分支结构1:If-else条件判断语句
1.格式
格式1:
if(条件表达式) {
语句块;
}
格式2:“二选一”
if(条件表达式) {
语句块1;
}else{
语句块2;
}
格式3:“多选一”
if (条件表达式1) {
语句块1;
} else if (条件表达式2) {
语句块2;
...
}else if (条件表达式n) {
语句块n;
} else {
语句块n+1;
}
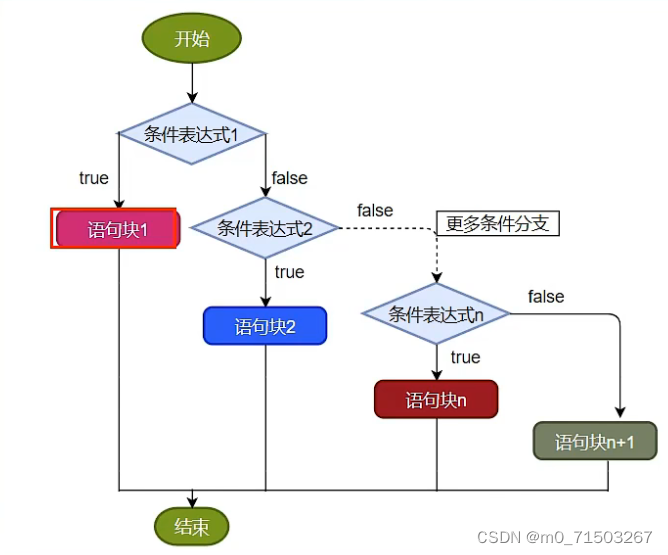
结论:
1.如果多个条件表达式之间没有交集(理解是互斥关系),则哪个条件表达式声明在上面,哪个声明在下面都可以。
如果多个条件表达式之间是包含关系,则需要将范围小的条件表达式声明在范围大的条件表达式的上面。否则,范围小的条件表达式不可能被执行。
案例:
由键盘输入三个整数分别存入变量num1、num2、 num3, 对它们进行排序(使用if-else if-else), 并且从小到大输出。
class IfElseTest2
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
int num1 = 30;
int num2 = 21;
int num3 = 44;
if(num1 >= num2){
if(num3 >= num1){
System.out.println(num2 + "," + num1 + "," + num3);
}else if(num3 <= num2){
System.out.println(num3 + "," + num2 + "," + num1);
}else{
System.out.println(num2 + "," + num3 + "," + num1) ;
}
}else{ // num1 < num2
if(num3 >= num2){
System.out.println(num1 + "," + num2 + "," + num3);
}else if(num3 <= num1){
System.out.println(num3 + "," + num1 + "," + num2);
}else{
System.out.println(num1 + "," + num3 + "," + num2);
}
}
}
}
1.从开发经验上讲,没有写过超过三层的嵌套if-else结构。
2.如果if-else中 的执行语句块中只有一行执行语句,则此执行语句所在的一对{}可以省略。但是,不建议省略
如何从键盘获取不同类型(基本数据类型、String类型)的变量:使用Scanner类。
1.使用Scanner获取不同类型数据的步骤
步骤1: 导包import java. util. Scanner
步骤2:提供(或创建)一个Scanner类的实例
步骤3:调用Scanner类中的方法,获取指定类型的变量
步骤4:关闭资源,调用Scanner类的close()
2. 案例:小明注册某交友网站,要求录入个人相关信息。如下:
请输入你的网名、你的年龄、你的体重、你是否单身、你的性别等情况。
//步骤1: 导包import java. util. Scanner;
import java.util.Scanner;
class ScannerTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//步骤2:提供(或创建)一个Scanner类的实例
Scanner scan = new Scanner (System. in);
System. out. println("欢迎光临你来我往交友网");
System . out. print("请输入你的网名: ");
//步骤3:调用Scanner类中的方法,获取指定类型的变量
String name = scan. next();
System. out. print("请输入你的年龄: ");
int age = scan. nextInt( );
System. out. print("请输入你的体重: ");
double weight = scan. nextDouble();
System. out. print("你是否单身( 单身: true; 不单身: false) : ");
boolean isSingle = scan. nextBoolean( );
System . out. print("请输入你的性别: (男\\女)");
char gender = scan. next() . charAt(0);
System . out. println("网名: " + name + ",年龄:" + age + ",体重: " + weight + ",是否单身:" + isSingle + ",性别:" + gender);
System.out. println("注册完成,欢迎继续进入体验!");
//步骤4:关闭资源,调用Scanner类的close()
scan.close();
}
}
3. Scanner类中提供了获取byte \ short \ int \ long \float \double \boolean \ String 类型变量的方法。
注意,没有提供获取char类型变量的方法。需要使用next(). charAt(0)
如何获取一个随机数?
