目录
博主不出意外地当几个月的鸽子,之前的博客一定会赶上的(咕咕)。

我们直接先开始C++的学习。
1.C++关键字
我们来看看C++的关键字,这里只是观看顺便方便后面复习。
| asm | do | if | return | try | continue |
| auto | double | inline | short | typedef | for |
| bool | dynammic_cast | int | signed | typeid | public |
| break | else | long | sizeof | typename | throw |
| case | enum | mutable | static | union | wchar_t |
| catch | explicit | namespace | static_cast | unsigned | default |
| chr | export | new | struct | using | friend |
| class | exturn | operator | switch | virtual | register |
| const | false | private | template | void | true |
| const_cast | float | protected | this | volatile | while |
| delete | goto | reinterpret_cast |
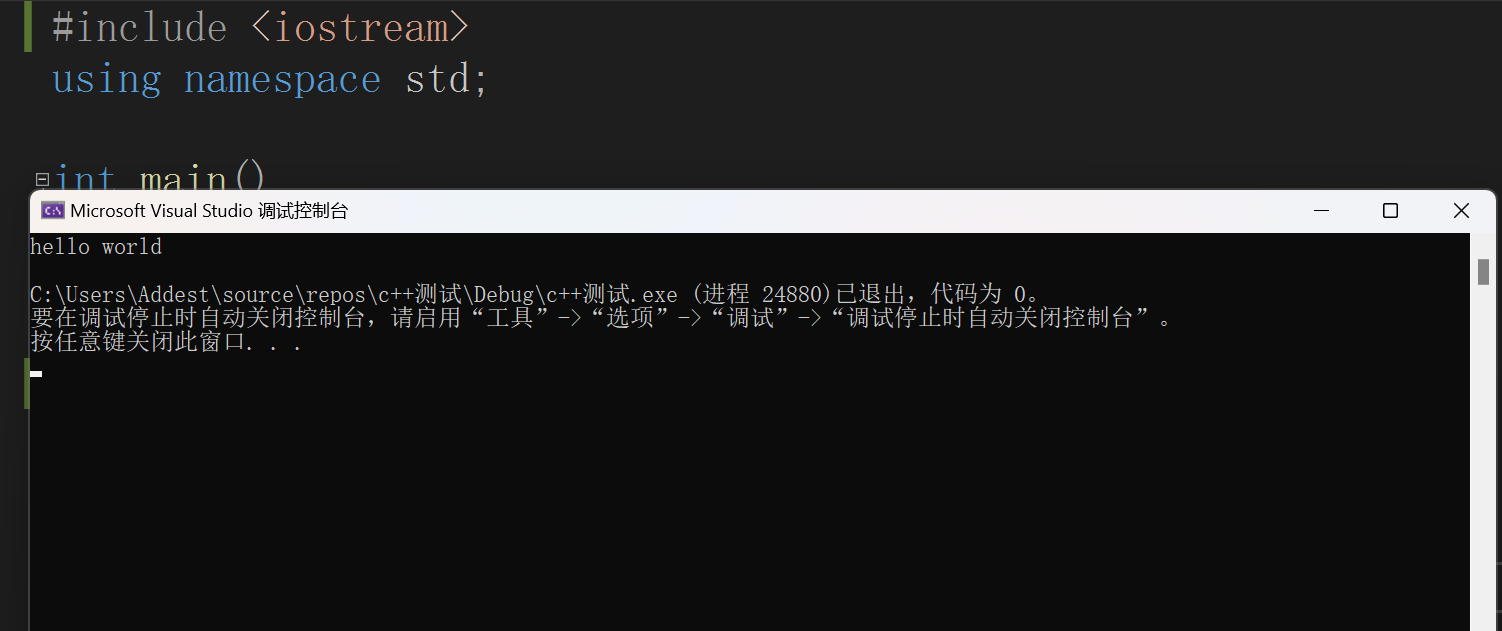
我们先从一段代码来了解C++,既然我们学C语言是从“hello world”开始的,那我们来看看C++是如何输出“hello world”的。
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
return 0;
}
2.命名空间 namespace
我们写一段c语言来了解命名空间的作用。
#include<stdio.h>
#include<stdlib.h>
int rand = 10;
int main()
{
printf("hello world\n");
printf("%d\n", rand);
return 0;
}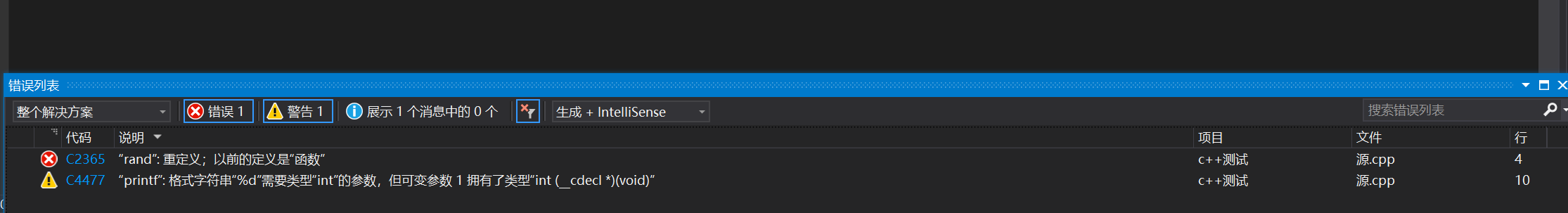
我们可以看见报错为重定义,这样的情况叫做命名冲突, 程序员 和 库 (这里是stdlib.h库里面的rand函数一样)还有一种情况就是发生在 程序员 和 程序员 之间(两个程序员命名函数一样)
不同的域是否可以定义同名
#include<stdio.h>
int x = 0;
int main()
{
int x = 1;
printf("hello world\n");
