Java中的类和对象(一)
在Java中一切皆对象
类和对象
什么是类?
描述对象的一些行为和方法
class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public static int hight;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public static void sleep() {
System.out.println("正在睡觉");
}
}
我们描述了一个学生类,类中有成员变量(定义在类的内部,方法的外部)(name,age,hight),成员方法(eat(),sleep())。
被static修饰的我们称为
静态成员变量(hight),表明是属于类的变量,只会存在一份
静态成员方法(sleep),并不依赖于对象,可以直接通过类名.调用这个方法
那么什么是对象?
通过描述产生了一个实体对象,主要通过new关键字来实例化对象
class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public static int hight;
public void eat() {
System.out.println("吃饭");
}
public static void sleep() {
System.out.println("正在睡觉");
}
}
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student=new Student();
Student student2=new Student();
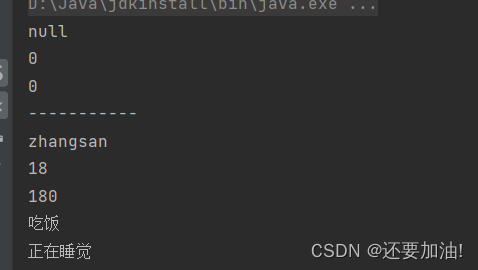
System.out.println(student.name);
System.out.println(student.age);
System.out.println(student.hight);
System.out.println("-----------");
student.name="zhangsan";
student.age=18;
student.hight=180;
System.out.println(student.name);
System.out.println(student.age);
System.out.println(student.hight);
student.eat();
Student.sleep();
}
}
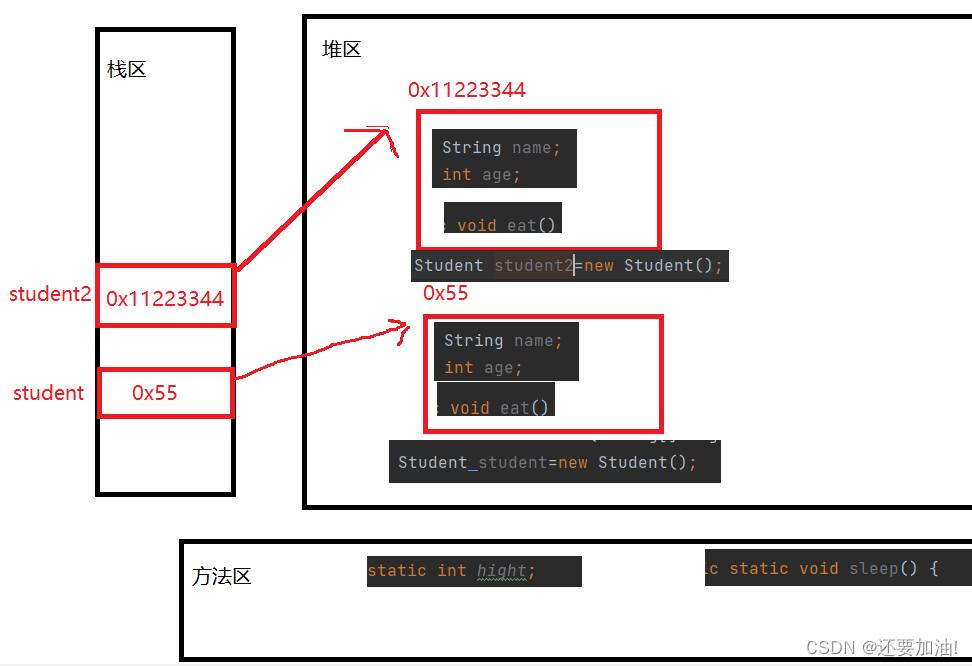
当我们没有进行初始化,编译器会默认初始值
同一个类可以创建多个对象
this关键字
表示当前对象的引用
用法1 this.成员变量
2 this.成员方法
3 this();调用其他构造方法
class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public static int hight;
public void setval(String name, int age ,int hight) {
this.name =name;
this.age=age;
this.hight=hight;
}
}
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student=new Student();
student.setval("zhangsan",18,180);
}
}
我们发现形参中的参数与成员变量同名,就需要用到this来区分
this();调用其他构造方法,那么构造方法是什么?
构造方法
名字必须与类名相同,在创建对象时,由编译器自动调用,并且
在整个对象的生命周期内只调用一次,没有返回值。
那么我们在之前程序中为什么没看到构造方法?
