一、点类
点类5-P156
MyPoint类表示二维平面中的一个点,具有两个double类型属性:
横坐标
纵坐标
并具有一个构造方法(与类同名的方法)和以下普通方法:
1 构造方法:接收两个double型数据作为参数,分别设定为横坐标和纵坐标。
2 构造方法:接收一个MyPoint类型对象,分别设定为相同的横坐标和纵坐标。
3 display()方法,无参数,输出坐标信息,格式形如“(10.0,20.0)”。
4 getInfo()方法,无参数,返回字符串类型的坐标信息,格式形如"(10.0,20.0)"。
5所有属性的置取方法。
6 updatePoint()方法,接收两个double型数据作为参数,分别设置为当前点的横纵坐标。
7 updatePoint()方法,接收一个MyPoint类型对象作为参数,将当前点坐标更新为参数的坐标值。
8 getDistance()方法,接收一个MyPoint类型对象作为参数,计算并返回double类型的两点间距离值。
9 getDistance()方法,接收两个double型数据参数,作为另一点横纵坐标,计算并返回double类型的两点间距离值。
要求编程实现上述类,使给定的Test类能正常运行,并实现指定的输出内容。
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyPoint p1 = new MyPoint(40,0);
MyPoint p2 = new MyPoint(0,30);
MyPoint p3 = new MyPoint(0,0);
int x1=20,y1=15;
showPoint(p1,p2);
System.out.println("distance: "+p1.getDistance(p2));
p1.updatePoint(x1,y1);
p2.updatePoint(p3);
showPoint(p1,p2);
System.out.println("distance: "+p2.getDistance(x1,y1));
}
private static void showPoint(MyPoint p1,MyPoint p2){
System.out.println("--------------");
System.out.println("p1: "+p1.getInfo());
System.out.println("p2: "+p2.getInfo());
}
}
【输入形式】
【输出形式】
--------------
p1: (40.0,0.0)
p2: (0.0,30.0)
distance: 50.0
--------------
p1: (20.0,15.0)
p2: (0.0,0.0)
distance: 25.0
import java.math.*;
public class Test
{
public static void main(String[] args) {
MyPoint1 p1 = new MyPoint1(40,0);
MyPoint1 p2 = new MyPoint1(0,30);
MyPoint1 p3 = new MyPoint1(0,0);
int x1=20,y1=15;
showPoint(p1,p2);
System.out.println("distance: "+p1.getDistance(p2));
p1.updatePoint(x1,y1);
p2.updatePoint(p3);
showPoint(p1,p2);
System.out.println("distance: "+p2.getDistance(x1,y1));
}
private static void showPoint(MyPoint1 p1,MyPoint1 p2){
System.out.println("--------------");
System.out.println("p1: "+p1.getInfo());
System.out.println("p2: "+p2.getInfo());
}
}
class MyPoint1{
private double x;
private double y;
public MyPoint1(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public MyPoint1(MyPoint1 point){
this.x=point.x;
this.y=point.y;
}
public void display(){
System.out.println("("+x+","+y+")");
}
public String getInfo(){
return "("+x+","+y+")";
}
public void updatePoint(double x,double y){
this.x=x;
this.y=y;
}
public void updatePoint(MyPoint1 point){
this.x=point.x;
this.y=point.y;
}
public double getDistance(double x,double y){
// double result1=Math.pow(x,2);
// double result2=Math.pow(y,2);
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((x - this.x), 2) + Math.pow((y - this.y), 2));
}
public double getDistance(MyPoint1 point){
return Math.sqrt(Math.pow((point.x - this.x), 2) + Math.pow((point.y - this.y), 2));
}
}