1.可以使用Java提供的API :Math类的random()
2. random()调用以后,会返回一个[0.0,1.0)范围的double型的随机数
3.需求1:获取一个[0, 100]范围的随机整数?
需求2:获取一个[1, 100]范围的随机整数?
4.需求:获取一个[a,b]范围的随机整数?
(int)(Math.random() * (b- a + 1)) + a
class RandomTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
double d1 = Math . random();
System . out .println("d1 ="+ d1);
int num1 = (int) (Math.random() * 101); //[0.0,1.0) --> [0.0,101.0) --->[0,100]
System. out. println("num1 ="+ num1);
int num2 = (int)(Math .random()*100) + 1; //[0.0,1.0) --> [0.0,100.0) --->[0,99] ---> [1,100]
}
}
分支结构2:switch-case的使用
1.语法格式
switch(表达式){
case常量1:
//执行语句1
//break;
case常量2:
//执行语句2
//break;
...
default:
//执行语句2
/ /break;
}
2.执行过程:
根据表达式中的值,依次匹配case语句。一旦与某一个case中的常量相等,那么就执行此case中的执行语句。
执行完此执行语句之后
情况1:遇到break,则执行break后, 跳出当前的switch-case结构
情况2:没有遇到break,则继续执行其后的case中的执行语句。 ----->case穿透
...
直到遇到break或者执行完所有的case及default中的语句,退出当前的switch-case结构
3.说明:
① switchswitch中的表达式只能是特定的数据类型。如下:byte \ short \ char \ int \ 枚举 \ String
② case后都是跟的常量,使用表达式与这些常量做相等的判断,不能进行范围的判断。
③ 开发中,使用switch-case时, 通常case匹配的情况都有限。
④ break:可以使用在switch-case中。一旦执行此break关键字,就跳出当前的switch-case结构
⑤ default: 类似于if-else中的else结构。
default是可选的,而且位置是灵活的。
4. switch-case 与if-else之 间的转换
①开发中凡是可以使用switch-case结构的场景,都可以改写为if-else。 反之,不成立
②开发中,如果一个具体问题既可以使用switch-case, 又可以使用if-else的时候,推荐使用switch-case.
为什么? switch-case相较于if-else效率稍高。
编写程序:从键盘上输入2023年的“month"和“day”,要求通过程序输出输入的日期为2023年的第几天。(case穿透)
import java.util.Scanner;
class SwitchCaseTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.使用Scanner,从键盘获取2023年的month、day
Scanner input = new Scanner(System.in);
System.out.println("请输入2023年的月份:");
int month = input.nextInt();//阻塞式方法
System.out.println("请输入2023年的天:");
int day = input.nextInt();
//假设用户输入的数据是合法的。后期我们在开发中,使用正则表达式进行校验。
//2.使用switch-case实现分支结构
int sumDays = 0;//记录总天数
//1方式1:不推荐。存在数据的冗余
/*
switch( month){
case 1 :
sumDays = day;
break;
case 2:
sumDays = 31 + day;
break;
case 3:
sumDays = 31 + 28 + day;
break;
case 4:
sumDays =31+28+31+day;
break;
//...