printf("%d\n", x);
printf("%d\n", ::x);
return 0;
}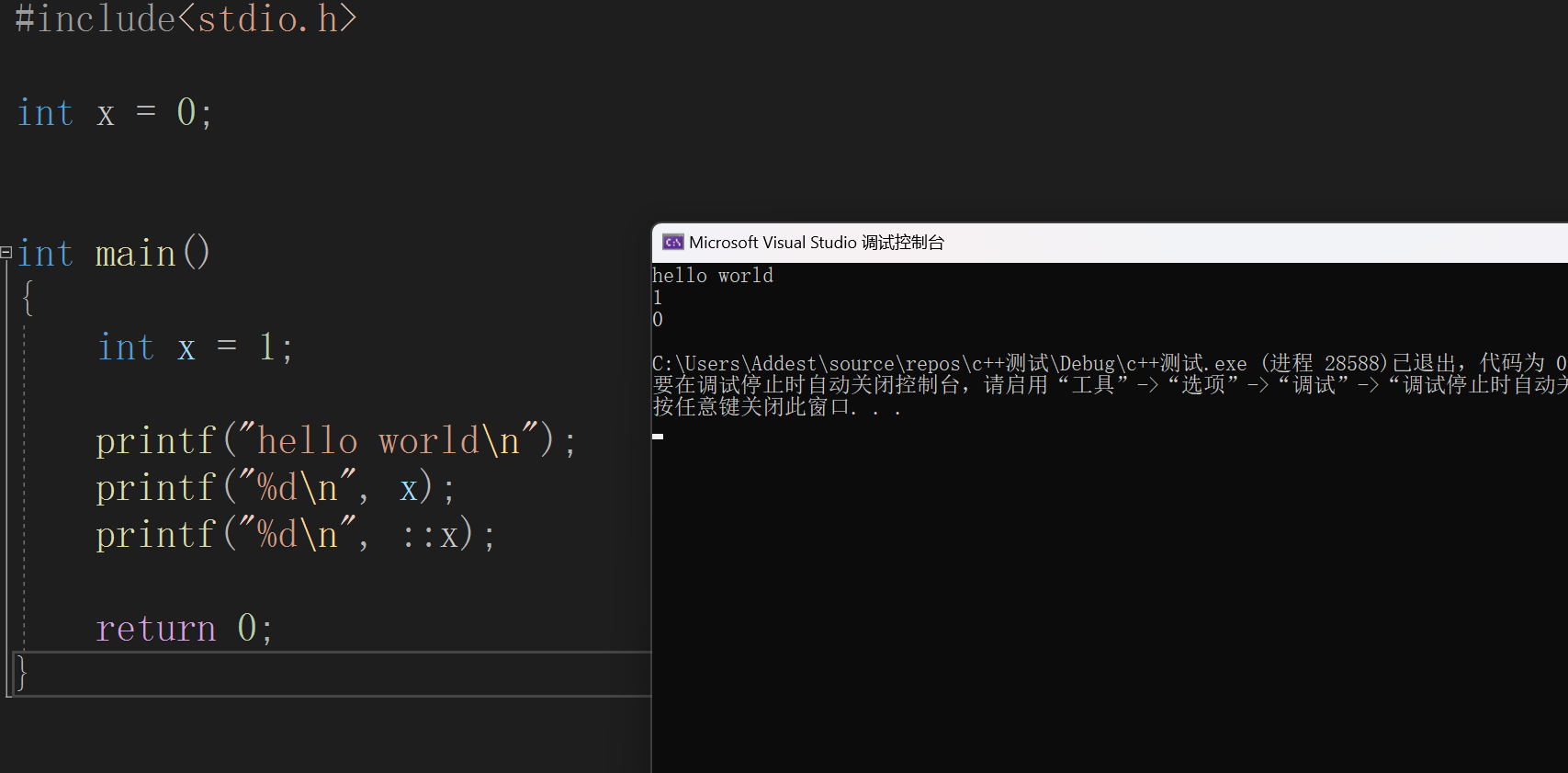
我们可以看见可以运行,打印出来的 x 遵循就近原则。
另外,在上述代码中我们我们可以发现当我们吧 x 改成 ::x 就能打印全局变量 x(0)了,:: 代表域作用限定符,::左边为空代表全局域。
下面我们来了解C++的域
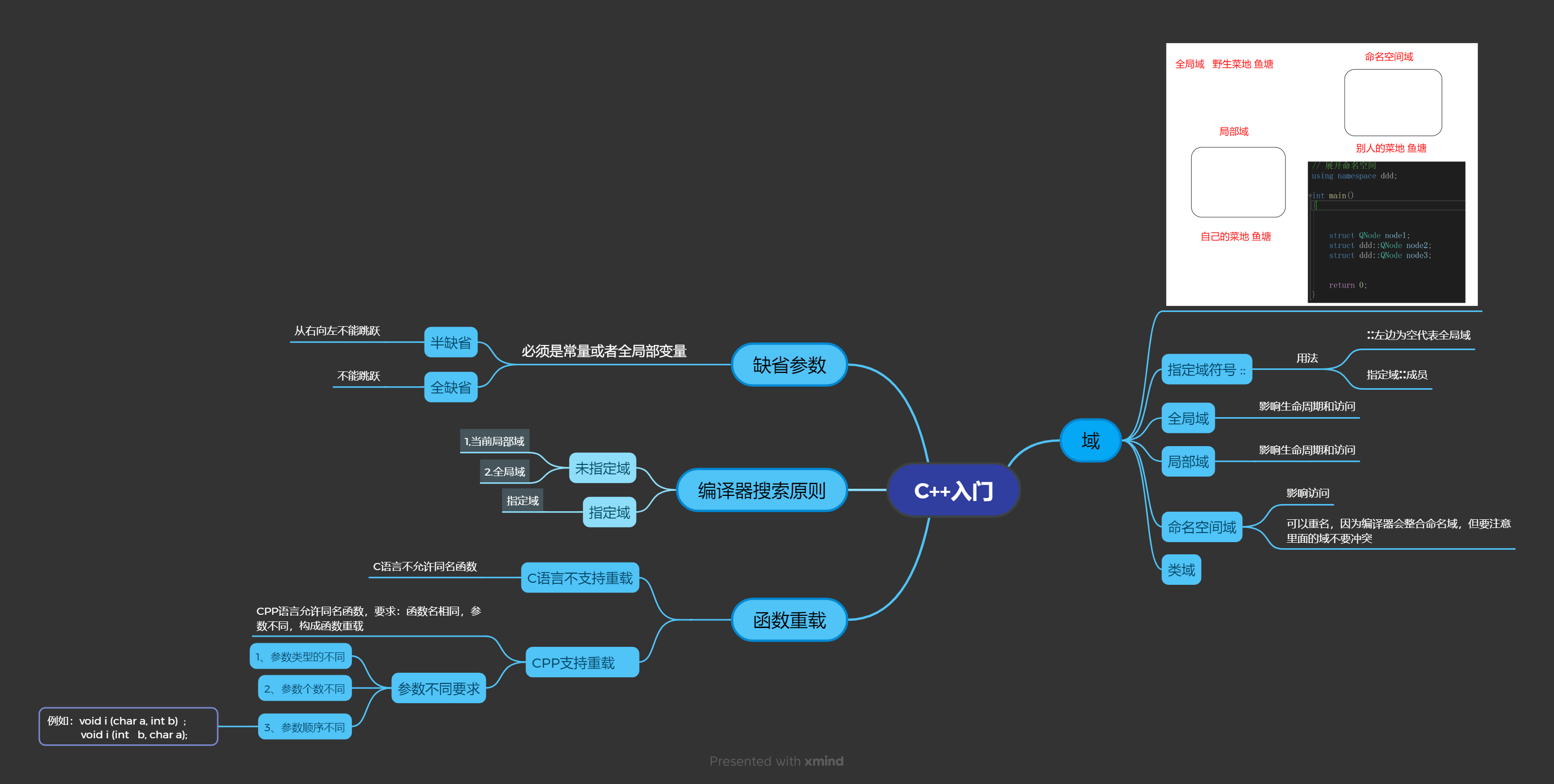
C++的域
全局域
局部域
命名空间域
类域(类和对象会介绍,暂时搁置)
全局域 影响生命周期和访问
局部域 影响生命周期和访问
命名空间域 影响访问
我们今天讲命名空间域namespace ,我们用一段代码来理解。
#include<iostream>
namespace bit1
{
int x = 0;
}
namespace bit1
{
int y = 1;
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", x);
printf("%d\n", y);
return 0;
}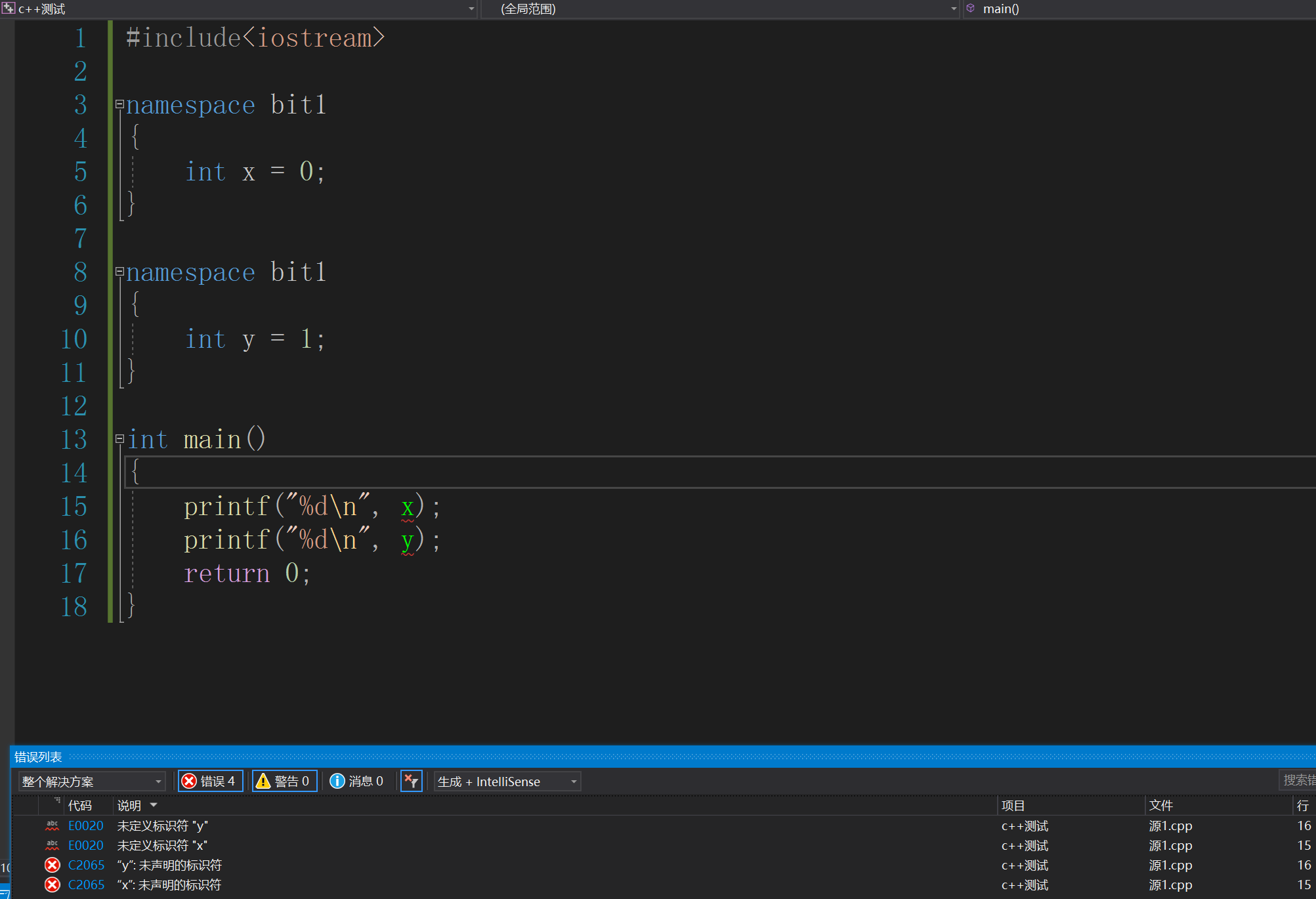
我们发现编译器会报错,这是为什么呢?这涉及到编译器的搜索原则,我们来看看。
编译器搜索域的原则
