。即在第 1 次冲突(i = 1)时经过处理得到一个新地址 H(1),如果在 H(1) 处仍然发生冲突(i = 2)时经过处理时得到另一个新地址 H(2) …… 如此下去,直到求得的 H(n) 不再发生冲突
Hash(key) 是哈希函数,m 是哈希表表长,取余目的是为了使得到的下一个地址一定落在哈希表中
F(i) 是冲突解决方法,取法可以有以下几种:
线性探测法:F(i) = 1, 2, 3, …, m - 1
二次探测法:F(i) = 1^2, -1^2, 2^2, -2^2, …, n^2(n ≤ m / 2)
伪随机数序列:F(i) = 伪随机数序列
链地址法
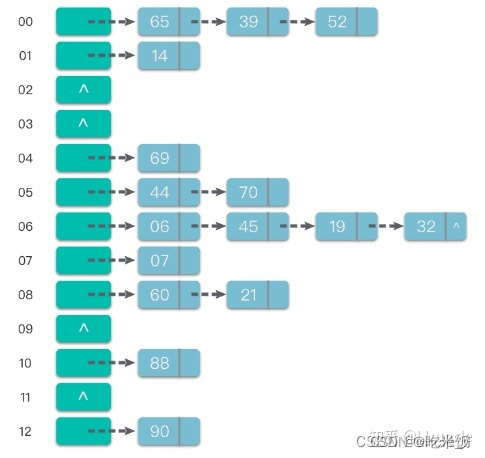
链地址法:将具有相同哈希地址的元素(或记录)存储在同一个线性链表中。 链地址法是一种更加常用的哈希冲突解决方法。相比于开放地址法,链地址法更加简单。 假设哈希函数产生的哈希地址区间为 [0, m - 1],哈希表的表长为 m。则可以将哈希表定义为一个有 m 个头节点组成的链表指针数组 T。
这样在插入关键字的时候,只需要通过哈希函数 Hash(key) 计算出对应的哈希地址 i,然后将其以链表节点的形式插入到以 T[i] 为头节点的单链表中。在链表中插入位置可以在表头或表尾,也可以在中间。如果每次插入位置为表头,则插入操作的时间复杂度为 O(1)。
而在在查询关键字的时候,只需要通过哈希函数 Hash(key) 计算出对应的哈希地址 i,然后将对应位置上的链表整个扫描一遍,比较链表中每个链节点的键值与查询的键值是否一致。查询操作的时间复杂度跟链表的长度 k 成正比,也就是 O(k)。对于哈希地址比较均匀的哈希函数来说,理论上讲,k= n//m,其中 n 为关键字的个数,m 为哈希表的表长。
相对于开放地址法,采用链地址法处理冲突要多占用一些存储空间(主要是链节点占用空间)。但它可以减少在进行插入和查找具有相同哈希地址的关键字的操作过程中的平均查找长度。这是因为在链地址法中,待比较的关键字都是具有相同哈希地址的元素,而在开放地址法中,待比较的关键字不仅包含具有相同哈希地址的元素,而且还包含哈希地址不相同的元素。
class HashMap<K, V> {
class Node<K, V> {
protected int hash;
protected K key;
protected V value;
protected Node<K, V> next;
public Node(int hash, K key, V value) {
this.hash = hash;
this.key = key;
this.value = value;
}
}
private Node<K, V>[] table;
private int size;
public HashMap(int capacity) {
table = new Node[capacity];
}
public void put(K key, V value) {
int hash = hash(key);
int index = hash & table.length - 1;
Node<K, V> firstNode = table[index];
//当前 index 下没有节点
if (firstNode == null) {
table[index] = new Node<>(hash, key, value);
size++;
} else {
//index 下已被某个结点占据
Node<K, V> curNode = firstNode;
//从该已被占据的节点处开始遍历
//while 循环
//如果当前结点有下一个结点并且当前结点的 key 不等于欲添加的 key,向后遍历
while (curNode.next != null && !curNode.key.equals(key)) {
curNode = curNode.next;
}
//退出 while 循环条件
//是最后一个结点或者 key 相等
//条件1:不是最后一个结点,欲添加的 key 等于当前结点的 key 值
if (curNode.next != null) {
curNode.value = value;
} else if (curNode.next == null && curNode.key.equals(key)) {
//条件2:欲添加的 key 等于最后一个结点的 key 值
curNode.value = value;
} else {
//条件3:欲添加的 key 不等于最后一个结点的 key 值
curNode = new Node<>(hash, key, value);
size++;
}
}
}
private int hash(K key) {
int h;
return (h = key.hashCode()) ^ (h >>> 16);
}
public V get(K key) {
int hash = hash(key);
int index = hash & table.length - 1;
Node<K, V> firstNode = table[index];
//当前结点没东西
if (firstNode == null) {
return null;
} else {
//有的话,遍历,找到相符结点
Node<K, V> curNode = firstNode;
while (curNode != null) {
if (curNode.key.equals(key) && curNode.hash == hash) {
return curNode.value;
}
curNode = curNode.next;
}
}
return null;
}
public boolean remove(K key) {
int hash = hash(key);
int index = hash & table.length - 1;
Node<K, V> firstNode = table[index];
//第一个结点为空
if (firstNode == null) {
return false;
} else {
//删除第一个结点