case 12:
sumDays =31 + 28+...+30+ day;
break;
}
*/
switch (month){
case 12:
sumDays += 30;
case 11:
sumDays += 31;
case 10:
sumDays += 30;
case 9:
sumDays += 31;
case 8:
sumDays += 31;
case 7:
sumDays += 30;
case 6:
sumDays += 31;
case 5:
sumDays += 30;
case 4:
sumDays += 31;
case 3:
sumDays += 28; //28:2月份的总天数
case 2:
sumDays += 31; //31:1月份的总天数
case 1:
sumDays += day;
break;
}
System.out.println("2023年" + month + "月" + day + "日是当前的第" + sumDays + "天");
input.close();//为了防止内存泄漏
}
}
循环结构之: for 循环
1. Java中规范了3种循环结构: for、 while、do-while
2.凡是循环结构,就一定会有4个要素:
①初始化条件
②循环条件---> 一定是boolean类型的变量或表达式
③循环体
④迭代部分
3. for循环的格式
for(①;②;④){
③
}
执行过程:① - ② - ③ - ④ - ② - ③ - ④ - ... - ②
4.应用场景:有明确的遍历的次数。for(int i = 1;i<=100;i++)
需求1:题目:输出50行HelloWorld
class ForTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求1:题目:输出50行HelloWorld
/*
System.out.println("HelloWorld")
System.out.println("HelloWorld")
System.out.println("HelloWorld")
System.out.println("HelloWorld")
System.out.println("HelloWorld")
*/
for(int i = 1 ;i <= 50; i++){
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
}
//此时编译不通过。因为i已经出了其作用域范围。
//System.out.println(i);
需求3:遍历1- 100以内的偶数,并获取偶数的个数,获取所有的偶数的和
class ForTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
int count = 0;//记录偶数个数
int sum = 0;//记录所有偶数的和
for (int i = 1;i <= 100 ; i++ ){
if (i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
count++;
sum += i;
}
}
System.out.println("偶数的个数为:" + count);
System.out.println("偶数的总和为:" + sum);
}
}
题目:输出所有的水仙花数,所谓水仙花数是指一一个3位数,其各个位上数字立方和等于其本身。
例如:153=1*1*1 + 3*3*3 + 5*5*5
class ForTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//遍历所有三位数
for (int i = 100 ; i <= 999 ; i++ ){
//针对于每一个三位数i,获取其各个位上数值
int ge = i % 10;
int shi = i % 100 /10;
int bai = i / 100;
//判断是否满足水仙花数的规则
if(i == ge * ge * ge + shi * shi * shi + bai * bai *bai){
System.out.println(i);
}
}
}
}
案例:输入两个正整数m和n,求其最大公约数和最小公倍数。
比如: 12和20的最大公约数是4,最小公倍数是60。
约数: 12为例,约数有1,2,3,4,6,12
20为例,约数有1,2,4,5,10,20
倍数:12为例,倍数有12, 24, 36,48, 60, 72,...
20为例,倍数有20, 40, 60, 80,...
class ForTest2{
public static void main(String[] args) {
int m=12;
int n=20;
//获取m和n中的较小值
int min=(m<n)?m:n;
//需求1:最大公约数
//方式1:
int result = 1;
for(int i = 1;i <= min;i++){
if(m % i == 0 && n % i == 0){
//System. out. println(i);
result = i;//将值覆盖了
}
}
System.out.println(result);
//方式2:推荐
for (int i = min;i >= 1;i--){
if(m % i == 0 && n % i == 0){
System.out.println("最大公约数为" + i);
break;//一旦执行,就跳出当前循环。
}
}
//需求2:最小公倍数
int max = (m > n)? m : n;
for (int i = max;i <= m * n;i++){
if (i % m == 0 && i % n == 0){
System.out.println("最小公倍数为" + i);
break;
}
}
}
}
说明:
1.我们可以在循环结构中使用break.一旦执行break,就跳出(或结束)当前循环结构。
2.如何结束一个循环结构?
