一、MongoDB批量操作
MongoDB对数据的操作分为Read Operations和Write Operations,Read Operations包含查询操作,Write Operations包含删除、插入、替换、更新几种操作。MongoDB提供客户端用bulk方式执行Write Operations,也就是批量写操作。在java driver中,对应MongoCollection的bulkWrite()方法,先来看下这个方法签名:
BulkWriteResult com.mongodb.client.MongoCollection.bulkWrite(List<? extends WriteModel<? extends Document>> requests)
这个方法要求传入一个List集合,集合中的元素类型为WriteModel,它表示一个可用于批量写操作的基类模型,它有以下几个子类DeleteManyModel、DeleteOneModel、 InsertOneModel、ReplaceOneModel、 UpdateManyModel、UpdateOneModel,从名字可以看出来它对应了删除、插入、替换、更新几种操作。该方法返回一个BulkWriteResult对象,代表一个成功的批量写操作结果,封装了操作结果的状态信息,如插入、更新、删除记录数等。
1、插入操作
(1)、批量插入
代码如下,该方法接收一个包含要进行插入的Document对象的集合参数,遍历集合,使用Document构造InsertOneModel对象,每个InsertOneModel实例代表一个插入单个Document的操作,然后将该实例添加List集合中,调用bulkWrite()方法,传入存储所有插入操作的List集合完成批量插入。
public void bulkWriteInsert(List<Document> documents){
List<WriteModel<Document>> requests = new ArrayList<WriteModel<Document>>();
for (Document document : documents) {
//构造插入单个文档的操作模型
InsertOneModel<Document> iom = new InsertOneModel<Document>(document);
requests.add(iom);
}
BulkWriteResult bulkWriteResult = collection.bulkWrite(requests);
System.out.println(bulkWriteResult.toString());
}
测试:下面通过一个main函数测试下。首先构造10万个Product实体对象,使用一个工具类将其转换成json字符串,然后解析成Document对象,保存到一个list集合中,然后调用上面编写的方法测试10万个对象插入时间。
TestMongoDB instance = TestMongoDB.getInstance();
ArrayList<Document> documents = new ArrayList<Document>();
for (int i = 0; i < 100000; i++) {
Product product = new Product(i,"书籍","追风筝的人",22.5);
//将java对象转换成json字符串
String jsonProduct = JsonParseUtil.getJsonString4JavaPOJO(product);
//将json字符串解析成Document对象
Document docProduct = Document.parse(jsonProduct);
documents.add(docProduct);
}
System.out.println("开始插入数据。。。");
long startInsert = System.currentTimeMillis();
instance.bulkWriteInsert(documents);
System.out.println("插入数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startInsert)+"毫秒");
结果:1560毫秒,多次测试基本在1.5秒左右

(2)、逐条插入
下面再通过非批量插入10万个数据对比下,方法如下:
public void insertOneByOne(List<Document> documents) throws ParseException{
for (Document document : documents){
collection.insertOne(document);
}
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("开始插入数据。。。");
long startInsert = System.currentTimeMillis();
instance.insertOneByOne(documents);
System.out.println("插入数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startInsert)+"毫秒");
结果:12068毫秒,差距非常大。由此可见,MongoDB批量插入比逐条数据插入效率提高了非常多。

补充:
MongoCollection的insertMany()方法和bulkWrite()方法是等价的,测试时间差不多,不再贴图。
public void insertMany(List<Document> documents) throws ParseException{
//和bulkWrite()方法等价
collection.insertMany(documents);
}
2、删除操作
(1)、批量删除
掌握了批量插入,批量删除就是依葫芦画瓢了。构造DeleteOneModel需要一个Bson类型参数,代表一个删除操作,这里使用了Bson类的子类Document。重点来了,这里的删除条件使用文档的_id字段,该字段在文档插入数据库后自动生成,没插入数据库前document.get("_id")为null,如果使用其他条件比如productId,那么要在文档插入到collection后在productId字段上添加索引
collection.createIndex(new Document("productId", 1));
因为随着collection数据量的增大,查找将越耗时,添加索引是为了提高查找效率,进而加快删除效率。另外,值得一提的是DeleteOneModel表示至多删除一条匹配条件的记录,DeleteManyModel表示删除匹配条件的所有记录。为了防止一次删除多条记录,这里使用DeleteOneModel,保证一个操作只删除一条记录。当然这里不可能匹配多条记录,因为_id是唯一的。
最新 MySQL 面试题整理好了,点击Java面试库小程序在线刷题。
public void bulkWriteDelete(List<Document> documents){