不指定域(默认):1、先搜索当前局部域 2、再搜索全局域
指定域 : 3、如果指定,直接去指定域搜索
因此我们将 x 和 y 加上指定域 ::
#include<iostream>
namespace bit1
{
int x = 0;
}
namespace bit1
{
int y = 1;
}
int main()
{
printf("%d\n", bit1::x);
printf("%d\n", bit1::y);
return 0;
}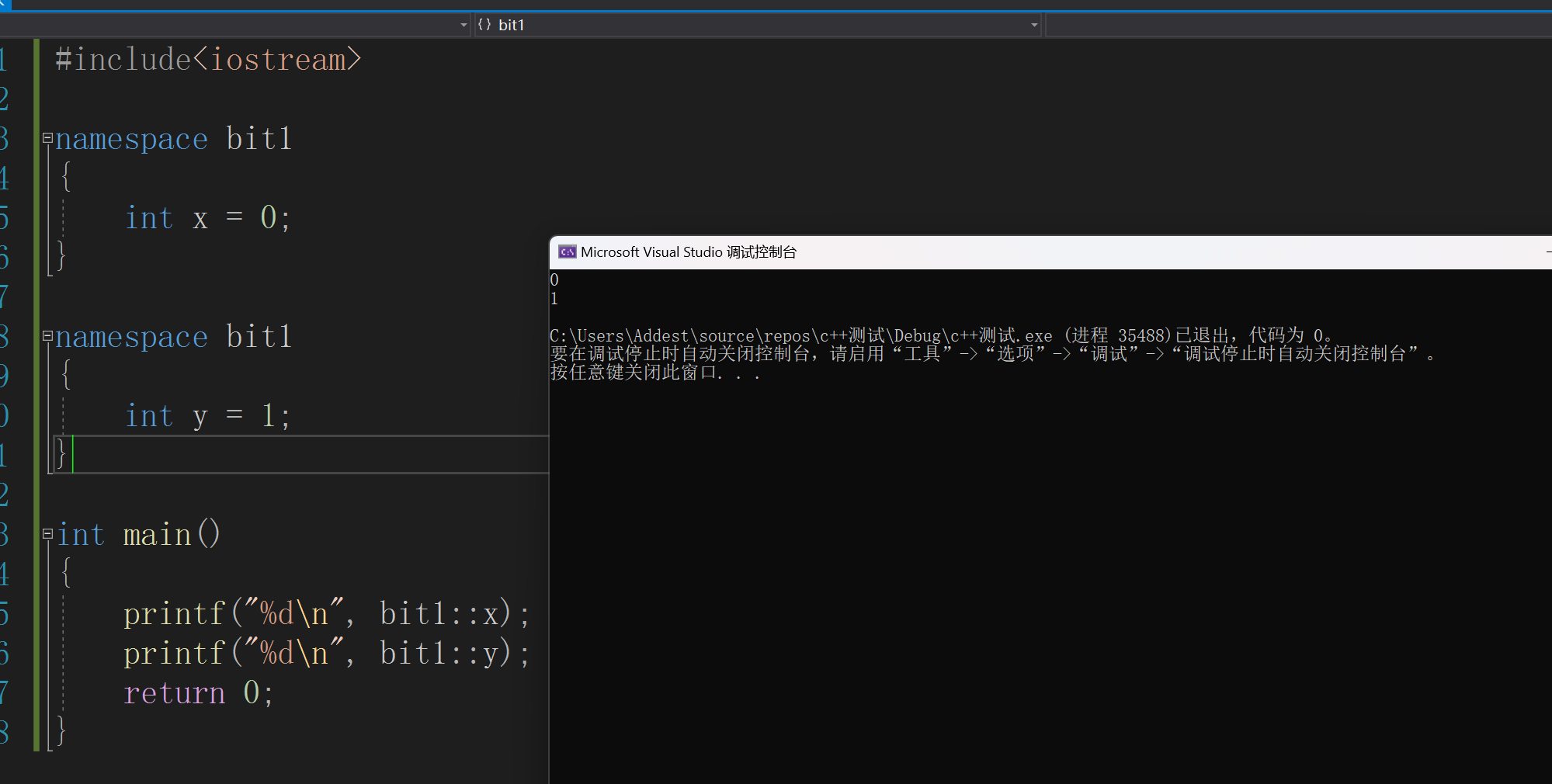
发现成功运行,同时我们发现namespace命名空间域是可以同名的(bit1) ,这是因为编辑器会将同名的命名空间域整合到一起,只要命名空间域里面没有重定义就可以正常运行。
我们来看刚开始写的C++代码
#include <iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
cout << "hello world" << endl;
return 0;
}
发现有一句using namespace std;
我们继续来看下面代码:
#pragma once
namespace ddd
{
struct QNode
{
int val;
struct QNode* next;
struct QNode* prev;
};
