目录
一、链表
1.定义
链表是一种物理存储单元上非连续、非顺序的存储结构,数据元素的逻辑顺序是通过链表中的指针链接次序实现的。链表由一系列结点(链表中每一个元素称为结点)组成,结点可以在运行时动态生成。每个结点包括两个部分:一个是存储数据元素的数据域,另一个是存储下一个结点地址的指针域。
2.功能的实现
<0>头文件
#ifndef LINKLIST_H
#define LINKLIST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#endif
typedef int LLTDataType;
typedef struct LinkedListNode
{
LLTDataType data;
struct LinkedListNode* next;
} LLNode;
LLNode* BuyLLNode(LLTDataType x); //创建数据为x的链表结点
LLNode* CreatLL(int n); //创建n个结点的链表
void LLPrint(LLNode *phead); //链表打印数据
void LLPushBack(LLNode **pphead,LLTDataType x); //链表尾插
void LLPushFront(LLNode **pphead,LLTDataType x);//链表头插
void LLPopBack(LLNode **pphead); //链表尾删
void LLPopFront(LLNode **pphead); //链表头删
LLNode* LLFind(LLNode *phead,LLTDataType x);//链表查找数据
void LLInsert(LLNode **pphead,LLNode *pos,LLTDataType x); //链表插入数据(在pos前)
void LLErase(LLNode **pphead,LLNode *pos); //链表删除pos位的数据
void LLInsertAfter(LLNode *pos,LLTDataType x); //链表在pos后插入数据
void LLEraseAfter(LLNode *pos); //链表删除pos后一位的数据
void LLDestroy(LLNode **pphead); //链表销毁<1>新建一个数据为x的链表结点
LLNode* BuyLLNode(LLTDataType x) //创建数据为x的链表结点
{
LLNode *newnode=(LLNode*)malloc(sizeof(LLNode));
if(!newnode)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data=x;
newnode->next=NULL;
return newnode;
}<2>创建n个结点的链表
LLNode* CreatLL(int n) //创建n个结点的链表
{
LLNode *phead=NULL,*ptail=NULL;
LLTDataType x;
for(int i=0;i<n;i++)
{
scanf("%d",&x);
LLNode *newnode=BuyLLNode(x);
if(!phead)
{
phead=ptail=newnode;
}else
{
ptail->next=newnode;
ptail=newnode;
}
}
return phead;
}
<3>链表打印数据
void LLPrint(LLNode *phead) //链表打印数据
{
LLNode *cur=phead;
while(cur)
{
printf("%d->",cur->data);
cur=cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
return;
} <4>链表尾插
void LLPushBack(LLNode **pphead,LLTDataType x) //链表尾插
{
assert(pphead);
LLNode *newnode=BuyLLNode(x);
if(!*pphead)
{
*pphead=newnode;
}else
{
LLNode *tail=*pphead;
while(tail->next)
{
tail=tail->next;
}
tail->next=newnode;
}
return;
}<5>链表头插
void LLPushFront(LLNode **pphead,LLTDataType x)//链表头插
{
assert(pphead);
LLNode *newnode=BuyLLNode(x);
newnode->next=*pphead;
*pphead=newnode;
return;
}<6>链表尾删
void LLPopBack(LLNode **pphead) //链表尾删
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
if((*pphead)->next)
{
LLNode *tail=*pphead;
while(tail->next->next)
{
tail=tail->next;
}
free(tail->next);
tail->next=NULL;
}else
{
free(*pphead);
