前言
我们知道,JDBC就是java后台连接数据库的纽带,当这个纽带连接上后,我们可以使用java语句去操控数据库信息,这个系统化的连接方式我们经常会使用,如果每次都要重写一遍那么多行代码,未免太麻烦了,因此,可以写一个方法,方法体就是获得一个Collection实例,而不仅仅是获取连接可以封装,任何经常写的代码都可以封装。在需要使用他的时候只需要调用某个方法就能快速得到我们想要的数据简化代码,提高代码复用性。
一,封装getCollection方法
有个jdbc.properties文件,里面存储着驱动地址,url,username,password,如何获得该文件的这些创建Collection实例必备的信息,来获得连接呢
jdbc.properties文件位置在src目录下,或者resources资源目录下,jdbc.properties文件内容如下
driverClass=com.mysql.jdbc.Driver
jdbcUrl=jdbc:mysql://localhost:3306/gp_01?serverTimezone=Asia/Shanghai&useUnicode=true&characterEncoding=utf8&useSSL=false
username=root
password=123456
public class JdbcUtils {
private static String driverClass;
private static String url;
private static String username;
private static String password;
//静态代码块,静态代码块在类文件加载阶段一定执行!!!并且有且只执行一次,用于程序初始化,预处理操作
static {
//1.获取properties文件
//JdbcUtils.class 反射知识,获得Class实例,即JdbcUtils类
//getClassLoader() 获得类加载器
InputStream resourceAsStream=JdbcUtils.class.getClassLoader().getResourceAsStream("jdbc.properties");
//2.创建Properties实例,底层是Map键值对存储
Properties properties = new Properties();
//3.加载properties文件
try {
properties.load(resourceAsStream);
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//4.将properties中的有效值提取出来
driverClass = properties.getProperty("driverClass");
url = properties.getProperty("jdbcUrl");
username = properties.getProperty("username");
password = properties.getProperty("password");
//5.加载驱动
try {
Class.forName(driverClass);
} catch (ClassNotFoundException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
//6.释放流资源
try {if(resourceAsStream != null)
resourceAsStream.close();
} catch (IOException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
}
//静态方法获得连接
public static Connection getConnection() throws SQLException {
return DriverManager.getConnection(url, username, password);
}
}
这样方法就封装好了,下面我们创建一个Collection试试效果,代码如下
public class MyTest {
@Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
//通过MyJdbcUtils调用静态方法,获得Collection实例
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
System.out.println(connection);
}
}
运行结果过如下
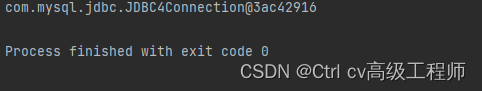
可以看到我们以后需要获得一个Collection实例,不再需要写一堆配置信息再去用户DriverManager获取,只需要让
JdbcUtils.getCollection(),就可以返回Collection实例。
二,封装获取PreparedStatement实例
2.1 PreparedStatement和Statement的区别
1. PreparedStatement需要的sql语句为用?(占位符)来替换值,并没有传入完整的sql语句,属于预编译。而Statement所需要的sql语句为字符串拼接
2. PreparedStatement在创建时就传入了一个sql模板,然后通过setString(int index,Object obj)给占位符?赋值,index 指的是第几个占位符,1开始,obj
是替代?的参数值,因为以及有了sql语句,后面调用executeQuery()和executeUpdate()就不需要再传入sql。也正是因为有了模板,后续给予不同参数使用它 时,使用相同模板,效率很高。而statement对于单次使用效率更高。
3. PreparedStatement解决了sql注入的问题,Statement没有解决,因为PreparedStatement有一个预编译的过程,
4. 就算传入占位符的数据中有sql关键字也都被认为是值。Statement所需要的是字符串拼接,传入的整个字符串被默认为sql语句,
如果用户手动拼接了字符串,那么会导致语句的改变
2.2 封装getPreparedStatement方法
代码如下
//Object... parameters 意思是多个Object类型数据
public static PreparedStatement getPreparedStatement(String sql,Connection connection,Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//获得元数据
ParameterMetaData parameterMetaData = preparedStatement.getParameterMetaData();
//获得字符串需要的参数个数
int count = parameterMetaData.getParameterCount();
//判断什么情况才需要给preparedStatement赋值
if(count != 0 && parameters != null && parameters.length == count){
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i + 1, parameters[i]);
}
}
return preparedStatement;
}
测试一下
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
String sql = "select * from student where name = ?";
PreparedStatement statement = JdbcUtils.getPreparedStatement(sql, connection, "skr");