方式1:循环条件不满足。( 即循环条件执行完以后是false)
方式2:在循环体中执行了break
循环结构之:while循环
1.凡是循环结构,就一定会有4个要素:
①初始化条件
②循环条件---> 一定是boolean类型的变量或表达式
③循环体
④迭代部分
2.while的格式
①
while(②){
③
④
}
3.执行过程:① - ② - ③ - ④ - ② - ③ - ④ - ... - ②
4. for循环与while循环可以相互转换!
5. for循环和while循环的小区别:初始化条件的作用域范围不同。while循环中的初始化条件在while循环结束后,依然有效。
6.应用场景:没有明确的遍历次数
class WhileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求1:遍历50次HelloWorld
int i = 1;
while(i <= 50){
System.out.println("HelloWorld");
i++;//- -定要小心!不要丢了
}
//需求2:遍历1-100以内的偶数,并获取偶数的个数,获取所有的偶数的和
int j=1;
int count = 0;//记录偶数的个数
int sum = 0;//记录偶数的总和
while(j <= 100){
if(j % 2 == 0){
System. out . println(j);
count++;
sum += j;
}
j++;
}
System.out.println("偶数的个数为:"+ count);
System.out.print1n("偶数的总和为:"+ sum);
}
}
随机生成一个100以内的数,猜这个随机数是多少?
从键盘输入数,如果大了,提示大了:如果小了,提示小了:如果对了,就不再猜了,并统计- -共猜了多少次。
提示:生成一个[a,b]范围的随机数的方式: (int)(Math. random() * (b - a + 1) + a)
import java.util.Scanner;
class WhileTest1 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.生成一个[1, 100]范围的随机整数
int random = (int) (Math.random() * 100) + 1;
//2.使用Scanner,从键盘获取数据
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System. in);
System.out.print("请输入1-100范围的一个整数: ");
int guess = scan. nextInt();
//3.声明一个变量,记录猜的次数
int guessCount = 0;
//4.使用循环结构,进行多次循环的对比和获取数据
while(random != guess ){
if(guess > random){
System . out . println("你输入的数据大了");
}else if(guess < random){
System.out.println("你输入的数据小了");
}//else{
// break;
//}
System.out.print("请输入1 -100范围的一个整数: ");
guess=scan.nextInt();
guessCount++;
}
//能结束结束,就意味着random和guess相等了
System.out.println("恭喜你!猜对了!");
System.out.println("共猜了" + guessCount + "次");
scan.close();
}
}世界最高山峰是珠穆朗玛峰,它的高度是8848.86米,假如我有一张足够大的纸,它的厚度是0.1毫米。
请问,我折叠多少次,可以折成珠穆朗玛峰的高度?
class WhileTest2 {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.声明珠峰的高度、纸的默认厚度
double paper = 0.1;//单位:毫米
double zf = 8848860;//单位:毫米
//2.定义一个变量,记录折纸的次数
int count = 0;
//3.通过循环结构,不断调整纸的厚度( 当纸的厚度超过珠峰高度时,停止循环)
while(paper <= zf){
paper *= 2;
count++;
}
System. out . println("paper的高度为:" + (paper / 1000) + ",超过了珠峰的高度"+ zf);
System. out . println("共折纸"+ count + "次");
}
}
循环结构之:do-while循环
1.凡是循环结构,就一定会有4个要素:
①初始化条件
②循环条件---> 一定是boolean类型的变量或表达式
③循环体
④迭代部分
2.do-while的格式
①
do{
③
④
}while(②);
执行过程:① - ③ - ④ - ②
3.说明:
① do-while循环至少执行一次循环体。
② for、while、 do-while循环三者之间是可以相互转换的。
③ do-while循环结构,在开发中,相较于for、while循环来讲,使用的较少。
如何选择
。遍历有明显的循环次数(范围)的需求,选择for循环
。遍历没有明显的循环次数(范围)的需求,选择while循环
。如果循环体语句块至少执行一次, 可以考虑使用do-while循环
。本质上:三种循环之间完全可以互相转换,都能实现循环的功能
class DoWhileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//需求2:遍历1-100以内的偶数,并获取偶数的个数,获取所有的偶数的和
int i=1;
int count = 0;//记录偶数的个数
int sum = 0;//记录偶数的总和
do{
if(i % 2 == 0){
System.out.println(i);
count++;
sum += i;
}
i++;
}while(i <= 100);