二、数学函数计算-方法重载
已知公式如下图,编程求f(x,y,z)的值 ,在Test类中实现x,y,z值 的输入及结果的输出 。
编写MyMath类,实现静态的4个重载方法f(),分别计算不同的函数值,使给定的Test类能正常运行,并实现指定的输出内容。
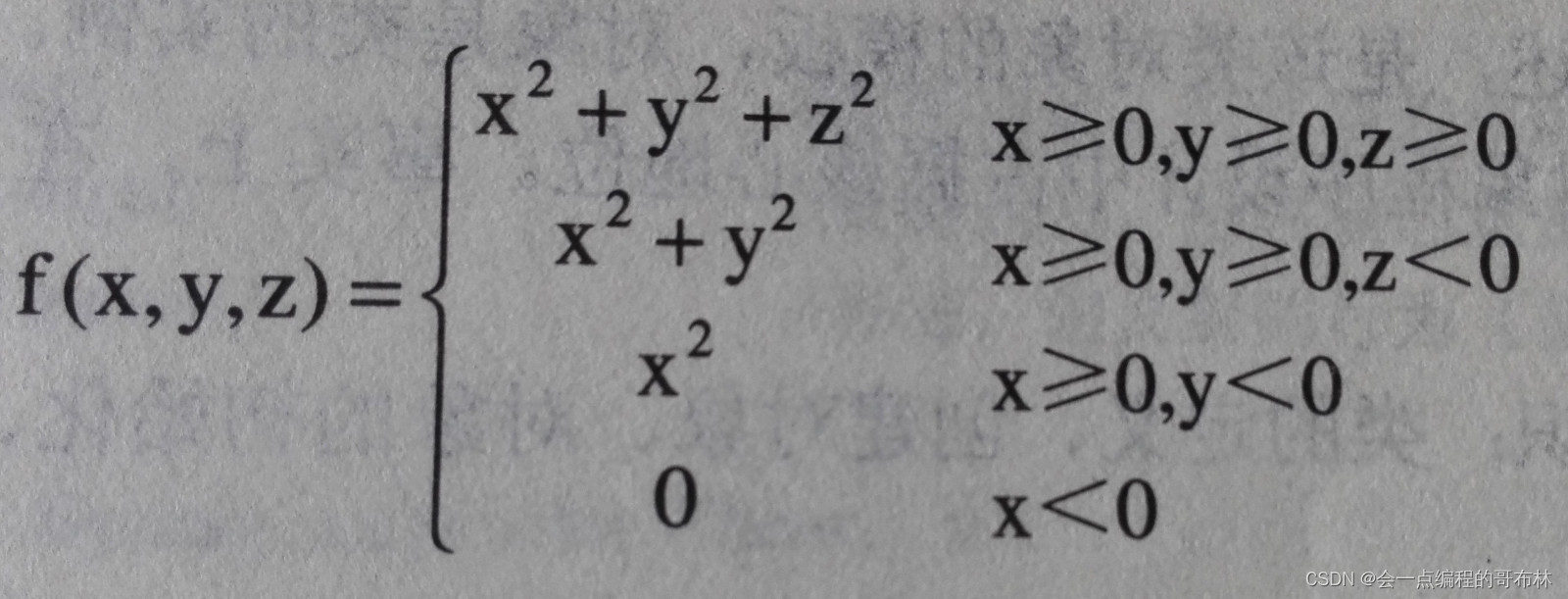
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
int x, y, z;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
x = in.nextInt();
y = in.nextInt();
z = in.nextInt();
in.close();
int result;
if (x < 0) {
result = MyMath.f();
} else if (x >= 0 && y < 0) {
result = MyMath.f(x);
} else if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && z < 0) {
result = MyMath.f(x, y);
} else {
result = MyMath.f(x, y, z);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
【输入形式】-1 2 5
【输出形式】0
import java.util.Scanner;
public class Test {
public static void main(String[] args){
int x, y, z;
Scanner in = new Scanner(System.in);
x = in.nextInt();
y = in.nextInt();
z = in.nextInt();
in.close();
int result;
if (x < 0) {
result = MyMth.f();
} else if (x >= 0 && y < 0) {
result = MyMth.f(x);
} else if (x >= 0 && y >= 0 && z < 0) {
result = MyMth.f(x, y);
} else {
result = MyMth.f(x, y, z);
}
System.out.println(result);
}
}
class MyMth{
public static int f(){
return 0;
}
public static int f(int x){
return x*x;
}
public static int f(int x, int y){
return x*x+y*y;
}
public static int f(int x,int y,int z){
return x*x+y*y+z*z;
}
}
三、钱类-方法重载和staic
编写Money类,要求具有yuan, jiao, fen三个int类型的属性及相应的置取方法,所表示的金额分别按元角分保存在各个属性中。
另外 ,还具有以下方法:
1 具有重载的四个set()方法,具体要求如下:
(1)参数为int类型,将参数值存入yuan, jiao和fen都置为0;
(2)参数为double类型,将参数值按分做四舍五入,然后分别存入对应的属性;
(3)参数为字符串String,对字符串中的数字做解析后,按分做四舍五入,将金额分别存入对应的属性;
(4)参数为Money类的对象,将参数中的金额分别存入对应的属性。
2 有两个可实现金额计算的方法
(1) times(int n)方法,参数为int,返回值为Money类对象,其中的总金额为当前对象的总金额乘以参数n
(2) add(Money money)方法,参数为Money类对象,返回值为Money类对象,其中的总金额为当前对象的总金额加上参数money中的总金额。
3 有一个静态方法,按照指定格式输出总金额
writeOut(String owner, Money money)方法,输出格式如“owner have/has XX Yuan XX Jiao XX Fen.”的字符串,所输出的的金额是参数money中的总金额。
字符串转浮点数可以使用静态方法:Double.parseDouble(String)。
要求编程实现类Money,使给定的Test类能正常运行,并实现指定的输出内容。
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Money myMoney = new Money();
Money yourMoney = new Money();
Money hisMoney = new Money();
Money herMoney = new Money();
int amountInt=365;
double amountDouble=254.686;
String amountString="368.244";
myMoney.set(amountInt);
Money.writeOut("I",myMoney);
yourMoney.set(amountDouble);
Money.writeOut("You",yourMoney);
hisMoney.set(amountString);
Money.writeOut("He",hisMoney);
herMoney.set(myMoney);
Money.writeOut("She",herMoney);
herMoney = yourMoney.times(3);
Money.writeOut("She",herMoney);
herMoney = yourMoney.add(hisMoney);
Money.writeOut("She",herMoney);