System.out.println(statement);
}
}
运行结果如下
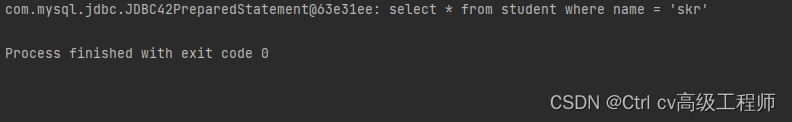
运行成功,这下我们获得PreparedStatement实例也简单了许多,只需要JdbcUtils调用getPreparedStatement方法
三. 封装关闭资源方法close
首先我们需要知道为什么需要封装这个方法,因为JDBC的资源关闭不想javase那样有jvm垃圾回收机制,资源会自动关闭,jdbc没有这个功能,而大量资源如果不关闭的话,会一直占用数据库大量的内存资源。我们应该知道资源的关闭也遵循那句话:先来后走,因此,当collection,statement,resultSet三个资源同时存在时,我们应该安装resultSet,statement,collection的顺序关闭,下面让我们来定义一个通用的关闭资源方法。
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement) {
close(statement, connection);
}
public static void close(Connection connection, Statement statement, ResultSet resultSet) {
close(resultSet, statement, connection);
}
//AutoCloseable... resources:多个AutoCloseable实例,通过源码我们可以知道collection,statement,resultSet都是 AutoCloseable的子类
static void close(AutoCloseable... resources) {
if (resources != null && resources.length > 0) {
Arrays.stream(resources).forEach(source -> {
try {
if (source != null) {
source.close();
}
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
});
}
}
当我们调用close()方法,传入两个或者三个AutoCloseable子类实例,会自动调用静态通用方法close,从而达到关闭资源的效果。
四. 封装update方法
不多说代码如下
public int update1(String sql,Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
//调用方法获得连接
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
//预加载
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = connection.prepareStatement(sql);
//获得需要的字符串参数个数
int num = preparedStatement.getParameterMetaData().getParameterCount();
//验证是否需要遍历给?赋值
if (num != 0 && parameters != null && parameters.length == num) {
//遍历参数
for (int i = 0; i < num; i++) {
preparedStatement.setObject(i+1,parameters[i]);
}}
//注:上面的代码可以替换成JdbcUtils.getPreparedStatement()方法,同样可以的到preparedStatement
//开始操作,并返回影响行数,
int s = preparedStatement.executeUpdate();
//关闭资源
JdbcUtils.close(connection,preparedStatement )
//返回影响数
return s ;
}
以后我们想要通过JDBC修改数据库数据,只需要调用这个方法就好了
测试代码如下
public class Test {
@org.junit.Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
int skr = JdbcUtils.update1("update student set age = ? where name = ?", 11, "skr");
System.out.println(skr);
}
}
运行结果如下
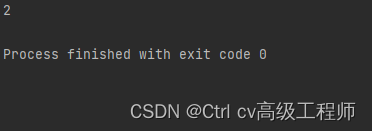
该update1()方法不仅可以使用修改数据库数据,还可以增添和删除数据,当然这些功能也可以归纳为修改数据。
五,封装select查询方法
这是一个非常重要方法,将使用jdbc操作数据库,查询出满足要求的字段和数据。对于数据的返回形式我们也可以加以一定的约束,这样不仅提高了方法的通用性,还提高了代码的规范性。返回数据类型可以归纳为以下六类
 下面来一一实现
下面来一一实现
5.1JavaBean规范对象
调用该方法时传入一个泛型类,在将查询结果以指定类的形式返回
public <T> T queryBean(String sql, Class<T> cls, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
// 1. 必要变量
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
// 【核心】泛型变量,泛型对应的具体数据类型由 Class<T> cls 约束
T t = null;
// 2. 获取数据库连接
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
try {
statement = getPreparedStatement(connection, sql, parameters);
// 4. 执行查询操作,得到 ResultSet 结果集对象
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
// 【核心】获取结果集元数据
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
while (resultSet.next()) { //resultSet结果集中有个指针,指针下移指向结果集的下一行元素,且若有元素返回true
// 实例化泛型约束之后对应具体数据类型对象
t = cls.getConstructor().newInstance();
// 字段个数
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
for (int i = 1; i <= columnCount; i++) {
BeanUtils.setProperty(t,
// 符合 JavaBean 规范对象,具体数据类型有 Class<T> cls
metaData.getColumnName(i),
// 从结果集元数据对象中,根据字段下标获取对应的字段名称,若数据表字段名称和类的属性名称不一致,则类属性获取不到数据库对应的值
resultSet.getObject(i));
// 从 ResultSet 结果集中,根据下标获取数据内容,返回值为 Object 类型
}
}
} catch (SQLException e) {
// SQL 异常,保留原类型进行抛出操作
throw e;
} catch (NoSuchMethodException | InstantiationException | IllegalAccessException | InvocationTargetException e) {