原因:当我们没有添加任何构造方法时,编译器会默认帮我们提供不带参数的构造方法 ,如果写了构造方法,编译器不再提供默认构造方法
class Student {
public String name;
public int age;
public int hight;
public Student() {}
public Student(String name ,int age ,int hight) {
this.name = name;
this.age = age;
this. hight = hight;
}
public Student(String name) {
this();
this.name=name;
}
}
public class Text {
public static void main(String[] args) {
Student student1=new Student();
Student student2=new Student("zhangsan",18,120);
Studnet student3=new Student("lisi");
}
}
student1调用了不带参数的构造方法,student2调用带3个参数的构造方法
student3调用了带1个参数的构造方法,但this();调用了不带参数的构造方法,就会去执行不带参数的构造方法。
面向对象程序三大特性之一:封装
封装:将数据和操作数据的方法进行有机结合,隐藏对象的属性和实现细节,仅对外公开接口来和对象进行交互。
总的来说,就是不能通过对象的引用来直接访问,需要通过一些手段来获取
我们会好奇,前面public是什么?
其实就是一个访问权限修饰符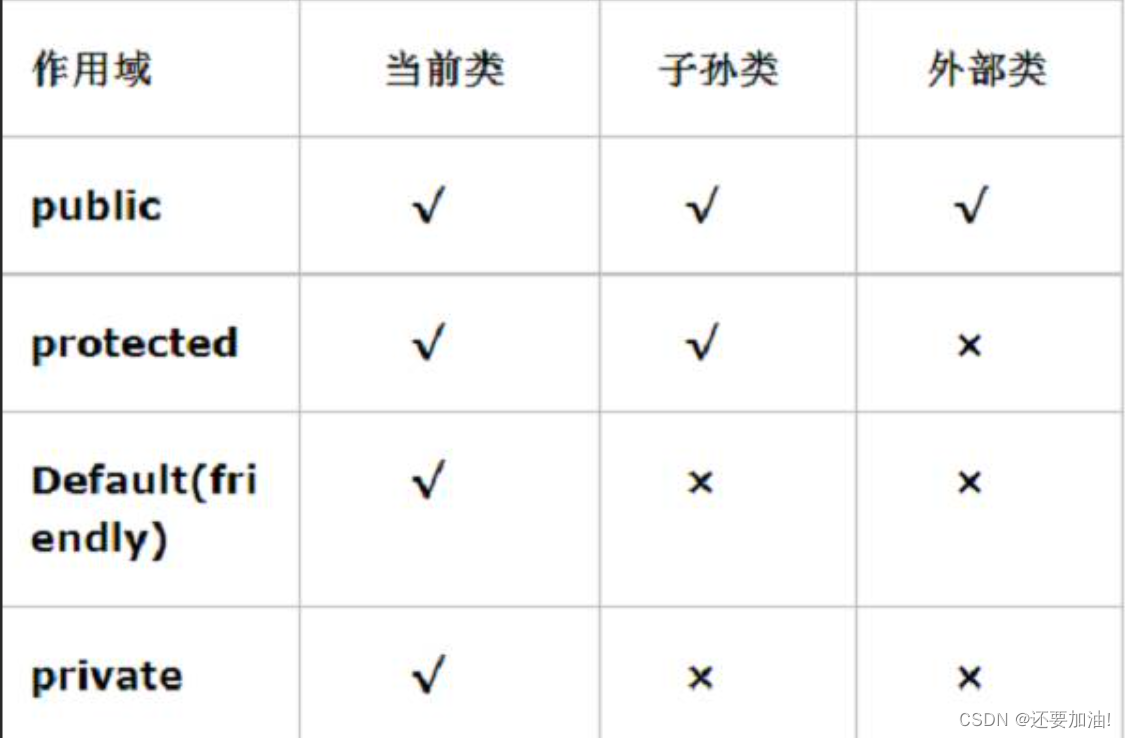
class Student {
private String name;
int age;
protected int hight;
public int white;
}
大小 private < 默认(什么都不写) < protacted <public
那么什么是包?
为了更好的管理类,把多个类收集在一起成为一组,称为软件包
如果当前类需要导入其他包,就需要import
那么什么是子类?请见下一章,谢谢你的观看,如有不对的地方望指出





















 7348
7348











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