List<WriteModel<Document>> requests = new ArrayList<WriteModel<Document>>();
for (Document document : documents) {
//删除条件
Document queryDocument = new Document("_id",document.get("_id"));
//构造删除单个文档的操作模型,
DeleteOneModel<Document> dom = new DeleteOneModel<Document>(queryDocument);
requests.add(dom);
}
BulkWriteResult bulkWriteResult = collection.bulkWrite(requests);
System.out.println(bulkWriteResult.toString());
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("开始删除数据。。。");
long startDelete = System.currentTimeMillis();
instance.bulkWriteDelete(documents);
System.out.println("删除数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startDelete)+"毫秒");
结果:2251毫秒

(2)、逐条删除
来看看在非批量下的删除
public void deleteOneByOne(List<Document> documents){
for (Document document : documents) {
Document queryDocument = new Document("_id",document.get("_id"));
DeleteResult deleteResult = collection.deleteOne(queryDocument);
}
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("开始删除数据。。。");
long startDelete = System.currentTimeMillis();
instance.deleteOneByOne(documents);
System.out.println("删除数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startDelete)+"毫秒");
结果:12765毫秒,比批量删除效率低很多
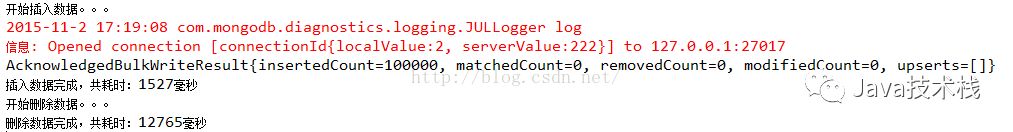
3、更新操作
(1)、批量更新
再来看看批量更新,分UpdateOneModel和UpdateManyModel两种,区别是前者更新匹配条件的一条记录,后者更新匹配条件的所有记录。对于ReplaceOneModel,表示替换操作,这里也归为更新,现在以UpdateOneModel为例进行讲解。UpdateOneModel构造方法接收3个参数,第一个是查询条件,第二个参数是要更新的内容,第三个参数是可选的UpdateOptions,不填也会自动帮你new一个,代表批量更新操作未匹配到查询条件时的动作,它的upser属性值默认false,什么都不干,true时表示将一个新的Document插入数据库,这个新的Document是查询Document和更新Document的结合,但如果是替换操作,这个新的Document就是这个替换Document。
这里会有个疑惑:这和匹配到查询条件后执行替换操作结果不一样吗?区别在于_id字段,未匹配查询条件时插入的新的Document的_id是新的,而成功执行替换操作,_id是原先旧的。
public void bulkWriteUpdate(List<Document> documents){
List<WriteModel<Document>> requests = new ArrayList<WriteModel<Document>>();
for (Document document : documents) {
//更新条件
Document queryDocument = new Document("_id",document.get("_id"));
//更新内容,改下书的价格
Document updateDocument = new Document("$set",new Document("price","30.6"));
//构造更新单个文档的操作模型
UpdateOneModel<Document> uom = new UpdateOneModel<Document>(queryDocument,updateDocument,new UpdateOptions().upsert(false));
//UpdateOptions代表批量更新操作未匹配到查询条件时的动作,默认false,什么都不干,true时表示将一个新的Document插入数据库,他是查询部分和更新部分的结合
requests.add(uom);
}
BulkWriteResult bulkWriteResult = collection.bulkWrite(requests);
System.out.println(bulkWriteResult.toString());
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("开始更新数据。。。");
long startUpdate = System.currentTimeMillis();
instance.bulkWriteUpdate(documents);
System.out.println("更新数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startUpdate)+"毫秒");
结果:3198毫秒
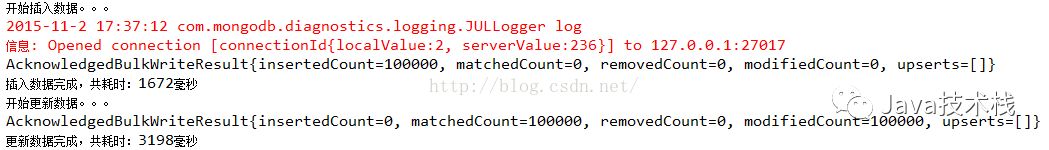
(2)、逐条更新
对比非批量下的更新
public void updateOneByOne(List<Document> documents){
for (Document document : documents) {
Document queryDocument = new Document("_id",document.get("_id"));
Document updateDocument = new Document("$set",new Document("price","30.6"));
UpdateResult UpdateResult = collection.updateOne(queryDocument, updateDocument);
}
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("开始更新数据。。。");
long startUpdate = System.currentTimeMillis();
instance.updateOneByOne(documents);