*pphead=NULL;
}
return;
}<7>链表头删
void LLPopFront(LLNode **pphead) //链表头删
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
LLNode *next=(*pphead)->next;
free(*pphead);
*pphead=next;
return;
}<8>链表查找数据
LLNode* LLFind(LLNode *phead,LLTDataType x)//链表查找数据
{
LLNode *cur=phead;
while(cur)
{
if(cur->data==x)
{
return cur;
}
cur=cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}<9>链表插入数据(在pos前)
void LLInsert(LLNode **pphead,LLNode *pos,LLTDataType x) //链表插入数据(在pos前)
{
assert(pphead);
assert(pos);
if(pos==*pphead)
{
LLPushFront(pphead,x);
}else
{
LLNode *pre=*pphead;
while(pre->next!=pos)
{
pre=pre->next;
}
LLNode *newnode=BuyLLNode(x);
newnode->next=pos;
pre->next=newnode;
}
return;
}<10>链表删除pos位的数据
void LLErase(LLNode **pphead,LLNode *pos) //链表删除pos位的数据
{
assert(pphead);
assert(*pphead);
assert(pos);
if(pos==*pphead)
{
LLPopFront(pphead);
}else
{
LLNode *pre=*pphead;
while(pre->next!=pos)
{
pre=pre->next;
}
pre->next=pos->next;
free(pos);//不用pos=NULL,因为函数无法改变外部变量
}
return;
}<11>链表在pos后插入数据
void LLInsertAfter(LLNode *pos,LLTDataType x) //链表在pos后插入数据
{
assert(pos);
LLNode *newnode=BuyLLNode(x);
newnode->next=pos->next;
pos->next=newnode;
return;
}
<12>链表删除pos后一位的数据
void LLEraseAfter(LLNode *pos) //链表删除pos后一位的数据
{
assert(pos);
if(!pos->next)
{
return;
}else
{
LLNode *nextnode=pos->next;
pos->next=nextnode->next;
free(nextnode);
nextnode=NULL;
}
return;
}<13>链表销毁
void LLDestroy(LLNode **pphead) //链表销毁
{
assert(pphead);
LLNode *cur=*pphead;
while(cur)
{
LLNode *nextnode=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=nextnode;
}
*pphead=NULL;
return;
}3.实例
main函数:
#include "linklist.h"
int main()
{
LLNode *phead=CreatLL(3);
LLPrint(phead);
LLPushBack(&phead,4);
LLPrint(phead);
LLPushFront(&phead,0);
LLPrint(phead);
LLPopBack(&phead);
LLPopFront(&phead);
LLPrint(phead);
LLInsert(&phead,phead->next,999);
LLPrint(phead);
LLErase(&phead,LLFind(phead,999));
LLPrint(phead);
LLInsertAfter(phead->next,999);
LLPrint(phead);
LLEraseAfter(LLFind(phead,999));
LLPrint(phead);
LLDestroy(&phead);
return 0;
}输出结果:
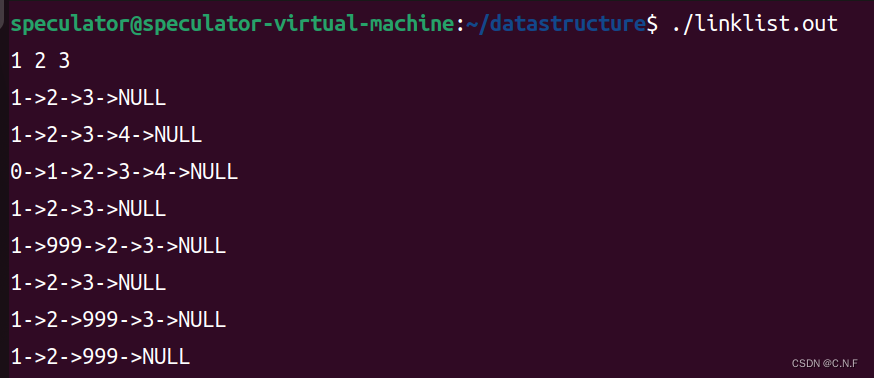
二、双向循环链表(带哨兵头结点)
1.结构
双向链表中每个结点不只有指向下一个节点(后继结点)的指针,还有一个指向上一个结点(前驱结点)的指针,节点包含的信息为:
- 指针域 prev/prior:用于指向当前节点的直接前驱节点
- 数据域 data:用于存储数据元素
- 指针域 next:用于指向当前节点的直接后继节点
而循环链表,则是把tail结点指向头结点,链表中不再有指向NULL的指针,即
tail->next=head
因此,在双向循环链表中,链表有两个方向进行访问,头尾结点相连后,找到尾节点也及其方便,各种功能见下文

