1.数列求值
P1453 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]数列求值 - New Online Judge
由于不知道到20190324项时数据会达到多大,因此用一个循环,因此输出,观察数据变化的轨迹,发现用long long 都不够,会溢出
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e7 + 1e6;
int a[N];
LL cnt;
int main()
{
a[1] = a[2] = a[3] = 1;
for (int i = 4; i <= 20190324; i++) {
a[i] = (a[i - 1] + a[i - 2] + a[i - 3]) ;
cout << a[i] << " ";
}
return 0;
}由于只需要输出最后四位数字,因此可以对10000取余,这样不会影响最后四位的大小(因为是从低位向高位进位,高位不会影响低位,因此截取四位以上的高位根本不会影响最后四位),同时也可以将数据大小控制在10000以下,就不会溢出了
由此得出AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 2e7 + 1e6;
int a[N];
LL cnt;
int main()
{
a[1] = a[2] = a[3] = 1;
for (int i = 4; i <= 20190324; i++) {
a[i] = (a[i - 1] + a[i - 2] + a[i - 3])%10000 ;
}
cout << a[20190324] << endl;
return 0;
}2.年号字串
P1463 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]年号字串 - New Online Judge
可以找找规律,然后发现在找规律的同时就能把题做出来,不过呢,在草稿纸上要写的清楚整洁,不然很容易出错
每一位有不同的权值,26进制,A到Z代表1到26
比如AA=1*26^0+1*26^1=27
又比如CBA=1*26^0+2*26^1+3*26^2
发现2019对应的字符串是3位,因而枚举3重循环,每层循环从1到26
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <= 26; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= 26; j++) {
for (int k = 1; k <= 26; k++) {
if (i * 26 * 26 + j * 26 + k == 2019) {
cout << i << endl;
cout << j << endl;
cout << k << endl;
return 0;
}
}
}
}
return 0;
}最后输出的是2 25 17,对应的字符串是"BYQ"
3.数的分解
P1464 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]数的分解 - New Online Judge
因为3个整数的顺序不同视为一种方法,所以只需枚举i
i只要枚举到700左右即可,因为此时j大于700,k大于700,总和已经超过了2019
j只要枚举到1010即可,即便此时i为1,k已经大于1010,所以总和已经超过了2019
写一个check函数,判断正整数是否包含2和4
k可以用2019-i-j表示,只要判断2019-i-j是否大于j即可
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
bool check(int x) {
int n = x;
while (n) {
if (n % 10 == 2 || n % 10 == 4) return false;
n /= 10;
}
return true;
}
int main()
{
LL res = 0;
for (int i = 1; i <= 700; i++) {
for (int j = i+1; j <= 1010; j++) {
if (check(i) && check(j) && check(2019 - i - j)&&2019-i-j>j) res++;
}
}
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}4.组队
P1462 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]组队 - New Online Judge
题意就是合理地选取1号位是哪个人,2号位是哪个人......
肯定选厉害的分数高的人,比如说A这个人1号位的分数是100,2号位的分数也是100,他在1号位和2号位都是最强的,但是,他只能担任一个位置,因此要合理地选择,因为数量比较少,肉眼都能看出,直接输出结果
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
int main()
{
cout << 98 + 99 + 98 + 97 + 98 << endl;
return 0;
}或者呢,枚举所有的情况,也就是用dfs确定五个位置的人选,每个位置都有20种情况,这样的解法是错的,因为这样会有某个人同时担任好几个位置的情况
错误代码:
错误代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
struct Select {
int a, b, c, d, e;
}s[30];
int res;
int cnt;
int st[30];
void dfs(int x) {
if (x <= 5) {
st[x] = 1;dfs(x + 1);st[x] = 2;dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 3; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 4; dfs(x + 1);
