定义:存取和读取数据的解决方案
作用:用于读写数据(本地文件、网络)
分类:
一种是:输出流和输入流。
一种是:字节流和字符流。


字节流
字节流——FileOutputStream(字节输出流)(byte数组)
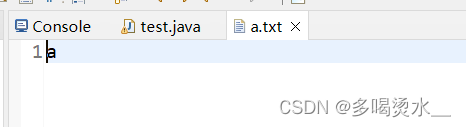
把程序中的数据写到本地文件中。

public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
f.write(97);
f.close();
}
}

FileOutputStream写数据的3种方式

1.一次写一个字节数据
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
f.write(97);
f.close();
}
}

2.一次写一个字节数组数据
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
byte[] b= {97,98,99,100,101};
f.write(b);
f.close();
}
}

3.一次写一个字节数组的部分数据
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
byte[] b= {97,98,99,100,101};
f.write(b,1,2);
f.close();
}
}

换行写和续写
换行写:再写一个换行符就可以了,windows中的换行符:\r\n
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("a.txt");
//第一个字符串
String str1=("gywiliydqwmz");
byte[] b1=str1.getBytes();
f.write(b1);
//换行符
String str2=("\r\n");
byte[] b2=str2.getBytes();
f.write(b2);
//第二个字符串
String str3=("666");
byte[] b3=str3.getBytes();
f.write(b3);
f.close();
}
}

续写:
打开续写开关即可,开关位置:创建对象的第二个参数;默认false:表示关闭续写,此时创建对象会清空文件;手动传递true:表示打开续写,此时创建对象不会清空文件。
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileOutputStream f=new FileOutputStream("a.txt",true);
//第一个字符串
String str1=("gywiliydqwmz");
byte[] b1=str1.getBytes();
f.write(b1);
//换行符
String str2=("\r\n");
byte[] b2=str2.getBytes();
f.write(b2);
//第二个字符串
String str3=("666");
byte[] b3=str3.getBytes();
f.write(b3);
f.close();
}
}

执行第二次没有清空,还继续传入程序中写好的字符。
字节流——FileInputStream(字节输入流)(byte数组)
把本地文件的数据读取到程序中。

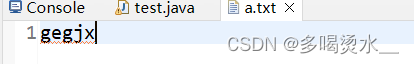
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流
FileInputStream f=new FileInputStream("a.txt");
//读取数据
int b1=f.read();
System.out.println((char)b1);
int b2=f.read();
System.out.println((char)b2);
int b3=f.read();
System.out.println((char)b3);
int b4=f.read();
System.out.println((char)b4);
int b5=f.read();
System.out.println((char)b5);
f.close();
}
}
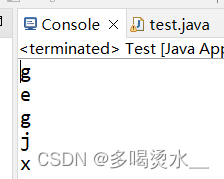
字节输入流循环读取(while)
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入流
FileInputStream f=new FileInputStream("a.txt");
//循环读取数据
int b;
while((b=f.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)b);
}
f.close();
}
}


一次读多个字节

一次读多个字节数据,具体读多少与数组长度有关,读取完成后会把数据存储在数组中,要把数组转成字符串,查看。
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream f=new FileInputStream("a.txt");
//读取数据
//定义数组长度
byte[] bytes=new byte[2];
int len1=f.read(bytes);//将读取到的数据放入数组中
System.out.println(len1);
String str1=new String(bytes, 0, len1);//将数组转换成字符串
System.out.println(str1);
int len2=f.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len2);
String str2=new String(bytes, 0, len2);
System.out.println(str2);
int len3=f.read(bytes);
System.out.println(len3);
String str3=new String(bytes, 0, len3);
System.out.println(str3);
//释放资源
f.close();
}
}


读和写的小练习
文件拷贝:把“D:\Date\c.txt”拷贝到当前模块下。
分析:先创建读流(input)、再创建写流(output),然后边读边写,最后再释放,先开的最后再关。
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//创建字节输入、输出流
FileInputStream fi=new FileInputStream("D:\\Date\\c.txt");
FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream("c.txt");
//边读边写
int b;
while((b=fi.read())!=-1) {
fo.write(b);
}
fo.close();
fi.close();
}
}



快速拷贝:
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
FileInputStream fi=new FileInputStream("D:\\Date\\c.txt");
FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream("c.txt");
//读取数据;
int len;
byte[] bytes=new byte[1024];
while((len=fi.read(bytes))!=-1) {
fo.write(bytes,0,len);
}
fo.close();
fi.close();
}
}
字符集
有ASCll字符集(美国)、GBK字符集(中国有汉字)、Unicode字符集(万国码)
一个字节8位。