2.功能实现
<0>头文件
#ifndef DCLINKLIST_H
#define DCLINKLIST_H
#include <stdio.h>
#include <stdlib.h>
#include <assert.h>
#include <stdbool.h>
#endif
typedef int DCLLDataType;
typedef struct DCLinkedListNode
{
DCLLDataType data;
struct DCLinkedListNode *next;
struct DCLinkedListNode *prev;
} DCLLNode;
DCLLNode* DCLLInit();//创建一个双向循环链表(哨兵头节点)
DCLLNode* BuyDCLLNode(DCLLDataType x);//创建一个新节点
void DCLLPrint(DCLLNode *phead);//打印链表数据
void DCLLPushBack(DCLLNode *phead,DCLLDataType x);//尾插
void DCLLPopBack(DCLLNode *phead);//尾删
void DCLLPushFront(DCLLNode *phead,DCLLDataType x);//头插
void DCLLPopFront(DCLLNode *phead);//头删
DCLLNode* DCLLFind(DCLLNode *phead,DCLLDataType x);//查找数据
void DCLLInsert(DCLLNode *pos,DCLLDataType x);//在pos前插入数据
void DCLLErase(DCLLNode *pos);//删除pos处的数据
bool DCLLEmpty(DCLLNode *phead);//检查链表是否为空
size_t DCLLSize(DCLLNode *phead);//计算链表大小
void DCLLDestroy(DCLLNode *phead);//链表销毁
<1>创建新节点
DCLLNode* BuyDCLLNode(DCLLDataType x)//创建一个新节点
{
DCLLNode *newnode=(DCLLNode*)malloc(sizeof(DCLLNode));
if(!newnode)
{
perror("malloc fail");
exit(-1);
}
newnode->data=x;
newnode->next=NULL;
newnode->next=NULL;
return newnode;
}<2>链表初始化(哨兵头结点)
DCLLNode* DCLLInit()//创建一个双向循环链表(哨兵头节点)
{
DCLLNode *phead=BuyDCLLNode(-1);//实际工程中,链表的数据类型不一定是int,所以一般不用哨兵头结点来存储链表大小
phead->next=phead;
phead->prev=phead;//这里把next和prev指向自己是为了让后续插入删除第一个数据时更简单
return phead;
}<3>打印链表数据
void DCLLPrint(DCLLNode *phead)//打印链表数据
{
assert(phead);
DCLLNode *cur=phead->next;
while(cur!=phead)
{
printf("%d->",cur->data);
cur=cur->next;
}
printf("NULL\n");
return;
}<4>尾插
void DCLLPushBack(DCLLNode *phead,DCLLDataType x)//尾插
{
assert(phead);//由于有哨兵头结点,此处插入数据也需要断言
DCLLNode *newnode=BuyDCLLNode(x);
DCLLNode *tail=phead->prev;
tail->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=tail;
newnode->next=phead;
phead->prev=newnode;
/* DCLLInsert(phead,x);
* 复用Insert函数让尾插更简单
*/
return;
}
<5>尾删
void DCLLPopBack(DCLLNode *phead)//尾删
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next!=phead);//没有数据则不能删,断言
DCLLNode *tail=phead->prev;
DCLLNode *newtail=tail->prev;
newtail->next=phead;
phead->prev=newtail;
free(tail);
/* assert(phead);
* assert(phead->next!=phead);
* DCLLErase(phead->prev);
*复用Erase函数让尾删更简单
*/
return;
}<6>头插
void DCLLPushFront(DCLLNode *phead,DCLLDataType x)//头插
{
assert(phead);
DCLLNode *newnode=BuyDCLLNode(x);