st[x] = 5; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 6; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 7; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 8; dfs(x + 1);
st[x] = 9; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 10; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 11; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 12; dfs(x + 1);
st[x] = 13; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 14; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 15; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 16; dfs(x + 1);
st[x] =17; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 18; dfs(x + 1); st[x] =19; dfs(x + 1); st[x] = 20; dfs(x + 1);
}
else {
cnt =s[st[1]].a + s[st[2]].b + s[st[3]].c + s[st[4]].d + s[st[5]].e;
}
res = max(res, cnt);
}
int main()
{
s[1] = { 97 ,90 ,0 ,0 ,0 };s[2] = { 92 ,85 ,96 ,0 ,0 };s[3] = { 0 ,0, 0, 0, 93};
s[4] = { 0 ,0 ,0 ,80, 86 };s[5] = { 89 ,83 ,97, 0, 0 };s[6] = { 82 ,86, 0 ,0, 0 };
s[7] = { 0,0,0,87,90};s[8] = { 0, 97 ,96, 0 ,0 };s[9] = { 0, 0 ,89 ,0 ,0 };
s[10] = { 95, 99 ,0 ,0, 0 }; s[11] = { 0, 0 ,96 ,97, 0 }; s[12] = { 0, 0, 0 ,93 ,98 };
s[13] = { 94 ,91 , 0 ,0 ,0 }; s[14] = { 0 ,83, 87, 0 ,0 }; s[15] = { 0 ,0 ,98 ,97, 98 };
s[16] = { 0 ,0 ,0 ,93 ,86 }; s[17] = { 98 ,83 ,99, 98 ,81 }; s[18] = { 93 ,87 ,92, 96, 98};
s[19] = { 0, 0, 0 ,89, 92 }; s[20] = { 0, 99 ,96, 95, 81 };
dfs(1);
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
}需要标记已经担任位置的人,就不能再去担任其它位置了
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
struct Select {
int a, b, c, d, e;
}s[30];
int res;
int cnt;
int st[30];
bool flag[30];
void dfs(int x) {
if (x <= 5) {
for (int i = 1; i <= 20; i++) {
if (!flag[i]) {
st[x] = i;
flag[i] = true;
dfs(x + 1);
flag[i] = false;
}
}
}
else {
cnt = s[st[1]].a + s[st[2]].b + s[st[3]].c + s[st[4]].d + s[st[5]].e;
}
res = max(res, cnt);
}
int main()
{
s[1] = { 97 ,90 ,0 ,0 ,0 }; s[2] = { 92 ,85 ,96 ,0 ,0 }; s[3] = { 0 ,0, 0, 0, 93 };
s[4] = { 0 ,0 ,0 ,80, 86 }; s[5] = { 89 ,83 ,97, 0, 0 }; s[6] = { 82 ,86, 0 ,0, 0 };
s[7] = { 0,0,0,87,90 }; s[8] = { 0, 97 ,96, 0 ,0 }; s[9] = { 0, 0 ,89 ,0 ,0 };
s[10] = { 95, 99 ,0 ,0, 0 }; s[11] = { 0, 0 ,96 ,97, 0 }; s[12] = { 0, 0, 0 ,93 ,98 };
s[13] = { 94 ,91 , 0 ,0 ,0 }; s[14] = { 0 ,83, 87, 0 ,0 }; s[15] = { 0 ,0 ,98 ,97, 98 };
s[16] = { 0 ,0 ,0 ,93 ,86 }; s[17] = { 98 ,83 ,99, 98 ,81 }; s[18] = { 93 ,87 ,92, 96, 98 };
s[19] = { 0, 0, 0 ,89, 92 }; s[20] = { 0, 99 ,96, 95, 81 };
dfs(1);
cout << res << endl;
return 0;
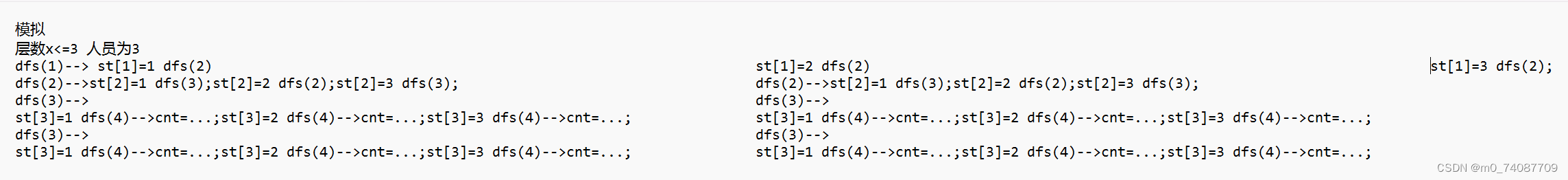
}进行模拟,由于写不开,只写了一小部分,但足以看出它的趋势
一共有5层,首先先进行第一层的放置,为1到20号(1到20循环),然后进行第二层的放置,为1到20号中不是前面层放置过的(if(!flag[i])),然后进行第三层的放置,为1到20中不是前面层放置过的,以此类推...