System. out . println("偶数的个数为:"+ count);
System. out. println("偶数的总和为:"+ sum);
//*********************************************
int num1 = 10;
while(num1 > 10){
System. out. println("while:hello");
num1--;
}
int num2 = 10;
do{
System. out . println("do-while:he1lo");
num2-- ;
}while(num2 > 10);
}
}
题目:模拟ATM取款
声明变量balance并初始化为0,用以表示银行账户的余额,下 面通过ATM机程序实现存款,取款等功能。
========ATM=======
1、存款
2、取款
3、 显示余额
4、退出
请选择(1-4):
import java.util.Scanner;
class DoWhileTest1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
//1.定义balance的变量,记录账户余额
double balance = 0.0;
boolean flag = true; //控制循环的结束
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System.in);//实例化Scanner
do{
//2.声明ATM取款的界面
System.out.println("========ATM=======");
System.out.println(" 1、存款");
System.out.println(" 2、取款");
System.out.println(" 3、 显示余额");
System.out.println(" 4、退出");
System.out.print("请选择(1-4):");
//3.使用Scanner获取用户的选择
int selection = scan. nextInt();
switch(selection){
//4.根据用户的选择,决定执行存款、取款、显示余额、退出的操作
case 1:
System.out.print("请输入存款的金额:");
double money1 = scan.nextDouble();
if(money1 > 0){
balance += money1;
}
break;
case 2:
System.out.print("请输入取款的金额:");
double money2 = scan.nextDouble();
if (money2 > 0 && money2 <= balance){
balance -= money2;
}else{
System.out.print("输入的数据有误或余额不足");
}
break;
case 3:
System.out.print("账户余额为:" + balance);
break;
case 4 :
flag = false;
System.out.print("感谢使用,欢迎下次光临^_^");
break;
default:
System.out.println("输入有误,请重新输入");
//break
}
}while(flag);
//关闭资源
scan.close();
}
}
无限循环结构的使用
1. 格式: while(true) 或 for(;;)
2.开发中,有时并不确定需要循环多少次,需要根据循环体内部某些条件,来控制循环的结束(使用break) 。
3.如果此循环结构不能终止,则构成了死循环!开发中要避免出现死循环。
class ForWhileTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
while (true){
System.out.println("I love you")
}
//死循环的后面不能有执行语句。
//System.out.println( "end");
}
}
案例:从键盘读入个数不确定的整数,并判断读入的正数和负数的个数,输入为0时结束程序。
import java.util.Scanner;
class ForWhileTest1{
public static void main(String[] args) {
Scanner scan = new Scanner(System. in);
int positiveCount = 0;//记录正数的个数
int negativeCount = 0;//记录负数的个数
while(true){
System.out.print("请输入-个整数(输入为0时结束程序): ");
int num = scan.nextInt(); //获取用户输入的整数
if(num > 0){ //正数
positiveCount++ ;
}else if(num < 0){ //负数
negativeCount++ ;
}else{ //零
System.out.println("程序结束");
break;
}
}
System.out.println("正数的个数为:" + positiveCount);
scan.close();
}
}嵌套循环的使用
1.嵌套循环:是指一个循环结构A的循环体是另一个循环结构B。
-外层循环:循环结构A
-内层循环:循环结构B
2.说明:
1)内层循环充当了外层循环的循环体。
2)对于两层嵌套循环来说,外层循环控制行数,内层循环控制列数。
3)举例:外层循环执行m次,内层循环执行n次,则内层循环的循环体共执行m * n次
4)实际开发中,我们不会出现三层以上的循环结构,三层的循环结构都很少见。
菱形点阵
class ForForTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
System.out.println("Hello World!");
//******
for (int i = 1;i <= 6;i++){
System.out.println('*');
}
System.out.println("\n###################");
/*