System.out.println("更新数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - startUpdate)+"毫秒");
结果:13979毫秒,比批量更新效率低很多

4、混合批量操作
bulkWrite()方法可以对不同类型的写操作进行批量处理,代码如下:
public void bulkWriteMix(){
List<WriteModel<Document>> requests = new ArrayList<WriteModel<Document>>();
InsertOneModel<Document> iom = new InsertOneModel<Document>(new Document("name","kobe"));
UpdateManyModel<Document> umm = new UpdateManyModel<Document>(new Document("name","kobe"),
new Document("$set",new Document("name","James")),new UpdateOptions().upsert(true));
DeleteManyModel<Document> dmm = new DeleteManyModel<Document>(new Document("name","James"));
requests.add(iom);
requests.add(umm);
requests.add(dmm);
BulkWriteResult bulkWriteResult = collection.bulkWrite(requests);
System.out.println(bulkWriteResult.toString());
}
注意:updateMany()、deleteMany()两个方法和insertMany()不同,它俩不是批量操作,而是代表更新(删除)匹配条件的所有数据。
最新 MySQL 面试题整理好了,点击Java面试库小程序在线刷题。
二、与MySQL性能对比
1、插入操作
(1)、批处理插入
与MongoDB一样,也是插入Product实体对象,代码如下
public void insertBatch(ArrayList<Product> list) throws Exception{
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement("insert into t_product value(?,?,?,?)");
int count = 1;
for (Product product : list) {
pst.setInt(1, product.getProductId());
pst.setString(2, product.getCategory());
pst.setString(3, product.getName());
pst.setDouble(4, product.getPrice());
pst.addBatch();
if(count % 1000 == 0){
pst.executeBatch();
pst.clearBatch();//每1000条sql批处理一次,然后置空PreparedStatement中的参数,这样也能提高效率,防止参数积累过多事务超时,但实际测试效果不明显
}
count++;
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
}
JDBC默认自动提交事务,切记在获取连接后添加下面一行代码,关闭事务自动提交。
connection.setAutoCommit(false);
测试:10万条数据
public static void main(String[] args) throws Exception {
TestMysql test = new TestMysql();
ArrayList<Product> list = new ArrayList<Product>();
for (int i = 0; i < 1000; i++) {
Product product = new Product(i, "书籍", "追风筝的人", 20.5);
list.add(product);
}
System.out.println("MYSQL开始插入数据。。。");
long insertStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.insertBatch(list);
System.out.println("MYSQL插入数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - insertStart)+"毫秒");
}
结果:7389毫秒,多次测试基本7秒左右
(2)、逐条插入
再来看看mysql逐条插入,代码如下:
public void insertOneByOne(ArrayList<Product> list) throws Exception{
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
for (Product product : list) {
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement("insert into t_product value(?,?,?,?)");
pst.setInt(1, product.getProductId());
pst.setString(2, product.getCategory());
pst.setString(3, product.getName());
pst.setDouble(4, product.getPrice());
pst.executeUpdate();
//conn.commit();//加上这句每次插入都提交事务,结果将是非常耗时
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
}
测试:10万条记录
System.out.println("MYSQL开始插入数据。。。");
long insertStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.insertOneByOne(list);
System.out.println("MYSQL插入数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - insertStart)+"毫秒");
结果:8921毫秒,基本比批量慢1秒多。
2、删除操作
(1)、批处理删除
删除的where条件是productId,这里在建表的时候没有添加主键,删除异常的慢,查了半天不知道什么原因。切记添加主键,主键默认有索引,所有能更快匹配到记录。
插播一条:如果你近期准备面试跳槽,建议在Java面试库小程序在线刷题,涵盖 2000+ 道 Java 面试题,几乎覆盖了所有主流技术面试题。