ASCll字符集编码与解码

GBK字符集编码与解码


Unicode字符集编码与解码



编码和解码方法

public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//编码:将一个字符串转为二进制
String str="ai你呢";
byte[] b1=str.getBytes();//将字符串转为字节,默认编码规则
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b1));
byte[] b2=str.getBytes("gbk");//指定编码规则
System.out.println(Arrays.toString(b2));
//编码和解码要采用相同的字符集,否则会出现乱码
//解码,将字节转为字符串
String s1=new String(b1);
System.out.println(s1);
String s2=new String(b2,"gbk");
System.out.println(s2);
}
}

字符流


FileReader——字符输入流(char类型数组)



空参Read()方法
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符输入流
FileReader fr=new FileReader("a.txt");
//read()方法:读取后解码,返回一个整数
int t;
while((t=fr.read())!=-1) {
System.out.print((char)t);
}
//释放资源
fr.close();
}
}


有参Read()方法
read(c):将读取,解码(解码后是一个十进制整数),强转放在一起,将强转后的字符放进一个数组中。
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符输入流
FileReader fr=new FileReader("a.txt");
//read(有参)方法:将读取,解码,强转放在一起,把强转后的字符放在数组中
int len;
char[] c=new char[2];//两个两个字节打印
while((len=fr.read(c))!=-1) {
System.out.print(new String(c,0,len));
}
//释放资源
fr.close();
}
}

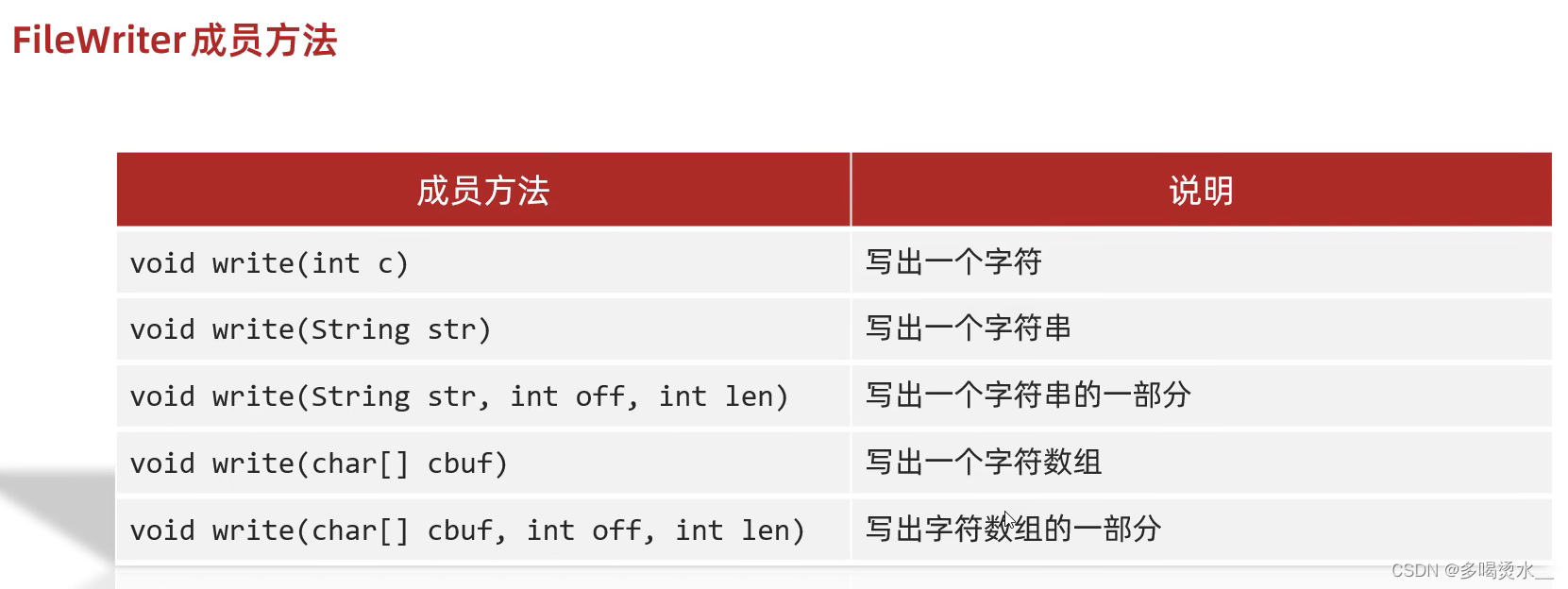
FileWriter——字符输出流(char类型数组)

public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//创建字符输出流
FileWriter fr=new FileWriter("a.txt");
//写入数据
fr.write("你好啊aaa");//写入一个字符串
//释放资源
fr.close();
}
}