// 反射操作异常,包装为 RuntimeException 运行时异常 抛出
throw new RuntimeException(e);
} finally {
JdbcUtils.close(connection, statement, resultSet);
}
return t;
}
测试
@Test
public void test() throws SQLException {
Object tselect = super.queryBean("select * from student where id = ?", Student.class, 1);
System.out.println(tselect);
}
运行结果如下
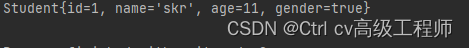
5.2 queryBeanList
传入泛型类,以指定类的集合List形式返回
public <T> List<T> queryBeanList(String sql, Class<T> cls, Object... parameters) throws SQLException, NoSuchMethodException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Connection connection = null;
PreparedStatement statement = null;
ResultSet resultSet = null;
//创建List集合
ArrayList<T> arrayList = new ArrayList<>();
connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
statement = getPreparedStatement(connection, sql, parameters);
resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
while (resultSet.next()){
T t = cls.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < count;i++) {
BeanUtils.setProperty(t,
metaData.getColumnName(i+1),
resultSet.getObject(i + 1));
}
arrayList.add(t);
}
JdbcUtils.close(connection,statement,resultSet);
return arrayList;
}
测试代码
@Test
public void test2() throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
for (Object o : super.queryBeanList(“select * from student where name = ?”, Student.class, “skr”)) {
System.out.println(o);
}
}
运行结果
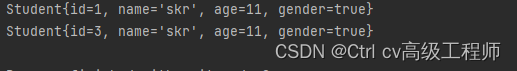
5.3 queryMap
返回数据以Map<String,Object>形式储存
public Map<String, Object> queryMap(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, IllegalAccessException {
Connection connection1 = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = getPreparedStatement(connection1, sql, parameters);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
//创建Map集合
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
while (resultSet.next()) {
for (int i = 0; i < count; i++) {
//向集合中添加数据
map.put(metaData.getColumnName(i + 1), resultSet.getObject(i + 1));
}
}
JdbcUtils.close(connection1,preparedStatement,resultSet);
return map;
}
测试代码
@Test
public void test4() throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Map map = super.queryMap("select * from student where name = ?", "skr");
System.out.println(map);
}
运行结果
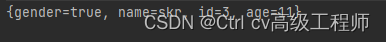
5.4 queryMapList
以List<Map<String,Object>>形式返回
public ArrayList<Map> queryMapList(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = getPreparedStatement(connection, sql, parameters);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
//创建List集合,里面的每个元素都是Map集合形式
ArrayList<Map> maps = new ArrayList<>();
while (resultSet.next()){
HashMap<String, Object> map = new HashMap<>();
for (int i = 1; i<= count;i++){
map.put(metaData.getColumnName(i), resultSet.getObject(i));
}
maps.add(map);
}
JdbcUtils.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
return maps;
}
测试代码
@Test
public void test5() throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
for (Object skr : super.queryMapList("select * from student where name = ?", "skr")) {
System.out.println(skr);
}
}
运行结果
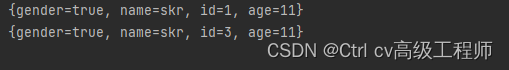
5.5 queryArray
结果以数组形式保存
public Object[] queryArray(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = handlePreparedStatement(connection, sql, parameters);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
//创建数组
Object[] o = new Object[count];
while (resultSet.next()){
for (int i =0;i<count;i++) {