void Init(struct QNode* phead);
void PushBack(struct QNode* phead, int x);
}#pragma once
namespace ddd
{
struct Node
{
int val;
struct Node* next;
};
struct Queue
{
struct Node* head;
struct Node* tail;
int size;
};
void Init(struct Queue* pq);
void Push(struct Queue* pq, int x);
}#include<stdio.h>
#include"List.h"
#include"Queue.h"
// 展开命名空间
//using namespace ddd;
int main()
{
struct QNode node1;
struct ddd::QNode node2;
struct ddd::QNode node3;
return 0;
} 
我们发现如果缺少using namespace ddd; 这句代码就会这样报错加上的话编译器没有问题

这和刚刚的域有关。
我们来看一张图
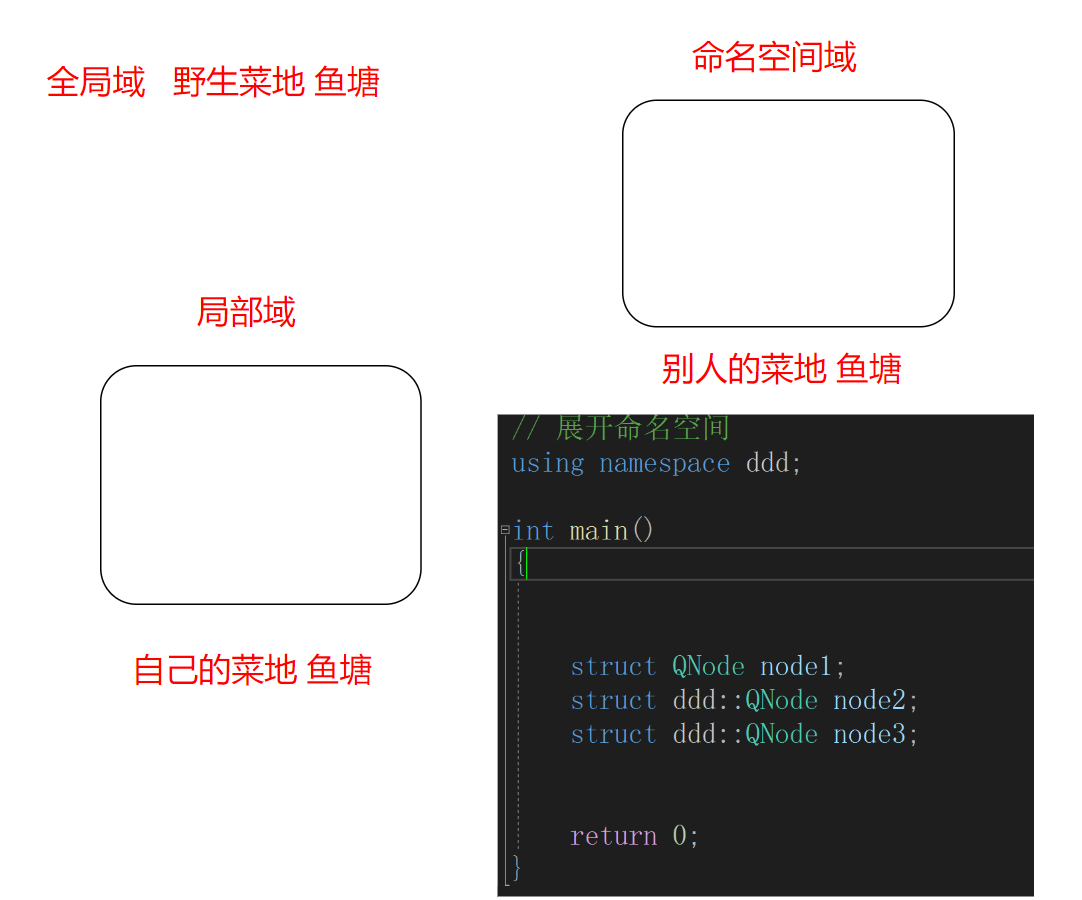
在没有指定条件下,我们是不能到别人家菜地摘菜的,等于命名空间域没有打开 。