newnode->next=phead->next;
phead->next->prev=newnode;
phead->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=phead;
/* assert(phead);
* DCLLInsert(phead->next,x);
* 复用INsert函数让头插更简单
*/
return;
}<7>头删
void DCLLPopFront(DCLLNode *phead)//头删
{
assert(phead);
assert(phead->next!=phead);//哨兵头结点不能删
DCLLNode *first=phead->next;
DCLLNode *second=first->next;
free(first);
phead->next=second;
second->prev=phead;
/* assert(phead);
* assert(phead->next!=phead);
* DCLLErase(phead->next);
* 复用Erase函数让头删更简单
*/
return;
}<8>查找数据
DCLLNode* DCLLFind(DCLLNode *phead,DCLLDataType x)//查找数据
{
assert(phead);
DCLLNode *cur=phead->next;
while(cur!=phead)
{
if(cur->data==x)
return cur;
cur=cur->next;
}
return NULL;
}<9>(在pos前)插入数据
void DCLLInsert(DCLLNode *pos,DCLLDataType x)//在pos前插入数据
{
assert(pos);
DCLLNode *prevnode=pos->prev;
DCLLNode *newnode=BuyDCLLNode(x);
prevnode->next=newnode;
newnode->prev=prevnode;
newnode->next=pos;
pos->prev=newnode;
return;
}<10>删除pos处的数据
void DCLLErase(DCLLNode *pos)//删除pos处的数据
{
assert(pos);
DCLLNode *bef=pos->prev;
DCLLNode *aft=pos->next;
free(pos);
bef->next=aft;
aft->prev=bef;
return;
}<11>检查链表是否为空(哨兵结点自己循环)
bool DCLLEmpty(DCLLNode *phead)//检查链表是否为空
{
assert(phead);
return (phead->next==phead);
}<12>计算链表长度(不算哨兵头结点)
size_t DCLLSize(DCLLNode *phead)//计算链表大小
{
assert(phead);
DCLLNode* cur=phead->next;
size_t size=0;
while(cur!=phead)
{
size++;
cur=cur->next;
}
return size;
}<13>销毁链表
void DCLLDestroy(DCLLNode *phead)//链表销毁
{
assert(phead);
DCLLNode *cur=phead->next;
while(cur!=phead)
{
DCLLNode *nextnode=cur->next;
free(cur);
cur=nextnode;
}
free(phead);
return;
}3.实例
main函数:
#include "dclinklist.h"
int main()
{
DCLLNode *phead=DCLLInit();
DCLLPushBack(phead,3);
DCLLPushBack(phead,4);
DCLLPushBack(phead,5);
DCLLPushFront(phead,2);
DCLLPushFront(phead,1);
DCLLPrint(phead);
DCLLPopBack(phead);
DCLLPopFront(phead);
DCLLPrint(phead);
DCLLInsert(DCLLFind(phead,3),99);
DCLLPrint(phead);
DCLLErase(DCLLFind(phead,4));
DCLLPrint(phead);
if(DCLLEmpty(phead))
printf("empty\n");
else
printf("not empty\n");
printf("size=%ld\n",DCLLSize(phead));
DCLLDestroy(phead);
phead=NULL;
return 0;
}输出结果:
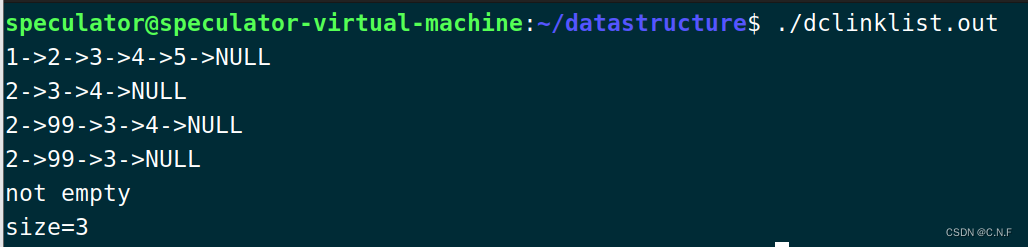
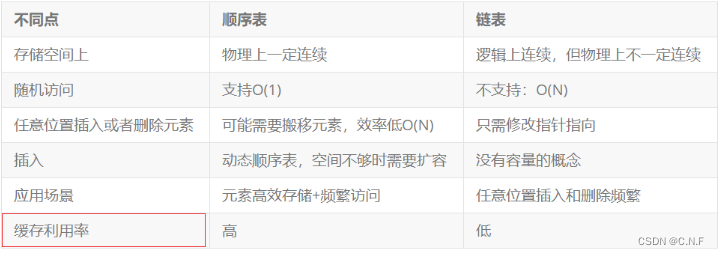
三、顺序表和(双向循环)链表的对比
























 284
284











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










