A. Two Towers
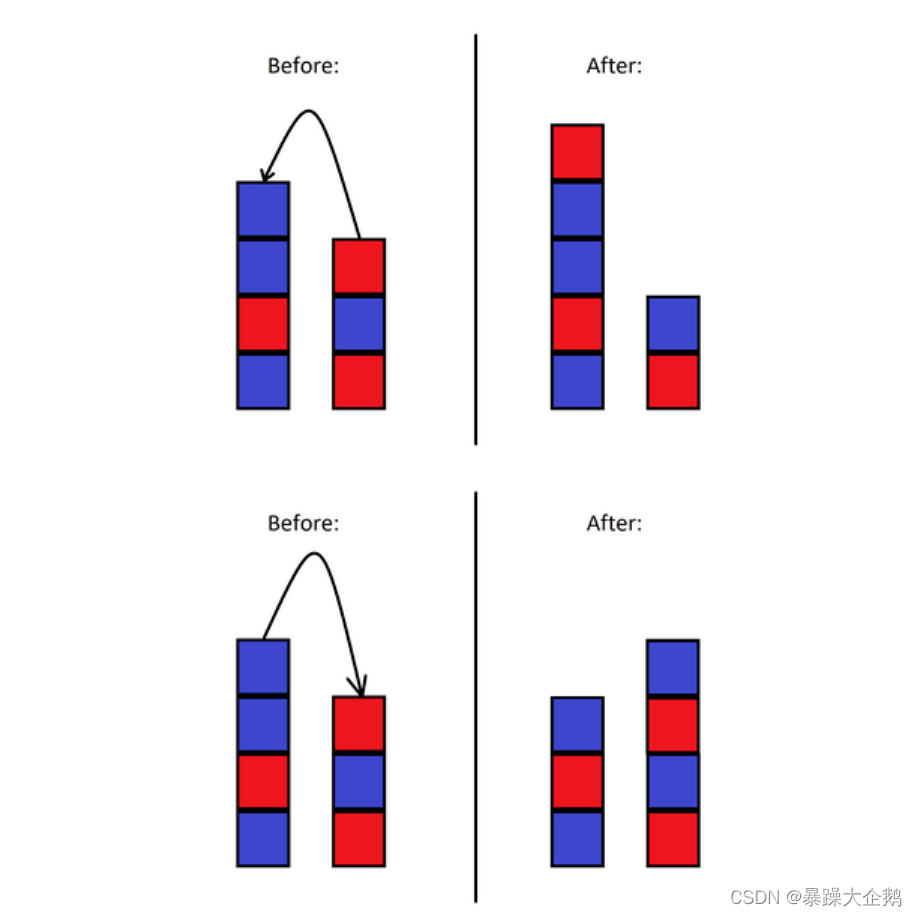
题解: 思维题,将A塔和B塔从塔顶处对接,遍历整个塔,记录相邻色块相同这种情况出现的次数k,如果k=1,输出YES,否则输出NO
//A
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int t, n, m;
int a[50];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t--){
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
char x;
cin >> x;
if (x == 'B')
a[i] = 0;
else
a[i] = 1;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= m; i++){
char x;
cin >> x;
if (x == 'B')
a[n + m - i + 1] = 0;
else
a[n + m - i + 1] = 1;
}
int k = 0;
for (int i = 2; i <= n + m; i++){
if (a[i] == a[i - 1]){
k++;
}
}
if (k > 1){
cout << "NO" << '\n';
}
else {
cout << "YES" << '\n';
}
}
} B. Ideal Point
题解:想要证明一个点x是Ideal Point,那么必然有一个区间的左端点等于x,有一个区间的右端点等于x,此时只要使用两个bool类型变量ok1,ok2记录是否出现这种情况即可
#include<bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int t, n, m;
int a[1000];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t--){
memset(a, 0, sizeof(a));
cin >> n >> m;
bool ok1 = 0, ok2 = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int x, y;
cin >> x >> y;
if (x == m){
ok1 = 1;
}
if (y == m){
ok2 = 1;
}
}
if (ok1 && ok2){
cout << "YES" << '\n';
}
else {
cout << "NO" << '\n';
}
}
} C. Tea Tasting

题解:这题是个缝合怪,前缀和,二分,差分都要用到,对于第i杯茶a[i],需要在区间[i,n+1]上使用二分,找到L,L是最后一个能完整喝上茶的人,此时需要有一个差分数组d,此时需要执行d[i]++, d[L+1]--,意思是从第i个人到第L个人能完整喝一个b[i],注意此时需要特判第L+1个人的答案,最后把差分数组还原输出答案
//C
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
int t, n;
int a[200001], b[200001], d[200001];
long long s[200001], ans[200001];
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> t;
while (t--){
memset(d, 0, sizeof(d));
memset(ans, 0, sizeof(ans));
cin >> n;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> a[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
cin >> b[i];
s[i] = s[i - 1] + b[i];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
int L = i, R = n + 1;
if (b[i] >= a[i]){
ans[i] += a[i];
}
else {
while (L + 1 < R){
int M = (L + R) / 2;
if (s[M] - s[i - 1] <= a[i]){
L = M;
}
else{
R = M;
}
}
d[i]++, d[L + 1]--;
if (L + 1 <= n){
ans[L + 1] += a[i] - (s[L] - s[i - 1]);
}
}
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
d[i] += d[i - 1];
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++){
ans[i] += 1LL * d[i] * b[i];
cout << ans[i] << " \n"[i == n];
}
}
}D. Triangle Coloring
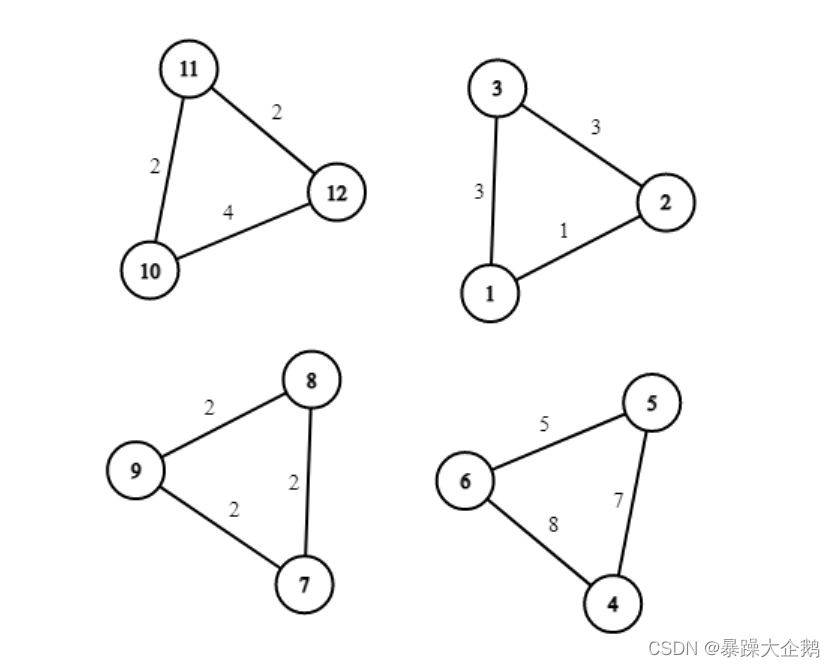
题解:题目思路非常清晰,难的是如何求解组合数,下面直接给出利用乘法逆元求解组合数C(a,b)的代码,其原理是扩展欧几里得定理和费马小定理,这里暂且当成一个模板函数使用,具体详解后期再补
//乘法逆元求组合数
int inv(int a){
return a == 1 ? 1 : (long long)(P - P / a) * inv(P % a) % P;
}
long long C(long long m, long long n){
if (m < 0)
return 0;
if (n < m)
return 0;
if (m > n - m)
m = n - m;
long long up = 1, down = 1;
for (long long i = 0; i < m; i++){
up = up * (n - i) % P;
down = down * (i + 1) % P;
}
return up * inv(down) % P;
}//D
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
const int P = 998244353;
int n;
int a[10];
int inv(int a){
return a == 1 ? 1 : (long long)(P - P / a) * inv(P % a) % P;
}
long long C(long long m, long long n){
if (m < 0)
return 0;
if (n < m)
return 0;
if (m > n - m)
m = n - m;
long long up = 1, down = 1;
for (long long i = 0; i < m; i++){
up = up * (n - i) % P;
down = down * (i + 1) % P;
}
return up * inv(down) % P;
}
int main(){
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
cin >> n;
unsigned long long ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 3){
cin >> a[0] >> a[1] >> a[2];
sort(a, a + 3);
if (a[0] == a[1] && a[1] == a[2]){
ans = ans * 3 % P;
}
if (a[0] == a[1] && a[1] < a[2]){
ans = ans * 2 % P;
}
}
