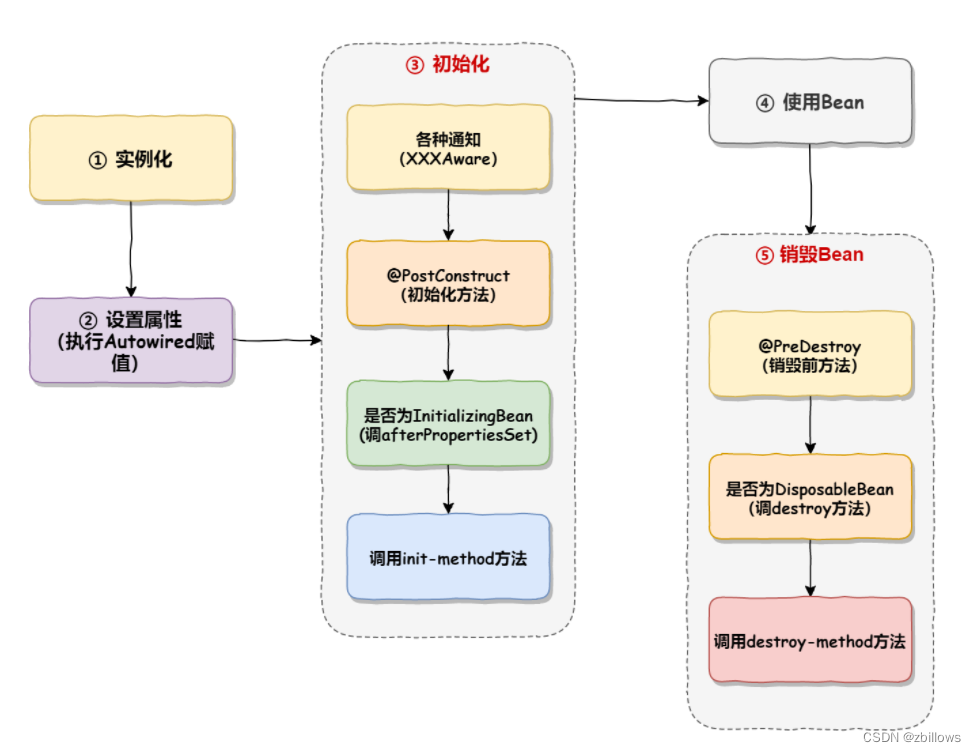
Bean的生命周期通常可以归结为以下几个阶段:
1.实例化(Instantiation):
Spring根据Bean的定义(如XML配置、Java配置或注解)来实例化Bean,这个阶段会分配内存空间给Bean,生成一个原始的、未配置的对象
2.属性赋值(Populate Properties):Spring设置Bean的属性,如依赖注入
3.初始化(Initialization):
a. 执⾏各种通知,如 BeanNameAware ,BeanFactoryAware ,ApplicationContextAware 的接⼝⽅法.
b. 执⾏初始化⽅法
▪ xml定义 init-method
▪ 使⽤注解的⽅式 @PostConstruct
▪ 执⾏初始化后置⽅法( BeanPostProcessor )
如果在<bean>定义中指定了init-method属性,则会调用指定的初始化方法。
如果Bean实现了BeanPostProcessor接口,Spring调用postProcessAfterInitialization()方法。
4.使用(In use by application):Bean现在可以被应用程序使用了。
5.销毁(Destruction):
当Bean对象不再被使用时,应该将其销毁并释放占用的内存空间。在Spring框架中,Bean的销毁可以通过配置文件中的destroy-method属性进行指定。
如果在<bean>定义中指定了destroy-method属性,则会调用指定的销毁方法。
尝试通过日常生活中的事物来类比这个过程。使用人的一生来类比Bean的生命周期
生命开始(出生)(实例化 )
起名字(属性设置)
上户口( 初始化)
长大(使用Bean)
生命结束(Bean销毁)
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;
import org.springframework.boot.CommandLineRunner;
import org.springframework.boot.SpringApplication;
import org.springframework.boot.autoconfigure.SpringBootApplication;
import org.springframework.context.ConfigurableApplicationContext;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;
@SpringBootApplication
public class SpringBeanApplication implements CommandLineRunner {
@Autowired
private BeanLifeComponent beanLifeComponent;
public static void main(String[] args) {
ConfigurableApplicationContext context =SpringApplication.run(SpringBeanApplication.class, args);
context.getBean(BeanLifeComponent.class);
context.close();
}
@Configuration
static class BeanConfig{
@Bean
public BeanLifeComponent beanLifeComponent(){
BeanLifeComponent beanLifeComponent = new BeanLifeComponent();
beanLifeComponent.setName("hello spring");
return beanLifeComponent;
}
}
@Override
public void run(String... args) throws Exception {
beanLifeComponent.use();
}
}
import jakarta.annotation.PostConstruct;
import jakarta.annotation.PreDestroy;
import org.springframework.beans.factory.BeanNameAware;
import org.springframework.stereotype.Component;
@Component
public class BeanLifeComponent implements BeanNameAware {
private String name;
public BeanLifeComponent() {
System.out.println("执行构造方法");
}
public void setName(String name) {
this.name = name;
System.out.println("设置name属性" + name);
}
@Override
public void setBeanName(String s) {
System.out.println("执行了setBeanName方法" +s);
}
@PostConstruct
public void postConstruct(){
System.out.println("执行了postConstruct方法");
}
public void use() {
System.out.println("使用 Bean name属性: " +name );
}
@PreDestroy
public void preDestroy() {
System.out.println("销毁方法执行");
}
}
在Spring框架中,@PostConstruct和@PreDestroy是两个重要的注解,它们分别用于标记在依赖注入完成后需要执行的方法和在Spring容器销毁bean之前需要执行的方法。
@PostConstruct
@PostConstruct注解用于在依赖注入完成后,初始化方法执行之前调用。这意味着,当你有一个bean,并且Spring容器完成了对这个bean的依赖注入后,紧接着就会调用被@PostConstruct注解的方法。
这个注解主要用于执行一些初始化逻辑,比如设置初始值、启动服务、加载数据等。由于它是在依赖注入之后调用的,所以你可以安全地访问任何通过依赖注入获得的资源。
@PreDestroy
@PreDestroy注解用于在Spring容器销毁bean之前调用。当Spring容器关闭时(例如,应用服务器停止时),它会先调用所有bean的@PreDestroy方法,然后再销毁这些bean。
这个注解主要用于执行一些清理逻辑,比如关闭文件句柄、释放数据库连接、停止服务等。由于它是在bean销毁之前调用的,所以你可以安全地执行一些清理操作,确保在bean被销毁之前资源得到正确释放。





















 1万+
1万+











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