public void deleteBatch(ArrayList<Product> list) throws Exception{
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement("delete from t_product where id = ?");//按主键查,否则全表遍历很慢
int count = 1;
for (Product product : list) {
pst.setInt(1, product.getProductId());
pst.addBatch();
if(count % 1000 == 0){
pst.executeBatch();
pst.clearBatch();
}
count++;
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
}
测试:10万条数据。
System.out.println("MYSQL开始删除数据。。。");
long deleteStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.deleteBatch(list);
System.out.println("MYSQL删除数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - deleteStart)+"毫秒");
结果:7936毫秒
(2)、逐条删除
代码如下
public void deleteOneByOne(ArrayList<Product> list) throws Exception{
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
PreparedStatement pst = null;
try {
for (Product product : list) {
pst = conn.prepareStatement("delete from t_product where id = ?");
pst.setInt(1, product.getProductId());
pst.executeUpdate();
//conn.commit();//加上这句每次插入都提交事务,结果将是非常耗时
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("MYSQL开始删除数据。。。");
long deleteStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.deleteOneByOne(list);
System.out.println("MYSQL删除数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - deleteStart)+"毫秒");
结果:8752毫秒,比批处理删除慢一秒左右。
3、更新操作
(1)、批处理更新
代码如下
public void updateBatch(ArrayList<Product> list) throws Exception{
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement("update t_product set price=31.5 where id=?");
int count = 1;
for (Product product : list) {
pst.setInt(1, product.getProductId());
pst.addBatch();
if(count % 1000 == 0){
pst.executeBatch();
pst.clearBatch();//每1000条sql批处理一次,然后置空PreparedStatement中的参数,这样也能提高效率,防止参数积累过多事务超时,但实际测试效果不明显
}
count++;
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("MYSQL开始更新数据。。。");
long updateStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.updateBatch(list);
System.out.println("MYSQL更新数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - updateStart)+"毫秒");
结果:8611毫秒
(2)、逐条更新
代码如下
public void updateOneByOne(ArrayList<Product> list) throws Exception{
Connection conn = DBUtil.getConnection();
try {
for (Product product : list) {
PreparedStatement pst = conn.prepareStatement("update t_product set price=30.5 where id=?");
pst.setInt(1, product.getProductId());
pst.executeUpdate();
//conn.commit();//加上这句每次插入都提交事务,结果将是非常耗时
}
conn.commit();
} catch (SQLException e) {
e.printStackTrace();
}
DBUtil.closeConnection(conn);
}
测试:10万条数据
System.out.println("MYSQL开始更新数据。。。");
long updateStart = System.currentTimeMillis();
test.updateOneByOne(list);
System.out.println("MYSQL更新数据完成,共耗时:"+(System.currentTimeMillis() - updateStart)+"毫秒");
结果:9430毫秒,比批处理更新慢了1秒左右
三、总结
本文主要是为了介绍bulkWrite()方法的使用,也就是MongoDB的批量写操作,通过实验可以看出MongoDB使用bulkWrite()方法进行大量数据的写操作比使用常规的方法进行写操作效率要高很多。文章也介绍了mysql几种写操作下批量和非批量的对比,可以看出他们批处理方式比非批处理快点,但没有MongoDB那么明显。
对于MongoDB与mysql的比较,批量操作下,MongoDB插入、删除、更新都比mysql快,非批量操作下,MongoDB插入、删除、更新都比mysql慢。当然只是一个初略的结论,文中并没有进行100条、1000条、10000条或更大的这样不同的数据对比,以及CPU内存使用情况进行监测,有兴趣的可以尝试下。

























 1307
1307











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