循环i横向同一层铺排,dfs纵向一层一层深搜

对比不判断是否用过,而直接st[x]=1;dfs(x+1);st[x]=2;dfs(x+1)...
同样进行模拟
同一层st[x]=1,st[x]=2,st[x]=3..st[x]=20横向铺排,dfs对于一个确定的一层,再往下一层一层深搜
5.等差数列
P1466 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]等差数列 - New Online Judge
看了题目后,应该是找规律的题
可以分情况讨论,一条一条列出来
第一次做:
 AC20%代码:
AC20%代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
int m1, m2;
bool flag1 = false, flag2 = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
if (a[i] % 2 == 1) flag1 = true;
else flag2 =true;
}
sort(a+1, a +1 + n);
m1 = m2 =a[2]-a[1];
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
m1 = max(m1, a[i] - a[i - 1]);
m2 = min(m2, a[i] - a[i - 1]);
}
if (flag1 && flag2) {
cout << a[n] - a[1]+ 1 << endl;
}
else {
if (m1 % m2 == 0) cout << (a[n] - a[1]) / m2 + 1 << endl;
else cout << (a[n] - a[1]) / 2 + 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}第二次进行修改:随便试了一组数据1 4 7 10 ,发现既有奇数又有偶数时,公差不一定为1

AC90%代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int a[N];
int main()
{
cin >> n;
int m1, m2;
bool flag1 = false, flag2 = false;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
if (a[i] % 2 == 1) flag1 = true;
else flag2 =true;
}
sort(a+1, a +1 + n);
m1 = m2 =a[2]-a[1];
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
m1 = max(m1, a[i] - a[i - 1]);
m2 = min(m2, a[i] - a[i - 1]);
}
if (flag1 && flag2) {
if (m1 % m2 == 0) cout << (a[n] - a[1])/m2 + 1 << endl;
else cout << a[n] - a[1]+ 1 << endl;
}
else {
if (m1 % m2 == 0) cout << (a[n] - a[1]) / m2 + 1 << endl;
else cout << (a[n] - a[1]) / 2 + 1 << endl;
}
return 0;
}虽然AC了90%,但是还是有很大的漏洞
找了一组数据:2 6 12 20,虽然最大的差是最小的差的倍数,但是公差并不是4,因为2+4=4,12+4=16,16+4=20,但是6+4=10,10+4不等于12,所以应该求所有的差的最大公约数
根本不需要分奇数偶数,公差求出,只要利用等差数列的性质代入公式(a[n] - a[1])/m+ 1即可,但是不要忘记公差为0的情况,此时项数即为 n
AC代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100010;
int n;
int a[N];
int gcd(int a, int b) {
if (b == 0) return a;
return gcd(b, a % b);
}
int main()
{
cin >> n;
int m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a+1, a +1 + n);
m=a[2] - a[1];
for (int i = 3; i <= n; i++) {
m= gcd(m,a[i]-a[i - 1]);
}
if (m) cout << (a[n] - a[1]) / m + 1 << endl;
else cout << n << endl;
return 0;
}然后我又将我的AC90%的代码加上了公差为0的情况,竟然AC了,可见数据有待加强,很明显2 6 12 20数据是不符合的
至于会不会出现%0的情况
如果是所有数都相等,即相邻的两个数差都为0,那么一开始m=a[2]-a[1]=0,然后是gcd(0,0),即a=0,b=0,那么直接返回a的值0,每次都是gcd(0,0),故m的值最终为0
如果某些数相等:
1.如果a[1]和a[2]相等,那么m一开始为a[2]-a[1]=0,然后是gcd(0,正数),返回gcd(0,0%正数)=gcd(0,0)=0,m最终为0
2.如果a[2]和a[3]相等,那么是gcd(正数a,0),返回正数a,比如说1 2 2 ,返回1,不符合最大公约数,但这不可能构成等差数列,也就是说不可能会出现这种情况,根本不需要考虑这种情况,从这可以看出以上写的这个gcd函数求两个数的最大公约数,最开始给的两个数,如果有0的话只能放在第一个位置(即a的位置)
6.后缀表达式
P1467 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]后缀表达式 - New Online Judge
AC30%代码:
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 200010;
int a[N];
LL s[N];
int main()
{
