稀疏数组的应用:
当一个数组中的大部分元素为0,或者为同一个值的数组时,可以使用稀疏数组来保存数组。
稀疏数组处理方法:
- 第一行用来记录数组一共几行几列,有多少个不同的值。
- 之后将具有不同值的元素的行和列及值依次记录在数组中,从而缩小程序规模。
举例说明:

图1-1
| 行(row) | 列(col) | 值(value) | |
| [0] | 11 | 11 | 2 |
| [1] | 1 | 2 | 1 |
| [2] | 2 | 3 | 2 |
图1-2
图1-1是一个二维数组,图1-2为该二维数组所对应的稀疏数组。
代码实现:
下列代码实现了二维数组和稀疏数组之间的相互转换。
public class sparseArray {
public static void main(String[] args) {
// 定义一个二维数组
int chess1[][] = new int[11][11];
chess1[1][2] = 1;
chess1[2][3] = 2;
// 输出二维数组
System.out.println("原始二维数组为:");
for (int[] row : chess1) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
/*将二维数组转换成稀疏数组*/
//1、将二维数组中的非零元素进行计数
int sum = 0;
for (int i = 0; i < chess1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (chess1[i][j] != 0) {
sum += 1;
}
}
}
//2、定义稀疏数组
int sparseArray[][]=new int [sum+1][3];
sparseArray[0][0]=11;
sparseArray[0][1]=11;
sparseArray[0][2]=sum;
//3、遍历二维数组,将二维数组非零值储存在稀疏数组中
int count=1;
for (int i = 0; i < chess1.length; i++) {
for (int j = 0; j < 11; j++) {
if (chess1[i][j] != 0) {
sparseArray[count][0]=i;
sparseArray[count][1]=j;
sparseArray[count][2]=chess1[i][j];
count++;
}
}
}
//4、将得到的稀疏数组进行输出
System.out.println("稀疏数组为:");
for (int[] row : sparseArray) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
/*将稀疏数组转换成为二维数组*/
//1、定义一个二维数组
int chess2[][]=new int[sparseArray[0][0]][sparseArray[0][1]];
//2、遍历稀疏数组,将其转换成二维数组
for(int i=1;i<sparseArray.length;i++) {
chess2[sparseArray[i][0]][sparseArray[i][1]]=sparseArray[i][2];
}
//3、输出转换后的二维数组
System.out.println("稀疏数组转换成的二维数组为:");
for (int[] row : chess2) {
for (int data : row) {
System.out.printf("%d\t", data);
}
System.out.println();
}
}
}
运行结果如下:
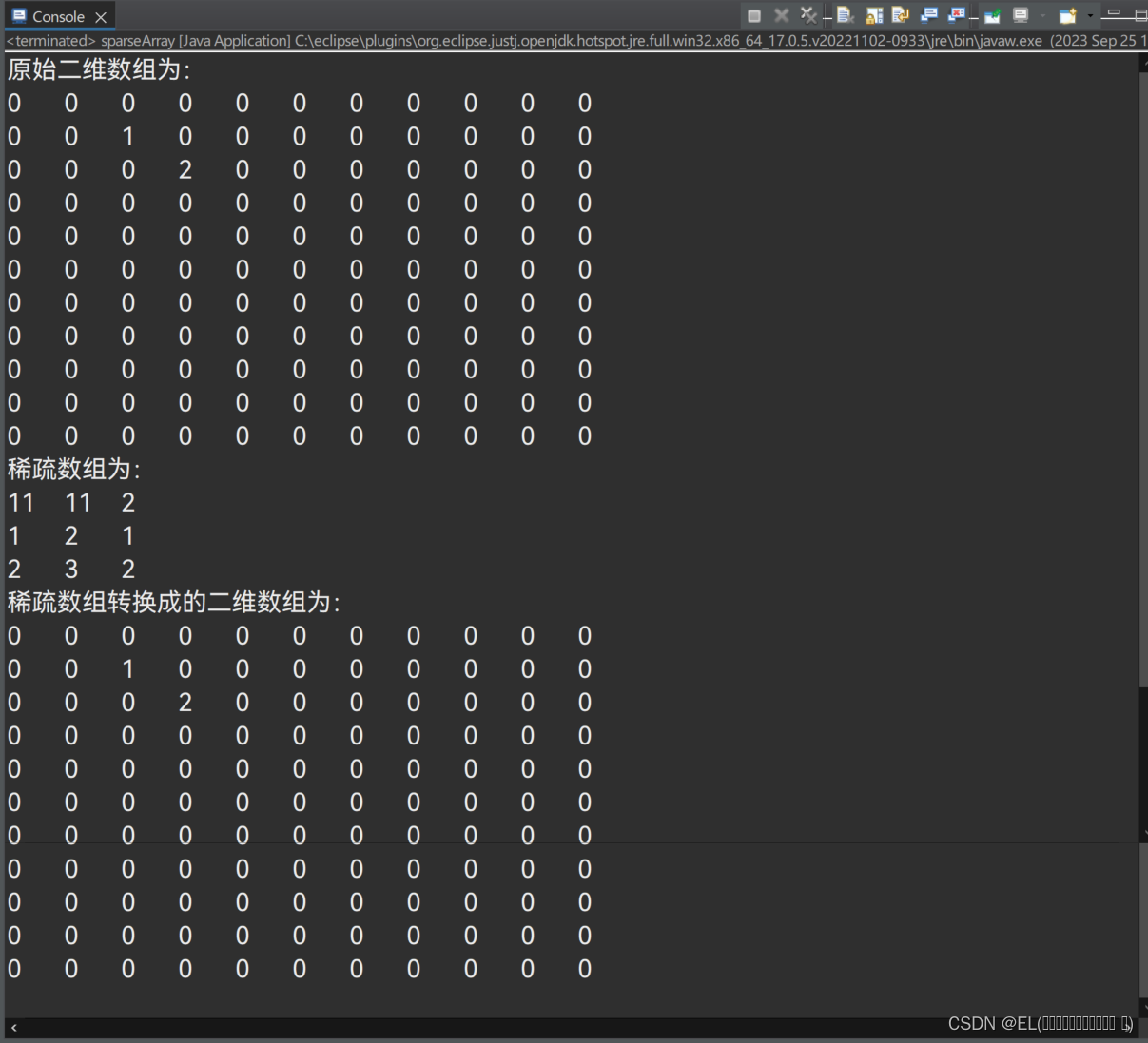




 本文介绍了稀疏数组的概念,如何通过统计非零元素并记录行、列和值来节省存储空间,以及提供了一个Java代码示例展示了二维数组到稀疏数组和反之的转换过程。
本文介绍了稀疏数组的概念,如何通过统计非零元素并记录行、列和值来节省存储空间,以及提供了一个Java代码示例展示了二维数组到稀疏数组和反之的转换过程。

















 738
738

 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?