o[i] = resultSet.getObject(i+1);
}
}
JdbcUtils.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
return o;
}
测试代码
@Test
public void test6() throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
for (Object skr : super.queryArray("select * from student where name = ?", "skr")) {
System.out.println(skr);
}
}
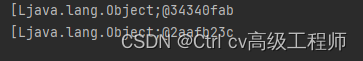
运行结果

数组遍历
5.6 querryArrayList
结果以List<Object[]>形式返回,List集合里的元素都是数组
public List<Object[]> queryArrayList(String sql, Object... parameters) throws SQLException {
Connection connection = JdbcUtils.getConnection();
PreparedStatement preparedStatement = getPreparedStatement(connection, sql, parameters);
ResultSet resultSet = preparedStatement.executeQuery();
ResultSetMetaData metaData = resultSet.getMetaData();
//创建集合
List<Object[]> objects = new ArrayList<>();
int count = metaData.getColumnCount();
while (resultSet.next()){
Object[] o = new Object[count];
for (int i =0;i<count;i++) {
o[i] = resultSet.getObject(i+1);
}
objects.add(o);
}
JdbcUtils.close(connection,preparedStatement,resultSet);
return objects;
}
}
测试代码
@Test
public void test7() throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
for (Object skr : super.queryArrayList(“select * from student where name = ?”, “skr”)) {
System.out.println(skr);
}
}
结果
六, 究极封装,一个方法得到任何你想要的数据类型返回值
通过上面的六个封装方法,我们想得到某个返回形式的数据,只需要调用对应的方法,你可能觉得已经很方便了,但是我想说远不止于此:只需一个方法就可实现实现上述功能。
大致思路:首先我们需要定义一个接口,接口里定义一个方法,让不同的实现类去实现他,重写他,完成返回不同形式返回值的功能
6.1 首先定义一个接口
public interface ResultSetHandler <T>{
T handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException;
}
6.2 写一个通用类
我们发现无论返回什么样的形式的数据,他们相当一部分的代码是相同的(得到result结果集,关闭资源),这部分代码可以封装到一个方法里
代码如下
public class My<T>{
public T skr(String sql, ResultSetHandler<T> handler, Object... parameters) throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, NoSuchMethodException {
//获取statement
PreparedStatement statement = JdbcUtils.getPreparedStatement(sql, JdbcUtils.getConnection(), parameters);
//获取结果集
ResultSet resultSet = statement.executeQuery();
//调用handle方法得到指定泛型形式数据
T handle = handler.handle(resultSet);
//关闭资源
JdbcUtils.close(JdbcUtils.getConnection(),statement,resultSet);
//返回数据
return handle;
}
}
6.3 先写一个实现类,传入resultSet,返回指定形式数据
这个实现类返回的是Student实例对象
public class BeanHandler<T> implements ResultSetHandler {
//
因为handle()方法没法传入具体泛型类,我们需要在属性声明,从而引入
public final Class<T> clz;
//构造方法
public BeanHandler(Class<T> clz) {
this.clz = clz;
}
//重写方法
@Override
//传入resultSet结果集
public T handle(ResultSet rs) throws SQLException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException {
//定义泛型类实例
T bean= null;
//获得元数据
ResultSetMetaData metaData = rs.getMetaData();
//获得参赛个数
int columnCount = metaData.getColumnCount();
//赋值
while (rs.next()){
bean = clz.getConstructor().newInstance();
for (int i = 0; i < columnCount; i++){
BeanUtils.setProperty(bean,metaData.getColumnName(i+1),rs.getObject(i+1));
}
}
//返回数据
return bean;
}
}
接下来再写个测试方法测试一下
@Test
public void test8() throws SQLException, InvocationTargetException, NoSuchMethodException, InstantiationException, IllegalAccessException {
Object wudi = new My().skr(“select * from student where name = ?”, new BeanHandler(Student.class), “skr”);
System.out.println(wudi);
}
*通用类调用通用方法,传入参数,参数一是sql语句,参数二是接口实例,也就是不同的实现类,占位符数据
看到这里大家应该就明白为什么可以用一个方法实现返回不同类型数据的功能,关键就在于这个接口实现类,当我们传入不同的实现类,他所返回的数据类型也不一样
所以相同的道理,我们只需要再写五个不同的实现类,就不一一列举了,大家参考目录五和目录六自己动手
总结
封装真N13























 820
820











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