******
******
******
******
******
*/
for(int j = 1;j <= 5;j++){
for(int i = 1;i <= 6;i++){
System. out. print('*');
}
System. out. println();
}
/*
i(第几行) j(每一行中*的个数)
* 1 1
** 2 2
*** 3 3
**** 4 4
***** 5 5
*/
for(int i = 1;i <= 5;i++){
for(int j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System. out. print("*");
}
System. out. println();
}
/*
i(第几行) j(每一行中*的个数) i + j = 7--> j = 7 - i
****** 1 6
***** 2 5
**** 3 4
*** 4 3
** 5 2
* 6 1
*/
for(int i = 1;i <= 6;i++){
for(int j = 1;j <= 7 - i;j++){
System. out . print("*");
}
System. out. println();
}
/*
i(第几行) j(每一行中-的个数) k(每一行中*的个数) 2*i + j = 10 --->j = 10 - 2*i
--------* 1 8 1 k = 2 * i - 1
* * * 2 6 3
* * * * * 3 4 5
* * * * * * * 4 2 7
* * * * * * * * * 5 0 9
* * * * * * *
* * * * *
* * *
*
*/
//上半部分
for(int i = 1;i <= 5;i++){
//-
for(int j = 1;j <= 10 - 2*i;j++){
System. out. print("-");
}
//*
for(int k = 1;k <= 2*i - 1;k++){
System.out.print("* ");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
九九乘法表
class NineNineTable{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for (int i = 1;i <= 9;i++){
for (int j = 1;j <= i;j++){
System.out.print(i + "*" + j + "=" + i * j + "\t");
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}bresk 和 continue关键字的使用
使用范围 在循环结构中的作用 相同点
break: Switch-case
循环结构中 结束(或跳出)当前循环结构 在此关键字的后面不能声明执行语句。
continue : 循环结构中 结束(或跳出)当次循环 在此关键字的后面不能声明执行语句。
2.了解带标签的break和continue的使用
3.开发中,break的使用频率要远高于continue。
演示:
class BreakContinueTest{
public static void main(String[] args) {
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
if(i % 4 == 0){
//break;
continue;
//编译不通过
//System.out.println("今晚上迪丽热巴要约我! ");
}
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
//**********************************************
label:for(int j = 1;j <= 4;j++){
for(int i = 1;i <= 10;i++){
if(i % 4 == 0){
//break;
//continue;
//了解
//break label;
continue label;
}
System.out.print(i);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
题目:找出100以内所有的素数(质数) ? 100000以内的呢?
质数:只能被1和它本身整除的自然数。比如:2,3,5,7,11,13,17,19,23,...
------->换句话说,从2开始到这个自然数-1为止,不存在此自然数的约数。
class PrimeNumberTest {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//方式1:
for(int i = 2;i <= 100;i++){ //遍历100以内的自然数
int number = 0; //记录i的约数的个数(从2开始,到i-1为止)
//判定i是否是质数
for(int j = 2;j < i;j++){
if(i % j == 0){
number++;
}
}
if(number == 0){
System.out .println(i);
}
}
//方式2:
for(int i = 2;i <= 100;i++){ //遍历100以内的自然数
boolean isFlag = true;
//判定i是否是质数
for(int j = 2;j < i;j++){
if(i % j == 0){
isFlag = false;
}
}
if(isFlag){//if(isFlag == true){
System.out .println(i);
}
}
}
}
100000以内的质数看文件:PrimeNumberTest1.java、 PrimeNumberTest2.java





















 666
666











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