int n, m;
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <= n+m+1; i++) cin >> a[i];
sort(a + 1, a + 1 + n+m+1,greater<int>());
for (int i = 1; i <= n+m+1; i++) s[i] = s[i-1] + a[i];
LL sum1 = s[n + m + 1] - s[n+1];
LL sum2 = s[n + 1] - s[0];
cout << sum2 - sum1 << endl;
return 0;
}中缀表达式:常见的运算表达式
后缀表达式:运算符在操作数后面,计算机从左至右进行扫描,遇到数字,直接入栈,遇到运算符号,就将栈最上面的两个数拿出来进行运算,再将结果进栈,前缀表达式则为从右往左扫描
总之,后缀表达式就是说在没有括号下,起到有括号的作用,就是说可以用括号
这样就使得5-4-3=-2变成5-(3-4)=5+1=6
 以上图片摘自acwing题解
以上图片摘自acwing题解
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<cmath>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 200010;
int a[N];
int n, m;
LL sum;
int main()
{
cin >> n >> m;
for (int i = 1; i <=n + m + 1; i++) {
cin >> a[i];
}
sort(a+1 , a +1 + n + m+1);
if (!m) {
for (int i = 1; i <=n + m + 1; i++) sum += a[i];
}
else {
sum = a[n + m+1 ] - a[1];
for (int i = 2; i <= n + m; i++) {
sum += abs(a[i]);
}
}
cout << sum << endl;
return 0;
}
7.迷宫
P1455 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]迷宫 - New Online Judge
用bfs
可以用联合类型pair入队,也可用结构体,用结构体的好处是可以增加一个变量path(string类型),拓展到某点tt时,就可以用tt.path=t.path+路径,这样就可以保存从开头到该点的所有路径
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
#include<queue>
using namespace std;
struct node {
int x, y;
string path;
};
const int N = 110;
int g[N][N];
int dx[4] = { 1,0,0,-1 }, dy[4] = { 0,-1,1,0 };
char pa[4] = { 'D','L','R','U' };
bool st[N][N];
void bfs() {
queue<node>q;
node t;
t.x = 1, t.y =1;
q.push(t);
st[1][1] = true;
while (q.size()) {
node t = q.front();
q.pop();
if (t.x ==30 && t.y ==50) {
cout << t.path << endl;
return;
}
for (int i = 0; i < 4; i++) {
node tt;
tt.x = t.x + dx[i], tt.y = t.y + dy[i],tt.path=t.path+pa[i];
if (tt.x >= 1 && tt.x <=30 && tt.y >= 1 && tt.y <=50&&g[tt.x][tt.y]==0&&!st[tt.x][tt.y]) {
q.push({ tt });
st[tt.x][tt.y] = true;
}
}
}
}
int main()
{
for (int i = 1; i <=30; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <=50; j++) {
char ch;
cin >> ch;
g[i][j] = ch - '0';
}
}
bfs();
return 0;
}8.完全二叉树的权值
P1457 - [蓝桥杯2019初赛]完全二叉树的权值 - New Online Judge
完全二叉树与满二叉树的区别:(23条消息) 满二叉树与完全二叉树的区别_满二叉树和完全二叉树的区别_鸭梨山大哎的博客-CSDN博客
先算出一共有几层(与多重背包的二进制优化方法一样),然后枚举每一层,算出每一层的和,然后记录和的最大值,以及是第几层
#include<iostream>
#include<algorithm>
#include<cstring>
using namespace std;
typedef long long LL;
const int N = 100;
int a[N];
LL sum[N];
LL max1=-2e9;
int imax=1;
int main()
{
int n;
cin >> n;
int k = 1;
int cnt = 0;
while (k<=n) {
a[++cnt] = k;
n -= k;
k *= 2;
}
if (n > 0) a[++cnt] = n;
for (int i = 1; i <= cnt; i++) {
for (int j = 1; j <= a[i]; j++) {
int x;
cin >> x;
sum[i] += x;
}
if (max1 < sum[i]) {
max1 = sum[i];
imax = i;
}
}
cout << imax << endl;
return 0;
}






















 545
545











 被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?
被折叠的 条评论
为什么被折叠?








