目录
并查集
操作:1.将两个集合合并 2.询问两个元素是否在一个集合之中
时间复杂度近乎O(1)
实现:每一个集合用树的形式来维护。树根的编号就是整个集合的编号,每个节点存储他的 父节点(P[x])。
问题①:如何判断树根 if(P[x]==x)
问题②:如何找集合的编号 whlie(P[x]!=x) x=P[x];
问题③:如何合并集合(P[x]=y)
问题④:如何求集合元素的个数
问题二优化: 1.按值合并(不明显)2.路径优化(走一遍,上边的P[x]全部指向根节点)
代码:
#include <iostream>
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
int p[N];
int find (int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
char ch[2];
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) p[i]=i;
while(m--)
{
int a,b;
scanf("%s%d%d",ch,&a,&b);
if(*ch=='M') p[find(b)]=find(a);
else {
if(find(a)==find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
}问题④代码实现:
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
int p[N],size[N];
int find(int x)
{
if(p[x]!=x) p[x]=find(p[x]);
return p[x];
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++){
p[i]=i;
size[i]=1;
}
while(m--)
{
string s;
int a,b;
cin>>s;
if(s=="C")
{
scanf("%d%d",&a,&b);
if(find(a)==find(b)) continue;
size[find(b)]+=size[find(a)];
p[find(a)]=find(b);
}else if(s=="Q1")
{
cin>>a>>b;
if(find(a)==find(b)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}else
{
scanf("%d",&a);
printf("%d\n",size[find(a)]);
}
}
return 0;
}小技巧:C++做题,出题人会在行末加空格或者回车,所以无论是读入字符串或者字符都用%s来读入,存储成字符串的格式,已确保不报错。
堆
基本结构:
完全二叉树(除了最后一层从左到右依次排布,上边节点都是满的)
小根堆:每个节点的左右儿子节点小于该节点,根节点为最小值
存储:
不同于链表的全新的存储方式,用一维数组、实现。下标从1开始比较方便。
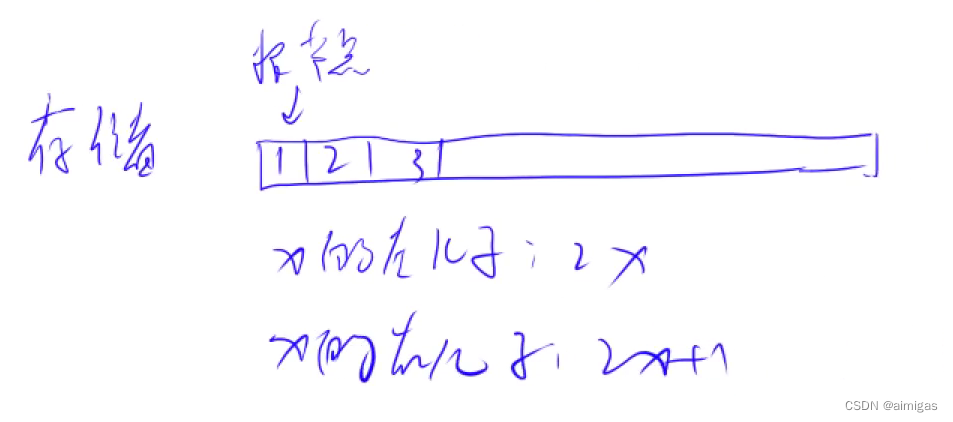
操作(维护一个数据集合): 主要是运用了两种操作 down(x);up(x);
在集合中插入一个数 heap(++size)=x; up(size);
求集合当中的最小值 heap(1);
删除集合中的最小值 heap(1)=heap(size); size--; down(1);
删除一个任意元素 heap(k)=heap(size); size--; down(k),up(k);
修改一个任意元素 heap(k)=x; down(k),up(k);
时间复杂度:up和down以及插入删除是log(n) 求最小值是log(1)
堆排序代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+10;
int h[N],cnt;
