前言
WebSocket是一种在网络应用程序中,使客户度端和服务器之间可以进行双向通信的协议。它允许数据可以在建立连接后进行实时交换,而不必依赖传统的HTTP请求-响应模式。WebSocket使得客户端和服务器之间的数据交换变得更加简单,允许服务端主动向客户端推送数据。
在WebSocket API中,浏览器和服务器只需要完成一次握手,两者之间就直接可以创建持久性的连接,并进行双向数据传输。
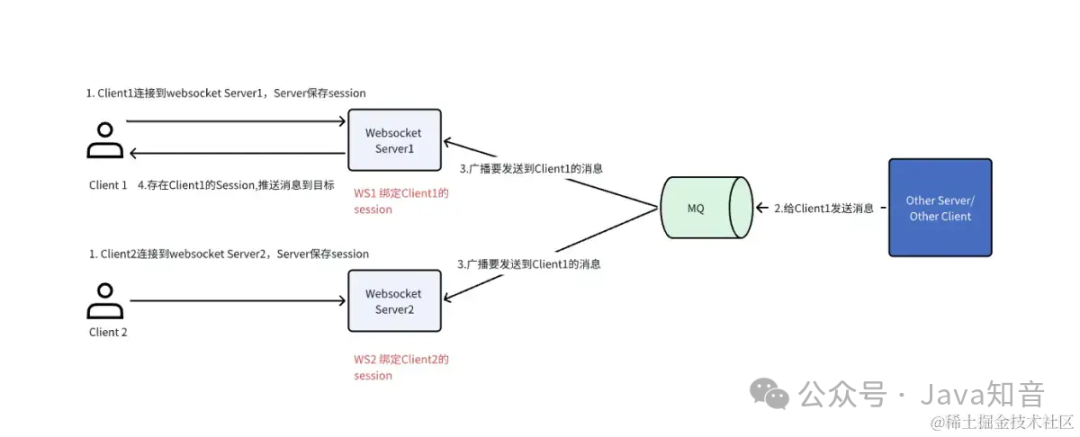
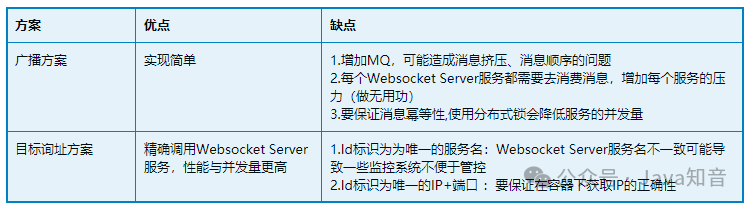
方案一:广播方案
-
Step1: 客户端连接到某个Websocket Server,在该websocket Server中建立userid和session的绑定关系
-
Step2: 其它服务或者客户端通过MQ广播消息所有Websocket Server(消息体中带有userid)
-
Step3: 所有Websocket Server 根据客户端userid找到对应session, 只有存在userid和session的绑定关系的Websocket Server才发送消息到客户端
代码演示
1.Websocket Server 建立userid和session的绑定关系
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{businessType}/{userId}")
@Component
public class WebSocketServer {
/**
* 若要实现服务端与单一客户端通信的话,可以使用Map来存放,其中Key可以为用户标识
* 注意:allSession 只记录当前机器的 客户端连接,不是所有session连接
*/
public static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Session> allSession = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
@Resource
private RedisService redisService;
/**
* 连接建立成功调用的方法
*
* @param session 可选的参数。session为与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(@PathParam(value = "businessType") String businessType, @PathParam(value = "userId") String userId, Session session, EndpointConfig config) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(userId)) {
return;
}
/**
* 加入到本地map
*/
allSession.put(userId, session);
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose(@PathParam(value = "userId") String userId, Session session) {
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(userId)) {
allSession.remove(userId);
}
}
/**
* 发生错误时调用
*
* @param
* @param
*/
@OnError
public void onError(@PathParam(value = "userId") String userId, Session session, Throwable error) {
}
/**
* 用户id
*
* @param userId
* @param message
*/
public void sendMessageToOneUser(Integer userId, String message, String msgId) {
if (userId == null) {
return;
}
Session session = allSession.get(String.valueOf(userId));
if (session != null) {
//所有Websocket Server 根据客户端userid找到对应session, 只有存在userid和session的绑定关系的Websocket Server才发送消息到客户端
session.getAsyncRemote().sendText(message);
} else {
System.err.println("session为空");
allSession.remove(userId + "");
}
}
}
2.所有Websocket Server 接收消息并处理
@Component
@RequiredArgsConstructor
public class CreateOrderConsumer implements BaseConsumer {
private final WebSocketServer webSocketServer;
@Override
public Action handleMessage(Message message) {
CreateOrderMessage createOrderMessage = JSON.parseObject(message.getBody(), LinkCreateOrderMessage.class);
try {
//业务校验省略...