System.out.println("Remember: A penny saved is a penny earned.");
}
}
import java.math.*;
public class Test{
public static void main(String[] args){
Money myMoney = new Money();
Money yourMoney = new Money();
Money hisMoney = new Money();
Money herMoney = new Money();
int amountInt=365;
double amountDouble=254.686;
String amountString="368.244";
myMoney.set(amountInt);
Money.writeOut("I",myMoney);
yourMoney.set(amountDouble);
Money.writeOut("You",yourMoney);
hisMoney.set(amountString);
Money.writeOut("He",hisMoney);
herMoney.set(myMoney);
Money.writeOut("She",herMoney);
herMoney = yourMoney.times(3);
Money.writeOut("She",herMoney);
herMoney = yourMoney.add(hisMoney);
Money.writeOut("She",herMoney);
System.out.println("Remember: A penny saved is a penny earned.");
}
}
class Money{
private int yuan;
private int jiao;
private int fen;
public Money(){
this.yuan=0;
this.jiao=0;
this.fen=0;
}
public void setYuan(int yuan) {
this.yuan = yuan;
}
public int getYuan() {
return yuan;
}
// jiao的setter和getter方法
public void setJiao(int jiao) {
this.jiao = jiao;
}
public int getJiao() {
return jiao;
}
// fen的setter和getter方法
public void setFen(int fen) {
this.fen = fen;
}
public int getFen() {
return fen;
}
public void set(int amount){
this.yuan=amount;
this.jiao=0;
this.fen=0;
}
public void set(double amount){
long totalFen=Math.round(amount*100);
this.yuan=(int)(totalFen/100);
totalFen %=100;
this.jiao=(int)(totalFen/10);
this.fen=(int)(totalFen%10);
}
public void set(String amount){
double parseAmount=Double.parseDouble(amount);
set(parseAmount);
}
public void set(Money money){
this.yuan=money.yuan;
this.jiao= money.jiao;
this.fen= money.fen;
}
public Money times(int n){
Money result=new Money();
long totalFen=(long) this.yuan*100+this.jiao*10+this.fen;
totalFen *=n;
result.yuan =(int)(totalFen /100);
totalFen %=100;
result.jiao =(int)(totalFen/10);
result.fen=(int)(totalFen%10);
return result;
}
public Money add(Money money){
Money result=new Money();
long totalFen1=(long) this.yuan*100+this.jiao*10+this.fen;
long totalFen2 =(long) money.getYuan()*100+money.getJiao()*10+ money.getFen();
long total = totalFen1+totalFen2;
result.yuan=(int) (total /100);
total %=100;
result.jiao=(int) (total / 10);
result.fen = (int)(total %10);
return result;
}
public static void writeOut(String owner , Money money){
System.out.println(owner + " have/has " + money.yuan + " Yuan " + money.jiao + " Jiao " + money.fen + " Fen.");
}
}
希望大家多多关注,多多点赞,祝大家心想事成,更上一层楼。





















 27万+
27万+

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