void down(int x)
{
int t=x;
if (x * 2 <= cnt && h[x * 2] < h[t]) t = x * 2;
if(x*2+1<=cnt&&h[x*2+1]<h[t]) t=x*2+1;
if(t!=x)
{
swap(h[x],h[t]);
down(t);
}
}
void up(int x)
{
while(x/2&&h[x/2]>h[x])
{
swap(h[x/2],h[x]);
x/=2;
}
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
scanf("%d%d",&n,&m);
cnt=n;
for(int i=1;i<=n;i++) cin>>h[i];
for(int i=n/2;i;i--) down(i);
while(m--)
{
cout<<h[1]<<" ";
h[1]=h[cnt];
cnt--;
down(1);
}
//for(int i=1;i<=m;i++) cout<<h[i];
return 0;
}模拟堆代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <string.h>
using namespace std;
const int N=1e6+1;
int h[N],hp[N],ph[N],cnt;
void heap_swap(int x,int y)
{
swap(hp[x],hp[y]);
swap(ph[hp[x]],ph[hp[y]]);
swap(h[x],h[y]);
}
void up(int x)
{
while(x/2&&h[x/2]>h[x])
{
heap_swap(x/2,x);
x/=2;
}
}
void down(int x)
{
int t=x;
if(x*2<=cnt&&h[x*2]<h[t]) t=x*2;
if(x*2+1<=cnt&&h[x*2+1]<h[t]) t=x*2+1;
if(t!=x)
{
heap_swap(t,x);
down(x);
}
}
int main()
{
int x,m;
string ch;
cin>>x;
while(x--)
{
cin>>ch;
if(ch=="I")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
cnt++;
m++;
hp[m]=cnt,ph[cnt]=m;
h[cnt]=x;
up(x);
}else if(ch=="PM")
{
cout<<h[1]<<endl;
}else if(ch=="DM")
{
heap_swap(1,cnt);
cnt--;
down(1);
}else if(ch=="D")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
x=ph[x];
heap_swap(x,cnt--);
down(x);
up(x);
}else if(ch=="C")
{
int x,y;
cin>>x>>y;
x=ph[x];
h[x]=y;
down(x);
up(x);
}
}
return 0;
}
哈希表
主要作用:把一个庞大的数据映射到从0到n ( 0-1e9映射到0-1e5 )
主要操作是添加和查找,删除操作不常用(不是删除,而是false)
注意点:取模的数,要是一个质数,并且离2的n次幂要远一些
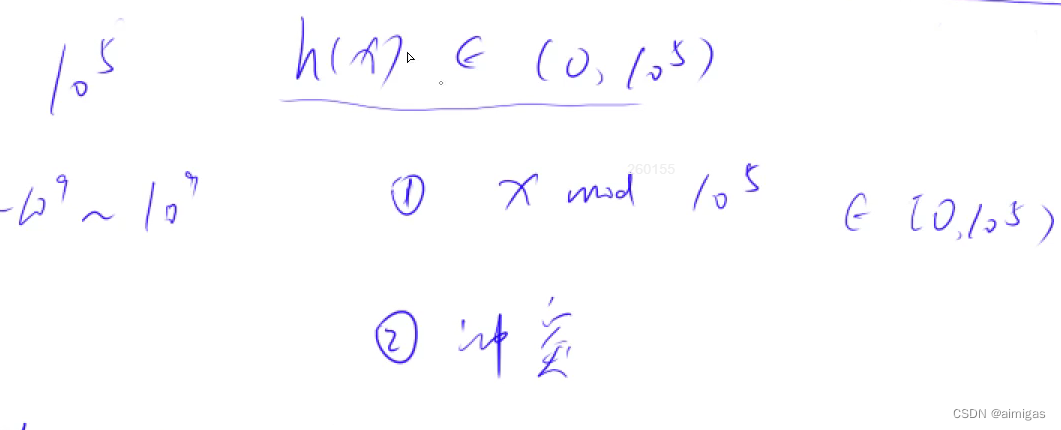
存储结构:
根据处理冲突的方式可以分为两种,二者选其一,都比较常用
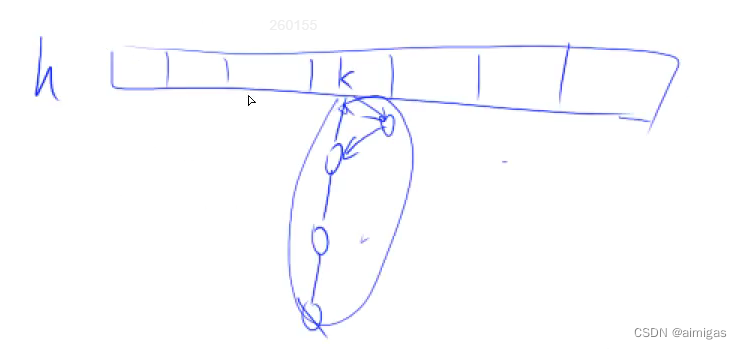
拉链法:
开一个从1到n的数组,单链表存储冲突值
拉链法代码
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
using namespace std;
const int N=100003;