但是有了using namespace std; 就等于菜地开放了,就可以去命名空间域访问了。
而using namespace std; std 是所有库的命名空间
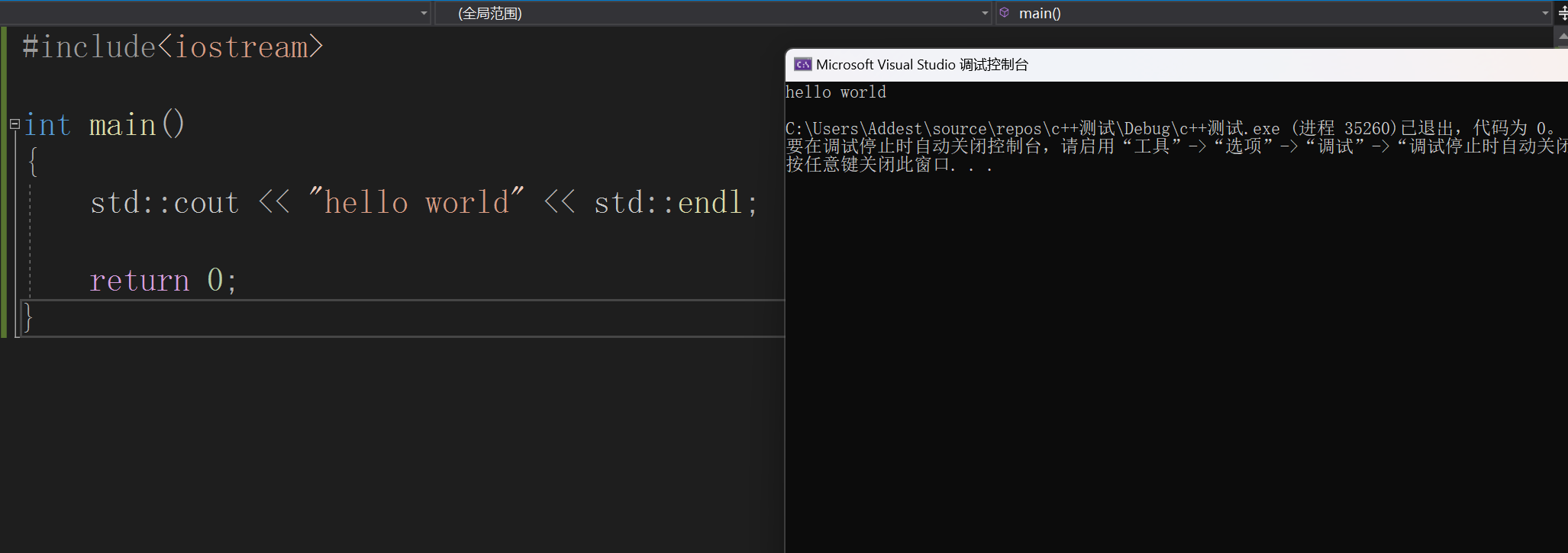
因此,我们也可以这样写:
#include<iostream>
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
return 0;
}
但是如果出现这样的情况
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int main()
{
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
std::cout << "hello world" << std::endl;
cout << "hello world" << endl;
return 0;
}最好还是使用展开空间。展开空间后还是没有指定域的情况下优先局部,然后全局。
3.<< 和 >>在C++的作用
<<
1.左移
int i = 100;
i = i << 1;
2.流插入 自动识别类型
cout << "hello world"<<endl;
>>
流提取
cin >> i >> ch;
cout << str << i << ch << endl;