ans = ans * C(n / 6, n / 3) % P;
cout << ans << '\n';
}还有一种方法,不过这种方法只可远观而不可亵玩焉,这是tourist的求解组合数模板,长达200行,不过用起来相当方便
//tourist模板
#include <bits/stdc++.h>
using namespace std;
#ifdef LOCAL
#include "algo/debug.h"
#else
#define debug(...) 42
#endif
template <typename T>
T inverse(T a, T m) {
T u = 0, v = 1;
while (a != 0) {
T t = m / a;
m -= t * a; swap(a, m);
u -= t * v; swap(u, v);
}
assert(m == 1);
return u;
}
template <typename T>
class Modular {
public:
using Type = typename decay<decltype(T::value)>::type;
constexpr Modular() : value() {}
template <typename U>
Modular(const U& x) {
value = normalize(x);
}
template <typename U>
static Type normalize(const U& x) {
Type v;
if (-mod() <= x && x < mod()) v = static_cast<Type>(x);
else v = static_cast<Type>(x % mod());
if (v < 0) v += mod();
return v;
}
const Type& operator()() const { return value; }
template <typename U>
explicit operator U() const { return static_cast<U>(value); }
constexpr static Type mod() { return T::value; }
Modular& operator+=(const Modular& other) { if ((value += other.value) >= mod()) value -= mod(); return *this; }
Modular& operator-=(const Modular& other) { if ((value -= other.value) < 0) value += mod(); return *this; }
template <typename U> Modular& operator+=(const U& other) { return *this += Modular(other); }
template <typename U> Modular& operator-=(const U& other) { return *this -= Modular(other); }
Modular& operator++() { return *this += 1; }
Modular& operator--() { return *this -= 1; }
Modular operator++(int) { Modular result(*this); *this += 1; return result; }
Modular operator--(int) { Modular result(*this); *this -= 1; return result; }
Modular operator-() const { return Modular(-value); }
template <typename U = T>
typename enable_if<is_same<typename Modular<U>::Type, int>::value, Modular>::type& operator*=(const Modular& rhs) {
#ifdef _WIN32
uint64_t x = static_cast<int64_t>(value) * static_cast<int64_t>(rhs.value);
uint32_t xh = static_cast<uint32_t>(x >> 32), xl = static_cast<uint32_t>(x), d, m;
asm(
"divl %4; \n\t"
: "=a" (d), "=d" (m)
: "d" (xh), "a" (xl), "r" (mod())
);
value = m;
#else
value = normalize(static_cast<int64_t>(value) * static_cast<int64_t>(rhs.value));
#endif
return *this;
}
template <typename U = T>
typename enable_if<is_same<typename Modular<U>::Type, long long>::value, Modular>::type& operator*=(const Modular& rhs) {
long long q = static_cast<long long>(static_cast<long double>(value) * rhs.value / mod());
value = normalize(value * rhs.value - q * mod());
return *this;
}
template <typename U = T>
typename enable_if<!is_integral<typename Modular<U>::Type>::value, Modular>::type& operator*=(const Modular& rhs) {
value = normalize(value * rhs.value);
return *this;
}
Modular& operator/=(const Modular& other) { return *this *= Modular(inverse(other.value, mod())); }
friend const Type& abs(const Modular& x) { return x.value; }
template <typename U>
friend bool operator==(const Modular<U>& lhs, const Modular<U>& rhs);
template <typename U>
friend bool operator<(const Modular<U>& lhs, const Modular<U>& rhs);
template <typename V, typename U>
friend V& operator>>(V& stream, Modular<U>& number);
private:
Type value;
};
template <typename T> bool operator==(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return lhs.value == rhs.value; }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator==(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return lhs == Modular<T>(rhs); }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator==(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) == rhs; }