int h[N],e[N],ne[N],idx;
void insert (int x)
{
int k=(x%N+N)%N;
e[idx]=x;
ne[idx]=h[k];
h[k]=idx++;
}
bool find(int x)
{
int k=(x%N+N)%N;
for(int i=h[k];i!=-1;i=ne[i])
if(e[i]==x)
return true;
return false;
}
int main()
{
memset(h,-1,sizeof h);
int n;
cin>>n;
while(n--)
{
string s;
cin>>s;
if(s=="I")
{
int x;
cin>>x;
insert(x);
}else{
int x;
cin>>x;
if(find(x)) puts("Yes");
else puts("No");
}
}
return 0;
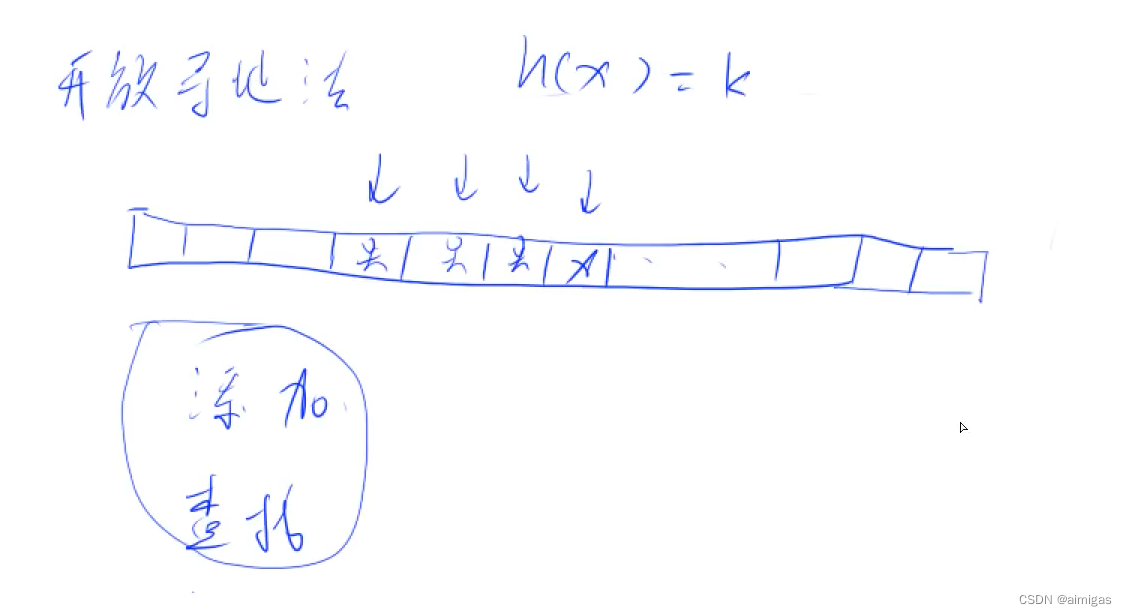
}开放寻址法:
只开了一维数组,长度开到题目数据范围的2到3倍
开放寻址法代码
#include <cstring>
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
const int N = 200003, null = 0x3f3f3f3f;
int h[N];
int find(int x)
{
int t = (x % N + N) % N;
while (h[t] != null && h[t] != x)
{
t ++ ;
if (t == N) t = 0;
}
return t;
}
int main()
{
memset(h, 0x3f, sizeof h);
int n;
scanf("%d", &n);
while (n -- )
{
char op[2];
int x;
scanf("%s%d", op, &x);
if (*op == 'I') h[find(x)] = x;
else
{
if (h[find(x)] == null) puts("No");
else puts("Yes");
}
}
return 0;
}
字符串哈希方式:
字符串前缀哈希法
注意:
不能映射成0
rp足够好,不存在冲突
取值时候p=131或13331,Q=2的64次方,此时99.9%无冲突
usinged long long 溢出正好相当于取模

求前缀哈希,可以利用前缀哈希求任意子串的哈希
时间复杂度O(1),除了KMP可以用来求循环节,其他情况都不如字符串哈希
#include <iostream>
#include <algorithm>
#include <cstring>
#include <cstdio>
using namespace std;
typedef unsigned long long ULL;
const int P=131,N=1e6+10;
int h[N],p[N];
ULL query (int x,int y)
{
return h[y]-h[x-1]*p[y-x+1];
}
int main()
{
int n,m;
cin>>n>>m;
string x;
cin>>x;
p[0]=1;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
p[i+1]=p[i]*P;
h[i+1]=h[i]*P+x[i];
}
while(m--)
{
int x1,x2,y1,y2;
cin>>x1>>y1>>x2>>y2;
if(query(x1,y1)==query(x2,y2)) printf("Yes\n");
else printf("No\n");
}
return 0;
}






















 241
241











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