if (firstNode.key.equals(key) && firstNode.hash == hash) {
table[index] = firstNode.next;
return true;
} else {
//不是头节点
Node<K, V> curNode = firstNode;
while (curNode.next != null) {
if (curNode.next.key.equals(key) && curNode.next.hash == hash) {
curNode.next = curNode.next.next;
return true;
} else {
curNode = curNode.next;
}
}
//没返回 true ,指定没找到
return false;
}
}
}
public void resize() {
Node<K, V>[] newTable = new Node[this.table.length * 2];
for (int i = 0; i < this.table.length; i++) {
//对oldTable中每一个结点rehash()
rehash(i, newTable);
}
this.table = newTable;
}
public void rehash(int index, Node<K, V>[] newTable) {
//获取当前位置下的节点
Node<K, V> curNode = table[index];
if (curNode == null) {
return;
}
Node<K, V> lowListHead = null;//低位的头
Node<K, V> lowListTail = null;//低位的尾
Node<K, V> highListHead = null;//高位的头
Node<K, V> highListTail = null;//高位的尾
//currentNode是oldtable下index位置的第一个节点
while (curNode != null) {
//得到当前节点在新table中的位置
int newIndex = hash(curNode.key) & (newTable.length - 1);
//int newIndex = getIndex(currentNode.key, newTable);
//如果和index相等,则直接放
if (newIndex == index) {
//把该位置所有节点链成一个链表,最后统一放
if (lowListHead == null) {
lowListHead = curNode;
lowListTail = curNode;
} else {
lowListTail.next = curNode;
lowListTail = lowListTail.next;
}
} else {
//newIndex和index不等
if (highListHead == null) {
highListHead = curNode;
highListTail = curNode;
} else {
highListTail.next = curNode;
highListTail = highListTail.next;
}
}
curNode = curNode.next;
}
//将index位置连上当前lowList
if (lowListTail != null) {
lowListHead.next = null;
newTable[index] = lowListHead;
}
//将index+table.length位置连上当前highList
if (highListTail != null) {
highListTail.next = null;
newTable[index + this.table.length] = highListHead;
}
}
public Iterator<Node<K, V>> iterator() {
return new Itr();
}
class Itr implements Iterator<Node<K, V>> {
private Node<K, V> nextNode;
private Node<K, V> curNode;
private int curIndex;
public Itr() {
if (HashMap.this.size == 0) {
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < HashMap.this.table.length; i++) {
if (table[i] != null) {
this.nextNode = table[i];
this.curIndex = i;
return;
}
}
}
@Override
public boolean hasNext() {
return nextNode != null;
}
@Override
public Node<K, V> next() {
this.curNode = nextNode;
this.nextNode = nextNode.next;
if (this.nextNode == null) {
//表明当前位置的链表已经遍历完毕
for (int i = curIndex + 1; i < HashMap.this.table.length; i++) {
if (table[i] != null) {
this.nextNode = table[i];
curIndex = i;
break;
}
}
}
return curNode;
}
@Override
public void remove() {
if(this.curNode == null){
return;
}
K currentKey = this.curNode.key;
HashMap.this.remove(currentKey);
this.curNode = null;
}
}
}





















 361
361











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