template <typename T> bool operator!=(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return !(lhs == rhs); }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator!=(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return !(lhs == rhs); }
template <typename T, typename U> bool operator!=(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return !(lhs == rhs); }
template <typename T> bool operator<(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return lhs.value < rhs.value; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator+(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) += rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator+(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) += rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator+(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) += rhs; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator-(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) -= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator-(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) -= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator-(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) -= rhs; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator*(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) *= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator*(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) *= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator*(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) *= rhs; }
template <typename T> Modular<T> operator/(const Modular<T>& lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) /= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator/(const Modular<T>& lhs, U rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) /= rhs; }
template <typename T, typename U> Modular<T> operator/(U lhs, const Modular<T>& rhs) { return Modular<T>(lhs) /= rhs; }
template<typename T, typename U>
Modular<T> power(const Modular<T>& a, const U& b) {
assert(b >= 0);
Modular<T> x = a, res = 1;
U p = b;
while (p > 0) {
if (p & 1) res *= x;
x *= x;
p >>= 1;
}
return res;
}
template <typename T>
bool IsZero(const Modular<T>& number) {
return number() == 0;
}
template <typename T>
string to_string(const Modular<T>& number) {
return to_string(number());
}
// U == std::ostream? but done this way because of fastoutput
template <typename U, typename T>
U& operator<<(U& stream, const Modular<T>& number) {
return stream << number();
}
// U == std::istream? but done this way because of fastinput
template <typename U, typename T>
U& operator>>(U& stream, Modular<T>& number) {
typename common_type<typename Modular<T>::Type, long long>::type x;
stream >> x;
number.value = Modular<T>::normalize(x);
return stream;
}
constexpr int md = 998244353;
using Mint = Modular<std::integral_constant<decay<decltype(md)>::type, md>>;
int main() {
ios::sync_with_stdio(false);
cin.tie(0);
int n;
cin >> n;
Mint ans = 1;
for (int i = 0; i < n; i += 3) {
vector<int> a(3);
for (int j = 0; j < 3; j++) {
cin >> a[j];
}
sort(a.begin(), a.end());
if (a[0] < a[1]) {
ans *= 1;
}
if (a[0] == a[1] && a[1] < a[2]) {
ans *= 2;
}
if (a[0] == a[1] && a[1] == a[2]) {
ans *= 3;
}
}
for (int i = n / 6 + 1; i <= n / 3; i++) {
ans *= i;
}
for (int i = 1; i <= n / 6; i++) {
ans /= i;
}
cout << ans << '\n';
return 0;
}





















 3159
3159











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