4.缺省参数
1.声明和定义不能同时给 (如果给的值不一致,编译器无法确定值,C++也不允许,所以给声明)
2.(必须是常量或者全局部变量)
1.全缺省
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
void Func(int a = 0)
{
cout << a << endl;
}
int main()
{
Func(1);
Func();
return 0;
} 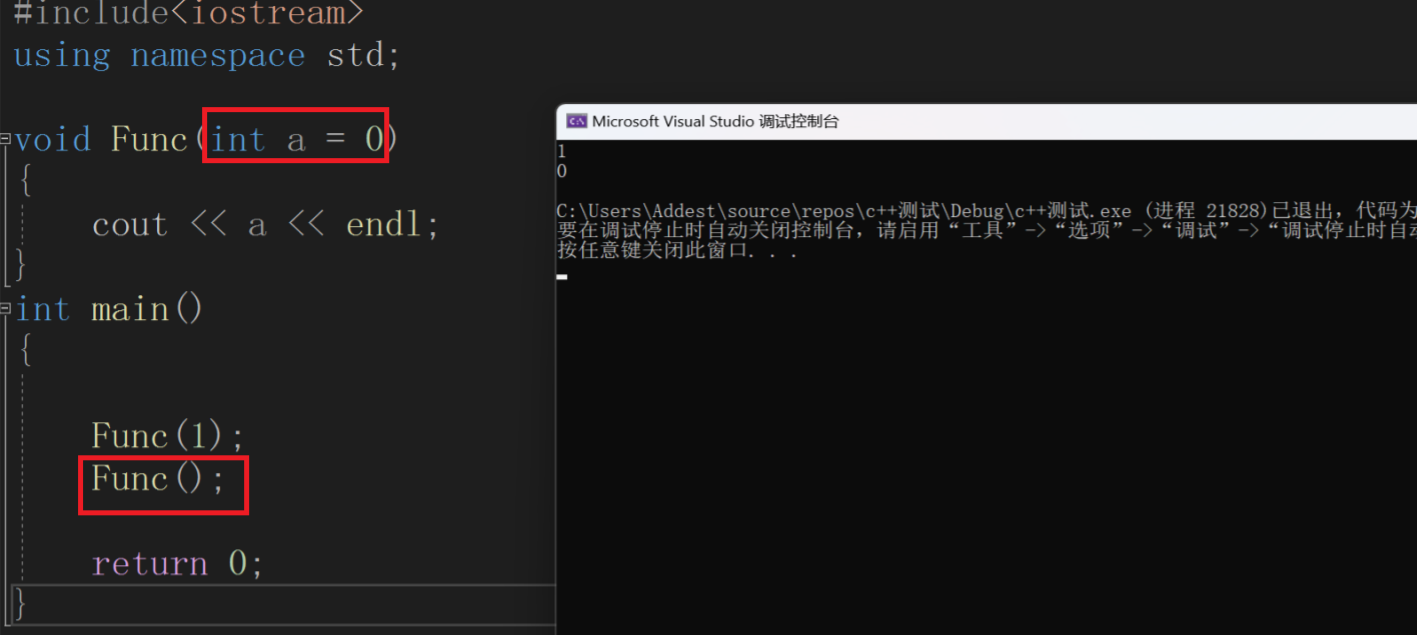
相比于我们之前学的C语言, Func 中的形参有了值,我们调用 Func 也没有传值,输出的是形参a的值。
给个更明显的例子
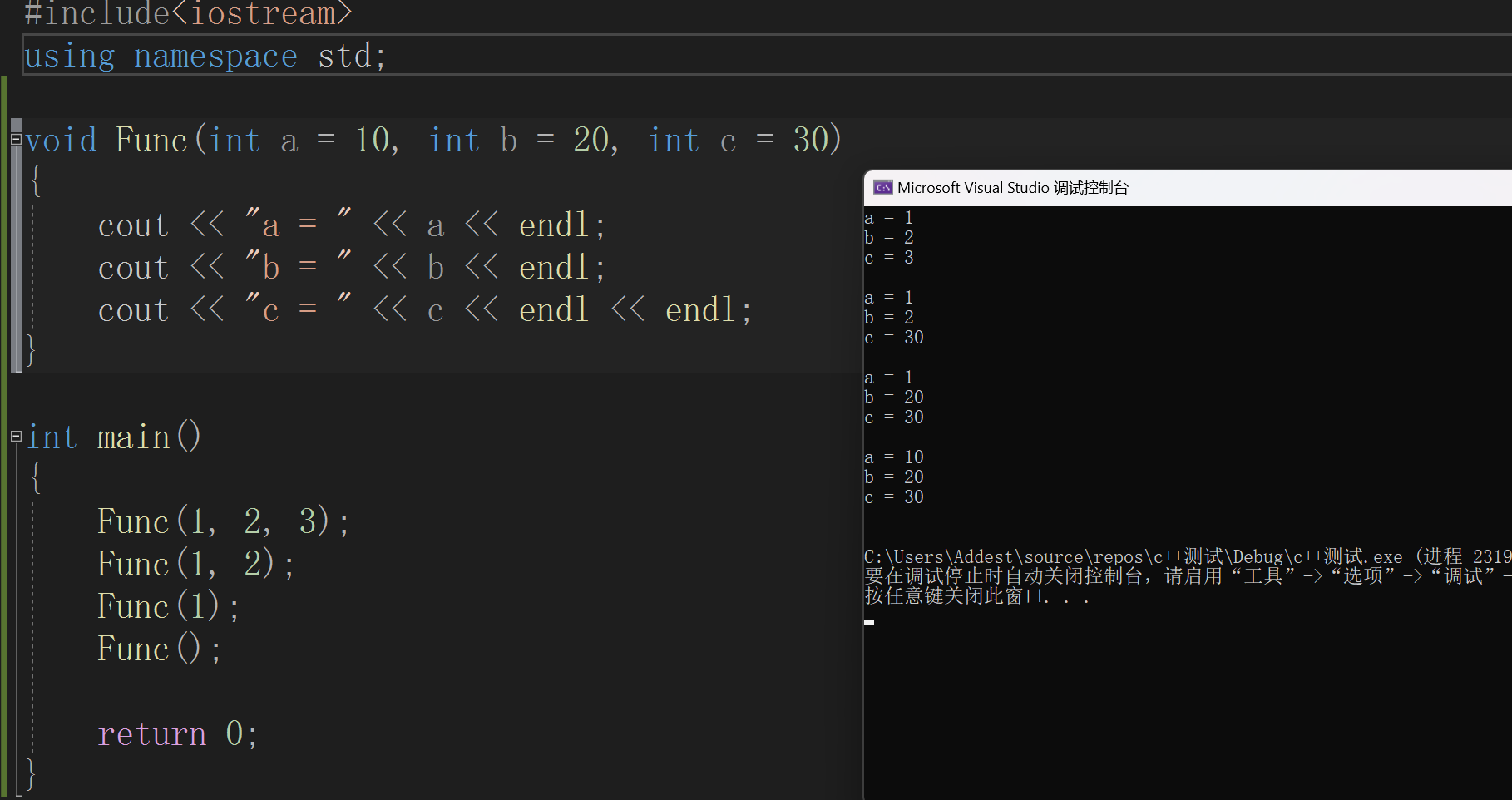
但是注意,传值不能跳跃地传。
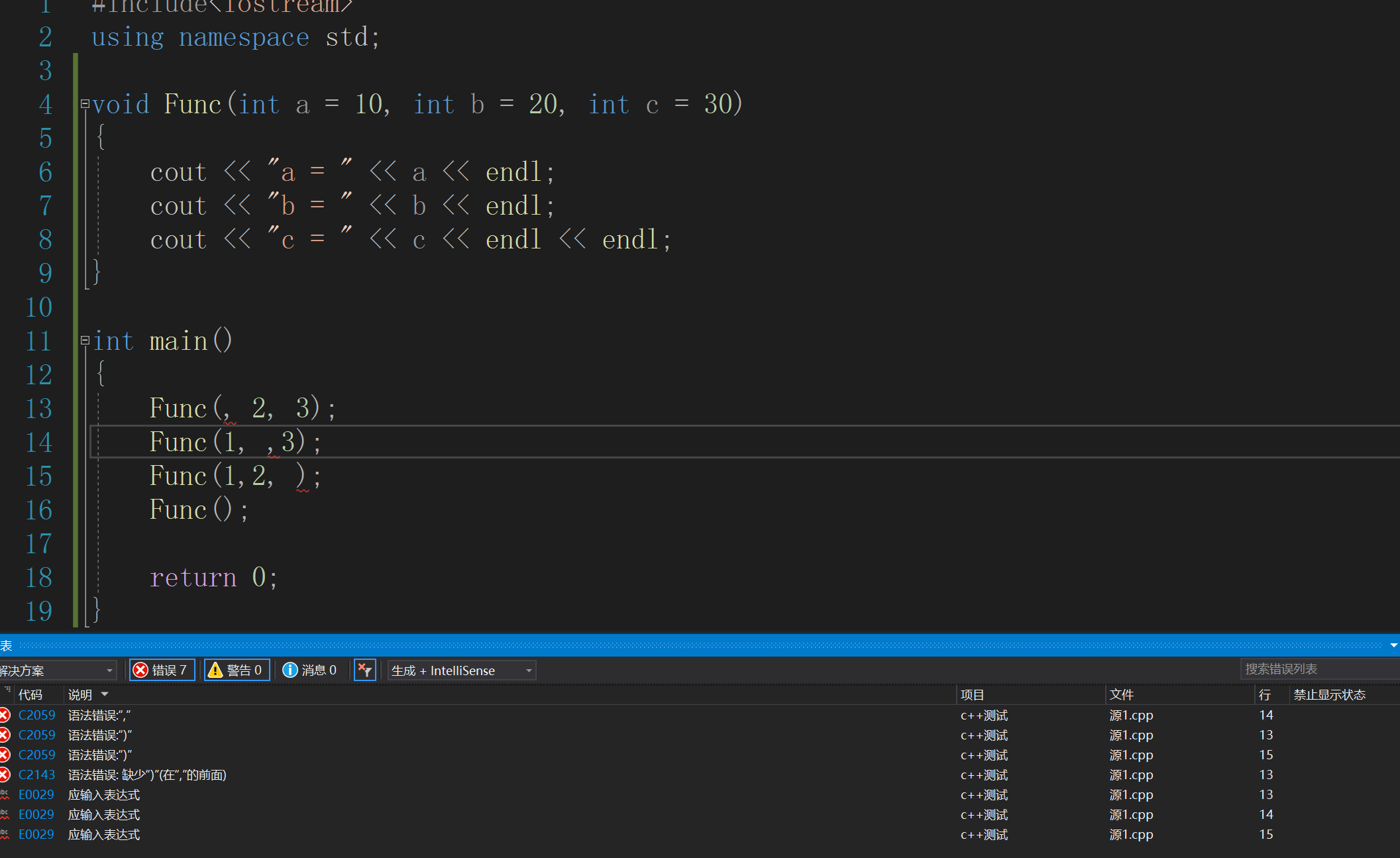
2.半缺省
半缺省规定从右往左连续给(不能连续给)。
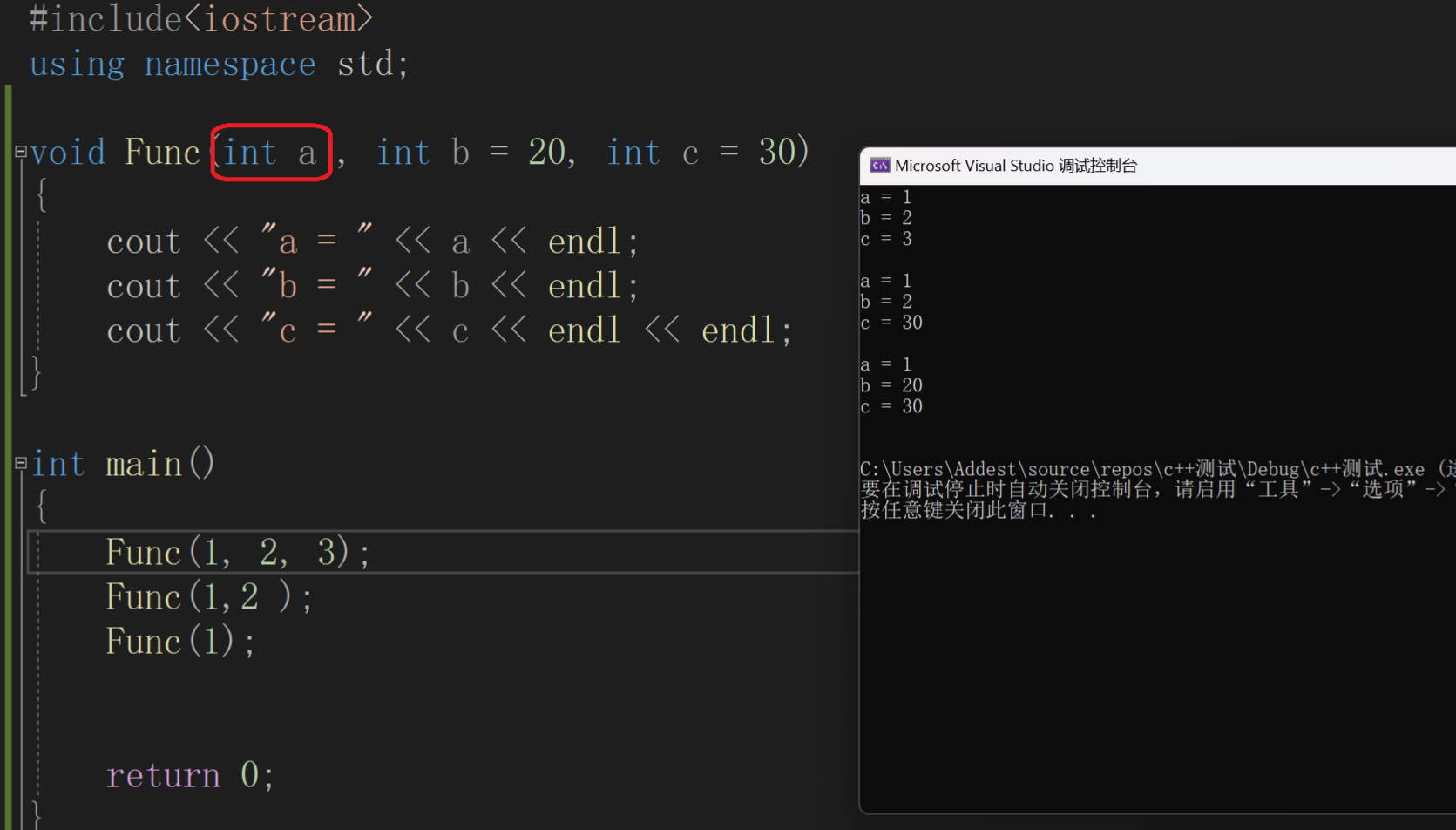
Func函数中形参a没有赋值,有部分形参没有参数,这就叫做半缺省。
5.函数重载
1.C语言不支持重载: C语言不允许同名函数
2.CPP支持重载 :CPP语言允许同名函数,要求:函数名相同,参数不同,构成函数重载
参数不同的情况有
1、参数类型的不同
2、参数个数不同
3、参数顺序不同(本质还是类型不同) void i (char a, int b) ; void i (int b, char a);
#include<iostream>
using namespace std;
int Add(int left, int right)
{
cout << "int Add(int left, int right)" << endl;
return left + right;
}
double Add(double left, double right)
{
cout << "double Add(double left, double right)" << endl;
return left + right;
}
int main()
{
Add(1, 2);
Add(1.11, 2.22);
return 0;
}
我们可以看见,C++自动匹配运行成功。
C语言不支持重载 链接时,直接用函数名去找地址,有同名函数,区分不开
CPP 函数名修饰规则,名字中引入参数类型,各个编译器自己实现了一套
好了,今天的博客就到这里,希望今年尽量不当鸽子。我们下篇博客见!























 1077
1077











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