字符输入流与字符输出流底层原理类似,都是先写入缓冲区中。

字符输出流的方法:

综合练习
练习1:拷贝文件夹,考虑到子文件夹
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//将一个文件夹拷贝
//创建一个对象表示原文件
File f1=new File("D:\\Date\\aaa");
//目的文件夹
File f2=new File("D:\\Date\\dest");
copy(f1, f2);
}
//创建一个方法进行文件夹的拷贝
public static void copy(File f1,File f2) throws IOException {//(原文件,目标文件)
f2.mkdirs();
//进入文件,进行遍历
File[] files=f1.listFiles();
for(File file:files) {
//判断是否为文件,是拷贝
if(file.isFile()) {
//文件,拷贝用字节流,读取方法
FileInputStream fi=new FileInputStream(file);//读,原文件
FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream(new File(f2,file.getName()));//写,目标文件(父级路径,子级路径)
byte[] b=new byte[1024];
int len;
while((len=fi.read(b))!=-1) {
fo.write(b,0,len);
}
fo.close();
fi.close();
}else {
//文件夹
//递归方法
copy(file,new File(f2,file.getName()));
}
}
}
}



练习2:文件加密
为了保证文件的安全性,就需要对原始文件进行加密存储,再使用的时候再对其进行解密处理。加密原理:对原始文件中的每一个字节数据进行更改,然后将更改以后的数据存储到新的文件中。
解密原理:读取加密之后的文件,按照加密的规则反向操作,变成原始文件。
分析:加密和解密文件其实相当于拷贝,只不过对拷贝内容进行异或。例如:100^10为110;110^10=100,^为异或,这个过程就相当于加密和解密。
加密:
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//文件加密
//创建文件对象和加密对象
FileInputStream fi=new FileInputStream("a.txt");
FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream("m.txt");//将文件a的内容加密到文件b
//加密处理
int len;
while((len=fi.read())!=-1) {
fo.write(len^10);//原字节数异或10写入文件
}
fo.close();
fi.close();
}
} 加密后:
加密后:
解密:
其实相当于将两者路径一调换
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//文件加密
//创建文件对象和加密对象
FileInputStream fi=new FileInputStream("m.txt");
FileOutputStream fo=new FileOutputStream("l.txt");
//加密处理
int len;
while((len=fi.read())!=-1) {
fo.write(len^10);//原字节数异或10写入文件
}
fo.close();
fi.close();
}
}
![]() 解密后:
解密后: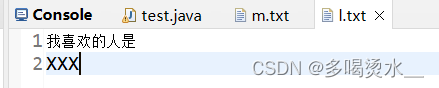
练习3:修改文件中的数据
文本文件中有以下的数据:2-1-9-4-7-8
将文件中的数据进行排序,变成以下的数据:1-2-4-7-8-9
分析:
先读取文件内容,将文件内容赋值给StringBuilder容器,将容器转为字符串,利用字符串中的方法对字符进行切割,将数字切割出来,为字符数组,创建一个集合将字符数组中的数组存入,利用for循环,将字符型数组变成int类型,再加入到集合中,利用Collections方法,对集合进行排序。
再写出,利用for循环获取数字,写入到文件中,进行判断索引位置,要对其格式输出。
public class test {
public static void main(String [] args) throws IOException {
//读取,将文件内容赋给一个容器
FileReader fr=new FileReader("m.txt");
StringBuilder sb=new StringBuilder();
int len;
while((len=fr.read())!=-1) {
sb.append((char)len);
}
fr.close();
//排序
String s=sb.toString();//赋给一个字符串
String[] arr=s.split("-");//将字符串按-切割
ArrayList<Integer> list=new ArrayList<>();//将数组添加到集合中
for (String str : arr) {
int i=Integer.parseInt(str);
list.add(i);
}
Collections.sort(list);
System.out.println(list);
//写出
FileWriter fw=new FileWriter("l.txt");
//获取集合中的元素按规定格式写出
for(int i=0;i<list.size();i++) {
if(i==list.size()-1) {
fw.write(list.get(i)+"");
}else {
fw.write(list.get(i)+"-");
}
}
fw.close();
}
}

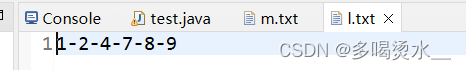






















 6883
6883











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