//调用WebSocketServer的sendMessageToOneUser方法,里面根据客户端userid找到对应session, 只有存在userid和session的绑定关系的Websocket Server才发送消息到客户端
webSocketServer.sendMessageToOneUser(createOrderMessage.getUserId(), JSON.toJSONString(linkActionRes),message.getMsgID());
} catch (Exception e) {
e.printStackTrace();
return Action.ReconsumeLater;
}
return Action.CommitMessage;
}
}
方案二:目标询址方案(推荐)
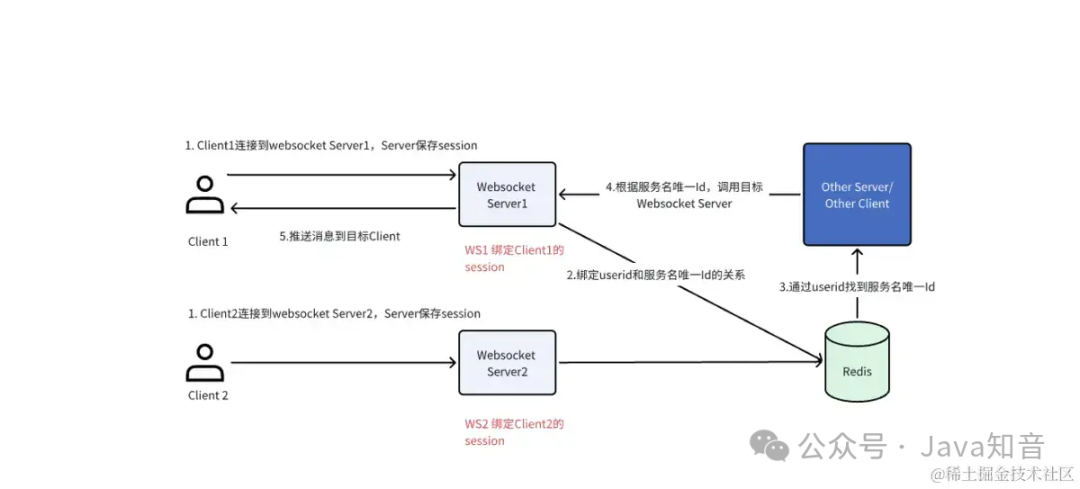
Id标识有两种实现形式:
-
为唯一的服务名:每一个WebSocketServer生成唯一的服务名(
serviceName="XXX-" + IdUtil.oneId())并注册到naocs服务组册中心,uesrid与其绑定,服务适用方使用Feign 或其它RPC调用http://{serviceName}/xxx/xxx到指定WebSocketServer -
为唯一的IP+端口:每一个WebSocketServer 获取自己IP+端口,uesrid与其绑定,服务调用方使用该IP+端口
代码演示(唯一Id为唯一的服务名的形式)
1.绑定userid和服务名唯一Id的关系(以ApplicationName形式为例)
@SpringBootApplication
public class WsApplication {
public static void main(String[] args) {
//动态服务名
System.setProperty("myApplicationName", "WS-" + IdUtil.oneId());
SpringApplication.run(WsApplication.class, args);
}
}
spring:
application:
#随机名字,做ws集群使用
name: ${myApplicationName}
@ServerEndpoint("/websocket/{businessType}/{userId}")
@Component
public class WebSocketServer {
/**
* 若要实现服务端与单一客户端通信的话,可以使用Map来存放,其中Key可以为用户标识
* 注意:allSession 只记录当前机器的 客户端连接,不是所有session连接
*/
public static ConcurrentHashMap<String, Session> allSession = new ConcurrentHashMap<>();
/**
*
*/
private String myApplicationName = System.getProperty("myApplicationName");
@Resource
private RedisService redisService;
/**
* 连接建立成功调用的方法
* 关键代码
* @param session 可选的参数。session为与某个客户端的连接会话,需要通过它来给客户端发送数据
*/
@OnOpen
public void onOpen(@PathParam(value = "businessType") String businessType, @PathParam(value = "userId") String userId, Session session, EndpointConfig config) {
if (StringUtils.isEmpty(userId)) {
return;
}
/**
* 加入到本地map
*/
allSession.put(userId, session);
//绑定userid和服务名唯一Id的关系
redisService.hset(WS_MAPPING, userId + "", myApplicationName);
}
/**
* 连接关闭调用的方法
*/
@OnClose
public void onClose(@PathParam(value = "userId") String userId, Session session) {
if (StringUtils.isNotEmpty(userId)) {
allSession.remove(userId);
}
}
/**
* 发生错误时调用
*
* @param
* @param
*/
@OnError
public void onError(@PathParam(value = "userId") String userId, Session session, Throwable error) {
}
/**
* 用户id
*
* @param userId
* @param message
*/
public void sendMessageToOneUser(Integer userId, String message) {
if (userId == null) {
return;
}
Session session = allSession.get(String.valueOf(userId));
if (session != null) {
//所有Websocket Server 根据客户端userid找到对应session, 只有存在userid和session的绑定关系的Websocket Server才发送消息到客户端
session.getAsyncRemote().sendText(message);
} else {
System.err.println("session为空");
allSession.remove(userId + "");
}
}
}
2.Websocket Server提供的调用接口
@RestController
@RequestMapping("push")
public class WebSocketPushController {
@PostMapping("{userId}")
public void pushMessage(@PathVariable Long userId, @RequestBody Object message) {
webSocketServer.sendMessageToOneUser(userId, message);
}
}
3.调用方通过nacos调用目标Websocket Server
//业省略
MyApplicationName myApplicationName = redisService.hget(WS_MAPPING, userId + "");
Feign:
http://${myApplicationName}/push/{userId}
来源:juejin.cn/post/7306451559928348709




















 4119
4119











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








